Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 20.9 Interaction of Radiation With Matter: Chapter 20 Nuclear Physics
Uploaded by
Aleeha Hassan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views9 pagesThe document summarizes the interaction of various types of radiation with matter. It discusses how alpha, beta, gamma, and neutron particles interact and lose energy through ionization and other processes. Alpha particles travel in a straight path until coming to rest, while beta particles are more easily scattered. Gamma rays interact mainly through photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, or pair production depending on their energy. Neutrons are highly penetrating but can be slowed by hydrogen-containing materials through indirect ionization.
Original Description:
gr 11 ch 20 notes
Original Title
Chapter_20_Nuclear_Physics_(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the interaction of various types of radiation with matter. It discusses how alpha, beta, gamma, and neutron particles interact and lose energy through ionization and other processes. Alpha particles travel in a straight path until coming to rest, while beta particles are more easily scattered. Gamma rays interact mainly through photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, or pair production depending on their energy. Neutrons are highly penetrating but can be slowed by hydrogen-containing materials through indirect ionization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views9 pagesTopic 20.9 Interaction of Radiation With Matter: Chapter 20 Nuclear Physics
Uploaded by
Aleeha HassanThe document summarizes the interaction of various types of radiation with matter. It discusses how alpha, beta, gamma, and neutron particles interact and lose energy through ionization and other processes. Alpha particles travel in a straight path until coming to rest, while beta particles are more easily scattered. Gamma rays interact mainly through photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, or pair production depending on their energy. Neutrons are highly penetrating but can be slowed by hydrogen-containing materials through indirect ionization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Chapter 20 Nuclear Physics
Topic 20.9
Interaction
of Radiation
With Matter
Presented by : Jawaria Hassan
1. Interaction of α – particles with Matter
An α particle travels a small distance in a medium before coming to
rest. This distance is called the range of a particle. As the particle
passes through a solid , liquid or gas it loses energy due to excitation
and ionization of atoms and molecules in matter. The ionization may be
due to direct collisions or through electrostatic attraction.
Ionization is the main interaction with the matter to detect the particle
or to measure its energy. The range depends on
1. Charge mass & energy of the particle
2. The density of medium and ionization potential of atoms in that
medium .
Since α particles are 7000 times more massive than
electrons thus it doesn’t suffer any appreciable
deflection from its straight path , provided it does not
approach too closely to the nucleus of the atom. Thus
the α particle continues producing intense ionization
along its straight path till it loses all its energy until it
comes to rest. It , then captures two electros from the
medium and becomes a helium atom
2. Interaction of β particles with matter
β particles also lose energy by producing ionization . However its
ionization ability is 100 times less than than that of alpha particles . This
occurs because β particles are easily deflected by collisions than
heavier alpha particles. Thus the path of β particles isn’t straight but
much staggered or scattered. The range of β particles is measure by the
effective depth of penetration into the medium and not by the length
of eractive path. If the density of the material is greater than the range
will be shorter. Alpha & beta particles both radiate X-rays photns when
they are slowed down b the electric field of the charged particles in the
solid material.
3. Interation of ϒ – rays with matter
Photons of ϒ rays are being uncharged cause very little ionization.
Photons are removed from a beam of by either scattering or absorption
medium. They interact with matter in three distinct ways , depending
mainly on their energy.
i. At low energies the dominant process removes photons from a
beam which is the photoelectric effect.
ii. At intermediate energies , the dominant process is Compton
scattering.
iii. At higher energies the dominant process is pair production.
In air ϒ rays intensity falls off as the inverse square of the distance from
the source , in the same manner as light from a lamp. In solids the
intensity decreases exponentially with increasing depth of penetration into
the material. The intensity I of a beam after passing through a distance X
0
in the medium is reduced to inetensity I given by the relation I = I e * -μх ,
0
where μ is the linear absorption coefficient of the medium and it depends
on the energy of photon as well as property of the material. .
The particles alpha , beta and gamma procude fluorescence when they
strike substances like zinc-sulphide , sodium iodide etc.
