Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Relative Density
Uploaded by
Britney valladares0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views6 pagesRelative density is a ratio that compares the density of a substance to a reference material, usually water. A relative density less than 1 means the substance is less dense than water and will float, while a relative density greater than 1 means the substance is denser than water and will sink. It is calculated by dividing the density of the substance by the density of water. Two examples are provided to demonstrate calculating relative density.
Original Description:
Original Title
relative density.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRelative density is a ratio that compares the density of a substance to a reference material, usually water. A relative density less than 1 means the substance is less dense than water and will float, while a relative density greater than 1 means the substance is denser than water and will sink. It is calculated by dividing the density of the substance by the density of water. Two examples are provided to demonstrate calculating relative density.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views6 pagesRelative Density
Uploaded by
Britney valladaresRelative density is a ratio that compares the density of a substance to a reference material, usually water. A relative density less than 1 means the substance is less dense than water and will float, while a relative density greater than 1 means the substance is denser than water and will sink. It is calculated by dividing the density of the substance by the density of water. Two examples are provided to demonstrate calculating relative density.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
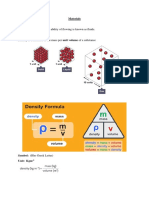
Relative density
• Relative density, is the ratio of the
density of a substance to the density of a
given reference material.
• Usually, the reference material is water.
Hence, relative density is also defined as
a ratio of density of particular substance
with that of water.
• If a substance's relative density is less
than 1 then it is less dense than the
reference; if greater than 1 then it is
denser than the reference.
• If the relative density is exactly 1 then the
densities are equal; that is, equal
volumes of the two substances have the
same mass.
• If the reference material is water then a
substance with a relative density less
than 1 will float in water. For example, an
ice cube, with a relative density of about
0.91, will float.
• A substance with a relative density
greater than 1 will sink.
•• Relative density (RD) or is a
dimensionless quantity, as it is the ratio
of either densities or weights.
• = =
• where is relative density, ρsubstance is the
density of the substance being
measured, and ρwater is the density of
water.
• Remember: (By convention ρ, the Greek
letter rho, denotes density.)
Question # 1
•Calculate
the R.D. of aluminium
whose density is 2700 kg, the
density of water being 1000 kg.
Question # 2
A bottle weighs 124 g when empty
and 344 g when full of water. The
same bottle weighs 289 g when
filled with oil. Find the relative
density of the oil.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Physical Quantities and MeasurementHarshita MunotNo ratings yet
- Notes - Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument8 pagesNotes - Physical Quantities and MeasurementAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Relitive DensityDocument1 pageRelitive DensityShahid NiaziNo ratings yet
- Stephen Lower (2006) : Understanding Density and BuoyancyDocument14 pagesStephen Lower (2006) : Understanding Density and BuoyancyApril RojoNo ratings yet
- PHY CH 2 VIIIBDocument10 pagesPHY CH 2 VIIIBAnvi PriyaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Properties of Fluids. BuoyancyDocument18 pages3.2 Properties of Fluids. BuoyancyAlibabaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Lesson 1 Introduction To MatterDocument11 pagesUnit 1: Lesson 1 Introduction To MatterAbeer Alnajjar عبير النجارNo ratings yet
- Pascal's PrincipleDocument15 pagesPascal's PrincipleIan SorzNo ratings yet
- 02ffd3 - Fluid Statics 04Document22 pages02ffd3 - Fluid Statics 04Abdul BasitNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy ResourceDocument41 pagesBuoyancy ResourceSurbhi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Floatation Notes.Document7 pagesFloatation Notes.Mandeep Singh PlahaNo ratings yet
- Density Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesDensity Reading ComprehensionSkandar Taj100% (1)
- Fluids MechanicsDocument23 pagesFluids MechanicsHamza MashoodNo ratings yet
- Density, Specific Gravity, and Specific Volume LectureDocument37 pagesDensity, Specific Gravity, and Specific Volume LectureAhmed Hassan Mina HamadNo ratings yet
- Material Properties Physical PropertiesDocument11 pagesMaterial Properties Physical PropertiesXiedrick SibongaNo ratings yet
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument22 pagesArchimedes PrincipleainaNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument6 pagesFluidsDebal Dev BasuNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Matter and DensityDocument28 pagesLESSON 2 - Matter and DensityKate OchaveNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Matter and DensityDocument28 pagesLESSON 2 - Matter and DensityKate OchaveNo ratings yet
- 6478 651939 1.+Fluid+MechanicsDocument29 pages6478 651939 1.+Fluid+MechanicsCharelle Hazel EzehNo ratings yet
- Density and Specific GravityDocument5 pagesDensity and Specific GravityLorielle OlivaNo ratings yet
- 03 DensityDocument34 pages03 DensityElyn SofiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 1-29-2004Document27 pagesLecture 6 1-29-2004احمد الدلالNo ratings yet
- Archimedes'PrincipleDocument14 pagesArchimedes'PrincipleDarenfangNo ratings yet
- Revised Expt 5 Physics LabDocument10 pagesRevised Expt 5 Physics LabWNo ratings yet
