Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cylinder Areas and Volumes Report
Uploaded by
Jorge Esperida0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views13 pagesUsable and ready-to-present PowerPoint Presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentUsable and ready-to-present PowerPoint Presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views13 pagesCylinder Areas and Volumes Report
Uploaded by
Jorge EsperidaUsable and ready-to-present PowerPoint Presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
CYLINDER
Its areas and volumes
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
The students will be able to:
Explain the properties of a cylinder
Measure and determine the surface area of a
cylinder
Measure and determine the volume of a cylinder
CYLINDER
We can picture the
cylinder by looking in
A cylinder is a three- a soda can.
dimensional solid figure
which has two identical
circular bases joined by a
curved surface at a
particular distance from
the center which is the
height of the cylinder.
CYLINDER
The bases are like circular disks. The line
passing from the center or joining the centers of
two circular bases is called the axis of the
cylinder shape.
The distance between the two bases is
called perpendicular distance and is
represented as height, “h”.
The two circular bases have a distance from the
center to the outer boundary which is known as
the radius of the cylinder, represented by “r”.
The cylinder is a combination of 2 circles + 1
rectangle.
PROPERTIES OF CYLINDER
A cylinder has one curved surface and two flat faces which are identical.
The two circular bases are congruent to each other.
Its size depends on the radius of the base and the height of the curved surface.
Unlike a cone, cube, or coboid, a cylinder does not have any vertex. It means
there is no specific corner present in the cylinder.
The base and the top of the cylinder are identical, i.e it has the same base —
either circular or elliptical.
4 TYPES OF CYLINDER
1. Right Circular Cylinder: If the
axis of the two parallel bases is
perpendicular to the center of the
base, it is called the right circular
cylinder.
4 TYPES OF CYLINDER
2. Oblique Cylinder: An oblique cylinder
is one whose sides lean over the base. In
this, the sides are not perpendicular to the
center of the base. The Leaning Tower of
Pisa is a real-world example of an
oblique cylinder.
4 TYPES OF CYLINDER
3. Elliptic Cylinder: A cylinder
whose base is in the form of
an ellipse is called an elliptic
cylinder.
4 TYPES OF CYLINDER
4. Right Circular Hollow Cylinder
or Cylindrical Shell:
It consists of two right circular
cylinders bounded one inside the
other. The point of the axis is
common and is perpendicular to the
central base. It is different from the
right circular cylinder since it is
hollow in nature, i.e. there is some
space or void present inside.
CYLINDER FORMULAS
The lateral Surface area of the cylinder = 2πrh square units
The total surface area of the cylinder, A = 2πr(r+h) square units
The volume of the Cylinder, V = πr2h cubic units.
Where,
“r” is the radius of the cylinder
“h” is the height of the cylinder
LATERAL SURFACE AREA OF
CYLINDER
Ex. A solid right circular cylinder has radius of 14 cm and height of 8 cm. Find its Curved
Surface Area (CSA).
Formula: 2Πrh
SOLUTION:
Radius of the cylinder (r) = 14 cm
Height of the cylinder (h) = 8 cm
LSAC = 2Πrh
figure. #1
= 2⋅ (22/7) ⋅ 14 ⋅ 8
= 704 sq.cm
So, the curved surface area of cylinder is 704 sq.cm
TOTAL SURFACE AREA OF A
CYLINDER
Ex. Find the total surface area of a cylindrical tin of radius 17 am and height 3
cm.
Solution:
TSA = 2πr(r+h)
= 2 (3.142){17(17+3)}
= 2 (3.142)(17)(20)
= 2136.56
Therefore, the total surface area is
VOLUME OF THE CYLINDER
Ex. Find the volume of the cylinder shown. Round to the neatest cubic centimeter.
SOLUTION:
The radius of the cylinder is 8 cm, and the height is 15 cm.
Substitute 8 for r and 15 for h in the formula V=πr2h
V=π(8)2(15)
Simplify.
V=π(64)(15)
≈3016
Therefore, the volume of the cylinder is about 3016 cubic centimeters.
You might also like
- Solid MensurationDocument60 pagesSolid MensurationBenePicar100% (2)
- Icse 10 SimilarityDocument3 pagesIcse 10 SimilarityTalha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 MATH13-1Document51 pagesLesson 2 MATH13-1akladffja100% (1)
- 10 MensurationDocument44 pages10 MensurationSridevi KamapantulaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1: CIRCLES Lesson 2.2 MISCELLANEOUS Planes: Week 3 and Week 4 Math 13 Solid MensurationDocument29 pagesLesson 2.1: CIRCLES Lesson 2.2 MISCELLANEOUS Planes: Week 3 and Week 4 Math 13 Solid MensurationDan Casurao100% (1)
- Volume of A Cylinder, Cone, and SphereDocument27 pagesVolume of A Cylinder, Cone, and SphereiLearnMathNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Maths Project PDFDocument13 pagesConic Section Maths Project PDFSiva Kumar100% (3)
- Spherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesFrom EverandSpherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 MATH13-1Document51 pagesLesson 7 MATH13-1akladffja75% (4)
- Summative 3 - Math 10Document3 pagesSummative 3 - Math 10Zetrock JezzNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume of 3d FiguresDocument13 pagesSurface Area and Volume of 3d Figuresapi-3731257100% (15)
- Mensuration FormulasDocument25 pagesMensuration FormulasIsrar Ahmad100% (1)
- Chapter 1.2 Dan 1.4 EnglishDocument12 pagesChapter 1.2 Dan 1.4 EnglishAnonymous t5pFAF0% (1)
- Cylinder - WikipediaDocument39 pagesCylinder - WikipediaNaniNo ratings yet
- Week 7 CylinderDocument30 pagesWeek 7 CylinderJulius Patrick Mallanao100% (1)
- CylinderDocument10 pagesCylinderSara XhaferiNo ratings yet
- Surface-Area Jiwanwala FaridkotDocument12 pagesSurface-Area Jiwanwala Faridkotapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Unit1-Properties and ShapesDocument10 pagesUnit1-Properties and ShapesMacha NuttsNo ratings yet
- CylinderDocument5 pagesCylinderCharmie AmanteNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IDocument10 pagesSolid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IAzha Clarice VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cylinder and Cone A. DefinitionDocument5 pagesCylinder and Cone A. DefinitionDeviana DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Properties and Shapes WordDocument2 pagesUnit1-Properties and Shapes WordMacha NuttsNo ratings yet
- Class X Cbse Pattern Chapterwise NotesDocument3 pagesClass X Cbse Pattern Chapterwise NotesROOPANo ratings yet
- Lesson 14-SphereDocument48 pagesLesson 14-SphereRia Grace P Abdon50% (4)
- Chapter 16Document9 pagesChapter 16sanjeevNo ratings yet
- Do You Know What A Cylinder IsDocument3 pagesDo You Know What A Cylinder IsMaria AngelLuna GonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Diagram Given Here Is of A Right Circular CylinderDocument2 pagesThe Diagram Given Here Is of A Right Circular CylinderRevaldy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- CURVED SURFACE SOLIDS Chapter 6Document35 pagesCURVED SURFACE SOLIDS Chapter 6tikafebriani52No ratings yet
- PT3 Group 9Document15 pagesPT3 Group 9Mikaela Angela CenaNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volumes: Done By: M.Vaishnavi Grade: 9PDocument17 pagesSurface Area and Volumes: Done By: M.Vaishnavi Grade: 9Pmahindra100% (1)
- Cone, Cylinder, and Sphere: Created By: Nurina Ayuningtyas Wahyu Fajar S. Yan Aditya P Yola Yaneta HDocument31 pagesCone, Cylinder, and Sphere: Created By: Nurina Ayuningtyas Wahyu Fajar S. Yan Aditya P Yola Yaneta HJR DevienteNo ratings yet
- SE SA of CylinderDocument5 pagesSE SA of CylinderPyla RamNo ratings yet
- Pyramid, Cylinder, Cone and SphereDocument11 pagesPyramid, Cylinder, Cone and SphereDrei Sal100% (2)
- A Study On Solids in Mathematics and Their ApplicationDocument4 pagesA Study On Solids in Mathematics and Their ApplicationAnjana mohandas WarrierNo ratings yet
- Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Summary NotesDocument4 pagesCylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Summary NotesAbdella KarimeNo ratings yet
- 3d Shapes - CylindersDocument23 pages3d Shapes - CylindersSetiawan TanadiNo ratings yet
- And VolumesDocument31 pagesAnd Volumesdev mittalNo ratings yet
- QuadrilateralsDocument52 pagesQuadrilateralsbrazcell domNo ratings yet
- How To Find Volume of A CylinderDocument4 pagesHow To Find Volume of A Cylinderapi-174648067No ratings yet
- Formula For The Curved Surface AreaDocument11 pagesFormula For The Curved Surface AreaJuhi GandhiNo ratings yet
- Cylinde R: Prepared By: Alipante, Mary Joy A. Bsed-Math1ADocument17 pagesCylinde R: Prepared By: Alipante, Mary Joy A. Bsed-Math1ARene Jay-ar Morante SegundoNo ratings yet
- Circle MathsDocument10 pagesCircle MathsAdhithy SkumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Mom1iDocument32 pagesChapter 2.1 Mom1iKarell Faye BatulanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 FSOLIMONDocument50 pagesLesson 2 FSOLIMONCris Angelo SalongaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration BasicsDocument9 pagesMensuration BasicsKimberly ArnoldNo ratings yet
- Surface AreaDocument26 pagesSurface Areaeoreou05No ratings yet
- CirclesDocument23 pagesCirclesDanna Marie OlioNo ratings yet
- Hello WorldDocument2 pagesHello WorldLaurie EliabNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument7 pagesIntroductionDhanush AnimationNo ratings yet
- Volume of A Sphere FormulaDocument7 pagesVolume of A Sphere Formulaapi-126876773No ratings yet
- CircleDocument3 pagesCircleJozil TolibasNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: Mrs. Avininder Kaur Anshika Roll No - 5Document6 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: Mrs. Avininder Kaur Anshika Roll No - 5Varun JainNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document23 pagesGroup 5Roge LynNo ratings yet
- Document 11Document6 pagesDocument 11Astitva KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume Class 10 PDF - Docx 1Document12 pagesSurface Area and Volume Class 10 PDF - Docx 1ABHISHEK J KNo ratings yet
- CircolDocument12 pagesCircol202130054No ratings yet
- Chapter13 SurfaceareasandvDocument35 pagesChapter13 SurfaceareasandvDeepakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document12 pagesChapter 19Ali AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Solid Geometry-3d PDFDocument27 pagesSolid Geometry-3d PDFpraveenshridharNo ratings yet
- F2 Math - CircleDocument3 pagesF2 Math - CircleHi KhorNo ratings yet
- Volume of A Sphere FormulaDocument7 pagesVolume of A Sphere Formulaapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Sphere Areas and Volumes ReportDocument21 pagesSphere Areas and Volumes ReportJorge EsperidaNo ratings yet
- Pyramid Areas and Volumes ReportDocument35 pagesPyramid Areas and Volumes ReportJorge EsperidaNo ratings yet
- Prism Areas and Volumes ReportDocument30 pagesPrism Areas and Volumes ReportJorge EsperidaNo ratings yet
- Cone Areas and Volumes ReportDocument10 pagesCone Areas and Volumes ReportJorge EsperidaNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal ReviewerDocument9 pagesPre Cal ReviewerJepoy dizon Ng Tondo Revengerz gangNo ratings yet
- Math8 LAS Q4 W5Document10 pagesMath8 LAS Q4 W5Eleazar Mata BarreraNo ratings yet
- CuboctahedronDocument13 pagesCuboctahedronapi-282361585No ratings yet
- Oxford University Press MOCK 18 (I) : MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part Paper 2Document14 pagesOxford University Press MOCK 18 (I) : MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part Paper 2Tsz Ho WongNo ratings yet
- Grade12 TrigDocument28 pagesGrade12 TrigmscstutorsNo ratings yet
- Types of Triangles Powerpoint Us M 2548742 Ver 5Document20 pagesTypes of Triangles Powerpoint Us M 2548742 Ver 5antonanojayNo ratings yet
- Class 9 MCQs On QuadrilateralsDocument10 pagesClass 9 MCQs On QuadrilateralsBalaji ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- Ai Skilling ProblemsDocument23 pagesAi Skilling ProblemsVenkat AravindNo ratings yet
- Aptitude QuestionsDocument3 pagesAptitude QuestionsNileshIndulkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 6 PDFSuriyagowthamNo ratings yet
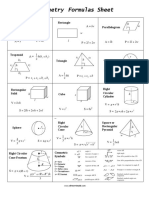
- Geometry Formulas Sheet: S W L A LW L HDocument1 pageGeometry Formulas Sheet: S W L A LW L HJohn Carlo SantosNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument22 pagesMathssinchanakalal33No ratings yet
- Mathematics Seven ThirdDocument4 pagesMathematics Seven ThirdJEWEL LUCKY LYN GUINTONo ratings yet
- Mathematics, Paper-I & Ii: InstructionsDocument9 pagesMathematics, Paper-I & Ii: Instructionssirichowdhary82No ratings yet
- Geometry m3 Topic B Lesson 5 TeacherDocument16 pagesGeometry m3 Topic B Lesson 5 TeacherAliyah Magtalas BuotanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Inverse TrigoDocument6 pagesWorksheet - Inverse TrigoAashiqueNo ratings yet
- Parabola - Formula Sheet - MathonGoDocument8 pagesParabola - Formula Sheet - MathonGoTimmy LNo ratings yet
- Scholarship Test 3mayDocument3 pagesScholarship Test 3mayanant_sahu_1No ratings yet
- Chapter-Two Part 1Document26 pagesChapter-Two Part 1Wiz Nati XvNo ratings yet
- 2007 - MTL - (Stylianides, A) Introducing Young Children To The Role of Assumptions in ProvingDocument28 pages2007 - MTL - (Stylianides, A) Introducing Young Children To The Role of Assumptions in ProvingSaul Miquias Victorio HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Benjamin 1-Grade 5 Geometry: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesDocument3 pagesBenjamin 1-Grade 5 Geometry: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given Choiceshean long chongNo ratings yet
- Complex Number Exercise Book PDFDocument26 pagesComplex Number Exercise Book PDFRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- Vectors Graphical & Analytical MethodsDocument47 pagesVectors Graphical & Analytical MethodsJean Bataanon CallejoNo ratings yet
- Benco 2021 Maths Test 2Document16 pagesBenco 2021 Maths Test 2fecofyleNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Maths Set 1: A) B) C) D)Document4 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Maths Set 1: A) B) C) D)JayaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Projection of PlanesDocument6 pagesAssignment - Projection of PlanesSurekha ChandranNo ratings yet
- Math SAT Section 8Document4 pagesMath SAT Section 8pureconfidence100% (1)