Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Products
Uploaded by
sahirbuleOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Products
Uploaded by
sahirbuleCopyright:
Available Formats
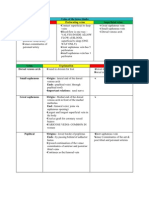
Reasons for Transfusion Life threatening blood loss Restore blood volume and adequate supply of oxygen Whole
ole blood transfusion slowly replaced by components transfusion Whole Blood Components Benefits: Blood stored for less than 24hrs Economy of blood, cost effective 350ml(45-55kg)/450ml(>55kg) + anticoagulant, lifespan = 35days Single donation for different patient Red cells, granulocytes, platelet, plasma protein Minimizes hazard of whole blood transfusion Lack coagulation factors, factor VIII, V Specific comp. for specific disease Transfer of unnecessary &harmful substance avoided Blood products Descriptions Usage Red cells conc. (Pack 200-250ml plasma removed Severe anemia (prevent cell) overload) Preparation: sedimentation, Haemolytic anemia centrifugation Double/triple CPDA bag balanced, Aplastic anemia centrifuged @ 5k rpm (4-6 Cel) Less plasma protein : minimum Lifespan as whole blood, SAGManaphylactic rxn saline-adenine-glucose-mannitol (42 days) Leucocytes poor packed cell At least 70% leucocytes removed, minimal RBC loss Double centrifugation, filtration Washing RBC with saline Freezing and glycerolization Plasma separated from whole blood Frozen within 6hrs, stored @ -30 Cel Double CDPA bags cent. @ 5k rpm 5 min 4 Cel (heavy spin) 250ml, 70-80 units of factors VIII, IX, vWF Administration: o Transfused within 24hrs of thawing o After thawing, store @ 2-6 Cel o ABO compatible is used Insoluble portion of plasma after FFP is thawed at 4C After cent, supernatant plasma expressed into satellite bag leaving 15ml of cryoadhering to wall Packs of cryo are placed in cryobath at 25C for protein to dissolve Cryopooling- contains 100 units of factor VIII, 250mg of fibrinogen, 70% of vWF Severe/recurrent febrile nonhaemolytic TR Urticarial (allergic) rxn
Fresh frozen plasma
Multiple coagulation deficiencies (liver disease, DIC, massive blood transfusion) Drug therapy reversal Warfarin Sodium, Dicumarol Immunodef synd. (infant with protein losing enteropathy) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Haemophilia, vWD, congenital and acquired fibrinogen def. Storage: o 1 yr shelf life o -30c or below o Rapidly thawed on request o Transfusion must be completed in 4hrs o ABO compatibility needed
Cryo precipitate
Blood products PRP & platelet conc.
Descriptions Plasma from 1st satellite bag is centr @5k rpm 22 Cel Express platelet poor plasma leaving behind 50ml platelet conc. Stored @ 22 Cel, in agitator 5 days Plasma & buffycoat extracted in satellite bag, by centrifuge 20ml of granulocyte conc or 1.25x10^9 recovered per donation Radiated with 1500rads sufficient w/o any damage to platelet & RBCs
Granulocyte conc.
Irradiated comp.
Usage Thrombocytopenia assoc w leukemia & aplastic anemia Dilutional thrombocytopenia DIC 1 unit increase platelet cu by 10k/ul so 6-10 unit necessary Compatibility not necessary BM showing myeloid hypoplasia Severe neutropenia Neonatal septicaemia unresponsive to antibiotic therapy BM transplantation Immunodef syndrome Immunosupr to chemo/radio Prevent graft vs host disease
Anemias Nutritional, HA, Malaria Transfusion of red cells if Hb <7gms/dl Megaloblastic anemia Transfusion is dangerous due to poor myocardial function BMF Severe anemia- red cells transfusion Thrombocytopenia platelet trnfusion Sickel Cell Disease Maintain sufficient normal HbA 30 % in circulation
CLINICAL SETTINGS Surgery/Trauma Little justification in preoperative transfusion > 1 unit requirement Thyroidectomy, open heart surgery, resection of abd aorta. Aortic aneurysm, vascular surgery, AV malformation, total hip replacement Autologous transfusion minimise blood loss or salvage the blood loss
O&G Rarely necessitates transfusion Transfusion needed in IDA or short birth interval Transfusion not treating cause of anemia Does not correct the non haematological effects of Iron deficiency Pediatric- exchange, top up transfusions, platelet
You might also like
- Patients - Intervention - Comparison - Outcome(s)Document4 pagesPatients - Intervention - Comparison - Outcome(s)sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Research Method (DLM Slide)Document5 pagesResearch Method (DLM Slide)sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Systemic ReviewDocument3 pagesSystemic ReviewsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- PeritoneumDocument20 pagesPeritoneumsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument28 pagesIntrosahirbuleNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument2 pagesLeukemiasahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Managing Difficult PatientDocument20 pagesManaging Difficult PatientsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- RCT NRCTDocument62 pagesRCT NRCTsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Teaching TY HaematinicsDocument66 pagesTeaching TY HaematinicssahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Patient Interview GuideDocument6 pagesMicrosoft Word - Patient Interview GuidesahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Teaching TY HaematinicsDocument69 pagesTeaching TY HaematinicssahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Mock Ospe (10 Q) Me 211Document10 pagesMock Ospe (10 Q) Me 211sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- PulmonaryDocument35 pagesPulmonarysahirbuleNo ratings yet
- CoverDocument7 pagesCoversahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Elective ApplicationDocument1 pageElective ApplicationsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Defense Mechanism of Upper Respiratory TractDocument41 pagesDefense Mechanism of Upper Respiratory Tractsahirbule100% (2)
- Benign and Malignant Neoplasia of URTDocument48 pagesBenign and Malignant Neoplasia of URTsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- BV Lower Limbs Arteries)Document2 pagesBV Lower Limbs Arteries)sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- BV Upper Limbs Arteries)Document2 pagesBV Upper Limbs Arteries)sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- BV Upper Limbs (Veins)Document1 pageBV Upper Limbs (Veins)sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- History Taking ReportDocument5 pagesHistory Taking ReportsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Mock Ospe (10 Q Answer) Me211Document14 pagesMock Ospe (10 Q Answer) Me211sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- BV of Lower Limbs (Veins)Document2 pagesBV of Lower Limbs (Veins)sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Mock Ospe Me211Document15 pagesMock Ospe Me211sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Mock Ospe (10 Q Questions) Me 211Document11 pagesMock Ospe (10 Q Questions) Me 211sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Mock Ospe (10 Q Answer) Me211Document14 pagesMock Ospe (10 Q Answer) Me211sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Mock Ospe (10 Q Answer) Me211Document14 pagesMock Ospe (10 Q Answer) Me211sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Me211 ObaDocument13 pagesMe211 ObasahirbuleNo ratings yet
- History Taking Report (Fried - Mamak Style)Document5 pagesHistory Taking Report (Fried - Mamak Style)sahirbuleNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Boston Scientific Corporation v. Mabey, 10th Cir. (2011)Document8 pagesBoston Scientific Corporation v. Mabey, 10th Cir. (2011)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- CHAP002 (Chapter 2 Information System Building Blocks)Document14 pagesCHAP002 (Chapter 2 Information System Building Blocks)Mohammed Atef0% (1)
- Visa For Student Visa D PDFDocument2 pagesVisa For Student Visa D PDFEmmanuel EspinoNo ratings yet
- Flowshield ESD ConductiveDocument2 pagesFlowshield ESD ConductiveRamkumar KumaresanNo ratings yet
- 1740 Purchasing Manager Interview Questions Answers GuideDocument11 pages1740 Purchasing Manager Interview Questions Answers GuideNaveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Managing People and OrganisationsDocument50 pagesManaging People and OrganisationsOmkar DesaiNo ratings yet
- Flash 29f800Document48 pagesFlash 29f800savidhamNo ratings yet
- Notes On Cash BudgetDocument26 pagesNotes On Cash BudgetJoshua P.No ratings yet
- Orthopaedic BiomechanicsDocument17 pagesOrthopaedic BiomechanicsIacobescu EmiliaNo ratings yet
- Leather Agra - JD WelfareDocument25 pagesLeather Agra - JD WelfareManjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- LPU/HRD/IC/200905/001/672/164 Dated: 05 Sep 2020: OutstandingDocument1 pageLPU/HRD/IC/200905/001/672/164 Dated: 05 Sep 2020: OutstandingadityamduttaNo ratings yet
- CSCPAPERSDocument54 pagesCSCPAPERSABHISHEK ANANDNo ratings yet
- Chap 010Document147 pagesChap 010Khang HuynhNo ratings yet
- 1536-Centrifugial (SPUN), FittingsDocument23 pages1536-Centrifugial (SPUN), FittingsshahidNo ratings yet
- Al-Cu Phase DiagramDocument4 pagesAl-Cu Phase DiagramSandeep YadavNo ratings yet
- DB858DG90ESYDocument3 pagesDB858DG90ESYОлександр ЧугайNo ratings yet
- Design Model Are Included in One Part of The Graves (2000) ModelDocument8 pagesDesign Model Are Included in One Part of The Graves (2000) ModelPourya HellNo ratings yet
- Student Data Chapter A4 Sampling Distributions r3Document18 pagesStudent Data Chapter A4 Sampling Distributions r3khaled mohamedNo ratings yet
- Python specializationFAQDocument2 pagesPython specializationFAQGenerowiczNo ratings yet
- Cuprinol - Wood - Preserver - Clear - (BP) Safety Data SheetDocument13 pagesCuprinol - Wood - Preserver - Clear - (BP) Safety Data SheetEdgar ArdinazoNo ratings yet
- Citect ModnetDocument5 pagesCitect ModnetKuncoroNuryantoNo ratings yet
- Exam PaperDocument2 pagesExam PapersanggariNo ratings yet
- Alabama Tenants HandbookDocument26 pagesAlabama Tenants HandbookzorthogNo ratings yet
- Assign Controlling Areas and Company Codes for Optimal Cost AccountingDocument4 pagesAssign Controlling Areas and Company Codes for Optimal Cost Accountingatsc68No ratings yet
- Cortisol II 2020-03 v6Document5 pagesCortisol II 2020-03 v6Parishan SaeedNo ratings yet
- D-Lux Railing System by GutmannDocument24 pagesD-Lux Railing System by Gutmannzahee007No ratings yet
- G.R. No. 201302 Hygienic Packaging Corporation, Petitioner Nutri-Asia, Inc., Doing Business Under The Name and Style of Ufc Philippines (FORMERLY NUTRI-ASIA, INC.), Respondent Decision Leonen, J.Document5 pagesG.R. No. 201302 Hygienic Packaging Corporation, Petitioner Nutri-Asia, Inc., Doing Business Under The Name and Style of Ufc Philippines (FORMERLY NUTRI-ASIA, INC.), Respondent Decision Leonen, J.SK Fairview Barangay BaguioNo ratings yet
- MEC-004 TMA: Harrod-Domar Model and Golden Age EquilibriumDocument11 pagesMEC-004 TMA: Harrod-Domar Model and Golden Age EquilibriumnitikanehiNo ratings yet
- Message From The Chairman: Section On International and Comparative AdministrationDocument12 pagesMessage From The Chairman: Section On International and Comparative AdministrationBrittany KeeganNo ratings yet
- Customer Guide Electrical Service Information FormDocument2 pagesCustomer Guide Electrical Service Information FormRyder BergerudNo ratings yet