Professional Documents
Culture Documents
An Approach To Design A Curve
Uploaded by
dextroprachi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views11 pagesBezier curves are parametric curves important in computer graphics and modeling smooth curves. They are defined by control points and the curve passes through the first and last points. Generalizations to higher dimensions are called Bezier surfaces. Bezier curves allow for smooth scalable curves and are widely used in computer graphics, modeling, and animation applications to outline object movement over time.
Original Description:
Original Title
Bazier Curves
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBezier curves are parametric curves important in computer graphics and modeling smooth curves. They are defined by control points and the curve passes through the first and last points. Generalizations to higher dimensions are called Bezier surfaces. Bezier curves allow for smooth scalable curves and are widely used in computer graphics, modeling, and animation applications to outline object movement over time.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views11 pagesAn Approach To Design A Curve
Uploaded by
dextroprachiBezier curves are parametric curves important in computer graphics and modeling smooth curves. They are defined by control points and the curve passes through the first and last points. Generalizations to higher dimensions are called Bezier surfaces. Bezier curves allow for smooth scalable curves and are widely used in computer graphics, modeling, and animation applications to outline object movement over time.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
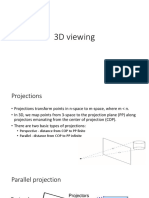
AN APPROACH TO DESIGN A CURVE
Bezier curve is a parametric curve important in
computer graphics and related fields.
Generalizations of Bezier curves to higher dimensions are called
Bezier surfaces.
In vector graphics, Bezier curves are an important tool used to
model smooth curves that can be scaled indefinitely.
Bezier curves were widely publicized in 1962 by the French
engineer Pierre Bezier, who used them to design automobile
bodies.
The curves were first developed in 1959 by Paul de Casteljau
using de Casteljau's algorithm, a numerically stable method to
evaluate Bezier curves.
Bezier curves are commonly referred to in image manipulation programs
such as InAdobe Illustrator, Adobe Photoshop, and GIMP are
combinations of Bezier curves.
Bezier curves are also used in animation as a tool to control motion in
applications such as Adobe Flash, Adobe After Effects, and Autodesk
3ds max.
Bezier curves are widely used in computer graphics to model smooth
curves.
In animation applications, such as Adobe Flash and Adobe Shockwave,
or in applications like Game Maker, Bézier curves are used to outline for
example movement. Users outline the wanted path in Bezier curves, and
the application creates the needed frames for the object to move along
the path.
Control points
Degree of curve/polynomial
Hull
Linear Bezier curves
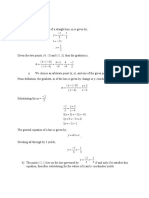
Given points P0 and P1, a linear Bezier curve is simply a straight line
between those two points. The curve is given by
Constructing Linear curves
Animation of a linear Bezier curve, t in [0,1] The t in the function for a
linear Bezier curve can be thought of as describing how far B(t) is from P0
to P1. For example when t=0.25, B(t) is one quarter of the way from point
P0 to P1. As t varies from 0 to 1, B(t) describes a curved line from P0 to P1.
Quadratic Bezier curves
A quadratic Bezier curve is the path traced by the function B(t), given
points P0, P1, and P2,
Constructing Quadratic curves
For quadratic Bezier curves one can construct intermediate points Q0
and Q1 such that as t varies from 0 to 1:
Point Q0 varies from P0 to P1 and describes a linear Bezier curve.
Point Q1 varies from P1 to P2 and describes a linear Bezier curve.
Point B(t) varies from Q0 to Q1 and describes a quadratic Bezier curve.
Cubic Bezier curves
Four points P0, P1, P2 and P3 in the plane or in three-dimensional space
define a cubic Bezier curve. The curve starts at P0 going toward P1 and
arrives at P3 coming from the direction of P2. Usually, it will not pass
through P1 or P2; these points are only there to provide directional
information. The distance between P0 and P1 determines "how long" the
curve moves into direction P2 before turning towards P3.
