Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asexual Reproduction Shan
Uploaded by
dame_pretty10120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views11 pagesthis slide talks about plant reproduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentthis slide talks about plant reproduction
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views11 pagesAsexual Reproduction Shan
Uploaded by
dame_pretty1012this slide talks about plant reproduction
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
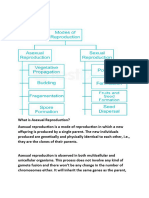
In Plants
By Jake, Erik, Louis and CJ
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction is a result of Meiotic Cell Division.
Parent cells divide into two identical daughter cells.
In Asexual reproduction the offspring are genetically identical to the
original.
In Asexual Reproduction there are no fusing off cells.
Unicellular Plants And Multi-cellular Plants can reproduce both
sexually and asexually.
Asexual Reproduction is not as complex and requires far less
energy.
Different Types of asexual reproduction are: Binary Fission,
Budding, Sporulation, Regeneration, Vegetative Propagation and
Cloning.
Binary Fission
Simplest type of asexual
reproduction.
Binary Fission involves a
one celled organism.
Binary Fission produces
new daughter cells.
Binary Fission begins with
DNA but doesnt exchange
genetic info.
The cells become an exact
replication of each other.
Budding
This is when a child grows
out of the parent.
Hydras and yeast are
examples of budding.
When the cell splits off the
nucleus divides equally but
its cytoplasm divides
unequally.
The parent and child could
stay connected and form a
colony or separate.
Sporulation
Spores contain a nucleus
and a small amount
cytoplasm.
Sporulation sprouts out of
decaying materials
releasing spores to make
more sprouts.
Some examples are bread
mold, mushrooms, mosses
and ferns.
Regeneration
Development of a new
organism from a peace of a
new parent.
Also helps with replacement of
body parts.
Some examples of
regeneration are sponges and
plantaria.
So if a starfish gets a leg torn
off it can be made into a new
starfish.
Vegetative Propagation
It is when a part of a plant grows
into a new plant.
Everything but seed reproduction
is considered vegetative
propagation.
Vegetative propagation can occur
naturally or unnaturally.
Types of natural vegetative
propagation are tubers, runner,
rhizomes and bulbs.
Types of unnatural vegetative
propagation are cuttings and
grafting.
Vegetative Propagation
Runners
Stems grow on top and across the
ground from the existing stem.
From the runner new plants grow
Some examples are strawberries
and some grasses.
Bulbs
Underground stems for food
storage
Food stored in large leafs
Each bulb develops into a new
plant.
One example of bulbs are onions.
Vegetative Propagation
Tubers
Underground stems that contain
stored food.
The eyes of potato can develop
into new plants.
Potato are one example of tubers.
Rhizomes
Long modified stems that grow
horizontally under the ground.
New plants grow off the roots.
Long grasses, ferns, and irises are
examples of rhizomes.
Vegetative Propagation
Cuttings
Pieces of a root or stem that in
certain conditions are made into
new plants.
Some examples are bananas, roses
and sugar cane
Grafting
Taking a part of a plant and
connecting it to another one.
Combining the two plants.
Some examples are seedless
oranges and grapes.
!!!!!!!!!!THE END!!!!!!!!!!
You might also like
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument11 pagesAsexual ReproductionKoushik KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Ppt.x.reproduction 10 23Document83 pagesPpt.x.reproduction 10 23ammara hyderNo ratings yet
- Types of Sexual ReproductionDocument22 pagesTypes of Sexual ReproductionAndjelyn AbalosNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction Grade 12 Yellow Biology Education For The Real WorldDocument34 pagesAsexual Reproduction Grade 12 Yellow Biology Education For The Real WorldChoolwe CheeloNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument87 pagesAsexual ReproductionJaden StanislausNo ratings yet
- Asexual Modes of ReproductionDocument34 pagesAsexual Modes of ReproductionTanveer MehtaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Plant ReproductionDocument48 pagesCHAPTER 5 Plant ReproductionNealieNo ratings yet
- Types of Asexual ReproductionDocument22 pagesTypes of Asexual ReproductionKCitylink InternetNo ratings yet
- Biology Activity: Asexual ReproductionDocument12 pagesBiology Activity: Asexual ReproductionTeddyNo ratings yet
- Plants and Reproduction PDFDocument22 pagesPlants and Reproduction PDFJohanna UrwinNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument9 pagesREPRODUCTIONshashwatdwivedi9000No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument17 pagesPlant Reproductionshaim xd.No ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction 1Document92 pagesAsexual Reproduction 1Zerica JohnNo ratings yet
- Types of Reproduction: Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesTypes of Reproduction: Asexual and Sexual ReproductionMarievic DavidNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument34 pagesAsexual Reproduction in PlantsBanana LatteNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - 4TH QUARTER First Topic - 20240412 - 003639 - 0000Document8 pagesGen Bio - 4TH QUARTER First Topic - 20240412 - 003639 - 0000Russell AggasidNo ratings yet
- 5abb5e0de4b090957d2bf398 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341Document20 pages5abb5e0de4b090957d2bf398 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341CLAWOPNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction: Name:-Siddhesh Taraate STD: - 10 Venus Sub: - BiologyDocument16 pagesAsexual Reproduction: Name:-Siddhesh Taraate STD: - 10 Venus Sub: - BiologysidNo ratings yet
- Methods of ReproductionDocument56 pagesMethods of ReproductionJhigo Villar Franco PascualNo ratings yet
- Science 7 UNIT 6 & 7 Study GuideDocument21 pagesScience 7 UNIT 6 & 7 Study GuideMae RicañaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Part 1 - Plants Asexual ReproductionDocument25 pagesChapter 10 Part 1 - Plants Asexual ReproductionNURUL AINUN MUHAMMAD NORNo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocument11 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual Reproductionmalicaymichelle20No ratings yet
- Asexual Multiplication of Horticultural PlantsDocument5 pagesAsexual Multiplication of Horticultural PlantsDr.Eswara Reddy SiddareddyNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument8 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproducesushantNo ratings yet
- Asexual Multiplication of Horticultural PlantsDocument7 pagesAsexual Multiplication of Horticultural PlantsDr.Eswara Reddy SiddareddyNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants PPT1Document17 pagesReproduction in Plants PPT1Hardik GulatiNo ratings yet
- Types of Asexual ReproductionDocument22 pagesTypes of Asexual ReproductionMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Asexual Repro NotesDocument23 pagesAsexual Repro NotesMs ZoyaNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument92 pagesReproductionJoana Jean SuymanNo ratings yet
- CH 8 - Asexual ReproductionDocument8 pagesCH 8 - Asexual ReproductionDivyansh JhaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Spectrum SquareDocument15 pagesReproduction Spectrum SquareAgastya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 3.1 Asexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument26 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 3.1 Asexual Reproduction in PlantsZaldy Emmanuel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction: Done By: Christy Cho Class: 3business Date: October 25, 2018Document8 pagesAsexual Reproduction: Done By: Christy Cho Class: 3business Date: October 25, 2018Kristy ChoNo ratings yet
- Asex UAL Repr Oduc Tion Revie W Shee T: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesAsex UAL Repr Oduc Tion Revie W Shee T: ObjectivesjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument25 pagesPlant ReproductionRAENA MARIE PENDRAS100% (1)
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument4 pagesReproduction in Plantsnell jaesNo ratings yet
- Asexual V Sexual ReproductionDocument16 pagesAsexual V Sexual ReproductionFi SonnetNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AlgaeDocument57 pagesReproduction in AlgaeNarendra Kumar100% (1)
- Aimee Science 5 Module 5 q2 Edit4Document37 pagesAimee Science 5 Module 5 q2 Edit4Bud JangNo ratings yet
- 1 ReproductioninOrganisms PDFDocument17 pages1 ReproductioninOrganisms PDFvishalukeyNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination in PlantsDocument49 pagesSeed Germination in PlantsbridgetnicolelimNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seeds and Its GerminationDocument18 pagesParts of The Seeds and Its GerminationNova Estrada KionisalaNo ratings yet
- II. Seed-GerminationDocument49 pagesII. Seed-GerminationAndrew GatesNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Reproduction in OrganismDocument11 pagesCh-1 Reproduction in OrganismNEERU JINDALNo ratings yet
- Reproduction, A Characeristic of Living ThingsDocument8 pagesReproduction, A Characeristic of Living ThingspilarmdNo ratings yet
- ,reproduction: Advantages of Asexual Reproduction IncludeDocument7 pages,reproduction: Advantages of Asexual Reproduction IncludeChoolwe CheeloNo ratings yet
- (Biology II) : de Mesa, Lance Christian M. Espiritu, Abram Paul C. Ignacio, Marinelle V. Napa, Hannah Grace PDocument125 pages(Biology II) : de Mesa, Lance Christian M. Espiritu, Abram Paul C. Ignacio, Marinelle V. Napa, Hannah Grace PDavis ShamolmolNo ratings yet
- Bio S4 C16 Reproduction 16.1 & 16.2Document24 pagesBio S4 C16 Reproduction 16.1 & 16.2thomasaquinasrevannoNo ratings yet
- 16.1 Asexual ReproductionDocument22 pages16.1 Asexual ReproductionEFFERUL MIFZALNo ratings yet
- Ms. Reeta Kaul Science Facilitator at M.L.Khanna D.A.V Public School, DwarkaDocument42 pagesMs. Reeta Kaul Science Facilitator at M.L.Khanna D.A.V Public School, DwarkaHu la laNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Gist 7Document16 pagesClass 10 Gist 7shreyan sahaNo ratings yet
