0% found this document useful (0 votes)
411 views22 pagesIndustrial Design in Product Development
The document discusses industrial design, its goals, importance, and process. It describes how industrial design aims to make products safe, easy to use, and aesthetically pleasing while communicating corporate image at low cost. The industrial design process involves investigating customer needs, conceptualizing designs, refining concepts, selecting a final concept, and coordinating with engineering and production. Industrial design plays different roles depending on whether a product is technology-driven or user-driven. The timing of industrial design involvement also depends on the product type. Quality assessment of industrial design considers the user interface, emotional appeal, maintainability, resource use, and product differentiation.
Uploaded by
yossy amelia faradeaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
411 views22 pagesIndustrial Design in Product Development
The document discusses industrial design, its goals, importance, and process. It describes how industrial design aims to make products safe, easy to use, and aesthetically pleasing while communicating corporate image at low cost. The industrial design process involves investigating customer needs, conceptualizing designs, refining concepts, selecting a final concept, and coordinating with engineering and production. Industrial design plays different roles depending on whether a product is technology-driven or user-driven. The timing of industrial design involvement also depends on the product type. Quality assessment of industrial design considers the user interface, emotional appeal, maintainability, resource use, and product differentiation.
Uploaded by
yossy amelia faradeaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction: Explains the overview and context of industrial design within the product development process.
- Goals for ID: Outlines the main objectives and outcomes desired from industrial design efforts.
- ID Importance to Product Design: Discusses the significance of industrial design in enhancing product usability and visual appeal.
- ID Goals: Describes specific goals related to product utility, appearance, and ease of maintenance.
- The ID Process: Details the stages involved in the industrial design process from conceptualization to production.
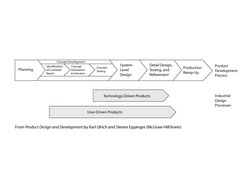
- Product Types from the ID Point of View: Analyzes different product types and their alignment with technology or user-driven approaches.
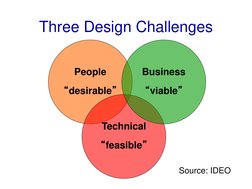
- Three Design Challenges: Introduces the key challenges faced in balancing design desirability, viability, and feasibility.
- Timing of ID Involvement: Explores when industrial design should be integrated into product development phases.
- Quality Assessment of ID: Examines criteria for evaluating the quality of industrial design efforts on product features.
- Industrial Design Chapter Example: Motorola RAZR: Provides a case study of the Motorola RAZR phone as an example of successful industrial design.
- Cost of Industrial Design: Analyzes the financial implications of industrial design on overall product development costs.