Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Warp Let Off Motion (Pengluluran Benang Lusi)
Uploaded by
sarah syahidatul f0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views12 pagesOriginal Title
Warp Let off Motion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views12 pagesWarp Let Off Motion (Pengluluran Benang Lusi)
Uploaded by
sarah syahidatul fCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Warp Let off Motion
(Pengluluran benang lusi)
• Tujuan : agar menjaga tegangan benang lusi
selama proses pertenunan konstan.
• Supaya mesin tenun berjalan lancar maka
panjang benang lusi yang diulur harus sama
panjang dengan panjang kain tenun yang
digulung ditambah mengkeret lusi.
Peralatan penguluran lusi
• 1. Pengulur lusi sistem pengereman
• 2. Pengulur lusi sistem negatif, mengulur lusi
dengan panjang tidak tetap.
• 3. Pengulur lusi sistem positif, mengulur lusi
dengan panjang tetap
Warp let off
Warp let off
• Notations:
• R = radius of warp on the beam
• r = beam ruffle radius
• Tt = tension in the chain on tight side (attached with the weight
lever)
• Ts = tension in the chain on slack side (attached with machine
frame)
• W= weight
• x = the distance between fulcrum point and chain on tight side
• y = the distance between fulcrum point and weight (variable)
• T = tension in the warp sheet (variable)
• F = frictional force at the beam ruffle
• Taking moments about the beam centre we
have:
• TR=Fr
• The frictional force F =Tt - Ts
• where μ= coefficient of friction between chain
and beam ruffle
• and θ = angle of wrap in radian made by the
chain on beam ruffle.
Warp let off
• Now, taking moments about the fulcrum H of
the lever, we have:
Warp let off
• Equation 5 shows that the condition needed to achieve a constant
warp tension is to maintain the ratio constant. Thus as beam radius
R reduces, the distance y must be reduced by moving the weight
towards the fulcrum H in regular interval to balance the warp
tension. For example, if the beam radius decreases by 25%, the
distance y must be reduced by 25% to maintain a constant warp
tension.
• As shown in Figures 9.7, the warp tension is maintained within a
small range from full beam to empty beam by shifting the weights at
regular intervals. It is also noted that the frequency of weight
shifting increases towards the beam is getting exhausted. This is
ascribed to the asymptotic relationship between warp tension and
warp radius on the beam.
Warp let off
• Positive Let-off
• In case of positive let-off warp, the warp tension is controlled by a
mechanism which drives the warp beam at a correct rate. In most of the
positive let-off systems, the backrest is not fixed but floating. It acts as a
warp tension sensing mechanism. As the tension in the warp increases,
the backrest is depressed. A Hunt positive let-off motion is ilustrated in
the Figure 9.8. There are two split pullyes made out of V-pulley. Motion
from crank shaft moves the top split pulley via a worm and worm wheel.
Top pulley in turn drives the bottom pulley through a belt. As the tension
on the warp increases the back rest goes down and the L-type lever with
weight lowers the diameter of the bottom pulley and essentially increases
the diameter of the top pulley through the necessary linkages. Now the
bottom pulley moves at a faster rate than it was earlier and the
connecting worm to the beam drive moves more to deliver extra warp in
order to reduce the warp tension.
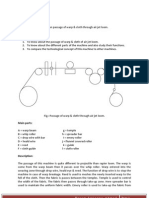
Electronics Take up & warp let off motions
Electronic units
You might also like
- Secondary Warp Let Off MotionDocument6 pagesSecondary Warp Let Off Motionfahriz fitra annasNo ratings yet
- ASTM E 29 Yr 13 PDFDocument5 pagesASTM E 29 Yr 13 PDFRosendo RizoNo ratings yet
- Cloth Design TheoryDocument73 pagesCloth Design TheoryBhayani50% (2)
- Type of Shed and Tappet Shedding MechanismDocument43 pagesType of Shed and Tappet Shedding MechanismAfjal Hossain Sujan100% (1)
- WeavingDocument49 pagesWeavingyogesh123789No ratings yet
- Weaving Chapter5 Beat-Up PDFDocument69 pagesWeaving Chapter5 Beat-Up PDFAbhijit BasakNo ratings yet
- Figure 7.1: Loom Timing Diagram For Shuttle Loom (Early Shedding)Document8 pagesFigure 7.1: Loom Timing Diagram For Shuttle Loom (Early Shedding)Prabhakaran JNo ratings yet
- Weaving Technology Ii: Basic Operations in Weaving ProcessDocument52 pagesWeaving Technology Ii: Basic Operations in Weaving ProcessZillur Rahman SaykatNo ratings yet
- Fabric Manufacture - I Assignment Presentation: Topic: Positive Let Off MechanismDocument10 pagesFabric Manufacture - I Assignment Presentation: Topic: Positive Let Off MechanismPrabhakaran JNo ratings yet
