Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distinguish Metallic, Ionic and Covalent Bonding in Terms of Electron Loss and Gain, or Electron Sharing
Distinguish Metallic, Ionic and Covalent Bonding in Terms of Electron Loss and Gain, or Electron Sharing
Uploaded by
LOL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views13 pagesgfdr bvfdvfd
Original Title
8. bonding
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentgfdr bvfdvfd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views13 pagesDistinguish Metallic, Ionic and Covalent Bonding in Terms of Electron Loss and Gain, or Electron Sharing
Distinguish Metallic, Ionic and Covalent Bonding in Terms of Electron Loss and Gain, or Electron Sharing
Uploaded by
LOLgfdr bvfdvfd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Distinguish metallic, ionic and covalent
bonding in terms of electron loss and gain,
or electron sharing.
Review ionic bonding
• Oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other with electrostatic
forces
Covalent bonding
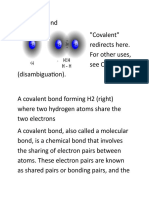
Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons. Covalent
bonds are formed between two atoms when both have
similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves
(i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar
ionization energies and electron affinities).
For example,
two hydrogen atoms bond covalently to form an H2 molecule; each
hydrogen atom in the H2 molecule has two electrons stabilizing it,
giving each atom the same number of valence electrons as the noble
gas He.
Hydrogen is an example of a diatomic molecule because it is made up
of 2 atoms.
Eg Fluorine (F2) Chlorine (Cl2) Oxygen (O2) nitrogen (N2)
There is a strong electrostatic attraction between each positively
charged nucleus and the negatively charged electrons that they share.
Properties of covalent compounds
https://study.com/academy/lesson/covalent-compounds-properties-
naming-formation.html
Make a list of the properties from the video
Metallic bonding
Metallic bonding is the type of bonding found in metallic elements. This
is the electrostatic force of attraction between positively charged ions
and delocalised outer electrons.
In metals the charged particles (electrons) are free to move around.
They are delocalized because they are not stuck in one location.
This ability for electrons to move enables them to conduct electricity.
Delocalised electrons are also responsible for a pure metal being
lustrous, the delocalized electrons on its surface reflect light
exceptionally well.
Some metals are used for their conductivity – eg power lines have a
core of steel and an outside layer of aluminum. Household wiring is
usually copper.
Metals and conductivity
You might also like
- Chemical Bond TypeDocument8 pagesChemical Bond TypeShabbir TamboliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PHY 351Document14 pagesTutorial 1 PHY 351MUHAMMAD AMMIRUL HAFIZ MD ZAININo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding MnewmowneeshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1Document68 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1Ridhima KamatNo ratings yet
- CHM 112 Aspect Note-Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesCHM 112 Aspect Note-Chemical BondingOluwatosin KoyejoNo ratings yet
- A Chemical Bond Is An Attraction Between Atoms That Allows The Formation of Chemical Substances That Contain Two or More AtomsDocument2 pagesA Chemical Bond Is An Attraction Between Atoms That Allows The Formation of Chemical Substances That Contain Two or More Atomscaguioajulius12No ratings yet
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 05Document10 pagesClass IX Chemistry Chapter 05Sam FisherNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding For B.tech 1st Year byDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding For B.tech 1st Year byJishnuNo ratings yet
- NEET Revision Notes For Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument21 pagesNEET Revision Notes For Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureTanushree DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument12 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureM. MuvafficaNo ratings yet
- Chemical CombinationDocument4 pagesChemical CombinationGodspower OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument132 pagesChemical BondingKowser mahmud100% (1)
- Notes1 Unit 1Document7 pagesNotes1 Unit 1arun iyer BitcoinminerandmathematicianNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry-Chemical Bonding and Molecular Struture - NotesDocument23 pages11 Chemistry-Chemical Bonding and Molecular Struture - NotesSumit MahatoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Covalent Bond?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Covalent Bond?Gunjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Notes-1Document5 pagesChemical Bonding Notes-1VigneshNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1 ChemistryDocument6 pagesAssignment#1 Chemistryzehrajamal03No ratings yet