“ Fluorescence is the property of absorbing radiant energy of high
frequency & reemitting energy of low frequency in the visible region of
electromagnetic spectrum “
4. Interaction of neutrons with matter
Neutrons being neutral particles are extremely penetrating
particles . To stop or slow them , neutrons must undergo a
direct collision with the nucleus or a particle that has a
mass comparable to it. Materials such as water or plastic
containing lower mass nuclei per unit volume are used to
stop neutrons. Neutrons produce a little indirect ionization
when they interact with materials containing H-atoms and
knock out protons.
Quiz
1. Which particle produces an indirect ionization while interacting with
a hydrogen containing material.
A. Gamma
B. Neutrons
C. Alpha
D. Beta
2. Which particle produces Fluorescence ?
A. Gamma B. Alpha C. Beta D. All of them
3. Which rays’ photons are uncharged?
A. Alpha
B. Gamma
C. Beta
D. None
4. _______ particle is 7000 times larger than the electron
E. Beta
F. Gamma
G. Neutron
H. Alpha
You might also like
- Chapter Five (Interaction of Radiation With Matter)Document8 pagesChapter Five (Interaction of Radiation With Matter)White HeartNo ratings yet
- Interactions of Ionizing RadiationsDocument52 pagesInteractions of Ionizing RadiationsMian SufyanNo ratings yet
- Nucleus Decay and Radiation PropertiesDocument12 pagesNucleus Decay and Radiation Propertiesnikhilpatel1986No ratings yet
- Interactionofradiation Drvandana 110828021807 Phpapp01Document47 pagesInteractionofradiation Drvandana 110828021807 Phpapp01Kumkumo Kussia KossaNo ratings yet
- Handout Static Electricity S3Document16 pagesHandout Static Electricity S3SUKU BUNGANo ratings yet
- Excess Carriers and Junction Concepts: Unit IIIDocument48 pagesExcess Carriers and Junction Concepts: Unit IIIThamizharasanNo ratings yet
- 2- Interactions of Radiation With Matter (تم حفظه تلقائيا)Document39 pages2- Interactions of Radiation With Matter (تم حفظه تلقائيا)Bashar BassamNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Radiation With MatterDocument16 pagesInteraction of Radiation With MatterRachit KanchanNo ratings yet
- Photon InteractionDocument30 pagesPhoton InteractionSathish JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Electron and Photon Interactions With Matter Martin Crnički University of RijekaDocument6 pagesElectron and Photon Interactions With Matter Martin Crnički University of RijekaMartin CrnickiNo ratings yet
- Experimental & Nuclear Physics 1Document110 pagesExperimental & Nuclear Physics 1Ghazi BhaiNo ratings yet
- Radiation Oncology PresentationDocument47 pagesRadiation Oncology PresentationAriful Islam PrantoNo ratings yet
- TO Radiation & Nuclear Physics: by HJ Shaharudin AliDocument40 pagesTO Radiation & Nuclear Physics: by HJ Shaharudin Aliizz isalahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Introduction To RadiationDocument36 pagesChapter 3 Introduction To Radiationhailemicael mesfinNo ratings yet
- Detecting Biological Effects of Radioactive MaterialsDocument37 pagesDetecting Biological Effects of Radioactive MaterialsAlyssaMaeCubillaNo ratings yet
- RADIOGRAPHY PRINCIPLESDocument63 pagesRADIOGRAPHY PRINCIPLESaasattiNo ratings yet
- Cm2-Interactions - Detection - Dosimetry ÇaouiDocument84 pagesCm2-Interactions - Detection - Dosimetry ÇaouiDouaa lkNo ratings yet
- Interaction Photons - MatterDocument9 pagesInteraction Photons - MatterdrpinnakavamsiNo ratings yet
- RADIOBIOLOGY Speaker Sharib Ahmed On 19-11-2013Document32 pagesRADIOBIOLOGY Speaker Sharib Ahmed On 19-11-2013Waqar Ahmed0% (1)
- Electric ChargeDocument4 pagesElectric ChargeDis DoodNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Lesson 1 - Basic Terminology & ConceptsDocument77 pagesStatic Electricity: Lesson 1 - Basic Terminology & ConceptsDERRICKKEANNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Electromagnetic Radiation and MatterDocument3 pagesInteraction of Electromagnetic Radiation and MatterMomo ItachiNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - Direct Current PDFDocument76 pagesElectrostatics - Direct Current PDFRita UmutoniNo ratings yet
- Element and Their Property UsesDocument2 pagesElement and Their Property UsesMa Anna HiyanNo ratings yet
- Interactions of Radioactive Materials with MatterDocument9 pagesInteractions of Radioactive Materials with MatterAlyssaMaeCubillaNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Charged Particles With Matter: Venika GanjirDocument22 pagesInteraction of Charged Particles With Matter: Venika GanjirvenikaNo ratings yet
- UNIT2 LasersLect 1 PHY109 June 19th 2021Document34 pagesUNIT2 LasersLect 1 PHY109 June 19th 2021Shakti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Interaction Types and Energy DepositionDocument16 pagesRadiation Interaction Types and Energy DepositionMohamed El-gammalNo ratings yet
- Solar ElectricityDocument40 pagesSolar Electricitysonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument301 pagesAtomic PhysicstomoNo ratings yet
- Shinam Final Thesis 18.09.2015Document69 pagesShinam Final Thesis 18.09.2015ishanNo ratings yet
- Laser: Vaneza Bea G. ABOGADODocument10 pagesLaser: Vaneza Bea G. ABOGADOVaneza Bea AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Notebook 16 PG 38-39Document2 pagesNotebook 16 PG 38-39api-334252501No ratings yet
- Electric Forces and Electric Fields-Final Report in Physics For TeachersDocument46 pagesElectric Forces and Electric Fields-Final Report in Physics For TeachersMaria Cristina DelmoNo ratings yet
- Radiation Physics - Interaction of Radiation With MatterDocument23 pagesRadiation Physics - Interaction of Radiation With MattergloriamarisNo ratings yet
- Terminologies: 1. Alpha ParticlesDocument7 pagesTerminologies: 1. Alpha ParticlesRalph MazinoNo ratings yet
- Icbc MS Id 000520Document9 pagesIcbc MS Id 000520محمد عامر الحكيميNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Radiation with Matter ExplainedDocument71 pagesInteraction of Radiation with Matter Explainedsh techNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 X-ray Production updatedDocument22 pagesLecture 3 X-ray Production updatedHaram KimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spectroscopy: Ricardo O. Louro Oeiras, Outubro 2015Document56 pagesIntroduction To Spectroscopy: Ricardo O. Louro Oeiras, Outubro 2015salvador lopezNo ratings yet
- Properties and uses of alpha, beta and gamma raysDocument3 pagesProperties and uses of alpha, beta and gamma raysAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Activity 1: Charge It!Document20 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Activity 1: Charge It!Mariles PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Sonic LaserDocument17 pagesSonic LaserPawan chandra UpretiNo ratings yet
- Virtual 2Document3 pagesVirtual 2Izzudin YafiNo ratings yet
- 11-Dual NatureDocument5 pages11-Dual NatureAyushi KapoorNo ratings yet
- VIRTUAL ACTIVITIES: TYPES OF CHEMICAL BONDSDocument5 pagesVIRTUAL ACTIVITIES: TYPES OF CHEMICAL BONDSPaulha CastillaNo ratings yet
- 1.6 BondingDocument17 pages1.6 BondingMahmoud TahaNo ratings yet
- Greg Herman Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection 814-865-6391 Gsh12@psu - EduDocument132 pagesGreg Herman Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection 814-865-6391 Gsh12@psu - EduSpoiled BratNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document2 pagesElectricity 1Wasiq Hossain AnimNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction in CrystalDocument67 pagesX-Ray Diffraction in CrystalAnonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Modern Physics Hints: Atomic Structure, Spectra, Radiation, and MoreDocument21 pagesModern Physics Hints: Atomic Structure, Spectra, Radiation, and MoreOlajide HeritageNo ratings yet
- Week 3 B Chapter 12 X-Ray Interaction With Matter 55Document37 pagesWeek 3 B Chapter 12 X-Ray Interaction With Matter 55Hanan AliNo ratings yet
- Photon Energy and WavelengthDocument20 pagesPhoton Energy and WavelengthNeil Joseph LandinginNo ratings yet
