Professional Documents
Culture Documents
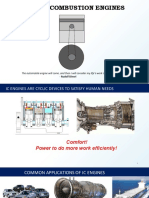
IC Engines
Uploaded by
kasateesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views12 pagesIC Engines
Uploaded by
kasateeshCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN
OTTO AND DIESEL
CYCLE
BY: JAIN NIKHIL PRAKASH
Automobile Engg. Dept.
Division E
OTTO CYCLE
• Nicolaus was a German
inventor
• Born in 1832 in Holzhausen
an der Haide
• His design was the first 4
stroke ICE to have any kind
of practicality
DIESEL CYCLE
• Invented by Rudolf
Christian Karl Diesel in
1893
• First engine was powered
by powdered coal
• Achieved a compression
ratio of almost 80
• Exploded, almost killed
Diesel
• First working engine
completed 1894 -
generated 13 hp
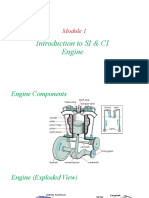
WORKING OF OTTO CYCLE
• Any 4 stroke engine is an Otto Engine
• The 4 strokes are: Intake, Compression,
Combustion/Power, Exhaust.
• The cycle is:
1-2: adiabatic compression
2-3: heat addition at constant volume
3-4: adiabatic expansion and rejection of heat at constant
volume
Working
Process 1-2 Piston moves from crank
end to cylinder head end (TDC, top
dead centre and minimum volume) as
the working gas with initial state 1 is
compressed isentropically to state
point 2, through compression ratio
Process 2-3 The piston is
momentarily at rest at TDC. During this
instant, which is known as the ignition
phase, the air/fuel mixture remains
Process 3-4 The increased high
pressure exerts a force on the piston
and pushes it towards the BDC.
Process 4-1 The piston is
momentarily at rest at BDC
DIESEL HOW LOOKS ?
WORKING OF DIESEL CYCLE Fuel injected
A
at TC
I
R
Air Combustion
Products
Actual
Cycle
Intake Compression Power Exhaust
Stroke Stroke Stroke Stroke
Qin Qout
Air
Diesel
Cycle
BC
Compression Const pressure Expansion Const volume
Process heat addition Process heat rejection
Process Process
Working
• Process 1 to 2 is isentropic
compression of the fluid (blue)
• Process 2 to 3
is reversible constant
pressure heating (red)
• Process 3 to 4 is isentropic
expansion (yellow)
• Process 4 to 1 is reversible
constant volume cooling
(green)
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN OTTO AND DIESEL
Uses In diesel engines, heating In petrol engines
systems
Made from Petroleum/ Crude oil Petroleum/ Crude Oil
Energy content 38.6 MJ/litre 34.6 MJ/litre
Made by Fractional distillation Fractional distillation
Torque (for 10L engine) 1000 Nm @ 2000 rpm 300Nm @ 4000 rpm
Power (for 10L engine) 490Hp @ 3500 rpm 600Hp @ 5500 rpm
Power = torque*RPM 210°C 246°C
CO2 emission More than Lower than diesel.
gasoline(petrol). Diesel
fuel produces
approximately 13% more
CO2 gas per gallon of fuel
burned, compared to gas
(petrol) engines.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN OTTO AND
DIESEL
Production of petrol vs diesel
• Petroleum is refined to produce petrol and diesel.
• Fractional Distillation process is used on petroleum and at
various temperatures, different by products are formed
from it.
• Petrol and diesel both are derived at varying temperatures
during refining process. Petrol is produced at temperature
between 35 degrees to 200 degrees while diesel is
produced at a boiling point of 250-350 degrees.
• After distillation, in order to use these byproducts as
commercially acceptable petrol and diesel, some blending
with other elements has to be done.
• Petrol is produced first in this process as it is produced at a
lower temperature than diesel.
THANK
YOU
SIR
You might also like
- Thermodynamic CYCLESDocument67 pagesThermodynamic CYCLESviperNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 IC Engine - DIESELDocument20 pagesLecture 3 IC Engine - DIESELMai Maiyaw100% (1)
- Unit 3 IC ENGINESDocument107 pagesUnit 3 IC ENGINESSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Engine CyclesDocument77 pagesEngine CyclesDANIEL MONISNo ratings yet
- Waste Pyrolysis Tire Oil As Alternative Fuel For Diesel EnginesDocument8 pagesWaste Pyrolysis Tire Oil As Alternative Fuel For Diesel EnginesTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 0engine, Pranit GaikarDocument86 pages0engine, Pranit Gaikaranushkat7347No ratings yet
- 3 Gas Power CyclesDocument32 pages3 Gas Power CyclesFikri Azim100% (2)
- Thermodynamic Cycles For CI Engines: Fuel Injection Starts Fuel Injection StartsDocument5 pagesThermodynamic Cycles For CI Engines: Fuel Injection Starts Fuel Injection StartsCrissa Ann EqueNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Desiel Engine and Diesel FuelDocument43 pagesThe Basics of Desiel Engine and Diesel FuelAnonymous JgZzTI0iNo ratings yet
- BE8256-Basic Mechanical Engineering - Unit IVDocument47 pagesBE8256-Basic Mechanical Engineering - Unit IVChem016No ratings yet
- Thermal Conversion ProcessesDocument24 pagesThermal Conversion ProcessesAl JawadNo ratings yet
- CH 1 IC ENGINES & RECIPROCATING MACHINESDocument49 pagesCH 1 IC ENGINES & RECIPROCATING MACHINESeyukaleb4No ratings yet
- A. Otto Cycle (Gasoline Engine)Document22 pagesA. Otto Cycle (Gasoline Engine)John Manuel BautistaNo ratings yet
- V1 Internal Combustion EngineDocument60 pagesV1 Internal Combustion Enginemohammad umairNo ratings yet
- CHE 305 - Gas Power CycleDocument22 pagesCHE 305 - Gas Power Cycleannie bungisngisNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms: Diesel PowerDocument1 pageGlossary of Terms: Diesel PowerRucky AroraNo ratings yet
- Diesel FuelDocument29 pagesDiesel FuelSisay SolomonNo ratings yet
- 2131905Document36 pages2131905inam vfNo ratings yet
- 637 Internal CombDocument40 pages637 Internal CombSRINIVAS TNo ratings yet
- Atd Ci Engine Combustion Phenomenon Unit-3Document34 pagesAtd Ci Engine Combustion Phenomenon Unit-3Aryan YadavNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument102 pages3 PDFMoujahed FarésNo ratings yet
- Introduction and HistotricalDocument44 pagesIntroduction and HistotricalTesfahun TegegneNo ratings yet
- The Diesel Cycle: c = 1005 J/Kg K c = 718 J/kg γ = 1.4 R = 287 J/kg KDocument11 pagesThe Diesel Cycle: c = 1005 J/Kg K c = 718 J/kg γ = 1.4 R = 287 J/kg Kأحمد صلاح الدينNo ratings yet
- Merged 429 14-18Document7 pagesMerged 429 14-18shubhamNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of An Engine Using Producer GasDocument53 pagesPerformance Analysis of An Engine Using Producer GasKIRAN CHERIYANNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument26 pagesThermodynamic Analysis of Internal Combustion EnginesKatu2010No ratings yet
- An Unending Search For Best Artificial Horse .. This Search Is A Biological Need of HumansDocument24 pagesAn Unending Search For Best Artificial Horse .. This Search Is A Biological Need of HumansShreyansh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Refinery and Petrochemical Processing DistillationDocument18 pagesRefinery and Petrochemical Processing Distillationrashid1986@hotmailNo ratings yet
- ICE Fuel BasicsDocument56 pagesICE Fuel BasicskristianNo ratings yet
- Gas Power CycleDocument31 pagesGas Power CycleAayush BastolaNo ratings yet
- Engine FinalDocument144 pagesEngine FinalEr. Narendra Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Ice CH4 2019-2020 PDFDocument28 pagesIce CH4 2019-2020 PDFMohamad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Otto CycleDocument22 pagesOtto CycleAbhijit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Lecture On: Dr. Nitesh MondalDocument10 pagesLecture On: Dr. Nitesh MondalNitesh MondalNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Terminology & CombustionDocument29 pages1.5 Terminology & CombustionSachin GautamNo ratings yet
- Otto CycleDocument7 pagesOtto CycleNitesh MondalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Van NessDocument76 pagesChapter 8 Van NessConrad MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Automobile QuestinDocument3 pagesAutomobile QuestinzcadNo ratings yet
- C. Prakash, DGM, Engine R&D, Ashok Leyland Limited, ChennaiDocument70 pagesC. Prakash, DGM, Engine R&D, Ashok Leyland Limited, ChennaiiocsachinNo ratings yet
- Agk 10Document47 pagesAgk 10Ferrandoski Garcia FarnósNo ratings yet
- Fuel Properties and Use of Hydrogen I.C.enginesDocument95 pagesFuel Properties and Use of Hydrogen I.C.enginesSiemensNo ratings yet
- Chambre Comb ANGLAISDocument15 pagesChambre Comb ANGLAISJérémie GuchetNo ratings yet
- Conceptos de NOxDocument48 pagesConceptos de NOxJESS100% (1)
- Development of Combustion EnginesDocument74 pagesDevelopment of Combustion EngineskristianNo ratings yet
- I C Engines: B. E. Semester: ViDocument42 pagesI C Engines: B. E. Semester: ViGeorgy KurienNo ratings yet
- KU1202 Intro To Eng and Design - 7 Combustion 2020 PDFDocument18 pagesKU1202 Intro To Eng and Design - 7 Combustion 2020 PDFmohammad arieqNo ratings yet
- MCL241 L8 Reciprocating IC Engines 2Document16 pagesMCL241 L8 Reciprocating IC Engines 2Aditi SamdarshiniNo ratings yet
- Module 1-2Document24 pagesModule 1-2HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Detroit Diesel 8.2 Liter Spec Sheet CollectionDocument6 pagesDetroit Diesel 8.2 Liter Spec Sheet CollectionAdrian Quintero100% (2)
- Ic Engines-Bme Ae&iDocument53 pagesIc Engines-Bme Ae&iAshitaNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Gas Power Cycles: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument15 pagesUnit I - Gas Power Cycles: Department of Mechanical EngineeringpvrbalaNo ratings yet
- Diesel MechanicsDocument40 pagesDiesel Mechanicsግሩም ግብርከNo ratings yet
- 01 - Engine BasicsDocument118 pages01 - Engine Basicsprem sagar100% (3)
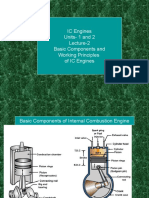
- IC Engines Units-1 and 2 Lecture-2 Basic Components and Working Principles of IC EnginesDocument47 pagesIC Engines Units-1 and 2 Lecture-2 Basic Components and Working Principles of IC EnginesRaviShankarDuggiralaNo ratings yet
- Mech9761: Week 2 at University of New South WalesDocument5 pagesMech9761: Week 2 at University of New South WalesKevin HuynhNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II Petroleum RefineryDocument77 pagesUNIT - II Petroleum RefineryrohanNo ratings yet
- Knocking and Anti KnockingDocument26 pagesKnocking and Anti KnockingsaadzzworldNo ratings yet
- AGR 318 Lec 3 - Engine Cons & CompDocument42 pagesAGR 318 Lec 3 - Engine Cons & CompHaikal SapurataNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Introduction Ot Mechanical Engineering, Role and Emerging TrendsDocument11 pagesIntroduction Ot Mechanical Engineering, Role and Emerging TrendskasateeshNo ratings yet
- Classification of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument51 pagesClassification of Internal Combustion EngineskasateeshNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine VS Diesel EngineDocument28 pagesPetrol Engine VS Diesel EnginekasateeshNo ratings yet
- Ic EngineDocument41 pagesIc Engineamitdhamija100% (7)
- Diesel EnginesDocument7 pagesDiesel EngineskasateeshNo ratings yet
- Principles of Air ConditioningDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Air ConditioningGeorgios Roumpies100% (2)
- Manual Mechanical WorkshopsDocument48 pagesManual Mechanical WorkshopskasateeshNo ratings yet
- CIM IntroductionDocument13 pagesCIM IntroductionVikram KedambadiNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument51 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturingkasateesh67% (3)
- Chapter1A CIM IntroductionDocument8 pagesChapter1A CIM IntroductionkasateeshNo ratings yet
