Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PETA MINDA Upsr THN 4 Yr 5 Yr 6
Uploaded by
Zabidi ZahariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PETA MINDA Upsr THN 4 Yr 5 Yr 6
Uploaded by
Zabidi ZahariCopyright:
Available Formats
TAHUN 4, TAHUN 5, TAHUN 6
PETA MINDA
MENYIASAT
ALAM
KEHIDUPAN
MENYIASAT
BUMI DAN
ALAM
SEMESTA
MENYIASAT
DUNIA
TEKNOLOGI
MENYIASAT
ALAM
BAHAN
MENYIASAT
ALAM
FIZIKAL
MENYIASAT
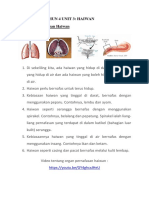
BENDA HIDUP
1. Benda Hidup Mempunyai Keperluan Asas
2. Benda Hidup Menjalani Proses Hidup
3. Haiwan Dan Tumbuhan Melindungi Diri
Keperluan Asas Manusia
Makanan
Tempat
perlindungan
Udara
Air
Bernafas
Melindungi dari
bahaya
sinaran matahari
hujan
Membekal tenaga
Tumbesaran
Kekal sihat
Minum
Tumbesaran
Kekal sihat
1.1 Memahami manusia mempunyai keperluan asas
Keperluan Asas Haiwan
Makanan
Habitat
Udara
Air
Bernafas
Melindungi diri
bahaya
sinaran matahari
hujan
Membekal tenaga
Tumbesaran
Kekal sihat
Minum
Tumbesaran
Kekal sihat
1.2 Memahami haiwan memerlukan keperluan asas
jenis :
lubang
gua
sarang
Keperluan Asas Tumbuhan
Udara
Cahaya
matahari
Air
Ada Keperluan Asas :
Tumbesaran sihat
Tumbesaran baik
Tidak layu
Tiada Keperluan Asas
Layu
Kekuningan
Mati
1.3 Memahami tumbuhan memerlukan keperluan asas
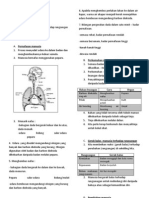
2.1 Menganalisa proses-proses hidup manusia
Menganalisa Proses-Proses
Hidup Manusia
Gerakbalas
Pernafasan
Pembiakan
Organ
Tarik nafas udara disedut
Hembus nafas udara dihembus
Hidung/Mulut Saluran udara Paru-paru
Proses melahirkan anak
Kadar pernafasan
Jumlah pergerakan dada
pada sesuatu masa
Organ
Mata - lihat
Hidung - hidu
Lidah - rasa
Telinga - dengar
Kulit - sentuh
Perkumuhan Nyahtinja
Paru-paru
( Karbon Dioksidsa
+ Wap Air)
Buah Pinggang
( air kencing + garam mineral )
Skin ( peluh + garam mineral)
Najis
Tujuan :
elak bahaya
elak kecederaan
elak kemalangan
untuk hidup
2.2 Menyedari tentang sesetengah perlakuan boleh mengganggu proses hidup
Tabiat yang mendatangkan bahaya
terhadap proses hidup
Merokok Mengambil Dadah
Minum
minuman keras
Akibatnya
kanser paru-paru
batuk
Akibatnya
gerak balas yang lambat terhadap
stimuli
terhoyong-hayang
boleh menyebabkan kemalangan
How to avoid
Menyertai kempen
Tidak menggalakkan tabiat dalam
kalangan Rakan sebaya
2.3 Menganalisis proses hidup haiwan
Proses hidup haiwan
Bernafas Berkumuh Membiak
Bertelur Beranak
Organ
Paru-paru
kera
burung
ikan paus
Insang
ikan
udang
book lung
ketam
Kulit lembap
katak
cacing tanah
Struktur trakea
belalang
Nyahtinja
Mengeluarkan bahan buangan
dari badan
kucing
harimau
kelawar
Ikan paus
ular
burung
Proses-proses
hidup tumbuhan
Tumbuhan bergerakbalas
terhadap rangsangan
air, cahaya matahari, sentuhan,
Graviti.
Kenapa tumbuhan membiak?
Untuk memastikan kemandirian spesies
Pelbagai cara tumbuhan membiak
Melalui biji , spora,, sulur, keratan batang, daun
Batang bawah tanah
Ramalkan apa yang akan berlaku
kalau tumbuhan tidak membiak
Tiada bekalan makanan
Pembiakan tumbuhan
biji balsam, jagung, durian
spora paku-pakis, cendawan
sulur pisang, nanas
Keratan batang ubi kayu, bunga raya
daun begonia, setawar
Batang bawah tanah halia,, keledek
Bahagian tumbuhan bergerakbalas
terhadap cahaya mataharii
pucuk
Bahagian tumbuhan bergerakbalas
terhadap graviti
akar
Bahagian tumbuhan
bergerakbalas terhadap air
akar
2.4 Memahami proses-proses hidup tumbuhan
Bahagian tumbuhan
bergerakbalas
terhadap sentuhan
Ciri-ciri khas haiwan melindungi
dirinya daripada bahaya/musuh
Tabiat haiwan melindungi dirinya
daripada bahaya /musuh
Kulit yang keras dan tebal
Melindungi dirinya daripada tercedera
Badak dan gajah
Cengkerang keras
Siput dan kura-kura memasukkan dirinya
Kedalam cengkerang apabila ada bahaya
Sisik keras
Tenggiling dan buaya mempunyai sisik
Keras untuk melindunginya daripada bahaya
Bulu deduri
Mengembangkan bulu dedurinya apabila
diserang musuh
landak
Tanduk
Menggunakan tanduk untuk menyerang musuh
Kambing dan rusa
Kuku yang tajam
Melindungi dirinya daripada musuh
bears, eagle, cat, singa
Menggulung
Tenggiling menggulung dirinya apabila ada
bahaya/musuh
cth: tenggiling, ulat gonggok
Semburan cecair hitam
Menghadkan penglihatan musuh
Cth: sotong
Camouflage
Bertukar warna kulit mengikut persekitaran
Sesumpah dan kuda belang
Tabiat pura-pura mati
Untuk menipu musuh
Cth: kumbang tanduk
3.1 memahami bahawa haiwan mempunyai ciri-ciri khas dan tabiat bagi melindungi diri daripada bahaya/musuh.