- Silicon Image Sensors Spectral ResponseDocument13 pagesSilicon Image Sensors Spectral ResponseGustavo Cao CancioNo ratings yet
- What is a Mass SpectrometerDocument11 pagesWhat is a Mass SpectrometerFiliz Kocayazgan ShanablehNo ratings yet
- Rad PhysicsDocument109 pagesRad PhysicsRicardo EdanoNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Physics Chapter 12 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10 Physics Chapter 12 Revision NotesGAMING IN MOODNo ratings yet
- Types of Ionizing RadiationDocument6 pagesTypes of Ionizing RadiationApurva SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Photon Conversion Concepts PDFDocument3 pagesPhoton Conversion Concepts PDFNoor MsdNo ratings yet
- Unit-6.1 The Figures of Speech PAGES 237-247-REVISIONDocument1 pageUnit-6.1 The Figures of Speech PAGES 237-247-REVISIONAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
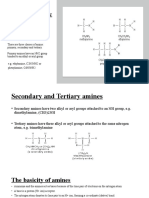
- Nitrogen Organic Compounds: - AminesDocument7 pagesNitrogen Organic Compounds: - AminesAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- Power Point IntoductionDocument7 pagesPower Point IntoductionAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- Trignometry-Non BoardDocument29 pagesTrignometry-Non BoardAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- Challan 200119Document2 pagesChallan 200119Aleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- (From Chapter 15-20) : The Reaction of Grignard Reagent With Ester. (1+2+4 7M)Document1 page(From Chapter 15-20) : The Reaction of Grignard Reagent With Ester. (1+2+4 7M)Aleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- 1st Rehearsal Grade 12-H Section-CDocument1 page1st Rehearsal Grade 12-H Section-CAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- 1s Rehearsal Grade 12-H Section-C KeyDocument4 pages1s Rehearsal Grade 12-H Section-C KeyAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
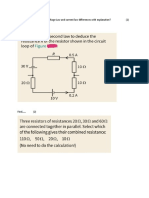
- Write Down The Kirchhoff's Voltage Law and Current Law Differences With Explanation?Document2 pagesWrite Down The Kirchhoff's Voltage Law and Current Law Differences With Explanation?Aleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- Rehearsal Examination - Chemistry Grade: 12Document1 pageRehearsal Examination - Chemistry Grade: 12Aleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- Rehearsal Examination - Chemistry Grade: 12Document1 pageRehearsal Examination - Chemistry Grade: 12Aleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- (From Chapter 15-20) : SECTION - D (26 Marks) NOTE: Attempt Any TWO Questions. (13×2 26M)Document3 pages(From Chapter 15-20) : SECTION - D (26 Marks) NOTE: Attempt Any TWO Questions. (13×2 26M)Aleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- 1st Rehearsal Grade 12-H Section-BDocument1 page1st Rehearsal Grade 12-H Section-BAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 SECTION-CDocument1 pageGrade 12 SECTION-CAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 SECTION-CDocument1 pageGrade 12 SECTION-CAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- G11. Mid Term McqsDocument15 pagesG11. Mid Term McqsAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-TITLEDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY-TITLEAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- 1s Rehearsal Grade 12-H Section-C KeyDocument4 pages1s Rehearsal Grade 12-H Section-C KeyAleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- (From Chapter 15-20) : The Reaction of Grignard Reagent With Ester. (1+2+4 7M)Document1 page(From Chapter 15-20) : The Reaction of Grignard Reagent With Ester. (1+2+4 7M)Aleeha HassanNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection - Guideline - Design and Validation of Shielding of Dental X-Ray Facility - 20220401Document14 pagesRadiation Protection - Guideline - Design and Validation of Shielding of Dental X-Ray Facility - 20220401Esteban PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry Final PDFDocument28 pagesNuclear Chemistry Final PDFaljon100% (2)
