Professional Documents
Culture Documents
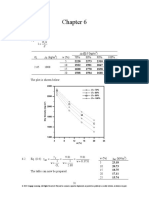
Design For Duct-1: Straight Duct Friction Loss (How To Decide " Mmaq/M", "Pa/M")
Uploaded by
Azrinshah Abu BakarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design For Duct-1: Straight Duct Friction Loss (How To Decide " Mmaq/M", "Pa/M")
Uploaded by
Azrinshah Abu BakarCopyright:
Available Formats
Design for Duct-1 Straight duct friction loss ( How to decide “ mmAq/m” , “Pa/m”)
Straight duct friction loss is as bellow;
2 2
L v L v
PT ・ ・ ・ PT ・ ・ ・ (darcy-Weisbach formula)
d 2g d 2
ΔPT : friction loss (mmAq) {Pa} λ: coefficient of duct friction loss d : internal diameter of duct (m) {m}
v : velocity of air (m/s) {m/s} g : gravity (m/s2) L: length of duct (m) {m}
γ: specific weight of air (kgf/m3) ρ: density of air {kg/m3}
Coefficient of duct friction loss is as bellow;
The fluid of inside duct is usually turbulence flow (Re >2,300). So coefficient od duct friction loss is as bellow
6 1
10 3
0.0055 1 (20,000 )
d Re
d : ratio of duct interior surface roughness to duct diameter Re: Reynolds number
(coefficient of duct friction loss can find Moody chart also.)
Reynolds number is as bellow;
vd
Re
: viscosity (m2 /s)
Design for Duct-1 Straight duct friction loss ( How to decide “ mmAq/m” , “Pa/m”)
Chart 1 : viscosity of air Chart 2 : density of air
X10-6
Relative Humidity RH % 飽和水 Relative Humidity RH %
DB DB
蒸気圧
℃ 0 40 50 60 70 80 ℃ 0 40 50 60 70 80
mm Hg
0 13.332 13.345 13.348 13.351 13.354 13.357
0 4.581 1.2931 1.2919 1.2916 1.2913 1.2910 1.2908
5 13.770 13.788 13.793 13.797 13.802 13.806
5 6.540 1.2698 1.2682 1.2678 1.2674 1.2669 1.2665
10 14.212 14.238 14.245 14.252 14.258 14.265
10 9.205 1.2474 1.2451 1.2446 1.2440 1.2434 1.2428
15 14.661 14.699 14.708 14.718 14.727 14.737
15 12.78 1.2258 1.2226 1.2219 1.2211 1.2203 1.2195
20 15.114 15.167 15.180 15.194 15.207 15.221
20 17.53 1.2048 1.2006 1.1996 1.1985 1.1975 1.1964
25 15.574 15.648 15.666 15.685 15.704 15.723
25 28.75 1.1846 1.1790 1.1776 1.1762 1.1748 1.1734
30 16.036 16.138 16.164 16.190 16.216 16.242
30 31.83 1.1651 1.1577 1.1558 1.1540 1.1522 1.1503
35 16.506 16.644 16.679 16.715 16.750 16.786
35 42.18 1.1462 1.1365 1.1341 1.1318 1.1294 1.1270
40 16.978 17.167 17.215 17.263 17.312 17.361
45 17.457 17.710 17.775 17.840 17.905 17.971 40 46.34 1.1278 1.1154 1.1123 1.1092 1.1061 1.1030
50 17.939 18.276 18.363 18.450 18.538 18.626 45 71.90 1.1101 1.0942 1.0903 1.0863 1.0823 1.0784
75 21.2 50 92.56 1.0929 1.0728 1.0678 1.0627 1.0577 1.0527
100 23.9 75 289.2 1.0144 0.9559 0.9413 0.9267 1.1922 0.8976
200 35.8 100 760.0 0.9464 0.8033 0.7675 0.7317 0.6958 0.6602
300 49.5 200 11,660 0.7463 - - - - -
400 64.5 300 64,440 0.6160 - - - - -
500 81.0
Chart 4 : Moody chart
Chart 3 : Ratio of interior surface roughness
Ratio of interior surface roughness material
ε= 5.00 Duct made by brick
ε= 2.00 Duct made by rough concrete
ε= 1.00 Duct made by wooden
ε= 0.5 Duct made by smooth concrete
ε= 0.3 G/I pipe (rusty interior surface)
ε= 0.18 G/I duct
ε= 0.15 G/I pipe
ε= 0.0015 Glass, AL, PVC, PE,duct
Design for Duct-1 Straight duct friction loss ( How to decide “ mmAq/m” , “Pa/m”)
Question : Calculate friction loss (mmAq/m or Pa/m) of G/I duct.
