Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 12
Uploaded by
Carl Adrian Valdez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views11 pagesThis document discusses climate change and the factors that influence it. It explains that climate refers to long-term weather patterns, not daily weather, and is influenced by the Earth's relationship with the sun. Key aspects of this relationship include the Earth's elliptical orbit, axial tilt and precession, and timing of solstices and equinoxes. The Milankovitch theory proposes that variations in these astronomical parameters, like eccentricity, obliquity, and precession, cause cyclical climate changes over thousands of years by altering sunlight intensity and distribution.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHAPTER 12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses climate change and the factors that influence it. It explains that climate refers to long-term weather patterns, not daily weather, and is influenced by the Earth's relationship with the sun. Key aspects of this relationship include the Earth's elliptical orbit, axial tilt and precession, and timing of solstices and equinoxes. The Milankovitch theory proposes that variations in these astronomical parameters, like eccentricity, obliquity, and precession, cause cyclical climate changes over thousands of years by altering sunlight intensity and distribution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views11 pagesChapter 12
Uploaded by
Carl Adrian ValdezThis document discusses climate change and the factors that influence it. It explains that climate refers to long-term weather patterns, not daily weather, and is influenced by the Earth's relationship with the sun. Key aspects of this relationship include the Earth's elliptical orbit, axial tilt and precession, and timing of solstices and equinoxes. The Milankovitch theory proposes that variations in these astronomical parameters, like eccentricity, obliquity, and precession, cause cyclical climate changes over thousands of years by altering sunlight intensity and distribution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
CHAPTER 12
CLIMATE CHANGE
Carl Adrian N. Valdez
• It is a current in a sense that it has been put
under international spotlight since the start of
the 21st century. Data that have been
accumulated are used by scientists to
determine if there really is a significant
change in the earth's climate. But what does
climate change mean? Doesn't the climate
always change?
• Climate is not similar to weather which is constantly
changing. Climate refers to the long-term weather
patterns prevailing over a given area of the planet . The
term comes from a Greek word klinein meaning “to
slope”. It evolved into klima, connoting a zone or region of
the Earth as characterized by its atmospheric conditions.
In ancient Greece, the orb of the sun stood at a high
angle in the sky at noon time as ships sailed toward the
north, and the daytime temperature of the air would get
colder. Hence the klima in the north was colder that in the
south.
• Another consideration in explaining
climate change is the interaction between
the sun and the Earth. The best way to
visualize this relationship is to look at the
orbit of the Earth around the sun. With the
sun in the center, the Earth moves in an
elliptical motion.
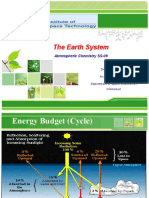
EARTH'S MOVEMENT AROUND THE SUN
• While the orbit remains an eclipse, its position or
orientation in space changes over time. Due to the
tilt of the Earth, the whole area does not receive an
equal amount of sunlight. The Earth spins around
its own axis, an imaginary line from the North Pole
to the South Pole, which dips and wobbles
gradually. The Earth could then be imagined like a
spinning top or trumpo, turning and woobling in its
path about the sun.
The elements of this interaction between the Sun and
the Earth are defined as follows;
• Aphelion refers to the point in the orbit of
the Earth farthest from the sun.
• Perihelion is the point in the orbit of the
Earth closest to the sun.
• Earth's axial tilt is the inclination angle of
the Earth's rotational axis in relation to a
line perpendicular to its orbital plane.
• Precession is the change of the
orientation of the rotational axis of the
Earth.
• Equinox refers to the time the sun at
noon is directly over the equator. It
happens twice a year and causes an
almost equal length of the day and night.
• Solstice happens when the sun at noon sits above
the Tropic of Cancer or Tropic of Capricorn . The
summer solstice has the longest period of daylight
in the year and the winter solstice has the shortest
period.
• Precession of the Equinox refers to the motion of
equinoxes relative to the precession of the Earth's
axis of rotation . It happens over thousands of
years.
Milankovitch Parameters
• The Milankovitch or astronomical theory of climate
change is an explanation for changes in the seasons
which result from changes in the earth's orbit around the
sun. The theory is named for Serbian astronomer Milutin
Milankovitch
• Milankovitch parameters, are astronomical greats that
cause cyclic variations. They affect global climate change
-seen over the periods of thousands of years - on the
rhythm at which ice ages and interglacials alternate.
That's because they determine the intensity and
distribution of sunlight on the earth.