- Formula Sheet 3Document31 pagesFormula Sheet 3Mohamed Hichem Guesmi100% (1)
- How GM Tube Count Rate Depends on Potential DifferenceDocument2 pagesHow GM Tube Count Rate Depends on Potential DifferenceRiaz Jokan100% (2)
- Chapter-50 Applications of Isotopes in Medicine: January 2017Document8 pagesChapter-50 Applications of Isotopes in Medicine: January 2017Saikumar SobaradNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Nuclear Chem Study GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 22 Nuclear Chem Study GuideVicky100% (2)
- Radiographic TestingDocument47 pagesRadiographic TestingsmrndrdasNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive Testing in ConcreteDocument34 pagesNon Destructive Testing in ConcreteManisha ThakurNo ratings yet
- 1-The Physics and Chemistry of Radiation AbsorptionDocument38 pages1-The Physics and Chemistry of Radiation AbsorptionliskatriNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Characterization of Gamma Radiation Shielding Capacity of Heavy Minerals-Based Composite MaterialsDocument9 pagesInvestigation and Characterization of Gamma Radiation Shielding Capacity of Heavy Minerals-Based Composite MaterialsMd.Helal HossainNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument4 pagesNuclear Chemistryapi-25889687No ratings yet
- UNIT 14-PHY 131-Chapter 29-Nuclear PhysicsDocument26 pagesUNIT 14-PHY 131-Chapter 29-Nuclear PhysicscharlieNo ratings yet
- E748 16 PDFDocument11 pagesE748 16 PDFFrancisco Pizarro100% (1)
- Compton Scattering ExperimentDocument3 pagesCompton Scattering ExperimentCollege of Computer Sciences BasirpurNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry Lesson OutlineDocument12 pagesNuclear Chemistry Lesson OutlineKate ComonicalNo ratings yet
- LB124 Scint User Manual - ENDocument100 pagesLB124 Scint User Manual - ENandreaNo ratings yet
- Ingenuity Series: V 3 - 5 - X / V 3 - 6 - X T o V 4 - 0 - 1Document353 pagesIngenuity Series: V 3 - 5 - X / V 3 - 6 - X T o V 4 - 0 - 1Nelson J Silva ANo ratings yet
- Space Settlement Design & ConstructionDocument69 pagesSpace Settlement Design & ConstructionKarin DaianaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7_ Atomic, nuclear and particle physics – IB PhysicsDocument19 pagesTopic 7_ Atomic, nuclear and particle physics – IB PhysicsVinisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- EMR Ranking & Calculation (Two Questions On Exam) - : Easy/mediumDocument12 pagesEMR Ranking & Calculation (Two Questions On Exam) - : Easy/mediumItzel NavaNo ratings yet
- Insight Science 9 - Workbook PDFDocument97 pagesInsight Science 9 - Workbook PDFDog Dog100% (2)
- Biological Effects of RadiationDocument6 pagesBiological Effects of RadiationZain Ul AbidinNo ratings yet
- Makalah FismodDocument19 pagesMakalah FismodRirinNo ratings yet
- 10 EM Spectrum of Light Compiled Questions v2Document4 pages10 EM Spectrum of Light Compiled Questions v2Hafez MurtzaNo ratings yet
- The Examination, Testing and Calibration of Tritium-In-Air Monitors For Radiation ProtectionDocument48 pagesThe Examination, Testing and Calibration of Tritium-In-Air Monitors For Radiation ProtectionMFNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers 1 Energy Topic 04 Nuclear Chemistry 1Document6 pagesChemistry For Engineers 1 Energy Topic 04 Nuclear Chemistry 1Kristine AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- 7.shashank M - Physical and Chemical Agents-1Document28 pages7.shashank M - Physical and Chemical Agents-1Manojna KMNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics Project Class 12Document9 pagesNuclear Physics Project Class 12Rohan Chakraborty73% (15)
- The Basics of Gamma Camera ImagingDocument53 pagesThe Basics of Gamma Camera ImagingSaeeda MunirNo ratings yet
- Medical Uses of Radioactive Calcium: Review of An Iaea Programme To Promote The Applications of Calcium-47Document3 pagesMedical Uses of Radioactive Calcium: Review of An Iaea Programme To Promote The Applications of Calcium-47Sela NaleNo ratings yet