Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Transmission by Babar 2
Uploaded by
Mananbozdar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesEngineering 6th term file 2
Original Title
Power transmission by Babar 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEngineering 6th term file 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesPower Transmission by Babar 2
Uploaded by
MananbozdarEngineering 6th term file 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
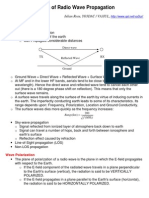
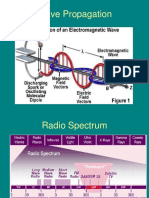
Wave propagation
• Once a radio signal has been radiated by antenna ,it travel or
propagate through space and will ultimately reach the receiving
antenna.
• Em signal can take one or more several paths to receiving antenna.
• Paths that radio signal takes depends upon many factors like frq of
signals , atmospheric conditions and time of day
Three paths that EM signal takes
Ground or surface waves
• It leaves the antenna and remains close to earth.
• It actually follow curvature of earth and travel at distance beyond
horizon
• Ground wave propagation is the strongest at low and medium freq
ranges.
• That is ,g waves are the main signal path for radio signal in
30khz to 3Mhz range
• The signal can propagate for hundreds and some times thousand
miles at these low freq.
• Am broadcast signals are propagate primerly by GW.
• At higher freq byond 3Mhz the earth begins to attenunate EM
signal.
Sky waves
• That signal is radiated by antenna into upper atmosphere where it is
bent or reflected back to earth.
• The bending of signal is caused by a region in upper atmosphere
called ionosphere .
• Ultraviolet radiation from sun cause upper atmosphere to inionize .
• That is to be become electrically charged
• Invisible layers exist above earth.
• At its lowest point ,ionosphere is approximately at 30mi above earth
and extends up to 250 mi above ground.
• Ionosphere is divided into D ,E and F layers
• D and E are weakly ionized because farthest from sun.
• They exists in day lights during
• During day lights hours try to absorbs radio signals in mediun freq
range from 300 khz to 3Mhz.
• F layers further F1 and F2 are highy ionized due to close to sun.
• F layer exists both daylight and nightime hours.
• Most effect on EM signals.
• Causes of refraction of radio signal.
• Refraction is bending of radio signal
• When radio signal goes into ionosphere and different level of
ionization cause radio waves to be gradually bent .
• Direction of bending signals depend upon angle at which radio
waves enters ionopshre and different degree of ionization of layers.
• When angle is large with respect to earth radio signals slightly bent
and pass on through ionosphere and are lost in space.
• If angle is smaller ,radio signal bent and reflected back to earth.
• Radio waves are sent back to earth with minimum loss and result
signal is propagate over extremely longer distance
• 3to 30Mhz
• Long distance communication
Space or direct waves
You might also like
- Space Wave PropagationDocument40 pagesSpace Wave Propagationece4 2015No ratings yet
- Unit-IV: Radiation & Propagation of WaveDocument30 pagesUnit-IV: Radiation & Propagation of WaveAK 1No ratings yet
- 8th Sem Notes-1Document62 pages8th Sem Notes-1KakjajaNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation: Areeba Shujaat (2012-TE-16)Document40 pagesWave Propagation: Areeba Shujaat (2012-TE-16)Areeba AyzazNo ratings yet
- Ec 306-AWP Module6 - 2Document33 pagesEc 306-AWP Module6 - 2Eshaan BangeraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication - 3Document41 pagesWireless Communication - 3joeykenyattaNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Radio WavesDocument17 pagesPropagation of Radio WavesNag Aditya GadeNo ratings yet
- Maheshwari Das Meghana BSDocument18 pagesMaheshwari Das Meghana BSTrung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- AWP Unit5Document31 pagesAWP Unit5GUNREDDY VISHNU VARDHAN REDDY100% (1)
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument92 pagesRadio Wave PropagationFufa OdaNo ratings yet
- Propagation of EMW in Various MediumDocument17 pagesPropagation of EMW in Various MediumSunil GAireNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation Through the IonosphereDocument108 pagesWave Propagation Through the Ionospherethe sanctuary phNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave Propagation GuideDocument102 pagesRadio Wave Propagation GuideDisha GoelNo ratings yet