X 500
Air volume:12,000CMH
700
Air condition:DB20℃ RH60%
Convert from rectangular duct to round duct
xb
a
a・b 5
0.125
d 1.3
2
a b
You might also like
- Greenshields S - DDocument1 pageGreenshields S - Dvalen_wiranataNo ratings yet
- FLOWDocument7 pagesFLOWKaren AtallahNo ratings yet
- GROUP 10... FinalDocument397 pagesGROUP 10... FinalkeethanNo ratings yet
- Propeller Design CalculationDocument8 pagesPropeller Design CalculationDave Carter100% (7)
- Heating coil-100MTDocument31 pagesHeating coil-100MTHeong Siew LinNo ratings yet
- The Dryfit Range For Modular Performance Adaption.: Sonnenschein A412 / 120 FTDocument2 pagesThe Dryfit Range For Modular Performance Adaption.: Sonnenschein A412 / 120 FTglukkerNo ratings yet
- Flood Model Study of Wardha River MJBDocument19 pagesFlood Model Study of Wardha River MJBmqwer9139No ratings yet
- Project: Plot 68 Amghara SITE: Kuwait Ac Unit: Pacu 01 General DataDocument1 pageProject: Plot 68 Amghara SITE: Kuwait Ac Unit: Pacu 01 General DataSajidNo ratings yet
- Latihan 2 - ContohDocument14 pagesLatihan 2 - ContohCindy NabillahNo ratings yet
- SHOABA PROJECT DUCT PRESSURE DROP ANALYSISDocument6 pagesSHOABA PROJECT DUCT PRESSURE DROP ANALYSISmohamedNo ratings yet
- Calculos ReactorDocument12 pagesCalculos ReactorjlhoyosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 - SI - Final SolutionsDocument10 pagesChapter 06 - SI - Final SolutionsDouglas FernandesNo ratings yet
- BC Outdoor AcDocument1 pageBC Outdoor Acmedtsl.cppNo ratings yet
- BCDocument1 pageBCmedtsl.cppNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document27 pagesDocument 1spalaniandavar07No ratings yet
- Pile SpringDocument6 pagesPile SpringHamidAffandyNo ratings yet
- Enugu Disco - Fixed Charge: Tariff Code 2012 2013 2014 2015Document2 pagesEnugu Disco - Fixed Charge: Tariff Code 2012 2013 2014 2015Tony AppsNo ratings yet
- Datos de Entrada: Suelo Ang de Fric. ɸ' Cohesion (C ) Kpa P.Espc. Kn/M3 P.Espc. Sat. Kn/M3 TipoDocument2 pagesDatos de Entrada: Suelo Ang de Fric. ɸ' Cohesion (C ) Kpa P.Espc. Kn/M3 P.Espc. Sat. Kn/M3 TipoPatricia Ercilia Chavez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- LAMPIRAN Bab 2 PotraitDocument27 pagesLAMPIRAN Bab 2 PotraitYoel LavenkiNo ratings yet
- Water Vapor and Saturation Pressure in Humid AirDocument6 pagesWater Vapor and Saturation Pressure in Humid AirchitradevipNo ratings yet
- Database of Air CoolerDocument60 pagesDatabase of Air CoolerHai Nguyen CongNo ratings yet
- D.7 Oil Compressibility: Vasquez and Beggs' CorrelationDocument10 pagesD.7 Oil Compressibility: Vasquez and Beggs' Correlationسحر سلامتیانNo ratings yet
- Water Content Sample Compaction Test ResultDocument157 pagesWater Content Sample Compaction Test ResultSuci Angraeni SaputriNo ratings yet
- Energia Aplicada ASTM D698-AASHTO T99Document7 pagesEnergia Aplicada ASTM D698-AASHTO T99Cristian QuispeNo ratings yet
- CALCULO DE LA RED DOMICILIARIA DE AGUA POTABLEDocument13 pagesCALCULO DE LA RED DOMICILIARIA DE AGUA POTABLECarlos Enrique Diaz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gas field production and reservoir parameters over timeDocument5 pagesGas field production and reservoir parameters over timeAlejandro RivasNo ratings yet
- Roca Gutierrez Deysi Yeraldin 20171482D: P (Kpa) X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Act 1Document6 pagesRoca Gutierrez Deysi Yeraldin 20171482D: P (Kpa) X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Act 1Deysi RocaNo ratings yet
- Roca Gutierrez Deysi Yeraldin 20171482D: P (Kpa) X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Act 1Document6 pagesRoca Gutierrez Deysi Yeraldin 20171482D: P (Kpa) X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Act 1Deysi RocaNo ratings yet