Haiwan mempunyai ciri-ciri khas dan
tabiat melindungi dirinya daripada
cuaca melampau dan membenarkan
mereka bermandiri
Cuaca panas
Cuaca sejuk
Kulit Berkedut
gajah, badak dan kerbau
Kehilangan haba melalui kulit berkedut
Berkubang
gajah, badak dan kerbau
menyejukkan badan dengan berkubang
dalam lumpur
Bonggol
Unta menyimpan makanan dan air dalam
bentuk lemak di dalam bonggolnya
Bulu tebal
Beruang kutub mempunyai bulu tebal untuk
mengelakkan kehilangan haba kepada
persekitaran sejuk
Lapisan lemak
Penguin, anjing laut dan ikan paus mempunyai
lapisan lemak di bawah kulit untuk mengekal haba
badan
Telinga kecil
Anjing laut dan singa laut mempunyai telinga kecil
untuk menhalang kehilangan haba badan
Hibernate
Beruang kutub tidur semusim bagi mengekang
hilangnya haba badan musim sejuk
3.2. Memahami bahawa haiwan mempunyai ciri-ciri khas dan tabiat melindungi dirinya daripada cuaca yang melampau
3.3. Memahami bahawa haiwan mempunyai ciri-ciri khas dan tabiat yang membenarkan mereka bermandiri
Ciri-ciri khas untuk melindungi
diri daripada musuh
Ciri-ciri yang
melindungi
tumbuhan
Duri
Beracun
Bulu halus
Menghasilkan
getah
Menutup anak
daun bila disentuh
3.4. Memahami tumbuhan mempunyai ciri-ciri khas untuk melindungi diri daripada musuh
Kawasan
berangin kuat
Kawasan kering
cth : kaktus
a. Akar tunjang untuk menyerap air
b. Batang sukulen yang boleh
menyimpan air
c. Duri mengurangkan kehilangan
air pada tumbuhan
cth: pokok kelapa, buluh,
pokok bakau
a. Batang yang mudah melentur
b. Mempunyai akar baniir
c. Dedaun tirus/berpisah
d. Dedaun jarum
3.5. Memahami tumbuhan mempunyai ciri-ciri khas untuk melindungi diri daripada kawasan kering dan angin kuat
Ciri-ciri khas
MENYIASAT
DAYA DAN TENAGA
1. Ukuran
1.3 Isipadu pepejal
1.1 Panjang
1.2 Luas
1.5 Jisim
1.6 Masa
1.7 Unit Piawai
1. Ukuran
1.4 Isipadu cecair
UKURAN
Panjang
Terminologi
Jarak di antara dua titik/
tempat/ kedudukan Pelbagai cara
ukuran
Pita ukur
jengkal
depa tali
pembaris
Alat piawai
Pita ukur
pembaris
Unit
mm cm m km
Teknik yang betul
Fokus penglihatan
hendaklah selari
dengan hujung objek
1.1. Memahami ukuran panjang
Luas
Luas adalah jumlah
ruang yang diliputi oleh
sesuatu objek
Terminologi
Menggunakan kad segiempat
sama 1 centimetre
Unit Piawai
- Millimetre persegi (mm
2
)
- Centimetre persegi (cm
2
)
- Metre persegi (m
2
)
- Kilometre persegi (km
2
)
- Menggunakan formula
Luas =panjang X lebar
1cm
1cm
Pelbagai cara mengukur luas
2cm
4cm
= 4cm X 2 cm
= 8cm
2
3cm
3cm
Meletakkan objek
seragam seperti jubin,
buku dan setemdi atas
permukaan sesuatu
objek
1.2. Memahami cara mengukur luas
Isipadu
Terminologi
Jumlah ruang yang dipenuhi/diliputi oleh pepejal/cecair.
1.3 Pepejal
1.4 Cecair
Formula
panjang x lebar x tinggi
Unit Piawai
mm
3
, cm
3
, m
3
Alat
Unit Piawai
Silinder penyukat
ml, l
Teknik yang betul
a) Ambil bacaan ukuran pada aras
bawah meniskus
b) Aras mata hendaklah pada aras
bawah meniskus.
1.3. Memahami cara menyukat isipadu pepejal
1.4. Memahami cara menyukat isipadu cecair
Jisim
Terminologi
Amaun jirim
terkandung dalam
sesuatu objek
Alat
Neraca
Elektronik
Neraca
Spring
Neraca
Palang
Dacing
Neraca
mikro
Neraca
Tuas
Unit Piawai
mg g kg
Teknik mengukur
1.5. Memahami cara mengukur jisim
Masa
Terminologi
Julat waktu di antara
dua peristiwa
Cara mengukur
sundial , sand clock ,
candle clock
Proses ulangan seragam
sesuatu peristiwa boleh
mengukur masa
-Ayunan bandul
-Kadar nadi
- lilin yang menyala
-Titisan air
-Pertukaran siang dan malam
Alat
Unit Piawai
saat , minit , jam
Jam Dinding , Jam Tangan
Jam Randik, Jam digital
Old clock
Pelbagai cara yang boleh mengukur masa
1.6. Memahami cara mengukur masa
Memudahkan
komunikasi dan
pemahaman
untuk ketepatan
dan ketekalan
Kepentingan Unit Piawai
1.7. Kesedaran kepentingan menggunakan unit piawai
MENYIASAT BAHAN
1. Memahami sifat bahan
Sifat Bahan
Penebat
Terapung di
atas air
Pengalir
elektrik
logam
Mengalir haba
Tenggelam di
dalam air
Membenarkan
cahaya melaluinya
Boleh diregang
kayu
batu
Gelang getah
kaca karbon plastik
logam
kayu
1.1. Memahami sifat bahan
CARA-CARA MENYIMPAN OBJEK
PANAS
Dilitupi dengan bahan penebat
eg. sabut, habuk kayu, polistirena
SEJUK
objek panas objek sejuk
Menghalang
pembebasan haba
Menghalang
penyerapan haba
1.2. Mengaplikasikan pengetahuan tentang sifat bahan dalam kehidupan seharian.
Bahan
Senarai objek dan bahan
berdasarkan bahan apa
Ia diperbuat.
