Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation 2
New Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation 2
Uploaded by
jaypasco790 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesMitosis is the process of cell division that results in two daughter cells. It occurs in the meristematic tissues found at the tips of roots and stems, which are responsible for plant growth. During mitosis, the genetic material in the nucleus duplicates and the copies are separated into two identical nuclei as the parent cell divides. The process involves several phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase - where the chromosomes condense, align, separate, and the new nuclei form. In plant cells, a cell plate forms across the center instead of a cleavage furrow to separate the daughter cells due to the rigid cell wall.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMitosis is the process of cell division that results in two daughter cells. It occurs in the meristematic tissues found at the tips of roots and stems, which are responsible for plant growth. During mitosis, the genetic material in the nucleus duplicates and the copies are separated into two identical nuclei as the parent cell divides. The process involves several phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase - where the chromosomes condense, align, separate, and the new nuclei form. In plant cells, a cell plate forms across the center instead of a cleavage furrow to separate the daughter cells due to the rigid cell wall.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation 2
New Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation 2
Uploaded by
jaypasco79Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two daughter cells. It occurs in the meristematic tissues found at the tips of roots and stems, which are responsible for plant growth. During mitosis, the genetic material in the nucleus duplicates and the copies are separated into two identical nuclei as the parent cell divides. The process involves several phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase - where the chromosomes condense, align, separate, and the new nuclei form. In plant cells, a cell plate forms across the center instead of a cleavage furrow to separate the daughter cells due to the rigid cell wall.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
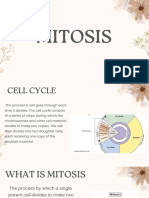
MITOSIS
What is mitosis in plants?
• Mitosis is the process that results in the formation of
new cells.
• Cells undergo mitosis, therefore, as part of plant
growth.
How mitosis occur in
-plants?
Mitosis in plants happens in the meristems of the plant
that are located at the tip of the stems and roots.
- These two areas are responsible to produce all the cells
the plants needs to grow.
MITOSIS
- Is the process in which a eukaryotic cell nucleus splits in
two, followed by division of the parent cell into two
daughter cells.
- The word “mitosis” means “threads”, and it refers to the
threadlike appearance of Chromosomes as the cell
prepares to divide.
PROPHASE
- Is the first stage of the M
phase.
- In prophase the chromatin
begins to coil and condense to
form chromosomes.
- They are coiling because they
are preparing to move around.
METAPHASE
- In metaphase, the spindle has
captured all the chromosomes
and lined them up at the
middle of the cell, ready to
divide.
- All the chromosomes align at
the metaphase plate.
ANAPHASE
- Anaphase is the third phase of
mitosis, the process that separates
the duplicated genetic material
carried in the nucleus of a parent
cell into two identical daughter
cells.
TELOPHASE
- Telophase in plant cell is different than that
in animal cell. Because of the rigid cell wall,
the plant cell can not form as a cleavage
furrow.
- Instead a new cell wall { known as the cell
plate } begins to form across the equator.
- As in the animal cell, the chromosomes
may be visible at this stage or the new
nucleus may be forming and thus may be
visible.
5th last cytokinesis
- Cytokinesis is accomplished through the formation of
cell plate.
- A collection of microtubules transport vesicles
containing cell wall materials to the center of the cell .
- There the vesicles fuse together, creating a flat,
membrane-enclosed disc-the cell plate.
THANK YOU!