- Copia de SILVER MEAL 2da EntregaDocument7 pagesCopia de SILVER MEAL 2da EntregaRaul HernandezNo ratings yet
- At Thermosorb DryerDocument8 pagesAt Thermosorb DryerJoelNo ratings yet
- Flow Meter Orifice CalculationDocument27 pagesFlow Meter Orifice CalculationLaksono BudiNo ratings yet
- Branch CableDocument8 pagesBranch CablevirgiawanpubgNo ratings yet
- Unit & Lifting Set Calculator: Data Input Calculation & Standard ResultDocument10 pagesUnit & Lifting Set Calculator: Data Input Calculation & Standard ResultAndreasSembiringNo ratings yet
- Decline Model 2Document21 pagesDecline Model 2Temitope BelloNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAS MEMBRANAS ZAID TEMSAMANIDocument9 pagesPRACTICAS MEMBRANAS ZAID TEMSAMANIjadouzi123No ratings yet
- Tabela 3 0.5 BarDocument1 pageTabela 3 0.5 BarAna BalbiNo ratings yet
- SI UnitsDocument7 pagesSI Units1122goodNo ratings yet
- Strong load springs for high tensionDocument1 pageStrong load springs for high tensionosbianiNo ratings yet
- 5a Lift and Drag Part II BLANKDocument4 pages5a Lift and Drag Part II BLANKbobNo ratings yet
- Hydrometer No. Average Temperature (°C) R R' - C +CDocument3 pagesHydrometer No. Average Temperature (°C) R R' - C +CRafiq MirNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Reconciliation Up To July-16Document4 pagesReinforcement Reconciliation Up To July-16Rajesh DeyNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering FundamentalsDocument30 pagesReservoir Engineering FundamentalsKhaled AdelNo ratings yet
- MAX DAYLY RAINFALL CALCULATIONDocument9 pagesMAX DAYLY RAINFALL CALCULATIONyuni maulidinaNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Reconciliation Up To July-16Document4 pagesReinforcement Reconciliation Up To July-16Rajesh DeyNo ratings yet
- C6 ReportDocument13 pagesC6 Reportfaizan_abidNo ratings yet
- Bulk Carrier Ship ProjectDocument147 pagesBulk Carrier Ship ProjectlakshmiNo ratings yet
- Calcula PattyDocument9 pagesCalcula Pattygabriela monica ancasi choqueNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid Production ReportDocument15 pagesAcetic Acid Production ReportArya Lodha100% (1)
- Triaxial Compression Test: Sample#2Document46 pagesTriaxial Compression Test: Sample#2muhammad junaidNo ratings yet
- Non-interacting tanks level experiment simulationDocument3 pagesNon-interacting tanks level experiment simulationAmit HanatNo ratings yet
- Percent Yield of Hydrogen Gas From Magnesium and HCL: Equation 1Document7 pagesPercent Yield of Hydrogen Gas From Magnesium and HCL: Equation 1Emanuel JaveNo ratings yet
- Relative Frequency Distribution Curve (Right Lane)Document8 pagesRelative Frequency Distribution Curve (Right Lane)Vibhanshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Standard Proctor Compaction Test ResultsDocument4 pagesStandard Proctor Compaction Test Resultstaufikkurrahman62860% (2)
- Omc MDD Curve - 407-18Document3 pagesOmc MDD Curve - 407-18Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Crusteam Nigeria Limited: All Bending Dimensions Are in Accordance With BS4466:1989 Shape CodeDocument2 pagesCrusteam Nigeria Limited: All Bending Dimensions Are in Accordance With BS4466:1989 Shape Codeorode franklynNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Mohammad Anas Ashraf GagaiNo ratings yet
- COTA (MSNM) OBS para s3 Long Parcial (KM) Long Acumulada (KM) Pendiente (Si)Document6 pagesCOTA (MSNM) OBS para s3 Long Parcial (KM) Long Acumulada (KM) Pendiente (Si)Sandra AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Analysis: For Reinforced Concrete Box CulvertDocument7 pagesHydraulic Analysis: For Reinforced Concrete Box Culvertmarkgil1990No ratings yet