The parametric form of the curve is:
Generalization
The Bezier curve of degree n can be generalized as follows. Given points
P0, P1,..., Pn, the Bezier curve is.
For example, for n = 5:
The basis function are real.
Bezier curve always passes through the first and last control points.
The degree of polynomial defining the curve segment is one less then the
number of defining polygon points. Therefore , for 4 control points degree is 3,
i.e. cubic polynomial.
The curve lies entirely within the convex hull formed by four control points.
The convex hull property for Bezier curve ensure that polynomial smoothly
follow the control points.
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Pertemuan 8 BezierDocument16 pagesPertemuan 8 Bezierali_chaemNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Bezier CurvesDocument11 pages5.3 Bezier CurvesPhenias ManyashaNo ratings yet
- Bezier Curve Notes Two-D SurfacesDocument4 pagesBezier Curve Notes Two-D SurfacesGp LoveNo ratings yet
- How Bezier Curve WorksDocument20 pagesHow Bezier Curve WorksHELL DOZERNo ratings yet
- Bezier To CircleDocument8 pagesBezier To CircleMarius DiaconuNo ratings yet
- BEZIERDocument20 pagesBEZIERstalinrajesh143No ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Imp QuesDocument23 pagesComputer Graphics Imp QuesDr. MANU SINGH KEC (CSE)No ratings yet
- Derivatives of A Bézier CurveDocument8 pagesDerivatives of A Bézier Curvechandraveer0709No ratings yet
- UNIT 2 CadmDocument29 pagesUNIT 2 Cadmtamilselvan nNo ratings yet
- Bezier ExcelDocument48 pagesBezier ExceltranthevutNo ratings yet
- Properties of Bezier CurvesDocument3 pagesProperties of Bezier CurvesVinit RaiNo ratings yet
- L7 PDFDocument37 pagesL7 PDFDarsh MenonNo ratings yet
- 4.bezier CurveDocument46 pages4.bezier CurveYashovardhan BangurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document15 pagesChapter 3naquibNo ratings yet
- Cams and LociDocument15 pagesCams and LociAnonymous hlRLVcMNo ratings yet
- Basic Curves and Surface Modeling - CADDocument69 pagesBasic Curves and Surface Modeling - CADDr. Ajay M PatelNo ratings yet
- Endsem 2023Document122 pagesEndsem 2023SUBHASHISH SAHOONo ratings yet
- CagdDocument9 pagesCagdjazzy075No ratings yet
- UNIT-4 3D Object Representations MethodsDocument6 pagesUNIT-4 3D Object Representations MethodsRajyalakshmi MNo ratings yet
- Synthetics Surfaces Unit IIDocument31 pagesSynthetics Surfaces Unit IITharun SaiNo ratings yet
- Drawing Bezier Curves: Assignment OnDocument8 pagesDrawing Bezier Curves: Assignment OnamitNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Bezier CurveDocument52 pagesUnit 2 Bezier CurvedeepakmitrNo ratings yet
- 202003281454236324akankhas Yadav Computer GraphicsDocument9 pages202003281454236324akankhas Yadav Computer Graphicsparatevedant1403No ratings yet
- Unit II Curves & SurfacesDocument57 pagesUnit II Curves & Surfacesvishwajeet patilNo ratings yet
- 17 Curve DetailsDocument49 pages17 Curve DetailsTommy KongNo ratings yet
- Vectors - Bezier CurvesDocument3 pagesVectors - Bezier CurvesJam Uly GastyNo ratings yet
- File 5e95c84ed158cDocument4 pagesFile 5e95c84ed158cNitesh MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document64 pagesUnit 3x055311No ratings yet
- Viewing JPDocument44 pagesViewing JPkaneeshaNo ratings yet
- Ret Walls MCNDocument8 pagesRet Walls MCNSuhas NatuNo ratings yet
- B-Spline Curves ND SurfacesDocument28 pagesB-Spline Curves ND SurfacesVikhyat SoodNo ratings yet