- Sky Wave Propagation OutlineDocument15 pagesSky Wave Propagation Outlinesophieee19No ratings yet
- 3 Without Audio - Ionospheric Wave Propagation ppt31Document27 pages3 Without Audio - Ionospheric Wave Propagation ppt31niji mathewsNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument70 pagesRadio Wave PropagationMeet ShahNo ratings yet
- Awp U-6Document48 pagesAwp U-6Gajula Venkat SaiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave Propagation: by Dr. Malik AbdurazzaqDocument30 pagesElectromagnetic Wave Propagation: by Dr. Malik AbdurazzaqMOHAMMADNo ratings yet
- AWP Unit6Document50 pagesAWP Unit6GUNREDDY VISHNU VARDHAN REDDYNo ratings yet
- For AwpDocument65 pagesFor AwpbrindkowsiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave Propagation (Lecture2)Document53 pagesElectromagnetic Wave Propagation (Lecture2)RJ BedañoNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CLASS WAVE PropagationDocument137 pagesGENERAL CLASS WAVE PropagationChris Osea AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations Form Basis of Electromagnetic WavesDocument31 pagesMaxwell's Equations Form Basis of Electromagnetic WavesDenzel Ivan PalatinoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Radio Wave PropagationDocument14 pagesBasics of Radio Wave PropagationSACIIDNo ratings yet
- Air Bone Communication TechniquesDocument25 pagesAir Bone Communication Techniques22 Yogi Prisma Caysar PradewaNo ratings yet
- Radio Theory: Air Waves in AviationDocument16 pagesRadio Theory: Air Waves in Aviationchand_basha_8No ratings yet
- Aircraft Radio Navigation Communication SystemsDocument192 pagesAircraft Radio Navigation Communication Systemspontoo100% (16)
- Radio Wave Propogation PDFDocument41 pagesRadio Wave Propogation PDFAnuj PatelNo ratings yet
- Space Communication: Key ConceptsDocument17 pagesSpace Communication: Key ConceptsKashyap PatelNo ratings yet
- Ground Wave PropagationDocument19 pagesGround Wave Propagationsophieee19100% (1)
- Radio Wave Propagation ModesDocument30 pagesRadio Wave Propagation ModesMd. HarunNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument4 pagesRadio Wave PropagationBenNo ratings yet
- At 2.1 Realization of Concepts in Radio Wave PropagationDocument3 pagesAt 2.1 Realization of Concepts in Radio Wave PropagationSam PunoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Radio Wave PropagationDocument10 pagesBasics of Radio Wave Propagationfred osterNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument9 pagesCommunicationJody EltrawyNo ratings yet
- Unguided MediaDocument16 pagesUnguided MediaAnirban Guha100% (1)
- Radio Waves: A Guide to Key Concepts and PropertiesDocument40 pagesRadio Waves: A Guide to Key Concepts and PropertiesMerlyCalvaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Telecommunication: The Propagation of Radio WavesDocument18 pagesElements of Telecommunication: The Propagation of Radio WavesYemuraiNo ratings yet
- 2 1 3propagation PDFDocument5 pages2 1 3propagation PDFFranco CarrettoNo ratings yet
- Radio-Wave Propagation: Electromagnetic Waves (TEM) - I.EDocument78 pagesRadio-Wave Propagation: Electromagnetic Waves (TEM) - I.EGowndaManiNo ratings yet
- 22 5 21Document26 pages22 5 21Charuruba NNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument43 pagesRadio Wave PropagationyagneshnmakwanaNo ratings yet
- PcomDocument4 pagesPcomapi-371405568No ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Ship's AntennasDocument29 pagesChapter 2-Ship's AntennasmendesNo ratings yet
- EC2353 Unit 5 Antenna and WaveDocument50 pagesEC2353 Unit 5 Antenna and Waveابراهيم السعيديNo ratings yet
- Microwave Signal PropagationDocument12 pagesMicrowave Signal PropagationAnonymous VqLEvzNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave Propagation 2Document80 pagesRadio Wave Propagation 2Juliana Nepembe100% (1)
- SkywaveDocument6 pagesSkywavechuck333No ratings yet
- Propagation and AntennaDocument105 pagesPropagation and AntennaSagnik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Radio WaveDocument14 pagesRadio WaveJithin KhanNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument28 pagesRadio Wave PropagationGrason Bautista MinguezNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Radiowaves ExplainedDocument6 pagesPropagation of Radiowaves ExplainedClaire AragoncilloNo ratings yet
- Basics of Radio Wave PropagationDocument9 pagesBasics of Radio Wave PropagationwakyzaiNo ratings yet
- Tropospheric Propagation1Document17 pagesTropospheric Propagation1Binal KamaniNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation1Document18 pagesWave Propagation1Rajasekhar TurakaNo ratings yet
- VHF Signal PropagationDocument18 pagesVHF Signal PropagationYacine KhlilNo ratings yet
- Skywaves: Skywaves Travel Towards The IonosphereDocument2 pagesSkywaves: Skywaves Travel Towards The IonosphereVS KRISHNA KUMARNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument18 pagesRadio Wave PropagationElisha The drummerNo ratings yet
- Attenuation, Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction and Propagation of Electromagnetic WavesDocument34 pagesAttenuation, Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction and Propagation of Electromagnetic WavesJonna AcaboNo ratings yet
- The Fast Track to Understanding Ham Radio PropagationFrom EverandThe Fast Track to Understanding Ham Radio PropagationNo ratings yet
- Numbers (Singular and Plural) Worksheet 4Document1 pageNumbers (Singular and Plural) Worksheet 4MananbozdarNo ratings yet
- FFC AdDocument1 pageFFC AdMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Gujranwala Electric Power Company (GEPCO) Junior Engineer NotesDocument11 pagesGujranwala Electric Power Company (GEPCO) Junior Engineer NotesAadil WaheedNo ratings yet
- Fauji Fertilizer Company Limited Management Trainees Test (Schedule 2021)Document1 pageFauji Fertilizer Company Limited Management Trainees Test (Schedule 2021)Alia KhanNo ratings yet
- GEPCO Approved Content WeightagesDocument1 pageGEPCO Approved Content WeightagesEnGr MuZamil ShAir CheemaNo ratings yet
- Gujranwala Electric Power Company (GEPCO) Junior Engineer NotesDocument11 pagesGujranwala Electric Power Company (GEPCO) Junior Engineer NotesAadil WaheedNo ratings yet
- MCQ of Transmission and DistributionDocument51 pagesMCQ of Transmission and DistributionMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Federal Public Service Commission: Sector F-5/1, Aga Khan Road, IslamabadDocument2 pagesFederal Public Service Commission: Sector F-5/1, Aga Khan Road, IslamabadMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Time Tables Mid ExamDocument2 pagesTime Tables Mid ExamMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- MCQ of Transmission and DistributionDocument51 pagesMCQ of Transmission and DistributionMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Slides For Internship ReportDocument16 pagesSlides For Internship ReportMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Pak Affair For StudentsDocument6 pagesPak Affair For StudentsAlina Naeem MohmandNo ratings yet
- MCQ of Transmission and DistributionDocument51 pagesMCQ of Transmission and DistributionMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Gujranwala Electric Power Company (GEPCO) Junior Engineer NotesDocument11 pagesGujranwala Electric Power Company (GEPCO) Junior Engineer NotesAadil WaheedNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation: - Once A Radio Signal Has Been Radiated by Antenna, It Travel orDocument1 pageWave Propagation: - Once A Radio Signal Has Been Radiated by Antenna, It Travel orMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Transmission and Distribution 5eea6a0f39140f30f369e735Document14 pagesMCQ On Transmission and Distribution 5eea6a0f39140f30f369e735MananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Slides For Internship ReportDocument16 pagesSlides For Internship ReportMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Radar: Objects at Distance at Distances That Cant Be Observed Visually. by Radar Conductive TargetsDocument1 pageRadar: Objects at Distance at Distances That Cant Be Observed Visually. by Radar Conductive TargetsMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- MINUTES OF 5th MEETING OF ONLINE ACADEMIC COUNCILDocument3 pagesMINUTES OF 5th MEETING OF ONLINE ACADEMIC COUNCILMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Type of Conductor Material For Transmission LineDocument8 pagesType of Conductor Material For Transmission LineMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission by BabarDocument21 pagesPower Transmission by BabarMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- Applied Maths-2017 UpdatedDocument2 pagesApplied Maths-2017 UpdatedMuhammad Ishtiaq100% (1)
- Zoology SubjectiveDocument1 pageZoology SubjectiveChaudhry ZaidNo ratings yet
- Theory and Performance of Electrical Machines by JB Gupta PDFDocument4 pagesTheory and Performance of Electrical Machines by JB Gupta PDFMananbozdar0% (2)
- Css Islamic History 2019Document1 pageCss Islamic History 2019Osama BalochNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering MCQ GuideDocument119 pagesElectrical Engineering MCQ GuideRoy Anthony T. BayonNo ratings yet
- Technical WritingDocument9 pagesTechnical WritingMananbozdarNo ratings yet
- MIT6 685F13 Quiz01ansDocument6 pagesMIT6 685F13 Quiz01ansAnonymous 9WNqHZNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and DrivesDocument123 pagesElectrical Machines and Drivesanon-427532100% (14)
- Relative Equilibrium of Liquids: Cengr 3260 - HydraulicsDocument14 pagesRelative Equilibrium of Liquids: Cengr 3260 - HydraulicsBry RamosNo ratings yet
- ShipHydro OE2044 SlidesDocument215 pagesShipHydro OE2044 SlidesMonika NathawatNo ratings yet
- 2 Ripple TankDocument10 pages2 Ripple TankAazan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 3Document2 pagesHydraulics 3IZNo ratings yet
- Christoph Schiller MOTION MOUNTAIN The Adventure of PhysicsDocument372 pagesChristoph Schiller MOTION MOUNTAIN The Adventure of PhysicsHariom SharmaNo ratings yet
- Relative Velocity Questions TuteDocument4 pagesRelative Velocity Questions TuteVenuja De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic ForceDocument2 pagesAerodynamic ForceViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Soal Fisika Kinematika EnglishDocument15 pagesSoal Fisika Kinematika EnglishnovianhabibieNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Oscillator & Rigid Rotor: Recap: - Separation of Variables For Solving Schrödinger EquationDocument9 pagesHarmonic Oscillator & Rigid Rotor: Recap: - Separation of Variables For Solving Schrödinger EquationDmidNo ratings yet
- Crystal Optics With Allowance For Spatial Dispersion Exciton Theory. IIDocument37 pagesCrystal Optics With Allowance For Spatial Dispersion Exciton Theory. IIbrian delgado de lucioNo ratings yet
- MOMENTUMDocument21 pagesMOMENTUMClare Andrea Egalla100% (1)
- 07a1ec09 Engineering MechanicsDocument4 pages07a1ec09 Engineering Mechanicsأشرف عليNo ratings yet
- Two 5 KG Bodies Approach Each Other, Both Having Speed of 2 M S - What Is The Total Momentum?Document20 pagesTwo 5 KG Bodies Approach Each Other, Both Having Speed of 2 M S - What Is The Total Momentum?Sam JordanNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICS Cengage JEE MAINS and AdvancedDocument210 pagesKINEMATICS Cengage JEE MAINS and AdvancedtaanusarvNo ratings yet
- Coupled Pendulum-Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCoupled Pendulum-Lab ReportAhh Doh100% (1)
- Tutorial Week 8 2013 1Document5 pagesTutorial Week 8 2013 1sujetagottraNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton and His Three Laws of MotionDocument4 pagesIsaac Newton and His Three Laws of MotionWarrid LumponganNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 2421 HW#1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesPHYSICS 2421 HW#1 Solutionsmalonz030% (1)
- Kinematics in Two Dimensions: Projectile and Circular MotionDocument11 pagesKinematics in Two Dimensions: Projectile and Circular MotionKapelsuNo ratings yet
- TES - Basic SUVAT QuestionsDocument1 pageTES - Basic SUVAT QuestionsDataDen Pro Account 2No ratings yet
- Classical and Relativistic MechanicsDocument7 pagesClassical and Relativistic MechanicsJosé Fernando Pérez PérezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study GuideDocument7 pagesMidterm Study GuidejohntothepNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document6 pagesAssignment 4gowricivilNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids-I: TorsionDocument20 pagesMechanics of Solids-I: TorsionNoor Ul Amin AwanNo ratings yet
- Forces On Cylinders and Plates in An Oscillating FluidDocument18 pagesForces On Cylinders and Plates in An Oscillating FluidMallikarjun BhandiwadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/11Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/11sangdeepNo ratings yet
- Engineering College: Course FileDocument2 pagesEngineering College: Course Filevenkateshyadav2116No ratings yet
- Robotics Trajectory PlanningDocument52 pagesRobotics Trajectory PlanningFinto RaphelNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 5 Using Newton's Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag ForcesDocument12 pages5.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 5 Using Newton's Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag ForcesnourNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-IIT-JEE Advanced Revision PackageDocument220 pagesPHYSICS-IIT-JEE Advanced Revision PackageChaitanya Pandey100% (1)