0% found this document useful (0 votes)
693 views15 pagesBus Duct Trunking System Overview
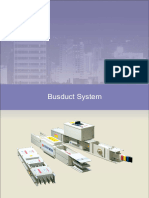
This document provides an overview of bus duct trunking systems. [1] It defines bus duct as sheet metal ducts containing copper or aluminum bars to conduct substantial electric currents as an alternative to power cables. [2] It describes common bus duct components and configurations. [3] The advantages of bus duct include easy installation, flexibility, compact design, excellent short circuit distribution of loads, and cost savings over cables.
Uploaded by
mahmoudCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Thermoplastic Silicone,
- Configuration,
- Installation Requirements,
- Gasket Rubber,
- System Voltage,
- Safety Requirements,
- Cable vs Bus Duct,
- Installation Tools,
- Insulation Voltage,
- Bus Duct
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
693 views15 pagesBus Duct Trunking System Overview
This document provides an overview of bus duct trunking systems. [1] It defines bus duct as sheet metal ducts containing copper or aluminum bars to conduct substantial electric currents as an alternative to power cables. [2] It describes common bus duct components and configurations. [3] The advantages of bus duct include easy installation, flexibility, compact design, excellent short circuit distribution of loads, and cost savings over cables.
Uploaded by
mahmoudCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Thermoplastic Silicone,
- Configuration,
- Installation Requirements,
- Gasket Rubber,
- System Voltage,
- Safety Requirements,
- Cable vs Bus Duct,
- Installation Tools,
- Insulation Voltage,
- Bus Duct
- What is the BUSDUCT?: Explains what a bus duct is, including its purpose and advantages as an alternative to cables.
- Some Types Of Bus Duct: Illustrates and describes different types of bus duct configurations.
- BUSDUCT Advantage: Outlines the advantages of using bus ducts, focusing on installation and cost benefits.
- Application: Describes various application areas for bus ducts, such as buildings and factories.
- Cable VS BUSDUCT: Compares cable and bus duct using several criteria like space and heat dissipation.
- Standards: Lists the standards related to bus ducts and their manufacturing.
- Material: Details the materials used in the construction of bus ducts.
- Accessories: Shows various accessories used with bus ducts and their functionalities.
- Request Specifications: Provides the specifications required for bus ducts in various settings.
- Site Survey: Indicates the section about performing site surveys for bus duct installation.
- Installation and Maintenance: Offers guidelines on installing and maintaining bus ducts, including safety requirements.
- Offer Sales: Contains sales offer details including pricing and terms.