Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ib Bio 1.2 2
Uploaded by
Madhavi Kapadia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
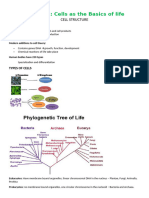
15 views41 pagesThe document outlines key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller, lack membrane-bound organelles, have circular DNA, divide via binary fission, and are unicellular. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, have membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts, contain linear DNA within a nucleus, can divide via mitosis or meiosis, and are often multicellular. Their cell walls also differ, with prokaryotes having peptidoglycan and eukaryotes having cellulose or chitin.
Original Description:
Original Title
IB BIO 1.2 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller, lack membrane-bound organelles, have circular DNA, divide via binary fission, and are unicellular. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, have membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts, contain linear DNA within a nucleus, can divide via mitosis or meiosis, and are often multicellular. Their cell walls also differ, with prokaryotes having peptidoglycan and eukaryotes having cellulose or chitin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views41 pagesIb Bio 1.2 2
Uploaded by
Madhavi KapadiaThe document outlines key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller, lack membrane-bound organelles, have circular DNA, divide via binary fission, and are unicellular. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, have membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts, contain linear DNA within a nucleus, can divide via mitosis or meiosis, and are often multicellular. Their cell walls also differ, with prokaryotes having peptidoglycan and eukaryotes having cellulose or chitin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 41
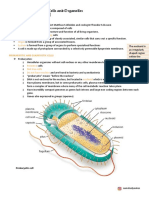
Mitochondria
– Cells with many mitochondria typically undertake energy-consuming processes
(e.g. neurons, muscle cells)
ER – Cells with extensive ER networks undertake secretory activities (e.g. plasma cells, exocrine
gland cells)
Lysosomes – Cells rich in lysosomes tend to undertake digestive processes (e.g. phagocytes)
Chloroplasts – Cells with chloroplasts undergo photosynthesis (e.g. plant leaf tissue but not root
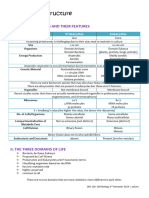
Outline the major differences between
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
PROKARY EUKARYO
Tiny (≈ 0.2 - 10 μm) OTE TEBigger (≈ 10 - 100 μm)
No membrane bound organelles Membrane bound organelles (1.2.U2)
Ribosomes
Division by binary fission, mitosis
Division by binary fission (1.2.U3) DNA or meiosis
Cell membrane
Cell wall with
Cell wall with peptidoglycan cellulose (plants) of chitin (fungus)
Cytoplasm
DNA in nucleoid DNA in nucleus
Essential functions of life (with nuclear membrane)
(no nuclear membrane)
Flagella moves laterally
Flagella rotates
DNA is linear and associated
DNA is circular and naked (3.2.U1) with histone proteins (3.2.U3)
Smaller 70s ribosomes Larger 80s ribosomes
Can have plasmids (3.2.U2) Does not have plasmids
Unicellular or multicellular (1.1.U4)
All unicellular (1.1.U4)
You might also like
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument23 pagesCell Structure and FunctionMoosa KhanNo ratings yet
- Maths AA SL Papers P1 CombinedDocument688 pagesMaths AA SL Papers P1 CombinedMadhavi Kapadia100% (1)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Bio SL Ib P 1 Exam MateDocument600 pagesBio SL Ib P 1 Exam MateMadhavi Kapadia100% (1)
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Week 3 - Bacteriology LectureDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNo ratings yet
- Year 3 Patterns in THEORETICAL PROBABILITY InvestigationDocument9 pagesYear 3 Patterns in THEORETICAL PROBABILITY InvestigationMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Greg Byrd Lynn Byrd and Chris Pearce Cambridge Checkpoint Mathematics Stage 8 Skills BuilderDocument146 pagesGreg Byrd Lynn Byrd and Chris Pearce Cambridge Checkpoint Mathematics Stage 8 Skills BuilderMadhavi Kapadia100% (1)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- Flagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesDocument18 pagesFlagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesEvangeline WongNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Cells PowerpointDocument7 pagesProkaryote Cells Powerpointrengar gamerNo ratings yet
- ProtozoansDocument13 pagesProtozoansGabrielle ForgetNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Venn DiagramDocument1 pageProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Venn DiagramAndrea JastillanaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of The Pathogenic ProkaryotesDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of The Pathogenic ProkaryotesjohnNo ratings yet
- 2 Types of Cells: The Cell: NUCLEUSDocument6 pages2 Types of Cells: The Cell: NUCLEUSDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of BacteriaDocument12 pages1.structure of BacteriaDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Lab Lecture 1: HistologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy Physiology Lab Lecture 1: HistologyTeddyNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document14 pagesCell (Biology)gigiuobohoNo ratings yet
- PDF Reference1-Lesson3-ProkaryotesvseukaryotesDocument3 pagesPDF Reference1-Lesson3-Prokaryotesvseukaryotesjg teNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Exercise 2Document5 pagesThe Cell: Exercise 2Jasmine Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 1.2 NotesDocument16 pages1.2 Notesyara hazemNo ratings yet
- 1.2 IntroductionDocument8 pages1.2 IntroductionmiftahNo ratings yet
- CeluarDocument7 pagesCeluarJef PerezNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pagesCell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- Organelle - WikipediaDocument42 pagesOrganelle - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Distinguished As Two Separate Points by An Optical InstrumentDocument4 pagesDistinguished As Two Separate Points by An Optical InstrumentSyeda Ulia TirmiziNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument19 pagesCell Ultrastructurezaydharoon419No ratings yet
- CellMolBio RevisionDocument11 pagesCellMolBio RevisionChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesDifferences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJess MCDNo ratings yet
- Endosymbiosis-Scl ActivityDocument1 pageEndosymbiosis-Scl ActivityZac DragoNo ratings yet
- Cell-The Unit of LifeDocument26 pagesCell-The Unit of LifeHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction To The CellDocument18 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To The CellThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifeharifire050No ratings yet
- Chem113lec Week 3.2Document5 pagesChem113lec Week 3.2Darryl orcaNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim Notes Module 1-4Document54 pagesBiology Prelim Notes Module 1-4kkanaksingh124No ratings yet
- Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellstapiwaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Document19 pagesCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- 7 Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells-SDocument6 pages7 Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells-SeNo ratings yet
- BIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Prokaryote and EukaryoteDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Prokaryote and Eukaryotejocelynmillano115No ratings yet
- Arsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17th Edition (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Document1,016 pagesReview of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17th Edition (Medicalstudyzone - Com)FaizNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Their SimilaritiesDocument1 pageThe Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Their SimilaritiesEnrique the ThirdNo ratings yet
- 2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1Document24 pages2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1saidatulNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17Th Edition Non Genuine PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology 17Th Edition Non Genuine PDFwilliam.collins296100% (22)
- Cell (Biology)Document4 pagesCell (Biology)Marella SatorreNo ratings yet
- 2 Learning Task in STM007 General Biology: No Cell Wall Nucleus Ribosomes Mitichondri ADocument3 pages2 Learning Task in STM007 General Biology: No Cell Wall Nucleus Ribosomes Mitichondri AMary Ann Dumpang RiveraNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Important Take AwaysDocument12 pagesBiotechnology Important Take AwaysRexel BarramedaNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument64 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanAdham EtmanNo ratings yet
- Genbio m2 Act AnsDocument1 pageGenbio m2 Act Anstamia syNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- AnimalVsHumanCell - PPT (SERVANO)Document3 pagesAnimalVsHumanCell - PPT (SERVANO)lorealtifhany.servanoNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions Topic 1.2 IB BiologyDocument4 pagesPractice Questions Topic 1.2 IB BiologySamantha DAIRONo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument3 pagesModule 2 Gen BioZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Nihar-Lecture5 - Ultrastructure of Cells Complete ClassDocument64 pagesNihar-Lecture5 - Ultrastructure of Cells Complete ClassRajnandni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells - PeTa2Document6 pagesProkaryote and Eukaryote Cells - PeTa2Robin-chwanNo ratings yet
- BTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Document55 pagesBTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Om JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology - 17th Ed PDFDocument1,011 pagesReview of Medical Microbiology and Immunology - 17th Ed PDFIshaanNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS Proving PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS Proving PhotosynthesisMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS Leaf and Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS Leaf and Gas ExchangeMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7: Photosynthesis and FoodDocument73 pagesTopic 7: Photosynthesis and FoodMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis MineralsDocument14 pagesPhotosynthesis MineralsMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument22 pagesFlowerMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Formative Task - 10a - TrishaDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum Formative Task - 10a - TrishaMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept 2Document5 pagesMole Concept 2Madhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- 0607 Functions P2Document27 pages0607 Functions P2Madhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil iGCSEDocument3 pagesCrude Oil iGCSEMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Physics ICSE Chapter 1Document2 pagesPhysics ICSE Chapter 1Madhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Hill Spring International School Grade 9 Div:...... Worksheet On Moles and Stoichiometry Name:...............Document6 pagesHill Spring International School Grade 9 Div:...... Worksheet On Moles and Stoichiometry Name:...............Madhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Application of Quadratic EquationDocument6 pagesApplication of Quadratic EquationMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- G 7 Magnetism WSDocument3 pagesG 7 Magnetism WSMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- GRADE-7 MATHEMATICS BssDocument2 pagesGRADE-7 MATHEMATICS BssMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Probability WS - StudentsDocument2 pagesProbability WS - StudentsMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Areas of Shapes Questions MMEDocument8 pagesAreas of Shapes Questions MMEMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Name: Teacher: Date: Score:: RotationsDocument2 pagesName: Teacher: Date: Score:: RotationsMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures: Gen. ScienceDocument31 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures: Gen. ScienceMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet