Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L2 Rules of Netiquette
Uploaded by
Rain Collins0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views12 pagesL2 Rules of Netiquette
Uploaded by
Rain CollinsCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Rules of Netiquette
• Online security, safety, and ethics
• Internet threats
• Protecting reputations online
• Copyright
• Contextualized online search and
research skills
At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to:
1. consider one’s and others’ safety when sharing
information using the Internet;
2. consider one’s and others’ reputation when using the
Internet;
3. determine and avoid the dangers of the Internet;
4. be responsible in the use of social networking sites; and
5. browse the Internet efficiently and properly through
proper referencing.
The Internet, truly, is a powerful tool. It
can be used to promote your business,
gain new friends, and stay in touch with
the old ones. It is also a source of
entertainment. But like most things in this
world, there is always “another side of
the coin.” The Internet is one of the most
dangerous places, especially if you do
not know what you are doing.
Internet safety, or online safety is the
knowledge of maximizing the user’s
personal safety and security risks to
private information and property
associated with using the internet,
and the self-protection form
computer crime in general.
Internet Threats:
1. Malware – stands for malicious software.
a. Virus- malicious program designed to replicate
itself and transfer from one computer to
another.(flash drives,CD’s and Internet) .
b. Worm- malicious program that transfers from one
computer to another by any type of
means.(computer network).
c. Trojan- malicious program that is disguised as a
useful program but once downloaded and
installed,leaves your PC unprotected and allows
hackers to get your information.
*Rogue security software – tricks the user into
posing that is security software.
d. Spyware – a program that runs in the background without
you knowing it ”spy”. Ability to monitor what you are currently
doing and typing.
* Keyloggers – used to record the keystroke done by the
user.Done to steal password and information.
e. Adware- a program designed to send you
advertisements,mostly pop-ups.
2. Spam – unwanted email mostly from bots or advertisers. It
can be used to send malware.
3. Phishing – Its goal is to acquire sensitive personal
information like passwords and credit card details.
* Pharming – a more complicated way of phishing where it
exploits the DNS (Domain Name System)
Think Before You Click
1. Before you post something on the web, ask these questions
to yourself: Would you want your parents or grandparents to see
it? Would you want your future boss to see it? Once you post
something on the web, you have no control of who sees your
posts.
2. Your friends depend on you to protect their reputation online.
Talk to your friends about this serious responsibility.
3. Set your post to “private.” In this way, search engines will
not be able to scan that post.
4. Avoid using names. Names are easy for search engines to
scan.
5. If you feel that a post can affect you or other’s reputation, ask
the one who posted it to pull it down or report it as
inappropriate.
If you create something—an
idea, an invention, a form of
literary work, or a research, you
have the right of how it should
be used by others. This is called
intellectual property.
Fair Use
Intellectual property may be used without
a consent as long as it is used in
commentaries,criticisms,search
engines,parodies,news report,research.
Cybercrime- a crime commited or
assisted through the use of the internet.