• They were co-drafted by serbian mathematician Milutin
Milanković. It is the eccentricity, obliquity and
precession,so parameters of the orbit and orientation of
mainly planets. The first scientific publication on this
subject was in 1976.
• The influence of the measure of these parameters on the
earth's temperature is due to the fact that the land
masses are not evenly distributed across the earth.
Variations in the climate can be investigated in the past,
for example, by means of sequencing stratigraphy over a
long period of time.
The three Milanković parameters are:
• Eccentricity: Variations in the eccentricity of the
Earth's orbit have a periodicity of 100,000 years
• Obliquity: The change of the angle of the Earth's
axis from the plane in which the Earth revolves
around the sun, of obliquy,has a periodicity of
41,000 years
• Precession: The precession of the earth's axis has
a periodicity of 26,000 years.
You might also like
- Movement of The EarthDocument21 pagesMovement of The EarthAqilah Taufik100% (1)
- STS Report Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesSTS Report Climate ChangeBoton, Ivan Ray C.No ratings yet
- MilankovitchDocument12 pagesMilankovitchSabarigirivasan LNo ratings yet
- Climate Change STSDocument8 pagesClimate Change STSGomez Agustin LeslieNo ratings yet
- Intro To Earth Interaction With SunDocument20 pagesIntro To Earth Interaction With SunktmihalekNo ratings yet
- M8 Assignment 1Document3 pagesM8 Assignment 1Nike ColeNo ratings yet
- As Interactions Between The Atmosphere and Various Other Geologic, Chemical, Biological, and Ge Ographic Factors Within The Earth SystemDocument2 pagesAs Interactions Between The Atmosphere and Various Other Geologic, Chemical, Biological, and Ge Ographic Factors Within The Earth SystemJenny PastorNo ratings yet
- Milankovitch Cycles - Earth ClimateDocument11 pagesMilankovitch Cycles - Earth ClimateJohn MarkakisNo ratings yet
- Milankovitch CyclesDocument19 pagesMilankovitch Cyclessandracorpu08No ratings yet
- Climate Change: Science, Technology and Society FinalsDocument29 pagesClimate Change: Science, Technology and Society FinalsRose Ann De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Milankovitch Cycles and GlaciationDocument2 pagesMilankovitch Cycles and GlaciationKrishna KaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document8 pagesLecture 04Mashrufa HussainNo ratings yet
- Module 7.1. Natural Processes of Variations in Climate Dotpoint 2Document16 pagesModule 7.1. Natural Processes of Variations in Climate Dotpoint 2Kaira JogNo ratings yet
- Earth's Origin: 1. The UniverseDocument10 pagesEarth's Origin: 1. The UniverseSamina HaiderNo ratings yet
- Clase 11 Ciclo AstronomicoDocument38 pagesClase 11 Ciclo AstronomicoEDGAR ANIBAL AJUCHÁN SAGUACHNo ratings yet
- STS Climate ChangeDocument38 pagesSTS Climate ChangeNetanya Gwyneth Catubuan100% (1)
- Milankovitch CyclesDocument3 pagesMilankovitch CyclesHJakansjakkaNo ratings yet
- Chap 03Document20 pagesChap 03api-240900456No ratings yet
- Ability To Use Celestial Bodies To Determine The Ships PositionDocument40 pagesAbility To Use Celestial Bodies To Determine The Ships PositionSandunMigaraNo ratings yet
- STS Climate Change ReportDocument38 pagesSTS Climate Change ReportNetanya Gwyneth Catubuan100% (1)
- Physical GeographyDocument16 pagesPhysical Geographyva560426No ratings yet
- Earth in The UniverseDocument28 pagesEarth in The UniverseJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Physical Geography 1Document16 pagesCH 7 Physical Geography 1arjun17697No ratings yet
- Milankovitch Cycles - Research TaskDocument2 pagesMilankovitch Cycles - Research TaskdanjfosterNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1684128696249 7063747727194389515Document3 pagesOrca Share Media1684128696249 7063747727194389515Ella CunananNo ratings yet
