Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre History
Uploaded by
sarashehab6780 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views9 pagesOriginal Title
Presentation (3)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views9 pagesPre History
Uploaded by
sarashehab678Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Pre history
• To learn about the historic evolution, people ideally depend on
documents and written records. These factors formulate their
pictures of the past. Yet, no written records are found for the
prehistory of humankind
• Prehistory is defined as a time before the action of writing was
developed. How do people then know their past you may
wonder? Since there were no written records, those who
delved into history depended in their stories on archeological
and biological evidence. Archeologists and anthropologists
used their information to create postulates about our early
records.
• Archeology and Anthropology
• Archeologists' job is to study and examine artifacts or objects
made of human remains. The range of the artifacts has no
limits. It may be as simple as art or as dangerous as weapons.
Other artifacts or objects may include buildings made by
people. These factors help enhance their studies.
• Some examples of fossils are skeletons and
footprints.
• Archeologists and anthropologists
• set their own scientific methods to move forward
with their work. They search on sites or cautiously
dig up land; they study early human life in Africa,
Europe, and Asia.
• Archeology is the study of past lives through the
assumptions of what people have left behind.
• Anthropology is known as the study of human life
and culture. Culture is based on what people wear,
the way they organize their society, and their
morals.
• Usually searches for human fossils or other artifacts
happen at different places around the globe. Archeologists
usually seek to uncover fossil remains of early humans.
Such remains include ancient cities and burial grounds.
This helps them together with anthropologists to present
evidence-based studies with better analysis and greater
understanding of ancient societies. Radiocarbon dating
determines the age of the artifacts and fossils for no more
than 50,000 years.
• Scientists previously used several elements in their
observations. For objects dating back to 200,000 years, they
depended on thermoluminescence, a form of luminescence
that is exhibited by certain crystalline materials, such as
some minerals, when previously absorbed energy from
electromagnetic radiation or other ionizing radiation is re-
emitted as light upon heating of the material. Another
evidence scientist used is analyzing the DNA, the
• Bands are the most primitive form of human organizations. This is
usually a loosely bound group of 25 to 60 people who are related by
kinship ties. The group cooperates in hunting and gathering activities
without any form of permanent leadership. Many a hunting and
gathering population in the world is even today found to live in Band
Societies.
• The Paleolithic Era
• The Paleolithic Era- or the old stone age- is a prehistoric period of
human history where humans from 100s of 1000s of years relied on
simple stone tools.
• People at that time gathered their daily food from hunting animals
such as buffalo, horses and bison, and from gathering nuts, berries,
and fruits. They used to carefully observe animal migration and
vegetative cycles to hunt successfully.
• Nomads was the term used to define
• Paleolithic people; these people mainly moved from one place to
another for survival purposes.
• Men and women at that age had a role in sustaining life by finding
• Use of Stones
• One of the hard stones early people used was flint. They used to
sharpen the edges of flint stones to manufacture pointed tools such
as hand axes. Over time, they developed better tools, and later they
invented the bow and arrow, harpoons, and fishhooks.
• Use of Fire
• Paleolithic people used fire as a heat source for cooking and
warmth especially while moving to colder areas. Fire kept people
safe by keeping wild animals away.Fire also helped them during the
Ice Age, where sheets of ice covered huge areas in Europe, North
America, and Asia.
• Arts
• Paleolithic people had an active role in building their own culture
as well.They realistically painted large animals such as lions,Oxen,
owls and many others by mixing mineral ores and fat to make
several paint colors.
• Paleolithic a Greek word that means old stone.Hunting depended
The Byzantine Empire
• With all the changes that took place in the western and eastern parts of the Roman
Empire, it continued to survive, although in different forms. into the fifth century .
The eastern part of the Roman Empire was not apart from all what went on in the
rest of the empire. The Eastern Roman Empire was also on its way to develop into a
new empire, that of the Byzantine.
• The eastern part of the Roman Empire came under the leadership of Emperor
Justinian who had a dream of restoring the whole of the Empire in the
Mediterranean. In 552, Justinian could attain his dream, and the whole
Mediterranean world including Italy North of Africa, Asia Minor, and other areas,
came under his control. The whole dream yet drifted in vain, and all areas
conquered were lost completely three years after Justinian’s death
• The Shift from a Roman to a Byzantine Empire
• Several factors threatened the accomplishments of Justinian. These included the
continuously declining population that was affected by the plague and the vast
territories that needed to be protected. These territories were far from the capital,
Constantinople, which made it difficult to provide enough military forces to protect
the different frontiers especially in the light of the empty treasury.
• The Romans started losing more land with the growth and unity of strong Arab
forces that swept through different areas and took control over several provinces.
Rome shrank in size and became known as the Eastern Roman Empire or the
Byzantine Empire. Consisting of the Balkans and Asia Minor, the Christian state,
adopted and applied in its practices the rules of Christianity. Laws and people
became infatuated with the Christian religion, and they believed that their patriarch
• Under the rule of Justinian, Constantinople was rebuilt to maintain its position as
the largest city in medieval Europe. It became a major hub and center for
commerce. Imports and exports of all kinds of products flourished. Products like fur,
silk, jewelry, ivory, spices, honey and others came in from Russia, China, India,
Balkans and South East Asia.
• The demand for silk increased dramatically during Justinian's ruling which made the
empire famous for this industry and for silk cloth in specific. Justinian also paid
enough attention to the empire's architecture and during his reign many palaces,
churches, and a huge arena known as the Hippodrome were built. Other projects
that flourished during this period included courts, schools, roads, underground
reservoirs, and others.
• The Hippodrome was an arena for chariot races and other forms of
entertainment.Many monuments and artworks were brought frost the different areas
in the empire to adorn it.
• The Byzantine formed a new dynasty with new emperors known as the
Macedonians, and with their ruling, the empire expanded only to conquer vast lands
around Europe including Syria, Crete, Cyprus, and Bulgaria. Macedonians ruled from
867 to 1081, and they were able to defend themselves against their enemies during
their reign. The popularity of commerce grew during this period as well.
Constantinople became a famous point for trade, and a place that attracted tourists
from around the world.
• The successors of the Macedonian dynasty failed to keep everything in order and by
the eleventh century, trouble increased between the Catholic Church of the West
You might also like
- Group 1 STSDocument148 pagesGroup 1 STSChloe SantosNo ratings yet
- Science and Technology Report (Stone Age)Document41 pagesScience and Technology Report (Stone Age)Clary100% (1)
- F. 1. There Are Many Reasons Why We Should Study History.: The Earliest SocietiesDocument2 pagesF. 1. There Are Many Reasons Why We Should Study History.: The Earliest SocietiesdurgaNo ratings yet
- Social Studies BookDocument28 pagesSocial Studies BookSiriwat WongudomsinNo ratings yet
- UCSP Ian Barrios ReportDocument13 pagesUCSP Ian Barrios ReportJamilla KeanyNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Reporting 3Document40 pagesUcsp Reporting 3Jeany Babe VitorNo ratings yet
- Assignment WHC Group1Document26 pagesAssignment WHC Group1narmtan05No ratings yet
- Ucsp Week 4Document26 pagesUcsp Week 4Irene AmansecNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Q3W4. PresentationDocument34 pagesUcsp Q3W4. PresentationVanessa Mae AguilarNo ratings yet
- Civilazation of WworldDocument24 pagesCivilazation of WworldMian Muhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- BS - MT - 02 - Indus Valley CivilizationDocument48 pagesBS - MT - 02 - Indus Valley CivilizationTearlëşşSufíåñNo ratings yet
- Art App. Unit 2Document46 pagesArt App. Unit 2CarlaJb EspirituNo ratings yet
- Civilization: Aboguin, Brian E. 201Ed-Bsed Socstud World History 2Document16 pagesCivilization: Aboguin, Brian E. 201Ed-Bsed Socstud World History 2Vinnie GognittiNo ratings yet
- The Emergence of Civilization: Neolithic Revolution & River Valley CivilizationsDocument39 pagesThe Emergence of Civilization: Neolithic Revolution & River Valley CivilizationsEula Marie ValladoresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - A History of The World PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 1 - A History of The World PDFJanvierNo ratings yet
- Civilization 2Document16 pagesCivilization 2breakkayden831No ratings yet
- Ebolusyong KulturalDocument64 pagesEbolusyong KulturalEmmanuel AbivaNo ratings yet
- Soc Sci - 2017 PDFDocument445 pagesSoc Sci - 2017 PDFJANORA M. JALALNo ratings yet
- PrehistoryDocument45 pagesPrehistoryAnonymous 7GXIcV100% (2)
- Western Civilization - A Short Survey The Ancient World The Prehistoric PeriodDocument8 pagesWestern Civilization - A Short Survey The Ancient World The Prehistoric PeriodUsoph Two PiecesNo ratings yet
- 11 History Themes in World History Goalias BlogspotDocument260 pages11 History Themes in World History Goalias BlogspotShamim SaifiNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1.docx 1Document11 pagesLESSON 1.docx 12023107565No ratings yet
- Ncert 11 HistoryDocument260 pagesNcert 11 HistoryAnonymous dTxnkppANo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes OverviewDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Notes Overviewcjchen2810No ratings yet
- UCSPDocument31 pagesUCSPEarl Oriel Manuel GacuscusNo ratings yet
- A Powerpoint Presentation ON:-: Early Social FormationsDocument46 pagesA Powerpoint Presentation ON:-: Early Social FormationsPALLAVI pallavi2No ratings yet
- Early Western Civilization Research Paper TopicsDocument5 pagesEarly Western Civilization Research Paper Topicsajqkrxplg100% (1)
- The History and Philosophy of Science Week 8Document35 pagesThe History and Philosophy of Science Week 8Xanny The SunNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - 6Document4 pagesWeek 5 - 6Krisia Diane BuanNo ratings yet
- World History and CivilizationDocument9 pagesWorld History and CivilizationmdaburahathelalsikderNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Architecture: Man Civilisations, Settlements and Broad CharacteristicsDocument28 pagesEvolution of Architecture: Man Civilisations, Settlements and Broad CharacteristicsShruti Nagpal KapurNo ratings yet
- UCSP Report DoneDocument49 pagesUCSP Report DoneFrench Aira MendozaNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Studies All Slide Quiz1Document183 pagesBangladesh Studies All Slide Quiz1Lover BoyNo ratings yet
- Cultural Evolution: Palaeolithic - Neolithic - Metal AgesDocument29 pagesCultural Evolution: Palaeolithic - Neolithic - Metal AgesPiolo Santos100% (1)
- Assignment Sa ArtAppDocument4 pagesAssignment Sa ArtAppBea Marella CapundanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Section 1&2 The Frist HumansDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Section 1&2 The Frist HumansIslam BourbalaNo ratings yet
- Piri Reis and Ottoman Discovery of The Great Discoveries: by Svat SoucekDocument50 pagesPiri Reis and Ottoman Discovery of The Great Discoveries: by Svat SoucekourbookNo ratings yet
- The History of Hospitality and TourismDocument37 pagesThe History of Hospitality and Tourismjessa histaNo ratings yet
- Unit Outline Introduction The West Before 1300Document21 pagesUnit Outline Introduction The West Before 1300api-324512227No ratings yet
- Reviewer For Art AppreciationDocument19 pagesReviewer For Art AppreciationChrishialaine Joy AbasNo ratings yet
- 23 Art in Early Civilization2Document8 pages23 Art in Early Civilization2JamesNo ratings yet
- 1694694682486.H 3 - TermsDocument3 pages1694694682486.H 3 - TermsAmaanNo ratings yet
- Making of A Global WorldDocument3 pagesMaking of A Global WorldsimoneNo ratings yet
- P Y P Y: Rehistor RehistorDocument10 pagesP Y P Y: Rehistor RehistorKatherine ScottNo ratings yet
- 1 Global PrehistoryDocument32 pages1 Global PrehistoryAreeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- First HumansDocument39 pagesFirst HumansKween CubillanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Earliest Beginnings: The Nature of HistoryDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Earliest Beginnings: The Nature of HistoryHimana Abdul MalikNo ratings yet
- HUMN Medieval ArtDocument4 pagesHUMN Medieval ArtOkumura YukioNo ratings yet
- Eastern-CivDocument37 pagesEastern-CivFritz louise EspirituNo ratings yet
- History NosDocument8 pagesHistory NosDavid SolisNo ratings yet
- History NoesDocument8 pagesHistory NoesDavid SolisNo ratings yet
- Historical Antecedents in The World: Stone AgeDocument7 pagesHistorical Antecedents in The World: Stone AgeKaelaNo ratings yet
- World History: Ancient History, United States History, European, Native American, Russian, Chinese, Asian, Indian and Australian History, Wars including World War I and II [4th Edition]From EverandWorld History: Ancient History, United States History, European, Native American, Russian, Chinese, Asian, Indian and Australian History, Wars including World War I and II [4th Edition]Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Intellectualrevolutions SummaryDocument13 pagesIntellectualrevolutions SummaryPhD PepperNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7-8 Written Report PDFDocument12 pagesLesson 7-8 Written Report PDFMikayah g.No ratings yet
- As The Environment ChangesDocument1 pageAs The Environment ChangesJeramel Teofilo ManaloNo ratings yet
- Algo TradingDocument982 pagesAlgo Tradingyogesh kannaNo ratings yet
- History of ArchitectureDocument23 pagesHistory of ArchitectureLauren EspinoNo ratings yet
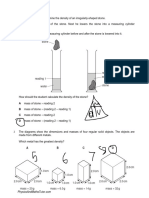
- Density (Multiple Choice) QPDocument15 pagesDensity (Multiple Choice) QPsarashehab678No ratings yet
- Explore Our Signature Steaks & Fresh Food Texas Roadhouse Menu RiyadhDocument1 pageExplore Our Signature Steaks & Fresh Food Texas Roadhouse Menu Riyadhsarashehab678No ratings yet
- Grades 9-12 4Document5 pagesGrades 9-12 4sarashehab678No ratings yet
- Grades 9-12 4Document5 pagesGrades 9-12 4sarashehab678No ratings yet
- Physics 2 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument74 pagesPhysics 2 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationHakim Abbas Ali Phalasiya100% (1)
- Spells Spell Book Generator 2nde v2 - 92Document292 pagesSpells Spell Book Generator 2nde v2 - 92I_NiemandNo ratings yet
- Linguistic AnthropologyDocument10 pagesLinguistic AnthropologyAliaNo ratings yet
- Nature, Goals and Perspectives in Anthropology, Sociology and Political ScienceDocument3 pagesNature, Goals and Perspectives in Anthropology, Sociology and Political ScienceDiana CustodioNo ratings yet
- Ethnoarchaeology or Simply Archaeology?Document7 pagesEthnoarchaeology or Simply Archaeology?TonyNo ratings yet
- PandamoniumDocument2 pagesPandamoniumChiranjivi NainiNo ratings yet
- Robert H. Winthrop - Dictionary of Concepts in Cultural Anthropology-Greenwood Pub Group (1991)Document382 pagesRobert H. Winthrop - Dictionary of Concepts in Cultural Anthropology-Greenwood Pub Group (1991)sanja špoljar vržinaNo ratings yet
- Who Are The LuoDocument16 pagesWho Are The LuojedicalleNo ratings yet
- Report On Tabon CaveDocument33 pagesReport On Tabon CaveAishlly Crystal OrtizNo ratings yet
- Anthropology: Cultural Anthropology Biological AnthropologyDocument3 pagesAnthropology: Cultural Anthropology Biological AnthropologyHannah Althea Hijan JocsonNo ratings yet
- Brenda Chalfin-Shea Butter Republic - State Power, Global Markets, and The Making of An Indigenous Commodity (2004)Document312 pagesBrenda Chalfin-Shea Butter Republic - State Power, Global Markets, and The Making of An Indigenous Commodity (2004)Caio Bonamigo DorigonNo ratings yet
- 4º Unit3 Test ACNSDocument4 pages4º Unit3 Test ACNSLucía PJNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Long Quiz DISSDocument9 pagesWeek 5 Long Quiz DISSShen EugenioNo ratings yet
- Historic Cockfight Among The Santals: An Anthropological ViewDocument9 pagesHistoric Cockfight Among The Santals: An Anthropological ViewakosiemNo ratings yet
- Module 15-The Gods and Goddesses of Egyptian MythologyDocument3 pagesModule 15-The Gods and Goddesses of Egyptian MythologyXiena Rose Abella BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Beowulf FemDocument14 pagesBeowulf FemLaura Rejón LópezNo ratings yet
- MuseumDocument8 pagesMuseumHashren Antasari0% (1)
- VILLANUEVA, Blitz Lyle B. (LA #2)Document2 pagesVILLANUEVA, Blitz Lyle B. (LA #2)Blitz Lyle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Pfaffenberger 1988 Fetishised Objects and Humanised Nature Towards An Anthropology of Technology PDFDocument18 pagesPfaffenberger 1988 Fetishised Objects and Humanised Nature Towards An Anthropology of Technology PDFEmiliano BentivengaNo ratings yet
- Baluba MythologyDocument2 pagesBaluba MythologyapurimemukaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Visayas MythologyDocument8 pagesPhilippine Visayas Mythologyapi-406238375No ratings yet
- Ancient Egypt The Gift of The NileDocument2 pagesAncient Egypt The Gift of The NilekeznicsatNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Anthropological PerspectiveDocument6 pagesTopic 3 Anthropological PerspectiveJhessai CornelNo ratings yet
- The Amduat-The Book of The Hidden ChamberDocument8 pagesThe Amduat-The Book of The Hidden Chamberyunyao ChenNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument4 pagesEnglish ProjectRohith KumarNo ratings yet
- Anthropology 408: History and Memory: SyllabusDocument6 pagesAnthropology 408: History and Memory: SyllabusCaterinaPredaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key + TapescriptDocument3 pagesAnswer Key + TapescriptThanh HuyenNo ratings yet
- Anthropology: An Introduction: Prepared By: Parisya B. Musa, PH.DDocument15 pagesAnthropology: An Introduction: Prepared By: Parisya B. Musa, PH.DTRISH BOCANo ratings yet
- Field Trip PortfolioDocument9 pagesField Trip PortfolioKristineNo ratings yet
- First Trip To EuropeDocument39 pagesFirst Trip To EuropeMary Rose Jose Gragasin100% (2)
- Steward J. 1942. The Direct Approach To Archaeology PDFDocument8 pagesSteward J. 1942. The Direct Approach To Archaeology PDFvalentinaNo ratings yet






















































![World History: Ancient History, United States History, European, Native American, Russian, Chinese, Asian, Indian and Australian History, Wars including World War I and II [4th Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/440027782/149x198/64189943ff/1698734847?v=1)