objek bahan sifat
pisau logam keras
Kertas
tisu
kayu lembut
Cermin
kereta
kaca Lut sinar
Kenapa bahan tertentu digunakan
untuk membuat sesuatu objek
Murah
Mudah
diperolehi
Kuat/kukuh
Berkualiti
tinggi
1.3. Mensintesis pengetahuan mengenai penggunaan bahan berdasarkan sifat bahan
Bahan semulajadi
Bahan buatan
manusia
kayu logam getah kapas plastik
kain tiruan
nilon
Mengurangkan
penggunaan
Mengguna
semula
Mengitar
semula
kertas beg plastik botol plastik kaca
Jenis Bahan
Mengguna semula, Mengurangkan penggunaan
dan Mengitar semula bahan
1.4. Mengetahui kepentingan mengguna semula bahan, mengurangkan penggunaan
bahan dan mengitar semula bahan
BAHAN
Objek berkarat
Objek tidak berkarat
Objek diperbuat daripada
logam dan keluli
Objek diperbuat daripada
kayu, kapas, getah, kulit
kaca dan sutera
*paku
*sudu
*pisau
*jarum
kapak
*gelas
*botol
*cawan
*pensil
pembaris
1.5. Memahami bahawa sesetengah bahan boleh berkarat
Pengaratan
Pelbagai cara mencegah
pengaratan
* Menyalut dengan
bahan tidak berkarat
* cat
* minyak
* gris
Pentingnya mencegah
pengaratan
*jangka hayat yang panjang
*memulihara bahan semulajadi
*menjimatkan kos
*cantik dipandang/ menawan
*Kesimpulan; Pengaratan dapat dicegah dengan mengelakkan logam
terdedah kepada air dan udara
1.6. Memahami bahawa pengaratan boleh dicegah.
MENYIASAT BUMI
DAN ALAM SEMESTA
1. SISTEM SURIA
Sistem Suria
Senarai ahli
Senarai urutan
planet
Planet bergerak
mengelilingi Matahari
-8 planet
-Satelit semulajadi
-Meteor
-Komet
-Asteroid
akronim:
Utarid ustazah
Zuhrah zuraidah
Bumi bungkus
Marikh makanan
Musytari masa
Zuhal zuhur
Uranus untuk
Neptun nenek
1.1. Memahami Sistem Suria
Saiz dan Jarak
relatif
Saiz relatif Matahari
dengan saiz Bumi
Saiz relatif Bumi
dengan saiz Bulan
Jarak relatif Bumi ke Matahari
berbanding jarak relatif dari Bumi
ke Bulan
Matahari
1
Bumi
100
Bumi
1
Bulan
4
Matahari
Bumi
Bulan
150 000 000 km
382 500 km
1 : 400
1.2. Memahami saiz dan jarak relatif antara Bumi, Bulan dan Matahari
Bumi
dalam
Sistem Suria
Menyatakan sebab
sesetengah planet tidak
kondusif untuk benda hidup
KESAN
Bumi adalah satu-satunya
planet dalam Sistem Suria
yang boleh menampung
hidupan
Lebih dekat jarak planet daripada
Matahari semakin panas permukaannya .
.Lebih jauh jarak planet daripada Matahari
semakin sejuk permukaannya
Ketiadaan air dan udara.
Bumi adalah planet berkedudukan ke-3 dari Matahari
Menerima cahaya dan haba yang cukup dari Matahari
Bumi mempunyai keupayaan menampung kehidupan
Atmosfera Bumi mengandungi udara
Terdapat air di Bumi
Lebih dekat :
Suhu di atas muka Bumi semakin tinggi.
Berlaku sejatan air di permukaan Bumi
Ketiadaan air menyebabkan suhu tinggi
Lebih jauh :
Suhu di atas muka Bumi semakin rendah.
Air membeku membentuk ais
Payah menampung kehidupan
1.3. Menghargai kesempurnaan kedudukan planet Bumi dalam Sistem Suria
MENYIASAT
TEKNOLOGI
1. TEKNOLOGI
1.1.Memahami kepentingan teknologi dalam kehidupan harian.
Had keupayaan manusia
dalam membuat sesuatu
Contoh had keupayaan
tidak berupaya melihat objek seni
tidak berupaya bercakap kuat
tidak berupaya berjalan jauh
tidak berupaya melihat objek jarak jauh
Alat untuk mengatasi had
keupayaan manusia
Mikroskop
- Penggunaan kanta unutk melihat objek seni dan mikrob
Mikrofon
- Meningkatkan kelangsingan suara
Telefon
- Untuk berkomunikasi jarak jauh
Kenderaan
- Memudahkan perjalanan jarak jauh dalam masa singkat
Teleskop, Binokular
- Untuk melihat objek jauh
Pengangkutan
Darat: haiwan basikal kereta keretapi
Udara : belon udara panas kapal udara peluncur
kapal terbang roket
Air : kanu rakit sampan feri kapal
Komunikasi
asap burung merpati telegraf telefon
Pembinaan
gua pondok rumah kayu apartmen
Perkembangan
teknologi
(contoh)
1.2. Memahami perkembangan teknologi
Pertanian
tajak bajak jentera jentuai
Senarai cabaran yang
dihadapi dalam kehidupan
harian
Idea untuk mengatasi cabaran
yang telah dikenal pasti
Alatan untuk mengatasi
cabaran
Tunjuk cara alatan yang
telah dicipta untuk
mengatasi cabaran
Teknologi
digunakan untuk
mengatasi
cabaran
Tidak mampu mengangkat dan
menggerak beban yang berat
Tidak mampu bergerak jauh
Lakaran model
sumbangsaran
. takal
.kereta sorong
Takal mengangkat beban dari
aras rendah ke aras tinggi
dengan senang
Kereta sorong memindah beban dengan
mudah
1.3 . Mensintesis cara teknologi digunakan untuk menyelesaikan masalah
1.4. Menganalisa teknologi memberi manfaat kepada manusia sejagat jika digunakan
secara bijaksana.