- Earth pdf-46Document11 pagesEarth pdf-46Sanjana DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Motions in The SkyDocument47 pagesMotions in The SkyBrasa Y. de AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Axial Tilt and SeasonsDocument3 pagesAxial Tilt and SeasonsCazz Dane ParkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Climate ChangeDocument33 pagesChapter 12 Climate ChangeDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document5 pagesLesson 3Huda MadiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Rotation and Revolution of The Earth 1Document19 pagesLesson 4 Rotation and Revolution of The Earth 1axilrich8No ratings yet
- Q4 - WK5 - ROTATION - REVOLUTION - SEASONS (1) (Repaired)Document87 pagesQ4 - WK5 - ROTATION - REVOLUTION - SEASONS (1) (Repaired)Paul EsparagozaNo ratings yet
- Relative Motion of Earth, Moon, SunDocument23 pagesRelative Motion of Earth, Moon, SunShahbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Geologists Have Shown That For About 80 Percent of The Past 1Document5 pagesGeologists Have Shown That For About 80 Percent of The Past 1CECILIA GUADALUPE HERNANDEZ HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- and Interactions: EarthDocument47 pagesand Interactions: EarthNagarajNo ratings yet
- Sci6 April8Document59 pagesSci6 April8Janmari FajardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Rotation and Revolution NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Rotation and Revolution NotesMERLIN ANTHONYNo ratings yet
- 3 Diagnostic Tes Hal 42-81Document40 pages3 Diagnostic Tes Hal 42-81antoniusNo ratings yet
- Lec 03 Earth Rotation SeasonsDocument30 pagesLec 03 Earth Rotation SeasonsAbiha MaryamNo ratings yet
- Earth in SpaceDocument16 pagesEarth in SpaceDefensor Pison GringgoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 The Solar System Viewpoint: CounterclockwiseDocument10 pages3.1 The Solar System Viewpoint: CounterclockwiseRahulShah007No ratings yet
- Page 273 - 281Document11 pagesPage 273 - 28105 陳宗榮 RYAN GERALD CHUANo ratings yet
- Air Sea Notes PDFDocument9 pagesAir Sea Notes PDFfyh2tp2fjkNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate AutosavedDocument44 pagesWeather and Climate Autosavedcrossline093No ratings yet
- Enviro Lec 1-2-,,19+26 OctoberDocument32 pagesEnviro Lec 1-2-,,19+26 OctoberAhmed HoshamNo ratings yet
- Week 3b - Motions of The EarthDocument27 pagesWeek 3b - Motions of The Earthamosadjartey42No ratings yet
- "A Unique Take On Climate Change?": Siva PrasadDocument24 pages"A Unique Take On Climate Change?": Siva PrasadAWS DEVELOPERNo ratings yet
- GEOG 111 The Earth in Space: Earth Shape, Size, Rotation, RevolutionDocument29 pagesGEOG 111 The Earth in Space: Earth Shape, Size, Rotation, RevolutionNyaaba EzekielNo ratings yet
- Earth Movements. MonicaDocument4 pagesEarth Movements. MonicaBencel May Diaz Paez100% (1)
- Rotation and Revolution of EarthDocument4 pagesRotation and Revolution of EarthKhalidNo ratings yet
- Milankovitch CyclesDocument11 pagesMilankovitch CyclesCarlos Andres Andrade100% (1)
- Lse 3069 - Dynamics of The Revolution of The EarthDocument12 pagesLse 3069 - Dynamics of The Revolution of The Earthmark shikaazeNo ratings yet
- The Restless UniverseDocument16 pagesThe Restless Universecheska jane narraNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Rotation and Revolution On The Earth: Presenter: Monique ThompsonDocument26 pagesThe Effects of Rotation and Revolution On The Earth: Presenter: Monique Thompsongian leepsuNo ratings yet
- Motions of The EarthDocument8 pagesMotions of The EarthnidhiNo ratings yet
- Earth-Sun Relationship: (Use With Notes and Homework Quiz Handout)Document27 pagesEarth-Sun Relationship: (Use With Notes and Homework Quiz Handout)sheil.cogayNo ratings yet
- Earth MomentDocument8 pagesEarth Momentpsah9582No ratings yet
- Rotation of EarthDocument42 pagesRotation of EarthNickmor OamlinNo ratings yet
- Sci6 - Q4 - Wks4-5 - The Effects of Earths Motions - DiculenDocument12 pagesSci6 - Q4 - Wks4-5 - The Effects of Earths Motions - Diculenjose fadrilanNo ratings yet
- 2010-08-12 103926 Mcqs For Artick LightDocument3 pages2010-08-12 103926 Mcqs For Artick LightCarl Adrian ValdezNo ratings yet
- Fas Wps OfficeDocument16 pagesFas Wps OfficeCarl Adrian ValdezNo ratings yet