- Ford Transit 2000 20061Document801 pagesFord Transit 2000 20061Lmibvg Klijkugfr50% (2)
- Instrument Transformers: - Current TransformerDocument45 pagesInstrument Transformers: - Current TransformerBona ChheuyNo ratings yet
- BS5588 SEC 1.1 Code of Practice For Single-Family Dwelling HousesDocument12 pagesBS5588 SEC 1.1 Code of Practice For Single-Family Dwelling HousestonyNo ratings yet
- STANLEY 45HW Electrified Mortise LockDocument6 pagesSTANLEY 45HW Electrified Mortise LocksacdawoodNo ratings yet
- Automate Pentru Arzatoare Brahma CM - SM - MMDocument6 pagesAutomate Pentru Arzatoare Brahma CM - SM - MMrtsNo ratings yet
- How Is Helium Made - HowStuffWorksDocument3 pagesHow Is Helium Made - HowStuffWorksait oubella marouaneNo ratings yet
- B257.OL3 - 002 - Safety and Design - Rev01Document70 pagesB257.OL3 - 002 - Safety and Design - Rev01megapoulpeNo ratings yet
- Eig SaratDocument51 pagesEig SaratTTIPLNo ratings yet
- The Age of Sustainable Development by Jeff-SachsDocument44 pagesThe Age of Sustainable Development by Jeff-SachsDarwin GilNo ratings yet
- Real Gas Flow Simulation in Damaged Distribution PipelinesDocument8 pagesReal Gas Flow Simulation in Damaged Distribution PipelinesJorge Andrés Palacio CardonaNo ratings yet
- If Above Ground, Minimum Distance Above Ground of Galvanized Wrought Iron and Galvanized Steep PipeDocument50 pagesIf Above Ground, Minimum Distance Above Ground of Galvanized Wrought Iron and Galvanized Steep PipeChristine Joyce RoseteNo ratings yet
- Research On Applications of Low Wind Speed Power in ASEANDocument127 pagesResearch On Applications of Low Wind Speed Power in ASEANGiang VuNo ratings yet
- NT 70/3 Me TC: Standard AccessoriesDocument12 pagesNT 70/3 Me TC: Standard AccessoriesAli Salik TradingNo ratings yet
- Shell Helix Ultra 5W-40: Performance, Features & BenefitsDocument2 pagesShell Helix Ultra 5W-40: Performance, Features & BenefitsMuhNo ratings yet
- Bsme Program of StudyDocument3 pagesBsme Program of StudyIan Joseph DalanginNo ratings yet
- Manuel de Partes 16V2000G63 OverhaulingDocument173 pagesManuel de Partes 16V2000G63 Overhaulingjorge luis ondarcuhuNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2024 (April 4 Shift 2) Question Paper With Solutions (PDF)Document14 pagesJEE Main 2024 (April 4 Shift 2) Question Paper With Solutions (PDF)Nick SinghNo ratings yet
- Gree Dehumidifier Service ManualDocument58 pagesGree Dehumidifier Service Manualjdv1234No ratings yet
- RotatingDocument6 pagesRotatingFarooq Ahmed Amir ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- PSX Power Solutions: Single Voltage Power SystemsDocument2 pagesPSX Power Solutions: Single Voltage Power SystemsMaria Paulina Hoyos BurgosNo ratings yet
- K 160 M Sileo: Centrifugal Circular Duct Fan 125WDocument9 pagesK 160 M Sileo: Centrifugal Circular Duct Fan 125WOscar Barres MoreiraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledJoanneNo ratings yet
- Consumer Reports Buying Guide 2022Document100 pagesConsumer Reports Buying Guide 2022hussien97% (35)
- Test Bank For Exercise Physiology Theory and Application To Fitness and Performance 10th Edition Scott Powers Edward HowleyDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Exercise Physiology Theory and Application To Fitness and Performance 10th Edition Scott Powers Edward HowleyRaven Tornow100% (32)
- Technical Manual Diaphragm Expansion VesselsDocument40 pagesTechnical Manual Diaphragm Expansion VesselsjosecevmspNo ratings yet
- HD270 DumpDocument4 pagesHD270 DumpBui Thanh DanhNo ratings yet
- Solar Water Heating SystemDocument1 pageSolar Water Heating SystemJiya RobertNo ratings yet
- BMW UpholstryDocument4 pagesBMW UpholstryМіша ШляхтаNo ratings yet
- D. K. Instruments Pvt. LTD.: Piston Type Flow SwitchDocument2 pagesD. K. Instruments Pvt. LTD.: Piston Type Flow Switchersanjeeb_456No ratings yet
- Solarfor™: Solar Power ForecastingDocument2 pagesSolarfor™: Solar Power ForecastingWilliam E. NuevoNo ratings yet