Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Class 11 Ion Pump
Uploaded by
Lokeshh Upadhyay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesThe document discusses different types of ion pumps in cell membranes. Ion pumps are integral membrane proteins that actively transport ions against their concentration gradient using cellular energy. Specifically, it mentions the sodium potassium pump, which maintains sodium and potassium levels inside and outside cells using ATP. The sodium potassium pump transports 3 sodium ions out and 2 potassium ions in per cycle. It also discusses the importance of ion pumps for nerve, muscle and water balance functions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of ion pumps in cell membranes. Ion pumps are integral membrane proteins that actively transport ions against their concentration gradient using cellular energy. Specifically, it mentions the sodium potassium pump, which maintains sodium and potassium levels inside and outside cells using ATP. The sodium potassium pump transports 3 sodium ions out and 2 potassium ions in per cycle. It also discusses the importance of ion pumps for nerve, muscle and water balance functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesChemistry Class 11 Ion Pump
Uploaded by
Lokeshh UpadhyayThe document discusses different types of ion pumps in cell membranes. Ion pumps are integral membrane proteins that actively transport ions against their concentration gradient using cellular energy. Specifically, it mentions the sodium potassium pump, which maintains sodium and potassium levels inside and outside cells using ATP. The sodium potassium pump transports 3 sodium ions out and 2 potassium ions in per cycle. It also discusses the importance of ion pumps for nerve, muscle and water balance functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
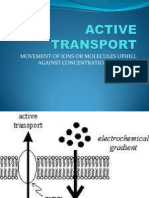
ION PUMP
The biological membrane present in cell of
eukaryotes contain protein for transport of nutrients
across the cell
These proteins are of two types .they are
a )Integral proteins (trans membrane)
b) Peripheral proteins
Hence , ion pump refers to channels of those integral
proteins that transport ions across the biological
membrane against the concentration gradient through
active transport .
Active transport
Active transport refers to the transport of
materials against the concentration gradient
(from low to high ) through the use of cellular
energy .
Transport occurs through channels of protein
in animal cell . These transport channels
/proteins use ATP as source of energy mainly.
And then they store energy released in the
form of potential energy. And these channels
use this potential energy for transport .
Sodium potassium pump
Sodium potassium pump is an enzyme based
mechanism that maintains the cellular concentration of
sodium and potassium ions inside and outside the cell
through active transport across the cell membrane .
It is an example of active primary transport . The energy
required during this transport is relased by ATP
molecules by autophosphorlyation.
ATP = ADP +phosphate + energy released
During one complete cycle , three sodium ions are
released out and 2 potassium ions are released inside
the cell .
Importance of sodium potassium pump
Functioning of nerve and muscle cells
Water balance
Creation of electrical potential across the
membrane
Sodium glucose pump
Sodium glucose pump is an enzyme based
mechanism that transport the glucose inside
the cell from extracellular fluid across the cell
membrane due to concentration gradient of
sodium ions .
This is very important as glucose is main
energy source to perform various functions
inside the cell.
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Active TransportDocument7 pagesActive Transportidokofavour2015No ratings yet
- Active Transport MechanismDocument46 pagesActive Transport MechanismnoblefxNo ratings yet
- Active Transport 1Document29 pagesActive Transport 1Reign Sevilla UlepNo ratings yet
- Sodium Potassium Pump Tutorial 20BOE10050Document8 pagesSodium Potassium Pump Tutorial 20BOE10050Yashi GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument51 pagesActive Transportericka khimNo ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration-1Document25 pagesEnergy and Respiration-1Rohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- Microbial NutritionDocument7 pagesMicrobial NutritionatifzeaNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument10 pagesActive TransportSylvia DuzonNo ratings yet
- "In The Name Of,, .": AllahDocument28 pages"In The Name Of,, .": AllahAqsa ArifNo ratings yet
- Movement of Ions or Molecules Uphill Against Concentration GradientDocument32 pagesMovement of Ions or Molecules Uphill Against Concentration Gradientraanja2No ratings yet
- 3 - kh201295 kh201295Document5 pages3 - kh201295 kh201295murtada gubaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-02-07 at 9.06.14 PMDocument92 pagesScreenshot 2023-02-07 at 9.06.14 PMMohammed RamzyNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Nutrition. Growth Factors. Nutrient Transport and MechanismsDocument3 pagesBacterial Nutrition. Growth Factors. Nutrient Transport and MechanismsmehekNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Transport MechanismsDocument1 pageThe Cellular Transport Mechanismsammarnarjis7No ratings yet
- 1st Year 2nd Week PHYS Lecture 6 2019 2020Document14 pages1st Year 2nd Week PHYS Lecture 6 2019 2020Ahmed TarekNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument12 pagesActive TransportReymah Nair NarendranNo ratings yet
- This Energy Is Harvested From ATP That Is Generated Through Cellular Metabolism.)Document4 pagesThis Energy Is Harvested From ATP That Is Generated Through Cellular Metabolism.)AnnEviteNo ratings yet
- This Energy Is Harvested From ATP That Is Generated Through Cellular Metabolism.)Document4 pagesThis Energy Is Harvested From ATP That Is Generated Through Cellular Metabolism.)Anne NicoleNo ratings yet
- Transport 2 PDF Lecture Elalamein 2021-22Document5 pagesTransport 2 PDF Lecture Elalamein 2021-22Ahmed MagdyNo ratings yet
- Transport Through Cell Membrane 11Document13 pagesTransport Through Cell Membrane 11Aastha LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Written Report: Sodium-Potassium Pump and Secondary Active TransportDocument2 pagesWritten Report: Sodium-Potassium Pump and Secondary Active TransportFe Tapnio CunananNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesModule 8 PhotosynthesisSeann ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1.4.A1 Structure and Function of The Sodium-Potassium Pumps For Active Transport and Potassium Channels For Facilitated Diffusion in AxonsDocument11 pages1.4.A1 Structure and Function of The Sodium-Potassium Pumps For Active Transport and Potassium Channels For Facilitated Diffusion in AxonsApollo AdairNo ratings yet
- Cell ExchangesDocument28 pagesCell ExchangesBenzerari ManaNo ratings yet
- Active Transport: By: Ann Gabrielle L. Evite STEM 12 - 1Document19 pagesActive Transport: By: Ann Gabrielle L. Evite STEM 12 - 1AnnEviteNo ratings yet
- Active Transport: By: Ann Gabrielle L. Evite STEM 12 - 1Document19 pagesActive Transport: By: Ann Gabrielle L. Evite STEM 12 - 1AnnEviteNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument13 pagesActive TransportJeongyeonnie OppaNo ratings yet
- What Is Resting Membrane Potential?: Mechanism of An Action PotentialDocument5 pagesWhat Is Resting Membrane Potential?: Mechanism of An Action PotentialAli InamNo ratings yet
- Energy and ATPDocument5 pagesEnergy and ATPMilka Rahman100% (1)
- Sistem Transport: Prokariot - EukariotDocument48 pagesSistem Transport: Prokariot - Eukariotemi agus trianiNo ratings yet
- Types of TransportsDocument13 pagesTypes of Transports88AKKNo ratings yet
- 116 - Transport Mechanisms in CellsDocument4 pages116 - Transport Mechanisms in Cellslastjoe71100% (1)
- Active Transport MethodsDocument13 pagesActive Transport Methodssrikanth100% (3)
- Practical Work 3Document7 pagesPractical Work 3Achraf RabadiNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 Energy and RespirationDocument34 pagesChap 12 Energy and RespirationGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Movement Across The Cell Membrane: AP Biology AP BiologyDocument39 pagesMovement Across The Cell Membrane: AP Biology AP Biologyanon_53206779No ratings yet
- BCB 203 Lecture 3Document26 pagesBCB 203 Lecture 3ShAkil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport SystemsDocument33 pagesMembrane Transport SystemsObiajulu Crystal OnyinyechiNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab For ReadingDocument57 pagesBiochem Lab For ReadingShaira Elyze GabrielNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Mitochondria and ChloroplastsDocument24 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Mitochondria and ChloroplastsCeline BlancoNo ratings yet
- Membrane-Based Energy Harvest in Mitochondrion Chloroplast With Notes v4-2022-2023Document25 pagesMembrane-Based Energy Harvest in Mitochondrion Chloroplast With Notes v4-2022-2023MARIA ISABILLE DUALLO MUSONGNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument14 pagesActive TransportRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Energy: Chapter 5 - The Working CellDocument26 pagesEnergy: Chapter 5 - The Working CellJohn Paul Coronel SinuhinNo ratings yet
- Biophysics AnswersDocument8 pagesBiophysics AnswersramNo ratings yet
- Bio PhysicsDocument8 pagesBio PhysicsSabika HassanNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Membranes FinalDocument77 pagesTransport Across Membranes FinalLorraine Eve Abila100% (1)
- Active Vesicular TransportDocument14 pagesActive Vesicular Transportsarah abarcaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Bio1 ReviewerRhea SuarezNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument19 pagesEnergy TransformationRicardo ErioNo ratings yet
- ASTATINE Group 4 - Facilitated and Active Membrane TransportDocument25 pagesASTATINE Group 4 - Facilitated and Active Membrane TransportjohndominicmmalubagoNo ratings yet
- Government College University Faisalabad Department of Bio-Information and BiotechnologyDocument5 pagesGovernment College University Faisalabad Department of Bio-Information and BiotechnologyShahzad Ahmad NomanNo ratings yet
- Ion Transporter: Jump To Navigationjump To Search Transmembrane Protein Biological MembraneDocument5 pagesIon Transporter: Jump To Navigationjump To Search Transmembrane Protein Biological MembraneHafiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document1 pageHomework 1Jeric CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Flow of Energy Part 1Document18 pagesFlow of Energy Part 1nancie8No ratings yet
- ActiveDocument1 pageActiveapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument31 pagesActive TransportKaran BhagdevNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: By: Linanda Islamiati N I M P 1 7 3 3 4 1 1 8 0 2 5Document9 pagesMetabolism: By: Linanda Islamiati N I M P 1 7 3 3 4 1 1 8 0 2 5Linanda IslamiatiNo ratings yet
- Mastering Biology Section 94 FlashcardsDocument8 pagesMastering Biology Section 94 Flashcardsyoongkang0122No ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet