Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exo and Endo Reactions Powerpoint 1 New 1 2
Uploaded by
Reka0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views17 pagesOriginal Title
Exo_and_Endo_Reactions_powerpoint_1_new_1_2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views17 pagesExo and Endo Reactions Powerpoint 1 New 1 2
Uploaded by
RekaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
1 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
2 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Exothermic and endothermic reactions
What are exothermic and endothermic reactions?
exothermic reactions release energy – they get hot
ex = out (as in ‘exit’)
thermic = relating to heat
endothermic reactions absorb energy – they get cold
en = in (as in ‘entrance’)
Most chemical reactions are exothermic.
3 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Exothermic reactions
Exothermic reactions release thermal energy (heat)
into their surroundings. Exothermic reactions can
occur spontaneously and some are explosive.
What are some examples?
combustion
respiration
neutralization of acids
with alkalis
reactions of metals with
acids
the Thermit Process.
4 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
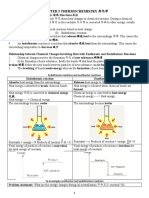
Reversible reactions and energy
Reversible reactions are exothermic in one direction and
endothermic in the other direction. For example:
endothermic
hydrated anhydrous
copper sulfate copper sulfate
+ water
CuSO4.5H2O CuSO4 + 5H2O
exothermic
The amount of energy transferred in each direction is
exactly the same.
5 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Magnesium and hydrochloric acid
6 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Exothermic reaction: energy transfer
What happens to energy in the reaction between magnesium
and hydrochloric acid?
No external heat source is used so the
heat released during the reaction must
come from the reactants.
During the reaction, chemical energy in
the reactants is converted to thermal
energy (heat). This causes the
temperature of the reaction mixture to
rise.
This thermal energy is eventually lost to
the surroundings and the temperature of
the reaction mixture returns to normal.
7 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Exothermic reaction: energy levels
8 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Exothermic reactions: summary
9 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
10 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Endothermic reactions
Endothermic reactions absorb thermal energy, and so
cause a decrease in temperature.
What are some examples?
thermal
decomposition, e.g.
calcium carbonate in
a blast furnace
photosynthesis
some types of
electrolysis
sherbet!
11 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Ammonium nitrate and water
12 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Endothermic reaction: energy transfer
What happens to energy in the reaction between
ammonium nitrate and water?
During the reaction, thermal energy
from the reaction mixture is converted
to chemical energy in the products.
This causes the temperature of the
reaction mixture to fall.
Thermal energy from the
surroundings is transferred to the
reaction mixture, and the temperature
eventually returns to normal.
13 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Endothermic reaction: energy levels
14 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Endothermic reactions: summary
15 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Exothermic or endothermic?
16 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Energy transfer: true or false?
17 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
You might also like
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionDocument25 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic ReactionCxNo ratings yet
- Energy Change During Chemical ReactionsDocument36 pagesEnergy Change During Chemical ReactionsMonday VerdejoNo ratings yet
- Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions: © Boardworks LTD 2005Document19 pagesEndothermic & Exothermic Reactions: © Boardworks LTD 2005Shelby Mikayla KosimaNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument49 pagesRates of ReactionTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- C19 Energy From Chemicals PC SlidesDocument51 pagesC19 Energy From Chemicals PC SlidesBasil ChinNo ratings yet
- Yr9 WK3&4 Exo&endo ReactionDocument16 pagesYr9 WK3&4 Exo&endo ReactionVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedDocument68 pagesChm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedNurfarhanah AsyknNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Thermochemistry 热化学: Endothermic reactions and exothermic reactionsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Thermochemistry 热化学: Endothermic reactions and exothermic reactionsJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Endoexothermic EnergyDocument38 pagesEndoexothermic EnergyMaram GhaziNo ratings yet
- Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument18 pagesExothermic and Endothermic ReactionsAngelika Bernal100% (1)
- Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions: Linking Energy Profile Diagrams To Thermometer ReadingsDocument28 pagesExothermic and Endothermic Reactions: Linking Energy Profile Diagrams To Thermometer ReadingsHanifa Uly AmrinaNo ratings yet
- Energetics Lesson 1Document13 pagesEnergetics Lesson 1Ghadeer AlkhayatNo ratings yet
- Exothermic ReactionsDocument25 pagesExothermic ReactionsazilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Energetics & ThermochemistryDocument180 pagesChapter 05 Energetics & ThermochemistryJishen ZhuNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry F5Document23 pagesThermochemistry F5Noor Adlizan AdlizNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes in ReactionsDocument2 pagesEnergy Changes in ReactionsShahid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Bonds and EnergyDocument19 pagesBonds and Energy1234lady100% (2)
- Thermochemistry: Learning Outcome Introductio N ApplicationDocument18 pagesThermochemistry: Learning Outcome Introductio N ApplicationDieHa ElDhaNo ratings yet
- A+ EDUCARE CLASS 8-CHEMISTRY Chemical Changes. (EM)Document5 pagesA+ EDUCARE CLASS 8-CHEMISTRY Chemical Changes. (EM)Arkeshwar I V80% (5)
- Chemical EnergyDocument12 pagesChemical EnergyMathews ZimbaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergyDocument12 pagesChemical EnergyFaiza RizwanNo ratings yet
- 1 Energy Changes in Chemical Reaction Printed VersionDocument8 pages1 Energy Changes in Chemical Reaction Printed VersionKamal AriffinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Thermochemistry-Exothermic and EndothermicDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Thermochemistry-Exothermic and EndothermicNadine TariganNo ratings yet
- Chapter4thermochemistry 150201074346 Conversion Gate02Document38 pagesChapter4thermochemistry 150201074346 Conversion Gate02eric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument37 pagesEnergeticsrheanna0076No ratings yet
- Energy Changes:: Change in Energy During Chemical ReactionDocument4 pagesEnergy Changes:: Change in Energy During Chemical ReactionadnanNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument40 pagesThermo Chemistrypipay vlogsNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionsDocument39 pagesReversible ReactionsUsmaanNo ratings yet
- 18cho101t Unit 4 Energy Calculations and Other Chemical Energy Transfer ProcessesDocument46 pages18cho101t Unit 4 Energy Calculations and Other Chemical Energy Transfer ProcessesHruday CoolkidNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument2 pagesEnergeticsAnonymous N3VvjVSTATNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionsDocument3 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic ReactionsAlex Le MeowNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionDocument70 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic Reactionactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Reviewer General General Chemistry 2Document1 pageReviewer General General Chemistry 2Clay 13No ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument11 pagesEnergeticsMuhammadJahangirAlamNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes OL NotesDocument4 pagesEnergy Changes OL NotesHooria AminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document13 pagesChapter 7Shafiqah AiradzNo ratings yet
- Energetics 1Document53 pagesEnergetics 1anellebrown299No ratings yet
- 15th of 19 Chapters) Energy Changes - GCE O Level Chemistry LectureDocument12 pages15th of 19 Chapters) Energy Changes - GCE O Level Chemistry LectureDylanNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemical Reactions - Kinetics, Energetics, TypesDocument21 pages9 Chemical Reactions - Kinetics, Energetics, TypesSia handaNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes Ws AnswersDocument2 pagesEnergy Changes Ws AnswersSanjiv Karthikeyan100% (1)
- Overview of Endothermic & Exothermic ReactionsDocument1 pageOverview of Endothermic & Exothermic ReactionsMary Anne BrionesNo ratings yet
- Ans For ReviewDocument3 pagesAns For Reviewsachi.laurelNo ratings yet
- Mce Igcse Chemistry PPT c08Document57 pagesMce Igcse Chemistry PPT c08Shabanito GamingNo ratings yet
- 5.1 EnergeticsDocument8 pages5.1 EnergeticsEldin EnggNo ratings yet
- Reactive Processes - Topic 1 - Heat of Reaction, Hear of FormationDocument6 pagesReactive Processes - Topic 1 - Heat of Reaction, Hear of FormationXclipsionNo ratings yet
- Energy Change in Chemical Reaction Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherDocument8 pagesEnergy Change in Chemical Reaction Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherMunshi LazimuzzamanNo ratings yet
- BHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy EnergeticsDocument59 pagesBHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy Energeticsabigail allenNo ratings yet
- C13 Enthalpy ChangeDocument19 pagesC13 Enthalpy ChangeKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Energetics ExerciseDocument37 pagesIGCSE Energetics ExerciseWilliam TsuiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics (Multiple Choice) QPDocument14 pagesChemical Energetics (Multiple Choice) QPRagesh DuduNo ratings yet
- How Far and How FastDocument5 pagesHow Far and How FastNisalNo ratings yet
- Termodinamika Reaksi Biokimia: Tik: Mahasiswa Mampu Mengaplikasikan Konsep Energi Bebas Dan Redoks Dalam Reaksi BiokimiaDocument80 pagesTermodinamika Reaksi Biokimia: Tik: Mahasiswa Mampu Mengaplikasikan Konsep Energi Bebas Dan Redoks Dalam Reaksi BiokimiaAngga PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Examples of Exothermic Reactions : NotesDocument6 pagesExamples of Exothermic Reactions : NotesAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- THERMOCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesTHERMOCHEMISTRYadikmuk100% (1)
- Chemistry Project OnDocument23 pagesChemistry Project OnGauravNo ratings yet
- CHP 7 - Chemical Energetics (Multiple Choice) QPDocument14 pagesCHP 7 - Chemical Energetics (Multiple Choice) QPDhrumeelNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CorrosionDocument76 pagesElectrochemical CorrosionMeshack NyitiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Energenetic (Thermochemistry) : BY: Hana Eva Loren Chemical Regular BDocument9 pagesChapter One Energenetic (Thermochemistry) : BY: Hana Eva Loren Chemical Regular BKaterina limbongNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and ExothermicDocument37 pagesEndothermic and Exothermicactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Blood - GCSE-Questions - 1.Rtf - Biology 1Document6 pagesBlood - GCSE-Questions - 1.Rtf - Biology 1RekaNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Blood 1.Pptx Biology 22Document5 pagesPart 2 Blood 1.Pptx Biology 22RekaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory - System - Exam - Ques - 1.rtf BiologyDocument5 pagesCirculatory - System - Exam - Ques - 1.rtf BiologyRekaNo ratings yet
- Part - 1 - Circulatory - System - 1.ppt Biology 2Document11 pagesPart - 1 - Circulatory - System - 1.ppt Biology 2RekaNo ratings yet
- B2.5.1 Proteins - B2.5.2 Enzymes: No Higher Tier ContentDocument3 pagesB2.5.1 Proteins - B2.5.2 Enzymes: No Higher Tier ContentRekaNo ratings yet
- Know It: by The End of This LessonDocument9 pagesKnow It: by The End of This LessonRekaNo ratings yet
- Depositional Landforms 7Document15 pagesDepositional Landforms 7RekaNo ratings yet
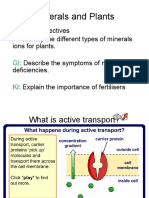
- Plant Minerals PPT 1Document11 pagesPlant Minerals PPT 1RekaNo ratings yet
- 2019 GAU PhySci GR 10 Jun Exam P2 EngDocument12 pages2019 GAU PhySci GR 10 Jun Exam P2 Engsandilemandoyi428No ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Lab ExerciseDocument4 pagesActivity 1 - Lab ExerciseJohn Joshua Latras ManticahonNo ratings yet
- Osmocote Pro 3-4M - 17-11-10 - DEFDocument2 pagesOsmocote Pro 3-4M - 17-11-10 - DEFFadzil A HalimNo ratings yet
- 16 Application of Neutralization TitrationDocument9 pages16 Application of Neutralization TitrationNguyen Quang KhaiNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Product NameDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet: Product NameakbarNo ratings yet
- Important-Question-ICSE-2010-Class-10th - Acids-Bases-Salts-CDocument5 pagesImportant-Question-ICSE-2010-Class-10th - Acids-Bases-Salts-CYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- CHEM101 - Exam 1 - Version B - Final - AnswersDocument7 pagesCHEM101 - Exam 1 - Version B - Final - AnswersSaudi ArabiaNo ratings yet
- 1001B B.P.S. X S.A. I Science Chapterwise 5 Printable Worksheets With Solution 2014 15Document111 pages1001B B.P.S. X S.A. I Science Chapterwise 5 Printable Worksheets With Solution 2014 15RajeevLochanNo ratings yet
- Catalysts 07 00059Document28 pagesCatalysts 07 00059Sankar SasmalNo ratings yet
- WHO HSE PHE EPE 11.01.07 EngDocument86 pagesWHO HSE PHE EPE 11.01.07 EngElisänder SilvaNo ratings yet
- p2 Trial SPM Perlis 2018 - SKEMADocument8 pagesp2 Trial SPM Perlis 2018 - SKEMAIzzati NorNo ratings yet
- Bohr Model Atoms and Ions PracticeDocument21 pagesBohr Model Atoms and Ions PracticeEmmette CoxNo ratings yet
- JFE's Super Abrasion-Resistant Steel PlateDocument4 pagesJFE's Super Abrasion-Resistant Steel PlateKYAW SOENo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Material 2.4819Document3 pagesData Sheet Material 2.4819BoberNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7a - Redox Process and Equilibrium K23Document36 pagesLecture 7a - Redox Process and Equilibrium K23Hải MinhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical VIVA Question XIIDocument3 pagesChemistry Practical VIVA Question XIIAmaan Ali khan100% (1)
- Gidakiiminaan (Our Earth) Language Map With Mine Sites and Known Ore Deposits.Document1 pageGidakiiminaan (Our Earth) Language Map With Mine Sites and Known Ore Deposits.Sarah LittleRedfeather KalmansonNo ratings yet
- Student Safety Sheets: Sodium Sulfites, Thiosulfate & PersulfateDocument1 pageStudent Safety Sheets: Sodium Sulfites, Thiosulfate & PersulfateOlaNo ratings yet
- Lime Softening PDFDocument16 pagesLime Softening PDFBiljana TausanovicNo ratings yet
- How To Select Valve MaterialsDocument12 pagesHow To Select Valve MaterialsrizalatanNo ratings yet
- Chem IA NUMERO 5Document4 pagesChem IA NUMERO 5BrittanyNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4 NomenclaturaDocument2 pagesTarea 4 NomenclaturaNatalia MerchanNo ratings yet
- 2087 4503 1 PBDocument8 pages2087 4503 1 PBaryadwi3007No ratings yet
- S 13 CRDocument6 pagesS 13 CRBardan RahmatanNo ratings yet
- SS PracticalDocument26 pagesSS PracticalShubham KaseraNo ratings yet
- Int. Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials: M. Vosough, N. Shahtahmasebi, M. BehdaniDocument6 pagesInt. Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials: M. Vosough, N. Shahtahmasebi, M. BehdanicatalinaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Acids and Bases Buffers and Titrations.)Document8 pagesProblem Set (Acids and Bases Buffers and Titrations.)Nate JamesNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument24 pagesStainless SteelsmrutiNo ratings yet
- Explosive Properties of Metal AmminesDocument2 pagesExplosive Properties of Metal AmminesJelena ZdravkovicNo ratings yet