Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Administration
Uploaded by
Verto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views30 pagesModule
Original Title
NETWORK ADMINISTRATION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentModule
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views30 pagesNetwork Administration
Uploaded by
VertoModule
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
Midterm Module
IT103 (NETWORK
ADMINISTRATION
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN
INSTRUCTOR
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS
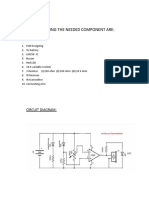
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
Is a symbolic drawing of a circuit showing how the components are
connected. The pictorial of a circuit appears close to an actual picture of
the circuit. Most importantly, the pictorial shows how each of the parts are
connected to each other. The schematic shows the same kind of
information but uses symbols that are more easily reproduced. The
advantages of using a schematic are that-the symbols used to represent each
component can be standardized. The schematic symbols used to represent
some of the most common components and parts used in computer
systems.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
LOGIC DIAGRAMS
These are standard logic symbols used in computer schematics. The Truth
Table shows the output condition of a given logic circuit for all the possible
combinations of input conditions.
LOGIC GATE
Has the ability to produce a predictable output for a given set of input conditions.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
SHOCK HAZARD
Factors affecting shock hazard. The danger from a
shock depends on three factors:
1. The voltage of the source.
2. The current the source can produce.
3. The path the current takes through your body.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
POWER SUPPLIES
Precautions Against Shock
1. Your safety always comes first. Do the job safely, even if this
requires more time and trouble.
2. Always turn off the equipment and unplug it before you
begin to work.
3. If you have to make tests while the equipment is operating,
turn the equipment on, make your tests carefully, and then turn
the equipment off again.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
POWER SUPPLIES
4. Be especially careful when working with those parts of the
equipment that carry high voltage. In monitors, especially
the Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), beware of the high voltage at
the picture tube and in the horizontal circuits.
5. Don’t work when you’re tired or rushed.
6. Try to do the work with one hand, while keeping your
other in your pocket. This “one-hand rule” reduces the
chance that a current will flow through the main part of your
body.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
MONITOR and TELEVISION SETS
A small monochrome (Black and White) monitor might
require 12,000 volts for this. On a larger color monitor, or a
color television, the voltage could be as high as 35,000 volts.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
1. VOM (Voltohmmilliammeter) - A VOM is battery powered and is used
with the current turned off. It's used to check continuity in a wire or
component and to measure the electrical current -- from 0 to 250 volts, AC
(alternating current, as in houses) or DC (direct current, as in batteries) --
flowing through the wire or component.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
2. DVM (Digital Voltmeter) - A digital voltmeter (DVM) measures an unknown
input voltage by converting the voltage to a digital value and then displays the
voltage in numeric form. DVMs are usually designed around a special type of
analog-to-digital converter called an integrating converter.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
3. VTM (Vacuum Tube Voltmeter) - The voltmeter which uses the vacuum tube
for amplifying the measured AC and DC voltage is known as the vacuum tube
voltmeter (VTM). The vacuum tube increases the sensitivity of the voltmeter
because of which it can detect the signal of very weak strength.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
4. Digital Logic Probes – can give more information on the signals flowing
through these circuits.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
5. Logic pulser – you may set the pulser to inject signals at the inputs of a device,
and then read the resulting pulses at the outputs with the logic probes.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
6. Current tracers – the current tracer or “short detector” can detect the tiny
amounts of current that pass through a circuit board trace without making direct
contact with the trace itself.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
7. Electronic thermometers – when IC’s and transistors fail, they often become
unusually hot. Professionals sometimes use electronic thermometers to detect
parts which have failed.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
8. Transistor tester – this type of tester allows you to make an in-circuit test, without
removing the transistors from the circuit board. The tester indicates whether the transistor is
working and it also allows you to measure the “gain” or output of the parts.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
9. Oscilloscopes – an oscilloscope or “scope” can give you a picture of a changing
electronic signal. The scope shows the changing value of a signal over a certain time
period. When the signal has a higher voltage, the display line moves upward on the
screen. A lower signal voltage moves the line down. The display moves from left to
right to show the passage of time.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
10. IC test clips – the test clip is designed to fit over the IC pins. You can then
make your test connections easily at the top of the clip. A test clip of this type
allows you to make an in-circuit test of an IC. Standard IC test clips (also called
“DIP Clips”) come in sizes to fit 14, 16, 20 and 40-pin ICs.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
11. Soldering irons – IC’s and transistors can easily be destroyed by overheating. For
this reason, you must choose carefully when you select a soldering iron for use with
digital circuits. The iron should deliver a limited amount of heat, quickly and
efficiently. Even if an iron is under powered, or the tip of the iron is dirty, the iron will
still produce enough heat to melt solder.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
12. Hot air rework station -With a hot air blower, electronic components are
easily desoldered from circuit boards and metal parts simply heated and deformed
without the use of a soldering iron. The hot air heats up the soldering joint, warms
the solder and detaches the components
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
13. Sponges – this is a soldering accessory that is never overlooked by the
experienced technician. Always keep a damp sponge rear your soldering
station, and wipe the tip of the hot iron frequently while you’re soldering.
This will keep the tip clean and shiny for maximum heat transfer.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
14. Heat sinks - A heat sink is a component that increases the heat flow away
from a hot device. It accomplishes this task by increasing the device's working
surface area and the amount of low-temperature fluid that moves across its
enlarged surface area.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
15. Solder-removal tools - A desoldering pump, colloquially known as a
solder sucker, is a manually-operated device which is used to remove solder
from a printed circuit board.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
16. IC removers and inserters - An IC extractor is a tool for safely and
quickly removing integrated circuits (ICs) from their sockets. The main
purpose of using this tool is to avoid bending the socket pins and to avoid
damage through electrostatic discharge (ESD).
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
17. Pencil eraser - The eraser does more than just eliminate dirt on your
keyboard: it can be applied to memory cards, game cartridges, and more.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
18. Wire strippers - A wire stripper is a small, hand-held device used to strip the
electrical insulation from electric wires.
a. Scissors type
b. Crimping tool
c. Automatic stripper
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
19. Tweezers - Needle-nose pliers: Used to hold small parts. Wire cutters:
Used to strip and cut wires. Tweezers: Used to manipulate small parts. Part
retriever: Used to retrieve parts from locations that are too small for your
hand to fit.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
20. Screwdrivers - Screwdriver, tool, usually hand-operated, for turning
screws with slotted heads. For screws with one straight diametral slot cut
across the head, standard screwdrivers with flat blade tips and in a variety of
sizes are used.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
21. Special wrenches - Wrenches are made in various shapes and sizes and
are used for gripping, fastening, turning, tightening and loosening things like
pipes, pipe fittings, and nuts and bolts. There are basically two major kinds of
wrenches: Pipe wrenches used in plumbing for gripping round (cylindrical)
things.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
HANDTOOLS USE IN SERVICING A
COMPUTER
22. Dental mirrors - Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal
yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer
to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle
from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner.
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
THANK YOU!!!
END OF THE MODULE!
EDWIN C. ARIMBUYUTAN, MLIS IT103
LECTURES
You might also like
- Biology Taxonomy Worksheet ANSWERSDocument3 pagesBiology Taxonomy Worksheet ANSWERSPsudopodNo ratings yet
- Electronics Explained: Fundamentals for Engineers, Technicians, and MakersFrom EverandElectronics Explained: Fundamentals for Engineers, Technicians, and MakersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Assignment On Training & Development Process of Uniliver BangladeshDocument9 pagesAssignment On Training & Development Process of Uniliver BangladeshMohaiminul Islam50% (2)
- Industrial Automation - Technical Interview QuestionsDocument27 pagesIndustrial Automation - Technical Interview QuestionsAnjali Sharma79% (19)
- Project On Intelligent Digital Security SystemDocument33 pagesProject On Intelligent Digital Security SystemprasannachandraNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Alonex Special Amp Industrial Electronic Equipment PDFDocument342 pagesAlonex Special Amp Industrial Electronic Equipment PDFthanh vanNo ratings yet
- batch007PPT1 PDFDocument37 pagesbatch007PPT1 PDFKranthi KumarNo ratings yet
- WorkshopDocument30 pagesWorkshopDarshan JainNo ratings yet
- Netsure 211 C23 User Manual (En)Document22 pagesNetsure 211 C23 User Manual (En)Vu Minh Tuan100% (1)
- Diamond Security System in A Museum With Loud 60dB SireN1Document50 pagesDiamond Security System in A Museum With Loud 60dB SireN1Midde ShekarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Iot-203103Document8 pagesIndustrial Iot-203103BagavathiNo ratings yet
- Interfacing With MicrocontrollerDocument44 pagesInterfacing With MicrocontrollerPradeep PoojaryNo ratings yet
- Electric Machines EEE241 LAB Report#1: Name Registration Number Teacher Date of SubmissionDocument7 pagesElectric Machines EEE241 LAB Report#1: Name Registration Number Teacher Date of Submissionbilal ahmedNo ratings yet
- Industrial Protection Over Smoke Temperature and LDRDocument58 pagesIndustrial Protection Over Smoke Temperature and LDRPradeep Avanigadda100% (2)
- Power Saving Conveyor For Industrial ApplicationDocument40 pagesPower Saving Conveyor For Industrial ApplicationjosephfelixNo ratings yet
- Pavan ReportDocument22 pagesPavan ReportDVG DEVIL HUNTER gamingNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering and Science Invention (IJESI)Document8 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering and Science Invention (IJESI)inventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Pressure Sensing TransmitterDocument10 pagesPressure Sensing TransmitterKrishnamurthy AnantharamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Eim New TRDocument3 pagesReviewer Eim New TRkim dofredoNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Transformer ProtectionDocument8 pagesArduino Based Transformer ProtectionAbdullah MdNo ratings yet
- DCL1000 enDocument23 pagesDCL1000 enTrần Dương Nhật HuyNo ratings yet
- Digital Countdown TimerDocument12 pagesDigital Countdown TimerJeremy RenderNo ratings yet
- LG Monitor Flantron L1810B Service ManualDocument42 pagesLG Monitor Flantron L1810B Service Manualandrik005No ratings yet
- ECI - Main ReportDocument47 pagesECI - Main ReportParthaSarathyNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Detection With ArduinoDocument20 pagesShort Circuit Detection With ArduinoAung MyatNo ratings yet
- Molded Case Circuit Breakers: Siemens STEP 2000 CourseDocument24 pagesMolded Case Circuit Breakers: Siemens STEP 2000 CourseArturo Ramirez PeñaNo ratings yet
- Manual Sanwa Dlc1000Document24 pagesManual Sanwa Dlc1000Arturo AlejandroNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab EXPERIMENTS - MergedDocument73 pagesADE Lab EXPERIMENTS - Mergedjainhassan4848No ratings yet
- 033 1v0 InstGde ACMains Monitor CAN Node 1v0Document13 pages033 1v0 InstGde ACMains Monitor CAN Node 1v0Jose Gregorio Molina0% (1)
- IT103 Special Topics MidtermDocument5 pagesIT103 Special Topics MidtermMiles FranNo ratings yet
- PC Based Appliances Controller Ag 111508Document8 pagesPC Based Appliances Controller Ag 111508Patel PratikNo ratings yet
- Undergrouand Fault DetectionDocument49 pagesUndergrouand Fault Detectionsarin.gagan100% (6)
- Report 3 AntitheftDocument21 pagesReport 3 AntitheftUttam AcharyaNo ratings yet
- WS 1020Document44 pagesWS 1020Sunil Sree NathNo ratings yet
- ECT158Document35 pagesECT158sabill arasyidNo ratings yet
- Group PresentationDocument21 pagesGroup PresentationShemsudin AhmedteibNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Introduction To Industrial Arts Part 2 (IEIAT - TLEHE8)Document8 pagesUnit 3 - Introduction To Industrial Arts Part 2 (IEIAT - TLEHE8)Vendivel KristineNo ratings yet
- 432 SymptomDocument26 pages432 SymptomA Fahrul AjiNo ratings yet
- Interactive Signal Interface Ins and OutsDocument12 pagesInteractive Signal Interface Ins and Outsbrianweb1972No ratings yet
- Water Level ControlDocument39 pagesWater Level Controlkrishna mohan pandeyNo ratings yet
- 250+ Electronics Mini Projects Ideas For Engineering Students PDFDocument26 pages250+ Electronics Mini Projects Ideas For Engineering Students PDFsumit valsangkarNo ratings yet
- 250+ Electronics Mini Projects Ideas For Engineering Students PDFDocument26 pages250+ Electronics Mini Projects Ideas For Engineering Students PDFsumit valsangkar100% (1)
- Eye Blink DocumentDocument38 pagesEye Blink Documentpavani13No ratings yet
- Overcurrent Protection System Using MicrocontrollerDocument14 pagesOvercurrent Protection System Using MicrocontrollerSritam Kumar deyNo ratings yet
- Accident AlertDocument35 pagesAccident AlertChandra SekarNo ratings yet
- MV Design GuideDocument81 pagesMV Design GuidejoseNo ratings yet
- Photosensitive Security System For TheftDocument4 pagesPhotosensitive Security System For TheftAditya Widya PranataNo ratings yet
- Door Sensor ProjectDocument6 pagesDoor Sensor ProjectMehmood ul Hassan100% (1)
- Atkinson DynamicsDocument28 pagesAtkinson DynamicsCarlos Alberto RuedaNo ratings yet
- User Manual Lqt40A: Tillquist Group AbDocument16 pagesUser Manual Lqt40A: Tillquist Group AbRamiro RosaNo ratings yet
- CPS1000E User Manual enDocument16 pagesCPS1000E User Manual enAdriano ManciniNo ratings yet
- IR Remote SwitchDocument2 pagesIR Remote SwitchVijay MirjeNo ratings yet
- Major ProjectDocument55 pagesMajor ProjectPRIYABRATA PRADHANNo ratings yet
- Beginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsFrom EverandBeginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNo ratings yet
- The Big 3: Lesson 2: Platform Technologies (ELEC4)Document38 pagesThe Big 3: Lesson 2: Platform Technologies (ELEC4)VertoNo ratings yet
- Platform Technologie S: Lesson 1-Elec4Document27 pagesPlatform Technologie S: Lesson 1-Elec4VertoNo ratings yet
- PE02 INTRODUTION TO RHYTHM AND DANCE - PPTMDocument44 pagesPE02 INTRODUTION TO RHYTHM AND DANCE - PPTMVertoNo ratings yet
- Acronym and Meaning of Computer TerminologiesDocument4 pagesAcronym and Meaning of Computer TerminologiesVertoNo ratings yet
- Research The Acronym and Meaning of The FollowingDocument4 pagesResearch The Acronym and Meaning of The FollowingVertoNo ratings yet
- The Big 3: Lesson 2: Platform Technologies (ELEC4)Document38 pagesThe Big 3: Lesson 2: Platform Technologies (ELEC4)VertoNo ratings yet
- APTET 2014 Social Question Paper II With Solutions PDFDocument47 pagesAPTET 2014 Social Question Paper II With Solutions PDFgayathriNo ratings yet
- Building Construction Costs Handbook 2019-2020Document89 pagesBuilding Construction Costs Handbook 2019-2020Rotich philipNo ratings yet
- Legend 1028KDocument2 pagesLegend 1028KAndres Fdo Mora DNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 3.1 Math 10Document2 pagesSummative Test 3.1 Math 10Christian DecenaNo ratings yet
- Rotak: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument18 pagesRotak: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineOvidiu BrinzanNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Lecture Lesson 1 Revised PDFDocument41 pagesUnderstanding The Self Lecture Lesson 1 Revised PDFKylie CuadraNo ratings yet
- JSEA - Hydro Test - 2833Document13 pagesJSEA - Hydro Test - 2833Amit Sharma100% (1)
- Arts NPSH TutorialDocument3 pagesArts NPSH TutorialDidier SanonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Translation Practice MarkDocument3 pagesUnit 2-Translation Practice MarkHương ThảoNo ratings yet
- PD 0018 Well Intervention Pressure Control Syllabus Level 3 4Document94 pagesPD 0018 Well Intervention Pressure Control Syllabus Level 3 4Salim AlgerianNo ratings yet
- (ANSI - AWS A5.31-92R) AWS A5 Committee On Filler Metal-SpecificationDocument18 pages(ANSI - AWS A5.31-92R) AWS A5 Committee On Filler Metal-SpecificationSivaram KottaliNo ratings yet
- C TADM70 73 Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesC TADM70 73 Sample QuestionsPriya ChNo ratings yet
- PDF EnglishDocument36 pagesPDF EnglishSanti CheewabantherngNo ratings yet
- Nursery Car Seat Supplement 2023Document40 pagesNursery Car Seat Supplement 2023doniNo ratings yet
- 10 AI Summer Vacation HWDocument2 pages10 AI Summer Vacation HWAyushi SinghNo ratings yet
- Training Guide: Administering Windows Server 2012Document33 pagesTraining Guide: Administering Windows Server 2012sabastianNo ratings yet
- Culture & CivilizationDocument21 pagesCulture & CivilizationMadhuree Perumalla100% (1)
- 02.03.05.06.01 - Manage Sales Rebate AgreementDocument11 pages02.03.05.06.01 - Manage Sales Rebate AgreementVinoth100% (1)
- Czujniki Temperatury MOTOMETERDocument7 pagesCzujniki Temperatury MOTOMETERhelp3rNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare Commemoration Volume 1966Document401 pagesShakespeare Commemoration Volume 1966Avijit MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 13 Ultrafiltration UnitDocument13 pagesExperiment 13 Ultrafiltration UnitKishen NaniNo ratings yet
- CasDocument2 pagesCasJamesalbert KingNo ratings yet
- V0 VSS VDD: Unit PIN Symbol Level Nominal Dimensions Pin Connections Function Mechanical Data ItemDocument1 pageV0 VSS VDD: Unit PIN Symbol Level Nominal Dimensions Pin Connections Function Mechanical Data ItemBasir Ahmad NooriNo ratings yet
- APP PinAAcle 900 Elemental Analysis of Beer by FAAS 012049 01Document3 pagesAPP PinAAcle 900 Elemental Analysis of Beer by FAAS 012049 01strubingeraNo ratings yet
- Practical FileDocument108 pagesPractical FileRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Prima Magistra:: Wulan Rahayu Syachtiyani, Novi TrisnawatiDocument12 pagesPrima Magistra:: Wulan Rahayu Syachtiyani, Novi TrisnawatiGita GloriaNo ratings yet
- BONENT Candidate Handbook PDFDocument28 pagesBONENT Candidate Handbook PDFParshanwa Johnson100% (1)