Disadvantages
KOMUNIKASI
Membolehkan manusia
mempelajari dan mengetahui
banyak perkara dalam dunia
PENGANGKUTAN
Membolehkan manusia bergerak
jauh dalam masa yang singkat
PERTANIAN
Mesin membantu dan memudahkan
menanam dan menuai tanaman
PEMBINAAN
Memudah dan mempercepatkan
pembinaan jalan, jambatan
dan bangunan
Bahan buangan yang bertambah
mengakibatkan pencemaran alam sekitar
Penggunaan bahan sumber semulajadi
yang berleluasa menyebabkan
kemusnahan alam sekitar
Penggunaan alatan berteknologi
yang kurang bijaksana dan tidak terkawal
menimbulkan Masalah Sosial
Pencemaran alam sekitar dan
penggunaan bahan kimia yang keterlaluan
mengakibatkan kesan buruk
terhadap kesihatan
TEKNOLOGI
Advantages
MENYIASAT
ALAM
KEHIDUPAN
MENYIASAT
BUMI DAN
ALAM
SEMESTA
MENYIASAT
TEKNOLOGI
MENYIASAT
ALAM
BAHAN
MENYIASAT
DAYA
DAN
TENAGA
MENYIASAT
ALAM KEHIDUPAN
1. MIKROORGANISMA
2. KEMANDIRIAN SPESIES
1.1 Memahami bahawa mikroorganisma adalah benda hidup
Mikroorganisma
Bakteria Kulat Protozoa Virus
Tidak dapat
dilihat dengan mata
kasar
Bertumbuh Bergerak Bernafas
Ciri-ciri
1.2. Memahami tentang mikroorganisma yang berguna dan berbahaya
Mikroorganisma
berguna dan berbahaya
Berguna Berbahaya
Boleh
menyebabkan
Demam
Keracunan
makanan
Makanan
basi
Pereputan
gigi
Membuat roti/Tapai
tempe/baja
Pencegahan
Penyakit
sakit perut
bisul
pereputan gigi
beguk
Membasuh
tangan
Meminum air yang
dimasak
Menutup mulut dan
hidung apabila
batuk atau bersin
Kemandirian spesies
haiwan
Haiwan melindungi telur atau anak daripada dimakan oleh pemangsa
Bagaimana haiwan menjamin
kemandirian spesiesnya
Sesetengah haiwan melindungi
telurnya atau menjaga
anaknya; ada juga haiwan yang
tidak berbuat demikian
Burung bersarang di tempat yang tinggi
Katak telur banyak dan dilitupi lapisan lendir
Lelabah menyimpan anak dalam kerandut di
bawah badannya
Ikan menyimpan anak di dalam mulutnya
Harimau - menyerang pemangsa untuk melindungi
anaknya
Penyu bertelur banyak dan menimbus telurnya
dalam pasir
Kangaru membawa anaknya dalam kantung
badannya
Gajah - sentiasa berada dalam kawanan
2.1. Memahami haiwan berlainan mempunyai cara-cara tersendiri untuk menjamin kemandirian spesies
Kemandirian
spesies
tumbuhan
Air
Mekanisme
letupan
Angin
Haiwan
ringan
lompang udara dalam
buah
kalis air
ringan
bersaiz kecil
bersayap
kering bila masak
meletup bila matang
berwarna cerah
boleh dimakan
berbau
mempunyai onak
kelapa
teratai
engkabang
Angsana
Lalang
buah getah
buah balsam
Chestnut
Rambutan
Mangga
Love grass
Mimosa
Agen pencaran Ciri-ciri istimewa
Contoh
2.2. Memahami pelbagai tumbuhan mempunyai cara-cara tersendiri untuk menjamin kemandirian spesies
Consequences
of
animals and plants
become extinct
Importance
shortage of food
resource
animals and plants species
may face extinction
2.3. Realising the importance of survival of their species
Food Chain
Animals and the
food they eat
Classify animals into
herbivore, carnivore
and omnivore
Producer Consumer Construct food chain
Green plant obtain
energy from
the sun to make
food.
Green
Plant as a producer
Herbivore :
Animals that eat plants only.
e.g.: cow, goat, deer
Carnivore:
Animals that eat other animals.
e.g.: tiger, lion
Omnivore:
Animals that eat plants and
other animals
Animals that eat plant
or other animals
are called consumers.
The food relationship
among living things
can be shown by
a food chain.
To construct food
chain It must start
with plant as
a producer.
In a food chain
the arrow
means eaten by
All living things need
food to survive.
Green plant can make their
own food.
However animals cannot
make their own food
3.1. Understanding food chain
Synthesizing food chain to construct food web
Food web
What will happen
If there is a change in
population of a certain
species in a food web ?
Food web of different habitats
What will happen
to a certain species
of animals if they
eat only one type
of food ?
Paddy field
garden
A change in the population
of a certain species
will effect the population
of other species
They will face difficulty
to survive if the
source of food
runs out
3.2. Synthesizing food chain to construct food web
INVESTIGATING
FORCE AND ENERGY
The Uses of Energy
Why energy
is needed?
- for living things to carry
out life processes.
Eg.: moving, breathing,
growing
The Sources of Energy
Sun
- main source of energy
- produces light and heat
Food
- food contains
stored energy
Wind
-Moving air
-Used to pump
water, drive
small sawmills
- to move, boil, melt,
or bounce non-living things
Fuel
Batteries
- wood, coal,
petroleum,
natural gas
- device that
generated
electrical energy
from chemical energy
Water
- moving or
falling water
produce
energy
1.1. Understanding the uses of energy
Energy can be transformed from
one form to another
Form of energy
Sound energy
Heat energy
Light energy
Electrical energy
Kinetic energy
Chemical energy
Potential energy
Energy can be
transformed
a) lighting a candle
Chemical energy
heat energy + light energy
b) Kicking a ball
Chemical energy
kinetic energy
Example of appliance that make use of
energy transform
a) Electric iron
Electrical energy heat energy
b) Radio
Electrical energy sound energy
c) Television
Electrical energy sound energy + light energy
1.2. Understanding that energy can be transformed from one form to another
Renewable and
non-renewable
energy
Renewable energy
Energy that
cannot be
replenished
Resources
solar, wind,
biomass fuel,
water
Non-renewable energy
Energy that can be
replenished when
it is used up
Resources
natural gas,
petroleum,
coal
Why use energy wisely
How to use energy wisely
Some energy
resources cannot
be replenished
when used up
To save
cost
Avoid
wastage
Reduce
pollution
Turn off the
television when
no one is
watching it
Switch off the
lights before
leaving
the room
1.3. Understanding renewable and non-renewable energy
Electricity Sources
Dry cell
Accumulator
Dynamo
Solar cell
Types of circuits
Name Symbol
Dry cell
Connecting
wire
Switch
Bulb
Symbols and
components Parallel circuit Series circuit
Differences
The bulb in the parallel circuit is brighter
than the bulb in the series circuit
2.1. Knowing the sources of electricity
2.2. Understanding a series circuit and a parallel circuit
PRECAUTIONS
Danger of mishandling
electrical appliances
Fire Burn Electric shock Electrocution
Safety precautions to be taken
when using appliances
Do not touch electrical
appliances with wet hand
Do not repair electrical
appliances on your own
2.3. Understanding the safety precautions to be taken when handling electrical appliances
Light
Can be reflected
Reflection of light
Side mirror of a car
Periscope Kaleidoscope
Travels in a
straight line
How shadow
is formed
When light is
completely or
partially blocked by
an opaque object
The light that falls
on objects bounces
off the objects and
comes to your eyes
mirror
3.1. Understanding that light travels in a straight line
3.2. Understanding that light can be reflected
Uses of reflection
How ?
Heat
Gain heat Loss heat
Cooler
Warmer
Measure temperature using
the correct technique
The effects of heat on matter
Matter expands
when heated
Matter contracts
when cooled
4.1. Understanding that temperature is an indicator of degree of hotness
4.2. Understanding the effects of heat on matter
1.1. Matter exist in the form of solid, liquid or gas
has mass
SOLID LIQUID GAS
fixed
volume
fixed shape
has mass
no permanent shape
fixed volume
no fixed
shape
has mass
no fixed
volume
can be
compressed
1.1 Matter exist in the form of solid, liquid or gas
solid liquid gas
water
milk
air
steam
wood
stone
Changing
states
of
water
gas - liquid
liquid - solid
liquid - gas
solid - liquid melting
Boiling
Affected by windy and hot
weather
evaporation
condensation
Freezing
1.2 . Understanding that matter can change from one state to another
WATER CYCLE
Circulation of water in
the environment
Formation of clouds
and rain
Importance of water
Changes in the states of
matter in the water cycle
Liquid to gas (evaporation)
Droplets of water will
become bigger and
heavier rain
evaporation
condensation
sea
Gas liquid (Condensation)
1.3 . Understanding the water cycle
Appreciating the importance
of water resources
To prevent living aquatic from being
destroyed and undergoing extinction
Reasons to keep our
water resources clean.
To ensure the cleanliness
of water supply
To regulate
the formation of
clouds and rain
To avoid infected
diseases
Ways to keep our water
resources clean
Keep the rivers clean
Cleanliness campaign
1.4. Appreciating the importance of water resources
PROPERTIES
taste
using litmus paper to identify
Properties of acidic, alkaline
and neutral substances
Changes in colour
of litmus papers
blue to red red to blue
no change
bitter
sour
ALKALI
ACID
NEUTRAL
SUBSTANCES
Taste bitter
Change red litmus
paper blue
Taste sour
change blue litmus
paper red
Other tastes salty / sweet
no changes in litmus paper
acid alkaline
neutral
2.1. Understanding the properties of acid, alkaline and neutral substances
acid
alkaline
INVESTIGATING
THE EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE
Show
directions
Indicates
Seasons
A group of stars that form a
certain pattern in the sky
Importance of
constellation
Identify constellation
What
constellation
Is ?
constellation
1.1. Understanding the constellation
Big Dipper
Scorpion Orion
Southern Cross
North
North
South
Kite or Cross
Scorpion
Hunter
Laddle
south
planting harvesting
desert
sea
Earth rotates on it axis
Earth rotates
and at the same time
moves around the Sun
Moon rotates on it axis
Moon rotates and at the same
time moves around the Earth
The Moon and
the Earth move
round the Sun at
the same time
The earth
rotates on its axis
from west to east
The changes
in length and position
of the shadow
throughout the day
2.1. understanding the movements of the Earth, the Moon and the Sun
The occurrence
of
day and night
It is day time for the part
of the Earth facing the Sun
It is night time for
the part of the Earth facing
away from the Sun
Day and night occur
due to the rotation of the Earth
on its axis
the Sun
the Earth
night-time
daytime
axis
west
east
2.2. Understanding the occurrence of day and night
Phases of the Moon
The Moon does not emit light
The Moon appears bright
when it reflects sunlight
Describe the phases
of the Moon
1-New moon, 3- New half moon, 5- Full moon
7- Old half moon
2.3. Understanding the phases of the Moon
The shapes of objects
in a structure
The shape of objects
Identify shapes in a structure
Cuboid
Cube
Cylinder
Sphere Cone Pyramid
Sphere
Cylinder
1.1. The shapes of objects in a structure
Shapes of objects that
are stable
The factors that affect
stability of objects
How base area
affects stability
How height affects stability
The strength
and
stability
of a structure
The factors that affect the
strength of a structure
Design a model that
is strong and stable
Cube, cone, cylinder
Height , base area
Bigger base area more stable
Smaller base area less stable
Lower object more stable
Higher object less stable
Types of materials used
Steel ,Iron, Wood
Suggested design for:
Bridge one with manila card and one with wood
1.2. The Strength and Stability of a Structure
INVESTIGATING
LIVING
THINGS
INVESTIGATING
EARTH
AND
UNIVERSE
INVESTIGATING
TECHNOLOGY
INVESTIGATING
MATERIALS
INVESTIGATING
FORCE
AND
ENERGY
INVESTIGATING
LIVING THINGS
Animals
Some
live in solitary
(Animals that live by themselves)
Some
live in groups
(Animals that live together)
zebra giraffes bees ants tiger lizard cat snake
For safety
For Food
To avoid competition for food
To avoid competition for space
Cooperation is a
form of interaction
1.1. Understanding that some animals live in groups and others live in solitary
Competition is a form of
Interaction among living things
Animals
Plants
Factors for competition
Food
Water
Mate
Shelter
Space
Limited food resources
Limited water resources
Trying to get mate to breed
Defending or looking for shelter
Defending or looking for space
Factors for competition
Nutrient
Sunlight
Water
Space
Limited sunlight can reach them
Limited water resources
Limited space
Limited nutrient
Reason
Reason
endangered species
Extinct animal
Endangered animal
Endangered plant
Dodo bird
Dinosaur
Auk bird
Desert rat
kangaroo
Mammoth
Quagga
Tasmanian wolf
Tiger
Turtle
Orang Utan
Panda
Rhinoceros
Hornbill
Blue Whale
Raflessia
Pitcher plant
Venus fly trap
Wild orchid
1.3. Understanding the responsibility of human beings in protecting endangered species
Responsibility of human beings
in protecting endangered species
Factors
of Extinction
ways to prevent
extinction
Illegal Hunting
Elephant Tusk
Tiger Skin & Bone
Blue Whale Fat
Giant Panda Fur
Rhinoceros - Horn
Illegal Logging
Cutting of trees
Forest clearing
The destruction of habitat
Excessive development
Water & air Pollution
Many habitats have been
destroyed
Extreme Weather
Long dry season
Flood
Forest fire
Campaign against excessive
logging
Educate the public about the
importance of protecting &
conserving animals & plant
Avoid consuming or buying
products made from
endangered species
Enforcing the law
Replanting
Selective logging
Setting up forest reserved
Setting rehabilitation centre
Encourage recycle , reuse &
reduce Campaign
Impact of human
activities on
environment
Environmental destruction
caused by human activities
Uncontrolled human
activities to the Earth
Environmental Destruction
Erosion
Landslide
Flash-Floods
Water & Air pollution
Illegal & Excessive
Logging
Clearing Forest
Improper management
of development
Erosion
Landslides
Flash-Floods
Loss of
habitats
Illegal & Excessive hunting
Improper management of
waste from factory
Improper management of
waste from household
Extinction of
endangered
species
Air &
water pollution
Water pollution
& flash flood
Excessive use of
fertilisers,
pesticides
& herbicides
Heavy usage of
motor vehicles
The Lost of habitat
The lose of raw material &food supplies
Climate changes
The rise in temperature on earth
Extinction of endangered species
The balance in nature is disturbed
The loss of the Earths natural water basin
Air &
water Pollution
Air pollution
1.4. Knowing the impact of human activities on environment
INVESTIGATING
FORCE
AND ENERGY
1.1. Understanding that push and pull are forces
FORCE
Pull an action of bringing an object
towards us
Push an action of moving an object
away
D
E
F
I
N
I
T
I
O
N
Effects
Move a stationary object
Stop a moving object
Change direction of moving object
Make object move faster or slower
Change the motion of an object
Change the shape of an object
Friction
Definition
-Force that apposes
the movement of an
object.
-Two surfaces in
contact
Effects
-Surfaces warm.
-Difficult to move
-Wear and tear.
-Slow down and
stop
Reduce
-Lubricant :oil, wax,
grease or water
-Air cushion
-Talcum powder
-Roller marbles
-Ball bearing
Advantages
1. Hold thing
2. Walk without slipping
3. Sharpen a knife
4. Slow down moving
Disadvantages
1. Wear and tear
2. Produce heat