- Bezier CurveDocument9 pagesBezier CurvePathul02No ratings yet
- Bezier & B-Spline CurveDocument3 pagesBezier & B-Spline Curveakshay_pundeNo ratings yet
- CG 5Document68 pagesCG 5pankajchandre30No ratings yet
- Berzier CurveDocument17 pagesBerzier CurveMuhammad AkhfafNo ratings yet
- Bezier Curves and B-Splines, Blossoming: New York UniversityDocument8 pagesBezier Curves and B-Splines, Blossoming: New York UniversityBalbirNo ratings yet
- CAD QuestionsDocument1 pageCAD QuestionsblackbirdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document112 pagesChapter 5Karthik RajashekarNo ratings yet
- Bézier Curve and SurfaceDocument24 pagesBézier Curve and SurfaceMechanicalFetrNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Lab Report Bezier Curve ImplementationDocument4 pagesComputer Graphics Lab Report Bezier Curve ImplementationNaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Vector and Geometry SpaceDocument66 pagesChapter 10 - Vector and Geometry SpaceRiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Geometric Modeling PDFDocument127 pagesUnit 2 Geometric Modeling PDFBaahuNo ratings yet
- 2 Parametric CurvesDocument10 pages2 Parametric CurvesPhenias ManyashaNo ratings yet
- 01 Construction of CurvesDocument27 pages01 Construction of CurvesAyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- CG 6Document26 pagesCG 6pankajchandre30No ratings yet
- Curves For Computer Aided Geometric DesignDocument21 pagesCurves For Computer Aided Geometric Designsri999No ratings yet
- Computer Graphics 2D TransformationsDocument34 pagesComputer Graphics 2D Transformations70061192 Bilal amjadNo ratings yet
- Lec 39Document30 pagesLec 39RamanNo ratings yet
- Surface RepresentationDocument53 pagesSurface Representationlp23mem4r06No ratings yet
- Construction Surveying & Layout/13637 - 05Document17 pagesConstruction Surveying & Layout/13637 - 05Eva MarquezNo ratings yet
- Curve Modeling-Bezier CurvesDocument37 pagesCurve Modeling-Bezier CurvesjayNo ratings yet
- Curve Representation 2. Parametric Curves 3. Non Parametric Curves 4. Cubic Splines 5. Bezier Curves 6. B-Spline CurvesDocument9 pagesCurve Representation 2. Parametric Curves 3. Non Parametric Curves 4. Cubic Splines 5. Bezier Curves 6. B-Spline CurvesSam SepiolNo ratings yet
- RCCM Notes FinalDocument17 pagesRCCM Notes FinalAdil AzeemNo ratings yet
- Bezier CurveDocument14 pagesBezier CurveSarthak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional RepresentationDocument33 pagesThree Dimensional RepresentationWafa ElgalhoudNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus: Mengxia Zhu Fall 2007Document26 pagesVector Calculus: Mengxia Zhu Fall 2007Lim Xiu XianNo ratings yet
- 6 2 Parametric Curves-2Document7 pages6 2 Parametric Curves-2CliffordTorresNo ratings yet
- Geometric Objects and Transformations - IDocument67 pagesGeometric Objects and Transformations - IraniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Magazine Volume 48 Issue 5 1975 (Doi 10.2307/2690063) Ian Richards - Impossibility PDFDocument15 pagesMathematics Magazine Volume 48 Issue 5 1975 (Doi 10.2307/2690063) Ian Richards - Impossibility PDFfNo ratings yet
- 06 1MA1 3H - Aiming For 9 Spring 2020 Mark Scheme (Set 1)Document14 pages06 1MA1 3H - Aiming For 9 Spring 2020 Mark Scheme (Set 1)AyishaNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document9 pagesQuestion 1mwidaniNo ratings yet