You might also like
- Mitosis Is A Process Where A Single Cell Divides Into Two Identical Daughter Cells (Cell Division)Document10 pagesMitosis Is A Process Where A Single Cell Divides Into Two Identical Daughter Cells (Cell Division)Holly Mc Kenzie Layson DalmanNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument67 pagesCell DivisionRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 5Document2 pagesLab Exercise 5Daks ZabateNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument4 pagesMitosisJeanelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument18 pagesMITOSISEdryan LambiquitNo ratings yet
- Mitosis - Cell MembraneDocument12 pagesMitosis - Cell MembraneJeanelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument17 pagesBiologyMuskan ShreeNo ratings yet
- Meosis 1Document12 pagesMeosis 1lyraiglesiajaneNo ratings yet
- BIO T4 KSSM Chapter 6 - DLPDocument62 pagesBIO T4 KSSM Chapter 6 - DLPcikguana79No ratings yet
- Mitosis Gcse BiologyDocument1 pageMitosis Gcse BiologycrainerNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument5 pagesMITOSISdeepaNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument12 pagesMITOSISLarissa PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument13 pagesMitosis and MeiosisS3 Oxibillo, Gabriel Dominic C.No ratings yet
- Genbio1 MitosisDocument11 pagesGenbio1 MitosisJessie Katrisha TayagNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: Objectiveskaran79No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument10 pagesMitosisSoulseekerNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISION-MitosisDocument28 pagesCELL DIVISION-MitosisAVINASH VARMANo ratings yet
- Mitosis: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatDocument28 pagesMitosis: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatAkiela JohnsonNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument27 pagesMitosisS3 Oxibillo, Gabriel Dominic C.No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument17 pagesCell DivisionGenevieve GanubNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisGwen GwynethNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument3 pagesMitosisSabina MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument28 pagesMitosis and MeiosisPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division:-: Presented By:-Priyanjali Saini Nursing Tutor H.C.N.SDocument28 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division:-: Presented By:-Priyanjali Saini Nursing Tutor H.C.N.SPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument4 pagesMitosisCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument28 pagesMITOSIShariz mikhaelNo ratings yet
- GROWTHDocument9 pagesGROWTHVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument12 pagesCell CycleRusselNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesANnur RAshidNo ratings yet
- Sem3 - Lab 5 - Phases of MitosisDocument4 pagesSem3 - Lab 5 - Phases of MitosisUnknownNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument3 pagesMitosissmooky 2064No ratings yet
- Cell Division - Key PointsDocument10 pagesCell Division - Key PointssivarajeshwarNo ratings yet
- Folio Kerja Kursus Biology SPMDocument29 pagesFolio Kerja Kursus Biology SPMzam_ir100% (2)
- Cell DivisionDocument52 pagesCell DivisionRamachandran Ram100% (1)
- CN 6 BioDocument2 pagesCN 6 BioJanna PaduaNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesThe Cell CycleAngelooNo ratings yet
- Sem3 - Lab 5 - Phases of MitosisDocument4 pagesSem3 - Lab 5 - Phases of MitosisUnknownNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - MitosisDocument5 pagesLesson 7 - MitosisReuben Al'jaldiNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Process ProjectDocument2 pagesMitosis Process Projectapi-242679288No ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument13 pagesMitosis and Meiosis420192420192No ratings yet
- Army Public School Gopalpur: Class - 11 Science Subject - BiologyDocument6 pagesArmy Public School Gopalpur: Class - 11 Science Subject - BiologyAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISION - Mitosis PDFDocument3 pagesCELL DIVISION - Mitosis PDFMohnish MNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument63 pagesCell CycleLovely PeñaredondoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2Document48 pagesGrade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2SHAIRA LYN CUMILANGNo ratings yet
- GEn. Bio Week 4 and Week 5Document3 pagesGEn. Bio Week 4 and Week 5VadePlaysCodNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument21 pagesBiotechnology NotesRommel BauzaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle w4Document49 pagesCell Cycle w4Janika RelenteNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument6 pagesCell Division MitosisIroldNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument6 pagesCell Division MitosisIroldNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument19 pagesMITOSISFranshel CaldozaNo ratings yet
- Inter Phase Is Followed by Mitosis. It Is The Nuclear Division Involves The Separation of Sister Chromatids. This Involves Four Stages NamelyDocument16 pagesInter Phase Is Followed by Mitosis. It Is The Nuclear Division Involves The Separation of Sister Chromatids. This Involves Four Stages NamelyKumaran JothiramNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAngelo Gomez BadatoNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisKiMii EstebanNo ratings yet
- Stages of Meiosis - 20240108 - 205848 - 0000Document30 pagesStages of Meiosis - 20240108 - 205848 - 0000Oviya.RNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Unit Presentation - 6554Document30 pagesCell Division Unit Presentation - 6554M Noaman AkbarNo ratings yet
- Interphase: Cell Cycle Nucleus Daughter CellsDocument4 pagesInterphase: Cell Cycle Nucleus Daughter CellsKàtrįńá Jøÿ ÅgùśtïńNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System of FishDocument14 pagesEndocrine System of Fishjaypasco79No ratings yet
- Janeths Thesis ProposalDocument24 pagesJaneths Thesis Proposaljaypasco79No ratings yet
- Chaetognaths, Echinoderms, and HemichordatesDocument21 pagesChaetognaths, Echinoderms, and Hemichordatesjaypasco79No ratings yet
- Immunesystemoffish Pptx-AutosavedDocument19 pagesImmunesystemoffish Pptx-Autosavedjaypasco79No ratings yet
- New DOC DocumentDocument1 pageNew DOC Documentjaypasco79No ratings yet
- Animal Behavior & Animal Ecological RelationshipsDocument4 pagesAnimal Behavior & Animal Ecological Relationshipsjaypasco79No ratings yet
- Ly Dear Detal 2004Document11 pagesLy Dear Detal 2004jaypasco79No ratings yet
- The Remarkable Diversity of FishDocument45 pagesThe Remarkable Diversity of Fishjaypasco79No ratings yet
- Sponges and PlacozoansDocument55 pagesSponges and Placozoansjaypasco79No ratings yet