Advantages/Disadvantages
1.2. Understanding the effects of a force
1.3. Analysing friction
Speed
A measurement on how fast an object moves
an object which
moves faster travels a
longer distance in a
given time
Definition
an object which move
faster takes a shorter
time travel a given
distance
Conclusion
Calculation
Formula
Speed = distance / time
Unit
km/h,
m/s ,
cm/s
2.1. Understanding speed
INVESTIGATING
MATERIALS
Unpleasent smell
eg. Fish with bad smell
Unpleasent taste
eg. milk turns sour
Changed colour
eg.vegetables, rice
Changed texture
eg. Yogurt turns curd
Mouldy
eg. Yogurt have many
black spots
Characteristics of
Spoilt Food
Food that has turned bad and
is not suitable to be eaten
Bacteria Fungus
Air
Water
Nutrient
Suitable
Temperature
( 5C - 65 C )
Suitable acidity
Food spoilage
1.1. Understanding food spoilage
Condition for
microbes to grow
What is
spoilt food
Microbes that
spoilt food
Food preservation
(Process whereby food turning
bad is slowed down)
Drying
Boiling
Cooling
Vacuum packing
Pickling
Freezing
Example :
fish, prawn, fruits
Reason :
Bacteria and fungi cannot
grow without water
Example :
Eggs, water
Reason :
Boiled will killed bacteria
and fungi
Example :
eggs, vegetables, fruits
Reason :
Cold temperature slow
down the growth of
bacteria and fungi
Example :
Biscuits, crackers,
Reason :
Bacteria and fungi
cannot grow
without water
Reason :
Prevents the growth
of bacteria and
fungi
Example :
Fruits, chili, fish
Bottling/
canning
Pasteurising Salting
Reason :
Bacteria and fungi
cannot active at a
very low temperature
Example :
Fish, meat
Reason :
Bacteria and fungi
cannot grow
without air
Example :
Meat, fish, fruits
Reason :
Destroy
microoganism
Example :
Milk, yogurt
Reason :
Bacteria and fungi
cannot grow in very
salt substances
Example :
Fish, eggs
Reason :
Dry the food
Example :
Fish, meat
Reason :
Slow down the
loss of water
Example :
Fruits
Smoking
Waxing
1. 2. Synthesising the concept of food preservation
The importance of
preserving food
Food can be kept
for a longer time
Easier to
store
Easier to
carry
To prevent the
wastage of food
1.3. Realising the importance of preserving food
Waste disposal
Gas
Liquid
Solid
From agricultural activities
From vehicles and open burning
Toxic materials
Rubbish
Sources of
wastes
Types of waste
Open burning
Littering
Chanelling- waste
factories into river
Releasing smoke
and dangerous gasses
Treat waste water
Keep environment
and home clean
Reuse and recycle
rubbish and waste
Reduce car
Build factories far
from home
The improper
ways disposal
Smoke dissolved
form weak acid
Kills plants & fish
Destroys building &
bridges
Rubbish thrown in
rivers or drain
Cause flash-floods
& water over flow
Kill plants & animals
in the river
Open burning
Cause asthma &
eye irritation
Air pollution
Disease
Cause by eating
polluted fish and plants
The harmful
effect
The proper
disposal ways
2.1. Understanding the effects of improper of on the environment
Animal extinction
Habitats destruction
Spoil natural beauty
Change Climate
Tin can
Plastic
Synthetic
Glass
Metal objects
Give out
poisonous gas
Unpleasant smell
Return nutrient to soil
Prevent rubbish
from accumulate
Paper
Wood
Food
Meat
Fungi
Bacteria
Waste that
can decay
Waste that decay
Waste that do not decay
Microbes that cause
waste to decay
Advantages of
waste decaying
Disadvantages of
waste decaying
What will happen if
waste do not decay
2.2. Understanding that some waste can decay
INVESTIGATING
THE EARTH & THE UNIVERSE
Eclipse of the moon
The Earth is
between the Sun
and the Moon
The Earth, the Moon
and the Sun are
positioned in a
straight line
The Earths position
blocks sunlight from
reaching the Moon
The Earths shadow is
formed on the Moon
surface and cause an
eclipse of the Moon
Sun
Moon
Earth
1.1. Understanding the eclipse of the moon
ECLIPSE OF THE SUN
The Moon is
between the Sun
and the Earth
The Earth, the Moon and
the Sun are positioned in
a straight line
The Moons blocks the
sunlight from reaching
the Earth
The Moons shadow
is formed on the
Earths surface
SUN
Earth
Moon
The place that experienced full eclipse is completely dark during the day time
PHASES OF THE SUN DURING THE ECLIPSE
1.2. Understanding the eclipse of the sun
INVESTIGATING
TECHNOLOGY
WHEEL AND AXLE
Simple machine
LEVER
WEDGE
PULLEY
GEAR
INCLINED PLANE
SCREW
-To carry or move heavy objects
- e.g. hammer , spoon , scissor
-To lift heavy objects easier
eg. stairs , slanting wooden plank
-To carry to move heavy objects easily
eg screw driver , car spanner
-To carry or lift objects to a higher place
eg. flag pole , crane
-To cut or separate objects
eg. knife , saw , axe
-To fix two objects together
eg. drill bit , spanner
-To move objects easily
eg. Gear in a watch
A device that allows us to use
less force to make work easier or faster
1.1. Understanding simple machines
Complex
machine
Made up of more
than one simple
machine
Wheelbarrow
Lever, wheel and axle
Crane
Gear, pulley, lever
Egg beater
Gear, wheel and axle
Bicycle
Gear, lever,
wheel and axle
Scissors
Lever, wedge
Hand drill
Wedge, wheel and axle
1.2. Analysing a complex machine
Machines
Life machine
Life machine
Difficulty in moving heavy things
Will not be able to travel from one
place to another place which is far
Help to move heavy things
Work in the fields is made easier and
productivity of agricultural product is
raised
Construction work is made easier and
can be completed faster
Help us travel from one place to
another
1.3. Appreciating the invention of machines that make life easier
You might also like
- Mind Map Upsr Latest 2013 THN 4 Yr 5 Yr 6Document93 pagesMind Map Upsr Latest 2013 THN 4 Yr 5 Yr 6Rasidah MohamadNo ratings yet