- 10.wave Optics. Byju'sDocument223 pages10.wave Optics. Byju'sSureka100% (1)
- Warp Stop MotionDocument8 pagesWarp Stop MotionIlhamsNo ratings yet
- Lecture ComberDocument20 pagesLecture ComberMD. Sharifuzzaman Joy100% (1)
- Aisc Bolting and Welding 190606215451 PDFDocument73 pagesAisc Bolting and Welding 190606215451 PDFthet naingNo ratings yet
- WeavingDocument16 pagesWeavingindrascope50% (2)
- The Effect of Weave Construction On Tear Strength of Woven FabricsDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Weave Construction On Tear Strength of Woven FabricsSuza Ahmed AuporboNo ratings yet
- Let Off MechanismDocument10 pagesLet Off MechanismTamanna Ahmed100% (2)
- Basic of Weaving-1Document11 pagesBasic of Weaving-1Boier Sesh Pata100% (1)
- Classification of Shuttle Picking MechanismDocument14 pagesClassification of Shuttle Picking MechanismSANJIT JANANo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Effect On Belts: Determining Angle of WrapDocument16 pagesCentrifugal Effect On Belts: Determining Angle of WrapARI BENINo ratings yet
- TappetDocument10 pagesTappetoronno5No ratings yet
- (1.1) Take-Up MechanismDocument26 pages(1.1) Take-Up Mechanismsukanya prasadNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Under Picking MechanismDocument3 pagesAssignment On Under Picking MechanismZAyedNo ratings yet
- Aring Diagram of A Tappet LoomDocument12 pagesAring Diagram of A Tappet LoomAfjal Hossain Sujan100% (1)
- Basic of LoomDocument9 pagesBasic of LoomShantnu MittalNo ratings yet
- Secondary MotionDocument7 pagesSecondary MotionamboklateNo ratings yet
- (1.2c) Auxiliary Mechanism-Weft Fork (Side)Document10 pages(1.2c) Auxiliary Mechanism-Weft Fork (Side)sukanya prasadNo ratings yet
- B Des FT 1 PDFDocument9 pagesB Des FT 1 PDFSushil Bishnoi0% (3)
- Sinkers by Diksha BTCH 7Document16 pagesSinkers by Diksha BTCH 7Diksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Picking in Projectile LoomDocument2 pagesPicking in Projectile LoomAniket Khot100% (2)
- Jute SpinningDocument20 pagesJute SpinningAbdus Salam Ratan100% (1)
- 05 Passage AirjetDocument2 pages05 Passage Airjetnil006No ratings yet
- Ornamantation in SelvagesDocument18 pagesOrnamantation in SelvagesSatish Kulkarni100% (1)
- Primary MotionsDocument59 pagesPrimary Motionsafroja hossainNo ratings yet
- Inspection of Waste Extracted by Different Machines of Spinning Department.Document3 pagesInspection of Waste Extracted by Different Machines of Spinning Department.Ammar Naeem BhattiNo ratings yet
- Knitting Terms and DefinitionDocument12 pagesKnitting Terms and DefinitionBirendra MeherNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our PresentationDocument40 pagesWelcome To Our PresentationAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Loop TransferDocument3 pagesLoop TransferAshraful Himel100% (1)
- Jute Drawing 11.26.22Document13 pagesJute Drawing 11.26.22Nayemur Rahman Chowdhury100% (1)
- Beating 1Document13 pagesBeating 1Joyonto HimoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Dobby Shedding (JBA)Document17 pagesLecture 5 Dobby Shedding (JBA)Sajib IglesiasNo ratings yet
- 4.tappet Shedding Mechanism of A Tappet LoomDocument10 pages4.tappet Shedding Mechanism of A Tappet LoomAfjal Hossain SujanNo ratings yet
- Two Neeedle Four Thread OverlockDocument6 pagesTwo Neeedle Four Thread OverlocktahaNo ratings yet
- 7 Weaving C4b Cam 09Document50 pages7 Weaving C4b Cam 09textiletr100% (1)
- Roving FrameDocument99 pagesRoving Frameirfanfakhar2No ratings yet
- 2.5 Pirn WindersDocument5 pages2.5 Pirn WindersCraig MartinNo ratings yet
- Examples of Emulsions: Machine Specification of Jute Softener MachineDocument3 pagesExamples of Emulsions: Machine Specification of Jute Softener MachinemohsinNo ratings yet
- Working Procedure of Comber MachineDocument3 pagesWorking Procedure of Comber MachineRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- WarpingDocument10 pagesWarpingKalyan Ray GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shed Geometry ElementsDocument21 pagesShed Geometry ElementsMuhammad Ahsan Mir100% (3)
- Practical Observation of Material Flow On Ring-Fame, Auto Cone Rotor SpinningDocument5 pagesPractical Observation of Material Flow On Ring-Fame, Auto Cone Rotor SpinningTalha saeedNo ratings yet
- Weft Knitting - 2Document23 pagesWeft Knitting - 2Mina Samy abd el zaherNo ratings yet
- Pattern and Selection DevicesDocument18 pagesPattern and Selection DevicesAtaur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Needle Punched NonwovenDocument14 pagesManufacturing of Needle Punched NonwovenKareena Kalla100% (1)