- Ejercicio Unidad 3 Estabilidad de TaludesDocument10 pagesEjercicio Unidad 3 Estabilidad de TaludesFERMIN CONDORI QUISPENo ratings yet
- Government Publications: Key PapersFrom EverandGovernment Publications: Key PapersBernard M. FryNo ratings yet
- SP - LOSS - WORKSHEET DuctingDocument9 pagesSP - LOSS - WORKSHEET DuctingAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- The Efficient Way To Prevent Water Carryover and Keep Your Indoor Air HealthierDocument1 pageThe Efficient Way To Prevent Water Carryover and Keep Your Indoor Air HealthierAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- System Effect Theory ExplainedDocument75 pagesSystem Effect Theory ExplainedAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure Calculator r3Document3 pagesStatic Pressure Calculator r3arshi_yusufNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure Calculator r3Document3 pagesStatic Pressure Calculator r3arshi_yusufNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure Calculator GuideDocument6 pagesStatic Pressure Calculator GuideNghiaNo ratings yet
- Day1 1 Airflow in A System Rad GaneshDocument28 pagesDay1 1 Airflow in A System Rad GaneshAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- 7.0 AcsuDocument2 pages7.0 AcsuAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Sample TagDocument1 pageSample TagAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- SuperPairFR Copper Insulated Pair CoilDocument1 pageSuperPairFR Copper Insulated Pair CoilAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Sun Cam ManualDocument27 pagesSun Cam ManualAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Sample BoardDocument1 pageElectrical Sample BoardAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Trocellen Thermal InsulationDocument2 pagesTrocellen Thermal InsulationAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- 4.0 FcuDocument2 pages4.0 FcuAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- IAQ Thermal Comfort QuestionaireDocument5 pagesIAQ Thermal Comfort QuestionaireAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Photo Retouch Using LightroomDocument10 pagesPhoto Retouch Using LightroomAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- HVAC Cooling Load Procedure Guideline Lo0Document62 pagesHVAC Cooling Load Procedure Guideline Lo0api-385802594% (36)
- BTKR1343 - Chapter 4b - Control Technique - RepetitionDocument56 pagesBTKR1343 - Chapter 4b - Control Technique - RepetitionAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Reply Form For InternshipsDocument1 pageReply Form For InternshipsAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- KVMRT Project FactsDocument1 pageKVMRT Project FactsAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Sig Cond Chap 3: Understand Purpose & Ops of Analog & Digital Sig CondDocument13 pagesSig Cond Chap 3: Understand Purpose & Ops of Analog & Digital Sig CondAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- HVAC Commisioning ChecklistDocument65 pagesHVAC Commisioning ChecklistBalakumar100% (13)
- Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 3 - Methods of Analysis PDFNisha Kamel100% (2)
- SSP Pumps in Sugar ProcessingDocument44 pagesSSP Pumps in Sugar Processingverderusa100% (1)
- En 353Document93 pagesEn 353kumarsathish2009No ratings yet
- Vegetation and Soil Relations of Land Use Types of Boot Subwatershed at Makiling Forest ReserveDocument21 pagesVegetation and Soil Relations of Land Use Types of Boot Subwatershed at Makiling Forest ReserveAnonymous p47liBNo ratings yet