- MIND MAP UPSR Latest 2013 THN 4 YR 5 YR 6Document93 pagesMIND MAP UPSR Latest 2013 THN 4 YR 5 YR 6sabri othmanNo ratings yet
- Modul Sains Tahun Tahun 3,4,5,6 SKKT 2Document24 pagesModul Sains Tahun Tahun 3,4,5,6 SKKT 2Asniza ManapNo ratings yet
- Nota Ulangkaji Sains Tahun 3-6 SKKTRDocument27 pagesNota Ulangkaji Sains Tahun 3-6 SKKTRDP Syahrom Kadir100% (3)
- Nota Ringkas SainsDocument10 pagesNota Ringkas SainsmilakamilaNo ratings yet
- Latihan TerminologiDocument21 pagesLatihan TerminologirozanaNo ratings yet
- Nota Sains THN 4Document12 pagesNota Sains THN 4Asnal KamalNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas SainsDocument10 pagesNota Ringkas SainsNaim RamlanNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas SainsDocument10 pagesNota Ringkas SainsNaim RamlanNo ratings yet
- Cara Hidupan Melindungi Diri Daripada Musuh Dan IklimDocument5 pagesCara Hidupan Melindungi Diri Daripada Musuh Dan IklimradiNo ratings yet
- Ting 2 Sains Bab 1 BiodiversitiDocument27 pagesTing 2 Sains Bab 1 BiodiversitiNorazrina Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Nota Ulangkaji Sains Tahun 3 6 SKKTRDocument27 pagesNota Ulangkaji Sains Tahun 3 6 SKKTRMOHD SUFINo ratings yet
- Penge Las AnDocument12 pagesPenge Las AnebycobbyNo ratings yet
- Nota Sains Tahun 4Document13 pagesNota Sains Tahun 4Jamrah JelaniNo ratings yet
- Setiap Haiwan Mempunyai Cara Pernafasan Yang Berbeza Kerana Setiap Haiwan MempunyaiDocument24 pagesSetiap Haiwan Mempunyai Cara Pernafasan Yang Berbeza Kerana Setiap Haiwan MempunyaicikgunorhanisahNo ratings yet
- Peta Minda Setiap Topik Tahun 5Document29 pagesPeta Minda Setiap Topik Tahun 5Suhaiza HaryaniNo ratings yet
- (A) Kepupusan HaiwanDocument5 pages(A) Kepupusan HaiwanwantzNo ratings yet
- Notapoket Sains UpsrDocument28 pagesNotapoket Sains UpsrNoor HayatiNo ratings yet
- Sains Tahun 6 Bab 5 Pemeliharaan & PemuliharaanDocument3 pagesSains Tahun 6 Bab 5 Pemeliharaan & PemuliharaanFazri Azies100% (3)
- Nota Sains Ting 2 Bab 3 (Kepelbagaian Biologi)Document7 pagesNota Sains Ting 2 Bab 3 (Kepelbagaian Biologi)Tuisyen Dewan Hj Ali91% (11)
- Mind Map Year 5Document26 pagesMind Map Year 5Zul Paker IsaNo ratings yet
- BiologiDocument5 pagesBiologiZura UmarNo ratings yet
- Assignment SCE3111 - Jadual Spesifikasi Ujian SainsDocument2 pagesAssignment SCE3111 - Jadual Spesifikasi Ujian SainsNurul Nadia Mohd ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sains Murid Galus UPSRDocument358 pagesSoalan Sains Murid Galus UPSRAnonymous P7TpAxNo ratings yet
- Nota Penting SAINS UPSRDocument10 pagesNota Penting SAINS UPSRMohdAsyrafAbdullahNo ratings yet
- HerbariumDocument10 pagesHerbariumrathiNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 Proses Hidup TumbuhanDocument2 pagesBab 4 Proses Hidup TumbuhanJuan DavisNo ratings yet
- T4 Unit 8 - BahanDocument14 pagesT4 Unit 8 - BahanHASIRULNIZAM BIN HASHIM SIK EH SIAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Cara Hidupan Melindungi Diri Daripada Musuh Dan IklimDocument5 pagesCara Hidupan Melindungi Diri Daripada Musuh Dan Iklimputih001100% (1)
- Nota Tahun 4 Unit 3 HaiwanDocument9 pagesNota Tahun 4 Unit 3 HaiwanShahrul Ikram Md ShariffNo ratings yet
- Sains UpsrDocument112 pagesSains UpsrJefferyUninNo ratings yet
- Nota Sains Tahun 3 (Semakan 2017)Document9 pagesNota Sains Tahun 3 (Semakan 2017)NOR AZURA BINTI GHAZALI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Lencana PengetahuanDocument30 pagesLencana PengetahuanSet En100% (1)
- Sains Tingkatan 2 Bab 3 BiodiversitiDocument26 pagesSains Tingkatan 2 Bab 3 BiodiversitiZul Carnine100% (2)
- Bab 2Document5 pagesBab 2Juan DavisNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Upsr Latest 2013 THN 4 Yr 5 Yr 6Document93 pagesMind Map Upsr Latest 2013 THN 4 Yr 5 Yr 6belacantunuNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2: Bab 3 - BiodiversitiDocument26 pagesSains Tingkatan 2: Bab 3 - BiodiversitiVyean A. Dungkit92% (51)
- SN NotaDocument6 pagesSN NotapriyaNo ratings yet
- P.P Nota Sains-Tingkatan-2-Bab-3-BiodiversitiDocument24 pagesP.P Nota Sains-Tingkatan-2-Bab-3-BiodiversitiVANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Tingkatan 2 SNDocument9 pagesBab 1 Tingkatan 2 SNBuku HitamNo ratings yet
- Pengawetan Kering Tumbuhan Dan Haiwan KecilDocument10 pagesPengawetan Kering Tumbuhan Dan Haiwan KecilIsmi 'AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Sejarah Bab1-Bab8 NotaDocument25 pagesSejarah Bab1-Bab8 NotaTiffany LeeNo ratings yet
- Kemahiran PerkhemahanDocument44 pagesKemahiran PerkhemahanAyu Hanis Khalid75% (4)
- Sains HayatDocument25 pagesSains HayatNur HafiyNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2 Bab 3 BiodiversitiDocument26 pagesSains Tingkatan 2 Bab 3 BiodiversitiVANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Tahun 5 Nota TuisyenDocument1 pageTahun 5 Nota TuisyenHeenisha LachemykandenNo ratings yet
- Nota Sains Tahun 6Document9 pagesNota Sains Tahun 6Taufik Alang67% (3)
- Skema Modul Sains Upsr Tahun 4Document31 pagesSkema Modul Sains Upsr Tahun 4Anonymous W4iAkulwaYNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Kepada Hutan Bakau PDFDocument19 pagesPengenalan Kepada Hutan Bakau PDFhistorianterusanxoxoNo ratings yet
- KGT Geografi T3Document33 pagesKGT Geografi T3YAU JIA YU MoeNo ratings yet
- Bab 3 BiodiversityDocument22 pagesBab 3 BiodiversityHyeeda Hassan100% (1)
- PteridophytaDocument7 pagesPteridophytaIra MardhatillahNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Persekitaran Terhadap TumbuhanDocument8 pagesPengaruh Persekitaran Terhadap Tumbuhanwan nur afiqahNo ratings yet
- Nota Sains Bab Tumbuhan Dan PengukuranDocument1 pageNota Sains Bab Tumbuhan Dan PengukuranAhmad Fahmi Mat KhadziNo ratings yet