Privacy Policy- tells the user how the
website will handle its data.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lunch and Learn PPT TemplateDocument39 pagesLunch and Learn PPT TemplateRaja GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Linkedin Merge Consolidation Form - 2018 - FinalDocument1 pageLinkedin Merge Consolidation Form - 2018 - FinalKelvin VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- CSA Incident Response ChecklistDocument7 pagesCSA Incident Response Checklistceh classNo ratings yet
- Enterprise FW 03-Security FabricDocument31 pagesEnterprise FW 03-Security FabricMarcos Vinicios Santos CorrêaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan on Internet Threat CategoriesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan on Internet Threat CategoriesRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Directions: Shades The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesDirections: Shades The Correct AnswerRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- DLP MediaDocument3 pagesDLP MediaRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Pandemic and Typhoon: Positive Impacts of A Double Disaster On Mental Health of Female Students in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesPandemic and Typhoon: Positive Impacts of A Double Disaster On Mental Health of Female Students in The PhilippinesRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ICT in Education, Commerce, Health and BankingDocument3 pagesBenefits of ICT in Education, Commerce, Health and BankingRain CollinsNo ratings yet
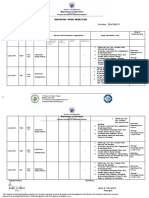
- Enclosure 4 Individual Work Week PlanDocument2 pagesEnclosure 4 Individual Work Week PlanRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- DLP AlibataDocument4 pagesDLP AlibataRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- DLP EnvironmentDocument5 pagesDLP EnvironmentRain CollinsNo ratings yet
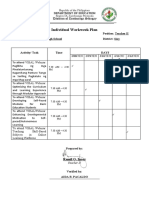
- Individual Workweek Plan: Ramil O. InsoyDocument1 pageIndividual Workweek Plan: Ramil O. InsoyRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- DLP AntiDocument3 pagesDLP AntiRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Individual Work Week Plan JUNE 08 12 2020 1Document2 pagesIndividual Work Week Plan JUNE 08 12 2020 1Rain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Final Semestral Grades for Grade 11 Ostrich SectionDocument2 pagesFinal Semestral Grades for Grade 11 Ostrich SectionRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Individual Workweek Plan for Teacher Ramil O. InsoyDocument1 pageIndividual Workweek Plan for Teacher Ramil O. InsoyRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Foodborne IllnessDocument3 pagesFoodborne IllnessRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Individual-Work-Week-Plan-JUNE-29 - JULY 01 - 03Document2 pagesIndividual-Work-Week-Plan-JUNE-29 - JULY 01 - 03Rain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Individual-Work-Week-Plan March 16 - 20Document1 pageIndividual-Work-Week-Plan March 16 - 20Rain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Individual-Work-Week-Plan March 23 - 27Document1 pageIndividual-Work-Week-Plan March 23 - 27Rain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Grad Letter HeadDocument1 pageGrad Letter HeadRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- RAT 2020 Least Learned Competencies Science 10Document2 pagesRAT 2020 Least Learned Competencies Science 10Rain CollinsNo ratings yet
- List Learned First Sem Second QuarterDocument1 pageList Learned First Sem Second QuarterRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- F-Secure Anti-Virus Provides Protection Against Viruses, Spyware, Infected E-Mail Attachments and OtherDocument1 pageF-Secure Anti-Virus Provides Protection Against Viruses, Spyware, Infected E-Mail Attachments and OtherRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Final Semestral Grades ReportDocument2 pagesFinal Semestral Grades ReportRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- BaybayinDocument1 pageBaybayinRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- District of Siay Regional Achievement Test (Rat) 2020 Consolidated Least Learned Competencies Media and Information Literacy 12Document1 pageDistrict of Siay Regional Achievement Test (Rat) 2020 Consolidated Least Learned Competencies Media and Information Literacy 12Rain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Grade 11Document1 pageGrade 11Rain CollinsNo ratings yet
- DisAssembly and Assembly ActualDocument14 pagesDisAssembly and Assembly ActualRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Trends and Network Class PDFDocument20 pagesTrends and Network Class PDFRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Edexcel Democracy and Participation 150921063450 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument20 pagesUnit 1 Edexcel Democracy and Participation 150921063450 Lva1 App6891 PDFRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Final Semestral Grades for Grade 11 Ostrich SectionDocument2 pagesFinal Semestral Grades for Grade 11 Ostrich SectionRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- Take-Home Assignment in Computer Communications: EDA 344/DIT423-Chalmers and Gothenburg UniversityDocument1 pageTake-Home Assignment in Computer Communications: EDA 344/DIT423-Chalmers and Gothenburg UniversityBlake BurgessNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 RL RSDocument2 pagesChapter 2 RL RSEhem, Rommel100% (1)
- NGIPS Transition GuideDocument2 pagesNGIPS Transition GuideGeorge JR BagsaoNo ratings yet
- Praktek-Cara Konfigurasi 3 Router Pada Packet TracerDocument3 pagesPraktek-Cara Konfigurasi 3 Router Pada Packet TracerWanda WinataNo ratings yet
- XML Payloads 1Document3 pagesXML Payloads 1Rahul MNo ratings yet
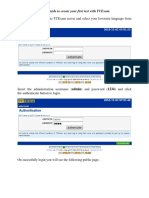
- Step-by-step guide to create your first test with TCExamDocument22 pagesStep-by-step guide to create your first test with TCExamHaftamu HailuNo ratings yet
- BC Docs Support SupportManual c02642109 c02642109 PDFDocument304 pagesBC Docs Support SupportManual c02642109 c02642109 PDFmarcusdznNo ratings yet
- Abhi Pandey - GA ResumeDocument2 pagesAbhi Pandey - GA ResumeAbhi PandeyNo ratings yet
- HTTP CatsDocument34 pagesHTTP CatsrandyNo ratings yet
- 3Document3 pages3playah hateNo ratings yet
- Datasaurus-Rex Google Analytics & YouTube DashboardDocument3 pagesDatasaurus-Rex Google Analytics & YouTube DashboardFaisal Azad JointoNo ratings yet
- خلاصة اسئلة الانترفيو مهندس الشبكات والسيسكو والآى تى وملحقة بالأجوبة التفصيلية ومضاف إليها ماتريال عربىDocument11 pagesخلاصة اسئلة الانترفيو مهندس الشبكات والسيسكو والآى تى وملحقة بالأجوبة التفصيلية ومضاف إليها ماتريال عربىAhmad DawaraNo ratings yet
- BT Cloud Voice Customer Firewall and Lan GuideDocument3 pagesBT Cloud Voice Customer Firewall and Lan GuideJim CollinsNo ratings yet
- Using LDAP To Manage UsersDocument57 pagesUsing LDAP To Manage UsersAlex Aeron50% (2)
- Security in Computing Brute Force Attack Demonstration ReportDocument27 pagesSecurity in Computing Brute Force Attack Demonstration ReportThe CarterNo ratings yet
- Brand Awareness: Digital Marketing For Business: Jagga Rangavinay Teja Royal 20171CSE0258Document14 pagesBrand Awareness: Digital Marketing For Business: Jagga Rangavinay Teja Royal 20171CSE0258neha SinghNo ratings yet
- Autocad 2022.problema Mouse Lento 3dconfigDocument7 pagesAutocad 2022.problema Mouse Lento 3dconfigHelton SouzaNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing NotesDocument17 pagesDigital Marketing NotesSuresh TanwarNo ratings yet
- GDP R Contents ListDocument2 pagesGDP R Contents ListNipun MistryNo ratings yet
- Vineet Sharma KeyloggerDocument51 pagesVineet Sharma KeyloggervineetNo ratings yet
- Quick Installation Guide Dvg-7111S: Voip Telephone AdapterDocument24 pagesQuick Installation Guide Dvg-7111S: Voip Telephone Adapterusr2suNo ratings yet
- Scrape Multiple Pages at Once Using VBADocument3 pagesScrape Multiple Pages at Once Using VBAangel saezNo ratings yet
- Individual Daily Log and Accomplishment Report: Department of EducationDocument2 pagesIndividual Daily Log and Accomplishment Report: Department of EducationjovelNo ratings yet
- Uk The Security Operations Maturity Model Quick Reference Guide For Defence BrochureDocument7 pagesUk The Security Operations Maturity Model Quick Reference Guide For Defence BrochureFlávio RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Web Development and Design Foundations With Html5 8th Edition Felke Morris Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesWeb Development and Design Foundations With Html5 8th Edition Felke Morris Solutions Manuallloydkieran71epfi100% (26)
- Digital Marketing PackagesDocument6 pagesDigital Marketing Packagesvipin agarwalNo ratings yet