- NIKE RSL Finished Product OriginalDocument65 pagesNIKE RSL Finished Product OriginalHasan SozeriNo ratings yet
- Arranging Dissimilar Centrifugal Pumps in Series and ParallelDocument8 pagesArranging Dissimilar Centrifugal Pumps in Series and ParallelPujo BagusNo ratings yet
- Eva TaneDocument1 pageEva TaneAsima AtharNo ratings yet
- BG - GB - 07 Lozovey PDFDocument608 pagesBG - GB - 07 Lozovey PDFalifia fitriNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Rolling and Sliding BearingsDocument29 pagesComparison of Rolling and Sliding Bearingsaravindangokul687No ratings yet
- Material GradesDocument32 pagesMaterial GradesMarius PopaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Worksheet-IDocument2 pagesElectrochemistry Worksheet-ISrijit SahaNo ratings yet
- Igcse e Waves With MSCDocument82 pagesIgcse e Waves With MSCaliNo ratings yet
- 3.4 - Atomic Structure 2C - Edexcel IGCSE 9-1 Chemistry QP 2Document12 pages3.4 - Atomic Structure 2C - Edexcel IGCSE 9-1 Chemistry QP 2Javed UddinNo ratings yet
- Choke Specification - CCI PDFDocument4 pagesChoke Specification - CCI PDFAakashRanjan100% (1)
- The Effect of Ultrasonic Cavitation On Some Physical Properties of Synthetic Lubricants and Vegetable Based OilsDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Ultrasonic Cavitation On Some Physical Properties of Synthetic Lubricants and Vegetable Based OilsmkmzafarNo ratings yet
- ChemCAD Presentation Explains Chemical Process SimulationDocument24 pagesChemCAD Presentation Explains Chemical Process SimulationJohn Unk100% (1)
- AS 5110 - 2011 (+A1) Recessed Luminaire BarriersDocument37 pagesAS 5110 - 2011 (+A1) Recessed Luminaire BarriersAhmed shawkyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Electrochemical Processes:: I Electroless PlatingDocument16 pagesUnit 5 Electrochemical Processes:: I Electroless PlatingDhivya NNo ratings yet
- D3039 3039MDocument12 pagesD3039 3039MMariana CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Model of The Wet Limestone Flue Gas Desulfurization Process For Cost OptimizationDocument9 pagesModel of The Wet Limestone Flue Gas Desulfurization Process For Cost OptimizationAnonymous knICaxNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Educationmildah241No ratings yet
- Method Statement For Sonic Tube GroutingDocument22 pagesMethod Statement For Sonic Tube GroutingKaushalye Mahanama DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- PCI Standard For Thin BrickDocument2 pagesPCI Standard For Thin BrickJohn CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Citrinin removal from foods by magnetic nanoparticlesDocument34 pagesCitrinin removal from foods by magnetic nanoparticlesDenise Esteves MoritzNo ratings yet
- TFA Course For Foremen & QC TechnDocument39 pagesTFA Course For Foremen & QC TechnPrabhu RajalingamNo ratings yet
- Surface Preparation Guide for Coating SuccessDocument9 pagesSurface Preparation Guide for Coating SuccessnnuekNo ratings yet
- Takex MC SeriesDocument2 pagesTakex MC SeriesNestor Dino DominiciNo ratings yet
- 26 Condition Reporting - 1 PDFDocument24 pages26 Condition Reporting - 1 PDFJoão Henrique Ribeiro BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Thrust Force and Torque in Drilling On Aluminium AlloyDocument7 pagesPrediction of Thrust Force and Torque in Drilling On Aluminium Alloyanilsamuel0077418No ratings yet
- Aluminum Die Casting GuideDocument2 pagesAluminum Die Casting GuideAndrei Todea0% (1)
- Research Article: Development of Quantum Simulator For Emerging Nanoelectronics DevicesDocument10 pagesResearch Article: Development of Quantum Simulator For Emerging Nanoelectronics DevicesandrewtomsonNo ratings yet