- Mid Advanced Acc. First09-10Document4 pagesMid Advanced Acc. First09-10Carl Adrian ValdezNo ratings yet
- Fruelda Vergara Law 202 Final Requirement PDFDocument73 pagesFruelda Vergara Law 202 Final Requirement PDFCarl Adrian ValdezNo ratings yet
- OWNER / PRESIDENT / CHAIRMAN 'S Name - Just Check The Website. No Google Research AnymoreDocument10 pagesOWNER / PRESIDENT / CHAIRMAN 'S Name - Just Check The Website. No Google Research AnymoreCarl Adrian ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument128 pagesCost AccountingCarl Adrian Valdez50% (2)
- Book of Cow Book of Chicken Book of CowDocument7 pagesBook of Cow Book of Chicken Book of CowCarl Adrian ValdezNo ratings yet
- Apology LetterDocument2 pagesApology LetterCarl Adrian ValdezNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document4 pagesCase 1Carl Adrian ValdezNo ratings yet
- Bul 172Document80 pagesBul 172Wolfgang KagermeierNo ratings yet
- Ch11 Homework Solutions PDFDocument94 pagesCh11 Homework Solutions PDFLEONARDO VIVANCOSNo ratings yet
- Hand-Drawn Timeline Infographics by SlidesgoDocument33 pagesHand-Drawn Timeline Infographics by SlidesgoNorRubianaAfiniShaleNo ratings yet
- Sci6 ST4 Q4Document3 pagesSci6 ST4 Q4xandra joy abadezaNo ratings yet
- Space Quiz For KidsDocument6 pagesSpace Quiz For KidsSakthidasan SankaranNo ratings yet
- LONG-TEST-SECOND Science 8Document2 pagesLONG-TEST-SECOND Science 8Manongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development ModelDocument39 pagesCurriculum Development ModelLovelydePerioNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Constellation DLPDocument22 pagesGrade-9 Constellation DLPJhenievy CabicoNo ratings yet
- A Multi Functional Two Chamber Airlock Node For A Common Habitat ArchitectureDocument22 pagesA Multi Functional Two Chamber Airlock Node For A Common Habitat ArchitecturebacondroppedNo ratings yet
- Parivartan Yoga - in Depth Guide & Review With Example HoroscopeDocument12 pagesParivartan Yoga - in Depth Guide & Review With Example HoroscopeRasika PrasadNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHSDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Science SHSjo_aligoraNo ratings yet
- Solar System SpiralDocument2 pagesSolar System Spiralcbu9734No ratings yet
- The Nebular Theory Yai FixDocument11 pagesThe Nebular Theory Yai FixAndreas SagalaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Planetary Volcanism Across The Solar System PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Planetary Volcanism Across The Solar System PDFjudy.hamamoto874100% (13)
- Apollo 11 Moon Landing by SlidesgoDocument53 pagesApollo 11 Moon Landing by SlidesgoJuan M.TNo ratings yet
- Phys12 c06 6 1Document9 pagesPhys12 c06 6 1Ruby Angel MannNo ratings yet
- Varaha MihiraDocument1 pageVaraha MihiraSavita BhabhiNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument10 pagesSolar SystemJames FulgencioNo ratings yet
- Soho 1 PDFDocument9 pagesSoho 1 PDFhcdmelloNo ratings yet
- COM 221 ARR DraftDocument17 pagesCOM 221 ARR DraftZack OverfieldNo ratings yet
- Visual Communication PortfolioDocument45 pagesVisual Communication PortfolioDiana DNo ratings yet
- Middle School Activities To Celebrate International Day of EducationDocument63 pagesMiddle School Activities To Celebrate International Day of Educationgabrielapecher84No ratings yet
- CBSE+9+Umang +gravitation+in+one+shotDocument115 pagesCBSE+9+Umang +gravitation+in+one+shotDushyant SinghNo ratings yet
- Celestial Mechanics 2Document3 pagesCelestial Mechanics 2Ranul JayawardenaNo ratings yet
- Telescope Book HistoryDocument24 pagesTelescope Book HistoryMd Chand AsiqueNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On SC - Unit1to3Document2 pagesQuestion Bank On SC - Unit1to3Gaurav BandhaokarNo ratings yet
- February 2019 Sky ChartDocument1 pageFebruary 2019 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNo ratings yet
- Big Bang ProjectDocument10 pagesBig Bang Projectapi-545588910No ratings yet
- Skills Test 2A : ListeningDocument4 pagesSkills Test 2A : ListeningMaridzeNo ratings yet
- Moon Phases PPT Notes 1Document16 pagesMoon Phases PPT Notes 1api-294483847No ratings yet