Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MOTION
MOTION
Uploaded by
Jeje Sciple0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views11 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views11 pagesMOTION
MOTION
Uploaded by
Jeje ScipleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
MOTION
Uniform Linear Motion &
Accelerated Linear Motion
Distance vs Displacement
Distance is a scalar quantity that
A refers to "how much ground an
Di object has covered" during its
sta
nc e motion.
Di Displacement is a vector quantity
sp that refers to "how far out of place
lac
em an object is"; it is the object's
en
t overall change in position.
B
Average Velocity vs Average Speed
Average velocity is the ratio of the displacement x that occurs
during a particular time interval t to that interval:
Average speed is a different way of describing “how fast” a
particle moves. Whereas the average velocity involves the
particle’s displacement x, the average speed involves the total
distance covered (for example, the number of meters moved),
independent of direction
Instantaneous Velocity & Speed
Instantaneous velocity is defined as the rate of change of
position for a time interval which is very small (almost zero).
Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of the instantaneous
velocity. It has the same value as that of instantaneous
velocity but does not have any direction.
Acceleration
When a particle’s velocity changes, the particle is said
to undergo acceleration (or to accelerate). For motion
along an axis, the average acceleration aavg over a
time interval t is
where the particle has velocity v1 at time t1 and then
velocity v2 at time t2. The instantaneous acceleration
(or simply acceleration) is
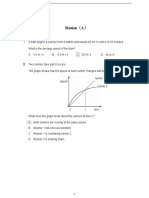
Uniform Linear Motion:
Constant Speed
Graphics
When an object moves at a
constant speed on a straight
line, then it is said that the
object performs Uniform
Linear Motion. The speed at
which an object does not
change over an interval 𝑡 so
that the acceleration is zero
The distance 𝑥 during 𝑡 with
speed 𝑣 is
Accelerated Linear Motion:
Constant Acceleration
Graphics
Add a Slide Title - 6
Click icon to add picture
Add a Slide Title - 7
Click icon to add picture Click icon to add picture
You might also like
- E MGH: Potential and Kinetic EnergyDocument2 pagesE MGH: Potential and Kinetic EnergyDominique Forde100% (1)
- SP1a Vectors and Scalars: Student BookDocument189 pagesSP1a Vectors and Scalars: Student BookHikmah Naufal HasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Motion in A Straight LineDocument28 pagesChapter 2 Motion in A Straight LinejashsumedhaNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line - CeLOEDocument31 pagesMotion in A Straight Line - CeLOEMuhammad GustianNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line CH3Document49 pagesMotion in A Straight Line CH3Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight LineDocument33 pagesClass 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight Linenick tyagiNo ratings yet
- PH110-CHAPTER 3 KinematicsDocument22 pagesPH110-CHAPTER 3 KinematicsNtape Knox Siwale100% (3)
- Motion Along A Straight Line: in This ChapterDocument22 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line: in This ChapterZiya Can OğuzNo ratings yet
- MF006 Lecture 3 - Uniform Accelerated Motion 1Document34 pagesMF006 Lecture 3 - Uniform Accelerated Motion 1Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1D - Study NotesDocument13 pagesKinematics 1D - Study NotesmadjerkmemesNo ratings yet
- 2023 05 05 0.12217238424629207Document26 pages2023 05 05 0.12217238424629207Arohan BuddyNo ratings yet
- B Motion in A Straight LineDocument24 pagesB Motion in A Straight Linef20230069No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument12 pagesChapter 2 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering: Department of Mechanical Engineering Phys 1A: Physics For Engineers IDocument9 pagesCollege of Engineering: Department of Mechanical Engineering Phys 1A: Physics For Engineers Ipablo escobarNo ratings yet
- Kinematika Gerak Lurus (1 Dimensi)Document39 pagesKinematika Gerak Lurus (1 Dimensi)Annisa NoerfadillahNo ratings yet
- H2 Notes - Tutorial - KinematicsDocument43 pagesH2 Notes - Tutorial - KinematicsWee Chee LimNo ratings yet
- 2-Motion Force EctDocument27 pages2-Motion Force Ectfeisya juniarNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument64 pagesKinematicsaruneshmarch2006No ratings yet
- Kinematics E 2018Document52 pagesKinematics E 2018sundararevathyhdNo ratings yet
- SMK Tat Beng Physics Form 4 2.1 Linear MotionDocument69 pagesSMK Tat Beng Physics Form 4 2.1 Linear MotionTee Ting QINo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line and Motion in A PlaneDocument23 pagesMotion in A Straight Line and Motion in A PlaneSasidaran SasiNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICSDocument12 pagesKINEMATICSMichael DanielsNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Motion in 1 DDocument51 pagesLec 2 - Motion in 1 DJugesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 11 Phy ln3 Notes 1629708273Document4 pages11 Phy ln3 Notes 1629708273Raje SwariNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument58 pagesKinematicsdevendraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension - 2024 NotesDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Motion in One Dimension - 2024 NoteseverlynkhwaweNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document8 pagesLecture 1souravcanflyNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Concepts (Uniform Motion - Motion With Constant Acceleration)Document12 pagesKinematic Concepts (Uniform Motion - Motion With Constant Acceleration)maryNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Kinematics PDFDocument19 pagesUNIT 3 Kinematics PDFparveezNo ratings yet
- ECE2022-Lecture 2P1-Particle Kinematics - Motion Along A Straight LineDocument85 pagesECE2022-Lecture 2P1-Particle Kinematics - Motion Along A Straight LineDuchin AnNo ratings yet
- Motion Notes CLASS 9Document12 pagesMotion Notes CLASS 9RitikNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A ParticleDocument47 pagesKinematics of A ParticleDarsh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Name: Nambio, Geraldine M. Physics I Student Number: 18B1010 Date: October 23, 2020 Section: BSES III-A KinematicsDocument8 pagesName: Nambio, Geraldine M. Physics I Student Number: 18B1010 Date: October 23, 2020 Section: BSES III-A KinematicsGeraldine NambioNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument88 pagesMotion Along A Straight LineRonald Abrasaldo SatoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight Line Revision Notes PDFDocument36 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight Line Revision Notes PDFrazi sharifNo ratings yet
- Kinematics NotesDocument16 pagesKinematics NotesCereal KillerNo ratings yet
- KinamaticsDocument10 pagesKinamaticsChathur ChandrasooryaNo ratings yet
- 1-1 - Kinematics Motion Along Straigt LineDocument14 pages1-1 - Kinematics Motion Along Straigt LineJoanna LeeNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument15 pagesKinematicsAmran AnwarNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument58 pagesMotionAl YsSa Ricafort MillabasNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics NotesDaniel KoNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument33 pagesMotion Along A Straight LineDastar KhawanNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument63 pagesKinema TicsTutor JamesNo ratings yet
- Stem General Physics 1 Week 2 Revised Module 1Document10 pagesStem General Physics 1 Week 2 Revised Module 1milimguinoNo ratings yet
- Physic Lesson 1Document6 pagesPhysic Lesson 1Jee RahimNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesDocument46 pagesClass 9 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument26 pagesMotion in A Straight LineSatyajit ManeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document9 pagesChapter 8NxndmxNo ratings yet
- Kinematics NotesDocument16 pagesKinematics Notesmuhammad umair100% (1)
- Describing Motion: Kinematics in One DimensionDocument56 pagesDescribing Motion: Kinematics in One DimensionReehmaMendinaNo ratings yet
- Motion: by Sandeep VermaDocument15 pagesMotion: by Sandeep Vermasandeep vermaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementDocument7 pagesKinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementTorettoNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Motion in Straight LineDocument56 pagesCh2 Motion in Straight Linecvxg5hk5xxNo ratings yet
- Uniform Motion:: Measuring The Rate of Motion of An Object: SpeedDocument7 pagesUniform Motion:: Measuring The Rate of Motion of An Object: SpeedLualuaNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument37 pagesMotionSAMRAT CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument51 pagesMotionpatrasrijit28No ratings yet
- Motion Notes PDFDocument21 pagesMotion Notes PDFSakshi SanghiNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineDocument12 pagesCH - 3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineVENKATESH CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Notes2Document10 pagesClass 9 Science Chapter 8 Notes2Official WorkNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional MotionDocument25 pagesOne Dimensional MotionRovshen BayramovNo ratings yet
- Explain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorFrom EverandExplain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorNo ratings yet
- Spheroidal Values For BLLM No. 1: Converting Local Grid To Local Geographic PositionDocument21 pagesSpheroidal Values For BLLM No. 1: Converting Local Grid To Local Geographic PositionDaniel TaylorNo ratings yet
- Plan ProfileDocument9 pagesPlan ProfileSinaNo ratings yet
- 2105 Pengecekan Pengajuan BAPP2 StackingDocument1 page2105 Pengecekan Pengajuan BAPP2 StackingSyahrul KamilNo ratings yet
- Longitude by Chronometer SUNDocument1 pageLongitude by Chronometer SUNBandar Almalki100% (1)
- Plane SailingDocument7 pagesPlane SailingLouise Megan LequinNo ratings yet
- Ch. 15 SHM SummaryDocument1 pageCh. 15 SHM SummaryAbhiNo ratings yet
- 250603DLDLD2401 - Exab00 - 01Document1 page250603DLDLD2401 - Exab00 - 01Mohammed HijaziNo ratings yet
- UCSAF Phase 3 60 Sites EPT-v1Document21 pagesUCSAF Phase 3 60 Sites EPT-v1Shafii TzNo ratings yet
- GEOL30005 Applied Geophysics: Challenge For Gravity ProcessingDocument16 pagesGEOL30005 Applied Geophysics: Challenge For Gravity ProcessingMartin NguyenNo ratings yet
- GE Report Lot 5948 Pob 4 IndangDocument3 pagesGE Report Lot 5948 Pob 4 IndangJan Gatchalian ReolaNo ratings yet
- Lecture17 Equations IsothermalSystems 4Document14 pagesLecture17 Equations IsothermalSystems 4shubhamNo ratings yet
- Confident Check For DGPS System - 21022022Document18 pagesConfident Check For DGPS System - 21022022zuharudin abdullahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5: NAME: Mahamud Mahamed Ahmed ID: 20-0501-1698Document3 pagesAssignment 5: NAME: Mahamud Mahamed Ahmed ID: 20-0501-1698Carab OfficialNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 15Document11 pagesPhysical Science Week 15Aleli Joy Profugo DalisayNo ratings yet
- Bennis Desrivieres: Pearson 7-8 Connected For SuccessDocument66 pagesBennis Desrivieres: Pearson 7-8 Connected For SuccessRex Lemuel AndesNo ratings yet
- Sph4up Group 5 Assignment 2 - RevisedDocument10 pagesSph4up Group 5 Assignment 2 - Revisedapi-390744685No ratings yet
- Linear Motion QDocument12 pagesLinear Motion QNgilah Mathew100% (3)
- General Navigation Test 2 With AnsDocument19 pagesGeneral Navigation Test 2 With AnsrohitNo ratings yet
- Momentum and ImpulseDocument4 pagesMomentum and ImpulseannmarieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2 SEPT 2011Document4 pagesTutorial Chapter 2 SEPT 2011Fareez SedakaNo ratings yet
- Learning Module For General Physics 1/ 12/quarter 1 Title: Kinematics (Motion in 2 Dimensions)Document20 pagesLearning Module For General Physics 1/ 12/quarter 1 Title: Kinematics (Motion in 2 Dimensions)GR MacopiaNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion (Jeemain - Guru)Document40 pagesLaws of Motion (Jeemain - Guru)Faltu SNo ratings yet
- 2.motion QP1Document6 pages2.motion QP1许某No ratings yet
- Quizziz April 28 2021Document1 pageQuizziz April 28 2021Angel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Schedule G-20 (Maths)Document2 pagesMechanics Schedule G-20 (Maths)sagarNo ratings yet
- Brgy. Lual BarrioDocument1 pageBrgy. Lual Barriokim aurinoNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Worksheet 0625Document6 pagesPhysics Practice Worksheet 0625emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Parallels and MeridiansDocument2 pagesParallels and MeridiansDevesh chauhanNo ratings yet