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument6 pagesArchimedes PrincipleRakshit Gupta100% (2)
- DensityDocument38 pagesDensityvectors academyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Unit 1 Properties of FluidsDocument13 pagesFluid Mechanics: Unit 1 Properties of FluidsPranjyoti SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocument27 pagesProperties of Fluids: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAhmedalaal LotfyNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity (Ust Template)Document22 pagesSpecific Gravity (Ust Template)JajaNo ratings yet
- Review 3rd P6 PTDocument11 pagesReview 3rd P6 PTsucceeded312No ratings yet
- Fluids At Rest Density: ρ= mass of thematerial volume of the material m VDocument4 pagesFluids At Rest Density: ρ= mass of thematerial volume of the material m VDerick PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Archimedes' Principle of FlotationDocument4 pagesArchimedes' Principle of FlotationANam MUkri92% (24)
- EAH 221-Aug 10th2009Document14 pagesEAH 221-Aug 10th2009imaniNo ratings yet
- Any Substance That Has The Ability of Flowing Is Known As FluidsDocument7 pagesAny Substance That Has The Ability of Flowing Is Known As FluidsprimalNo ratings yet
- Pharm LabDocument1 pagePharm LabMichelle CasilangNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings - Short NotesDocument3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings - Short Notesalok.coding123No ratings yet
- Density and Relative Density of A SubstanceDocument1 pageDensity and Relative Density of A SubstanceNOVASTAR222No ratings yet
- PDF document-49F9440362E1-1Document12 pagesPDF document-49F9440362E1-1Cally ChewNo ratings yet
- Practical Hydraulic: Chapter One Mass, Density and DisplacementDocument10 pagesPractical Hydraulic: Chapter One Mass, Density and DisplacementashrafsaberNo ratings yet
- Michael Adeleye, PH.D, P.G. Dip - EdDocument27 pagesMichael Adeleye, PH.D, P.G. Dip - Edlar dinchiNo ratings yet
- Is A Fart An Example of Diffusion, Expansion or Contraction?Document12 pagesIs A Fart An Example of Diffusion, Expansion or Contraction?Sharon RumminsNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Static FluidDocument30 pagesCh5 Static FluidALIF SYAKIR SATARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: FluidsDocument53 pagesChapter 7: FluidssptbalaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Physical Science: 5 EditionDocument72 pagesConceptual Physical Science: 5 EditionoperationmanagerNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics of Water PresentationDocument7 pagesPhysical Characteristics of Water PresentationEthanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Fluid Mechanics - StaticDocument27 pagesLecture 4 - Fluid Mechanics - StaticAhmed ShakerNo ratings yet
- Fluids GCDocument36 pagesFluids GClumine0755No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PTDocument23 pagesFluid Mechanics PTPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument7 pagesProperties of MatterAkhmad RiyantoNo ratings yet
- Physics Ias Materials Topic 02: Unit 02Document19 pagesPhysics Ias Materials Topic 02: Unit 02මේනුක සූවින්දNo ratings yet
- FMI Lecture 02Document18 pagesFMI Lecture 02Salman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Discovering Density PowerPointDocument8 pagesDiscovering Density PowerPointGiovanna CruzNo ratings yet
- Density NotesDocument4 pagesDensity NotesFaiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Ramanujan Institution O F Mathe Matics A N D Science: H.Chakradh ARDocument3 pagesRamanujan Institution O F Mathe Matics A N D Science: H.Chakradh ARSAI PRANEETH REDDY DHADINo ratings yet
- 1.4 DensityDocument37 pages1.4 DensityLaw PeterNo ratings yet
- Density: 1 HistoryDocument8 pagesDensity: 1 HistoryLirim SopajNo ratings yet
- CSEC French June 2008 P3Document13 pagesCSEC French June 2008 P3Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- CSEC French June 2013 P2Document7 pagesCSEC French June 2013 P2Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- Sheresse Kiele Melville: Plant ManagerDocument2 pagesSheresse Kiele Melville: Plant ManagerBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- CSEC French June 2017 P2Document16 pagesCSEC French June 2017 P2Britney valladares100% (1)
- CSEC French June 2012 P2Document9 pagesCSEC French June 2012 P2Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- CSEC French June 2006 P2Document5 pagesCSEC French June 2006 P2Britney valladares100% (1)
- CSEC French June 2010 P2Document9 pagesCSEC French June 2010 P2Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- TUT. 5 Trespass To PersonDocument2 pagesTUT. 5 Trespass To PersonBritney valladares0% (1)
- CSEC French June 2005 P2Document5 pagesCSEC French June 2005 P2Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- TUT. 7 Vicarious LiabilityDocument2 pagesTUT. 7 Vicarious LiabilityBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- TUT. 4 Nuisance (Public and Private)Document2 pagesTUT. 4 Nuisance (Public and Private)Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- TUT. 1 Tort Introduction (Nature)Document1 pageTUT. 1 Tort Introduction (Nature)Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- TUT. 3 DefamationDocument2 pagesTUT. 3 DefamationBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- TUT. 6 Liability For AnimalsDocument1 pageTUT. 6 Liability For AnimalsBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- Lect. 3.1 Co-OwnershipDocument23 pagesLect. 3.1 Co-OwnershipBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- CSEC French June 2005 P3Document14 pagesCSEC French June 2005 P3Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- CSEC Technical Drawing June 2013 P032Document6 pagesCSEC Technical Drawing June 2013 P032Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- Makandal Daaga Scholarship Text For WebsiteDocument1 pageMakandal Daaga Scholarship Text For WebsiteBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- LawUndergrad PDFDocument73 pagesLawUndergrad PDFBritney valladaresNo ratings yet