- Life Science Module 5 Lesson 1 and 2Document69 pagesLife Science Module 5 Lesson 1 and 2Mae AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Y10 Reproduction TeacherDocument143 pagesY10 Reproduction Teachervijayp22No ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument13 pagesAsexual Reproductionkritishaa8100No ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument24 pagesAsexual and Sexual ReproductionHeart VidalNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce NotesDocument11 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce NotesPlayer dude65No ratings yet
- Biology Most Important TopicsDocument27 pagesBiology Most Important TopicsShiv AgrawalNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of SAMR Model in Teaching IDocument191 pagesA Case Study of SAMR Model in Teaching IangelNo ratings yet
- Questions Paper Design: Subject: Biology (314) Class: Senior Secondary Paper Marks: 80 Duration: 03 HrsDocument4 pagesQuestions Paper Design: Subject: Biology (314) Class: Senior Secondary Paper Marks: 80 Duration: 03 Hrssurya75No ratings yet
- Science Investigatory Project For Grade 7 SSCDocument32 pagesScience Investigatory Project For Grade 7 SSCMatt Mc Henry HernandezNo ratings yet
- The Alkaline Diet GuideDocument5 pagesThe Alkaline Diet GuideMarchthirtyfirstNo ratings yet
- Vedantu Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocument28 pagesVedantu Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantNakul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Values of Datura: A Synoptic Review: Afsha Parveen, K. Vijula, K. V. Avinash, M. Ravishankar, D. V. LeeladharDocument5 pagesMedicinal Values of Datura: A Synoptic Review: Afsha Parveen, K. Vijula, K. V. Avinash, M. Ravishankar, D. V. LeeladharSiva Naga Prasad TadipartiNo ratings yet
- Ibervillea SonoraeDocument7 pagesIbervillea SonoraesandraNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Report On Bamboo and RattanDocument57 pagesPhilippine National Report On Bamboo and RattanolaNo ratings yet
- BOTANYDocument80 pagesBOTANYIsaiahNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plants Classification Grade 5 6Document7 pagesKingdom Plants Classification Grade 5 6Anam ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - The Research Problem: Introduction/Background of The StudyDocument4 pagesChapter I - The Research Problem: Introduction/Background of The StudyCha LinsengNo ratings yet
- Mapping of Significant Natural Resources: National Commission For Culture and The ArtsDocument7 pagesMapping of Significant Natural Resources: National Commission For Culture and The ArtsShari Ann Burato DatahanNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Fig Ficus Carica L As An AlternativDocument7 pagesCultivation of Fig Ficus Carica L As An AlternativDumar Palomino LeonelNo ratings yet
- Homemade Organic Raw Apple Cider VinegarDocument128 pagesHomemade Organic Raw Apple Cider VinegarkendocastroNo ratings yet
- Kanaka Rajesham 82-88Document7 pagesKanaka Rajesham 82-88Sundara VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- Sekercioglu 2006 HandbookOfTheBirdsOfTheWorld - Ecological Significance of Bird PopulationsDocument72 pagesSekercioglu 2006 HandbookOfTheBirdsOfTheWorld - Ecological Significance of Bird Populationsjjchaparro67% (3)
- Review On Thymus Vulgaris Traditional Uses and Pharmacological PDFDocument3 pagesReview On Thymus Vulgaris Traditional Uses and Pharmacological PDFPsicólogo Clinico clinicoNo ratings yet
- Update On Lignin Biosynthesis and StructureDocument11 pagesUpdate On Lignin Biosynthesis and StructurehashriNo ratings yet
- Diseases of PeaDocument7 pagesDiseases of PeaTaushif AhammedNo ratings yet
- 6bi04 Mark Scheme Edexcel A2 BiologyDocument18 pages6bi04 Mark Scheme Edexcel A2 BiologySumana MalekNo ratings yet
- Physiological Characteristics: Ceiba PentandraDocument6 pagesPhysiological Characteristics: Ceiba PentandraDianne GalangNo ratings yet
- Examples of Plants That Grow From Bulbs Lzel Tubers RunnersDocument10 pagesExamples of Plants That Grow From Bulbs Lzel Tubers RunnersAan de Gracia100% (1)
- Brahmi: "Herb of Grace": Dhara Patel, A.H.PDocument13 pagesBrahmi: "Herb of Grace": Dhara Patel, A.H.Psubash pNo ratings yet
- Inventory FormatDocument20 pagesInventory FormatVaibhav PrakashNo ratings yet
- Haploid CultureDocument6 pagesHaploid CultureManjunatha Bukkambudi KrishnaswamyNo ratings yet
- HYPHOZYMA - Antonie Van LeeuwenhoekDocument6 pagesHYPHOZYMA - Antonie Van LeeuwenhoekcharlesNo ratings yet
- Herbs For Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument4 pagesHerbs For Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseasegandhicgandhiNo ratings yet
- Phytopathogenic BacteriaDocument23 pagesPhytopathogenic BacteriamonochemistNo ratings yet
- SST 508Document126 pagesSST 508m.preethiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Fluoride and Salicylic Acid On Seedling Growth and Biochemical Parameters of Watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus)Document7 pagesEffect of Fluoride and Salicylic Acid On Seedling Growth and Biochemical Parameters of Watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus)Django BoyeeNo ratings yet