- Qpaper 1PUDocument22 pagesQpaper 1PUPradeep SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: by Anthony Carpi, PH.DDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding: by Anthony Carpi, PH.DRizqa Gusti NarawitaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Chemical BondingDe AktivedNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Bonds: Created By: Amalia Heryani, Safira S. Dewinda, Fanny Eka, Fridayova Meidiana, and Raka SabarDocument27 pagesThe Chemical Bonds: Created By: Amalia Heryani, Safira S. Dewinda, Fanny Eka, Fridayova Meidiana, and Raka SabarAmalia HeryaniNo ratings yet
- Chapt 2 Part 2&3 cmt352Document20 pagesChapt 2 Part 2&3 cmt352Siti Zulaika Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Chemical Bonding and Intermolecular ForceDocument10 pagesUnit - 3 Chemical Bonding and Intermolecular ForceKidu GideyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NotesDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Document88 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes Ch.2Document37 pagesManufacturing Processes Ch.2Hani BanatNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Chemical Bonds101Document22 pagesLec 2 Chemical Bonds101memoryboybooNo ratings yet
- LoloDocument6 pagesLoloapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Unit 4Document35 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Unit 4Rajiv Sharma100% (1)
- Chemistry NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry NotesSteve Niloy RoyNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistryzaryabfaraz314No ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document26 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Bhupinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 2Document31 pagesModule 1 Lecture 2Amirs AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Prepared By: Asuda Taha Mhamad Mahdi Helin Salh Miran Bakr Zhwan OmarDocument24 pagesChemical Bonding: Prepared By: Asuda Taha Mhamad Mahdi Helin Salh Miran Bakr Zhwan OmarLana OmarNo ratings yet
- 2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentDocument131 pages2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentanathinothandoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and PropertiesDocument21 pagesChemical Bonding and PropertiesRoshan Jawad ZafirNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Lec 3 MSRDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding Lec 3 MSRsiam137032No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5Hina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondDocument12 pagesCovalent BondCristine Joy AbantoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4Document17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 411 A Prasann JamaleNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Bonding and ForcesDocument2 pagesBonding and ForceslalamoveNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding and Chemical CompoundsDocument31 pagesCovalent Bonding and Chemical Compoundsahmad batataNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Handout Chapter 4Document17 pages11 Chemistry Handout Chapter 4Erreneo100% (1)
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument3 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazmatshahzad786786No ratings yet
- B. The Structure of SolidsDocument18 pagesB. The Structure of Solids852sx4h7cbNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument8 pagesChemical BondRohan lallNo ratings yet
- Why Water Is A DipoleDocument50 pagesWhy Water Is A DipoleRaviverma077No ratings yet
- Material Bonding Character Example: Primary Interatomic Bonds Ionic BondingDocument4 pagesMaterial Bonding Character Example: Primary Interatomic Bonds Ionic BondingCsir RimlaNo ratings yet
- Chemicalbonding 130616231436 Phpapp02Document15 pagesChemicalbonding 130616231436 Phpapp02satyakumar07770No ratings yet
- Chapter-4 NOTESDocument18 pagesChapter-4 NOTESAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 SenguptaDocument38 pagesPhysics 2 SenguptaSashank PrayagaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Chemical BondingDocument32 pagesLecture 3 Chemical BondingAhmed FouadNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsjoeldpenosNo ratings yet
- HamletDocument2 pagesHamletLOLNo ratings yet
- Geography Resoucres - 2013 Trial Paper Question SolutionDocument1 pageGeography Resoucres - 2013 Trial Paper Question SolutionLOLNo ratings yet
- 2019 HSC Mathematics Extension 2 PDFDocument24 pages2019 HSC Mathematics Extension 2 PDFLOLNo ratings yet
- 1984: Concepts, Terms, and Ideas Worth KnowingDocument1 page1984: Concepts, Terms, and Ideas Worth KnowingLOLNo ratings yet
- Film Techniques PDFDocument6 pagesFilm Techniques PDFLOLNo ratings yet
- CaptureDocument1 pageCaptureLOLNo ratings yet
- Faculty Advisor: Deborah Sherman (English) : Asperger Syndrome and Its Role in Literature and FilmDocument3 pagesFaculty Advisor: Deborah Sherman (English) : Asperger Syndrome and Its Role in Literature and FilmLOLNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Objects in Motion: OutcomeDocument1 pageChapter 5: Objects in Motion: OutcomeLOLNo ratings yet
- Macbeth's Crimes PDFDocument1 pageMacbeth's Crimes PDFLOLNo ratings yet