- Laws of ExponentsDocument30 pagesLaws of ExponentsAndi IremedioNo ratings yet
- Basic Queries in SQL:: SELECT FROM WHEREDocument13 pagesBasic Queries in SQL:: SELECT FROM WHEREمحمد مهدي الحسينيNo ratings yet
- R1.6 Scientific Notation Review ANSWERSDocument8 pagesR1.6 Scientific Notation Review ANSWERSNavam S PakianathanNo ratings yet
- Program Logic FormulationDocument57 pagesProgram Logic Formulationアテンヂド 彩92% (12)
- PreCalculus Unit 1 SummativeDocument2 pagesPreCalculus Unit 1 SummativeShams MughalNo ratings yet
- Leung. (2013) Teachers Implementing Mathematical Problem Posing in The Classroom - Challenges and Strategies. Educational Studies 83Document14 pagesLeung. (2013) Teachers Implementing Mathematical Problem Posing in The Classroom - Challenges and Strategies. Educational Studies 83X YNo ratings yet
- System Identification of A Hobby DC Motor Using A Low CostDocument6 pagesSystem Identification of A Hobby DC Motor Using A Low CostBrasoveanu GheorghitaNo ratings yet
- PDADocument52 pagesPDAIbrahim AnsariNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electrodynamics Lecture NotesDocument113 pagesAdvanced Electrodynamics Lecture NotesWouterNo ratings yet
- Time Series.Document97 pagesTime Series.Pranav Khanna100% (1)
- Field TheoryDocument42 pagesField TheoryMonica ThakurNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 of 5: Topic: 5.0 Functions and Graphs SUBTOPIC: 5.1 FunctionsDocument26 pagesLecture 1 of 5: Topic: 5.0 Functions and Graphs SUBTOPIC: 5.1 FunctionsNur Sakinah IdrisNo ratings yet
- Ch5 State Space Search Methods MasterDocument35 pagesCh5 State Space Search Methods MasterAhmad AbunassarNo ratings yet
- Applied MathsDocument2 pagesApplied MathsSereneMahNo ratings yet
- Infosys Practice Questions 2018Document160 pagesInfosys Practice Questions 2018Ganesh100% (1)
- Maths Sa1 Sp2Document15 pagesMaths Sa1 Sp2Shivam PandeyNo ratings yet
- Not Found: Cebu Technological UniversityDocument1 pageNot Found: Cebu Technological UniversityKaren Joyce LabajoNo ratings yet
- 03b 1MA1 3F June 2022 Examination Paper (Word) 2Document20 pages03b 1MA1 3F June 2022 Examination Paper (Word) 2iqraa8148No ratings yet
- Logic Design and Digital CircuitsDocument3 pagesLogic Design and Digital CircuitsShawn Michael SalazarNo ratings yet
- 2018 Book IntroductoryQuantumMechanicsDocument641 pages2018 Book IntroductoryQuantumMechanicsAlfangNo ratings yet
- Solution To CW Game Theory Part 3Document2 pagesSolution To CW Game Theory Part 3Francine Kye DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Approximation AlgorithmsDocument27 pagesApproximation AlgorithmsAman VermaNo ratings yet
- Fractional Equations Worksheet - 2Document14 pagesFractional Equations Worksheet - 2Parul AggarwalNo ratings yet
- HW9 SolsDocument4 pagesHW9 SolsDidit Gencar Laksana0% (1)
- (De Gruyer Studies in Mathematical Physics) Anna G. Chunovkina, Leonid A. Mironovsky, Valery A. Slaev-Metrology and Theory of Measurement-De Gruyter (2013)Document585 pages(De Gruyer Studies in Mathematical Physics) Anna G. Chunovkina, Leonid A. Mironovsky, Valery A. Slaev-Metrology and Theory of Measurement-De Gruyter (2013)Govinda Prasad DhunganaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Space FrameDocument24 pagesLesson 7 Space Framecriscab12345No ratings yet
- Final Synopsis Neetu GuptaDocument25 pagesFinal Synopsis Neetu Guptanarendrakum16No ratings yet