- Study of Transmitted Speed of Drafting Zone On Roving Frame (FL-16) and Ring Frame (Ry-5) by Gearing Method.Document5 pagesStudy of Transmitted Speed of Drafting Zone On Roving Frame (FL-16) and Ring Frame (Ry-5) by Gearing Method.Nain JNo ratings yet
- Yarn Count (Yarn Numbaring System)Document3 pagesYarn Count (Yarn Numbaring System)Mohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- NEEDLE THREADING (AutoRecovered)Document5 pagesNEEDLE THREADING (AutoRecovered)tahaNo ratings yet
- Simplexenhanced 150401131931 Conversion Gate01Document46 pagesSimplexenhanced 150401131931 Conversion Gate01د. م. فادي نقرشNo ratings yet
- Revised List of Mechanics of Fibrous Structures (TET) 2k19Document35 pagesRevised List of Mechanics of Fibrous Structures (TET) 2k19RAZA Khn100% (1)
- Let OffDocument3 pagesLet OffLondon StNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document6 pagesExperiment 4AkankshaNo ratings yet
- TwistDocument27 pagesTwistSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Belt Theory: Friction Drives - V-Belts and V-Ribbed BeltsDocument7 pagesBelt Theory: Friction Drives - V-Belts and V-Ribbed BeltsSai Sudheer KattaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Notes by TVK Sir DTU PDFDocument10 pagesFluid Mechanics Notes by TVK Sir DTU PDFBhoopesh JorwalNo ratings yet
- Arthur M. Young - The Geometry of Meaning: Chapter XII - Free WillDocument22 pagesArthur M. Young - The Geometry of Meaning: Chapter XII - Free WillNguyenNo ratings yet
- UH60L APART Study GuideDocument134 pagesUH60L APART Study GuideRodrigo LucasNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of A Heat Pipe Heat Exchanger Operating With A Low Global Warming Potential RefrigerantDocument8 pagesExperimental and Theoretical Analysis of A Heat Pipe Heat Exchanger Operating With A Low Global Warming Potential RefrigerantasalazarhNo ratings yet
- Linear and Quadratic Equations and Their Graphs (H) MSDocument2 pagesLinear and Quadratic Equations and Their Graphs (H) MSVindra Stacyann DhanrajNo ratings yet
- Solving Multi-Step EquationsDocument4 pagesSolving Multi-Step EquationsAli MakiNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument112 pagesClass NotesRahul NayakNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question Bank-3Document33 pagesPhysics: Question Bank-3MUSIC WORLDNo ratings yet
- Otonetics Tunics PR PRI ManualDocument41 pagesOtonetics Tunics PR PRI Manualtimothylee86No ratings yet
- 9-Introduction To Resistivity MeasurementsDocument24 pages9-Introduction To Resistivity Measurementsهيثم قاسم طاهر الميدمهNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3 Illumination System: Lecture Videos On YoutubeDocument7 pagesUNIT-3 Illumination System: Lecture Videos On YoutubeLavanya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- RP 18 MPT 001 TCR AlupcoDocument3 pagesRP 18 MPT 001 TCR AlupcoRonel John Rodriguez CustodioNo ratings yet
- 3x16 Rm+1x10 RM 2xRGY - DocxxDocument1 page3x16 Rm+1x10 RM 2xRGY - DocxxRasel AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To Differential EquationsDocument16 pages1 Intro To Differential EquationsJanina Christelle OrmitaNo ratings yet
- How The Sun Works: What Are We Trying To Figure Out?Document38 pagesHow The Sun Works: What Are We Trying To Figure Out?Michael ThomasNo ratings yet
- Change Your MotionDocument4 pagesChange Your MotionreynandcpcNo ratings yet
- SP TheoryDocument41 pagesSP Theoryaliyameen2006No ratings yet
- Exploring The Nature of ScienceDocument37 pagesExploring The Nature of ScienceQuenzil LumodNo ratings yet
- Applied Ocean Research: A B C D e FDocument21 pagesApplied Ocean Research: A B C D e FSumanta HaldarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2 Nov 2012 EngDocument15 pagesMathematics P2 Nov 2012 Engaleck mthethwaNo ratings yet
- Singularity FunctionsDocument1 pageSingularity FunctionsCharlie SiaNo ratings yet
- Past Papers 2013 To 2020Document63 pagesPast Papers 2013 To 2020Syed ZainNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - The Relationship Between Force and AccelerationDocument12 pagesExperiment 2 - The Relationship Between Force and Accelerationmuhammad asimNo ratings yet
- Gen Ed - MathDocument150 pagesGen Ed - MathJonathan EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIB Fully-Restrained (FR) Moment ConnectionsDocument29 pagesChapter IIB Fully-Restrained (FR) Moment ConnectionsHarshaVeeragandhamNo ratings yet
- Hiroshi Yamaguchi, Xin-Rong Zhang - Transcritical CO2 Heat Pump - Fundamentals and Applications-Wiley (2021)Document314 pagesHiroshi Yamaguchi, Xin-Rong Zhang - Transcritical CO2 Heat Pump - Fundamentals and Applications-Wiley (2021)Yahyaoui AminNo ratings yet
- CMP T1Document261 pagesCMP T1Aditi KaradeNo ratings yet