67% found this document useful (3 votes)
4K views29 pagesNXP Semiconductors Interview Insights
This document discusses various topics related to VLSI design verification including:
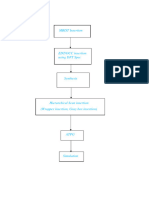
1. DFT flow including scan insertion and ATPG pattern generation.
2. The differences between functional and scan test patterns.
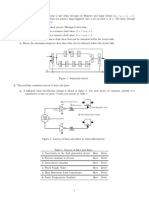
3. Causes and solutions for design rule check and timing issues.
4. Transition fault testing and the differences between pre-layout and post-layout simulations.
5. Formal and functional verification techniques.
Uploaded by
deepaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
67% found this document useful (3 votes)
4K views29 pagesNXP Semiconductors Interview Insights
This document discusses various topics related to VLSI design verification including:
1. DFT flow including scan insertion and ATPG pattern generation.
2. The differences between functional and scan test patterns.
3. Causes and solutions for design rule check and timing issues.
4. Transition fault testing and the differences between pre-layout and post-layout simulations.
5. Formal and functional verification techniques.
Uploaded by
deepaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd