Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Charger Introduction
Uploaded by
Alok ChaudharyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Charger Introduction
Uploaded by
Alok ChaudharyCopyright:
Available Formats
CHARGER WORK PRINCIPLE & TEST
Prepared By:-
Ajeet (Dep-SQM)
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 1
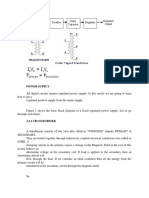
Working Principal
A mobile charger works on the simple principle of
conversion of AC to DC and Voltage Step down &
regulation work by rectifying and filtering the
electricity with the help of components.
Using the 4 key components which is the transformer,
rectifier, filter & regulator-
Rectifier
Transformer
Filter
Regulator IC
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 2
Working Principal
Rectifier converts the
Rectifier transformed AC signal
into a pulsating DC.
The Transformer steps
Transformer down voltage to
desirable voltage.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 3
Working Principal
The Filter eliminates the
fluctuations in order to produce
Filter a relative ripple free DC voltage.
A regulator is an important
device when it comes to
Regulator
power electronics as it controls
the power output.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 4
Working Principal
Rectifier Filter Transformer Regulator Load
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 5
Working Principal
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 6
Basic components of charger
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 7
Basic components of charger
1.RESISTOR
The resistor is an electronic component that has electrical
friction. This friction opposes the flow of electrons and thus
reduces the voltage placed on other electronic components
by restricting the amount of current that can pass through it.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 8
Basic components of charger
Resistor as a Fuse Resistor as a Load
An electrical safety device consisting of or including a wire In any electrical circuit we can calculate the load
or strip of fusible metal that melts and interrupts the circuit voltage on a resistor by putting parallel where we
when the voltage exceeds.
want.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS
Basic components of charger
2.Rectifier
A rectifier is an electronic device that converts an alternating current into a direct current by using one or more P-N
junction diodes.
A diode allows electric current to flow in one direction only. Types of rectifier defined as below.
A. Half wave rectifier
A half wave rectifier is defined as a type of rectifier that allows only one-half cycle of an AC voltage waveform to
pass while blocking the other half cycle .
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 10
Basic components of charger
B. Full wave rectifier
A full wave rectifier is defined as a rectifier that converts the complete cycle of alternating current into pulsating DC.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 11
Basic components of charger
B. Bridge wave rectifier
We can define bridge rectifiers as a type of full-wave rectifier that uses four or more diodes in a bridge circuit
configuration to efficiently convert alternating (AC) current to a direct (DC) current.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 12
Basic components of charger
3.Filter
A filter is a circuit arrangement that is capable of passing certain frequencies while attenuating the rest of the
frequencies. Thus, a filter circuit can pass the desired important frequencies from signals .
Low-pass π filter
High-pass T filter
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 13
Basic components of charger
4.Capacitor
A capacitor stores electrical energy when charged by a source & regulate the voltage.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 14
Basic components of charger
5.Inductor
The Inductor prevents current from making any sudden changes by producing large opposing voltages. It regulate to
current in charger.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 15
Basic components of charger
6.IC (integrated circuit) as Voltage Regulator
An integrated circuit is a set of electronic circuits of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of transistors
and other electronic components are integrated together on the chip. It is used regulate the voltage.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 16
Basic components of charger
7.Transformer
Transformer is DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit or electromechanical device that converts a source of
direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another. It is a device used in the power transmission of electric energy.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 17
Basic components of charger
7. Transistor (MOSFET)
Transistor is used mainly for amplification and also to provide constant charging
current. The transformer steps the 230 V down to something close to 5 V while
reducing the current up to (say) 300 to 500 mA. This is then rectified to a pulsating
DC at the frequency of the AC source.
8. PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly)
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly and relates to the component
placement onto the bare board or PCB. Multiple electronic components are
assembled to the circuit board and soldered into position.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 18
Basic key point for charger manufacturing
• Aging- Aging required with normal voltage 220Volt & High voltage to control the SMT components failure after
assembly of charger, it controlled the component failure. It controlled to reach NG charger at customer end.
• Ultrasonic welding- During assembly we should be do frequent drop test to control the welding cracking of
charger.
• Functional test- As per charger specification, output current & voltage should be same as charger
specification.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 19
The basic electrical performance requirements
1. Charger input voltage range and frequency
Input voltage range: 100V-240V;
Frequency: 50-60Hz:
2. Charger output characteristics
Including output voltage, current and accuracy, etc., generally represented by the output inflection point diagram.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 20
The basic electrical performance requirements of
3.Ripple
The ripple is due to the fact that after rectification and filtering, there are some AC components in the DC stable value.
This AC component superimposed on the DC stable value is called ripple. At present, the ripple of the charger is
generally ≤300mV for feature phones, and ≤200mV for smartphones.
4. Short circuit protection
It means that the charger has an automatic short-circuit protection function. When the output terminal is short-circuited,
charger will be in hiccup mode(sense circuit) or low-current output. When the fault is eliminated, the charger
components cannot be damaged, and the work should be normal function.
5. Overcurrent protection
When the current exceeds the maximum value, it plays a protective role for the charger. Generally, the overcurrent point
of the charger is set at 1.1-1.5 times of the rated current.
6. Efficiency
Efficiency = output power/input power * 100%.
7. temperature rise
It refers to the temperature difference between the surface temperature of the charger shell and the test room
temperature. Generally, the temperature rise of the charger is 40°C MAX
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 21
The basic electrical performance requirements
8. Input leakage current
After the charger is connected to the main supply, there is a small voltage between the USB iron shell and the ground,
which is obtained by the formula: voltage/10000, and the general requirement is ≤0.25mA.
9. Backflow current
It refers to adding 5V DC voltage to the output port of the charger, and the current through the charger should be less
than 5mA as observed by the series ammeter.
10. Insulation resistance
Insulation resistance is the most basic insulation index of electrical equipment and electrical circuits. The insulation
resistance of the charger refers to the insulation resistance between the input and the output.
11. High pressure
The highest voltage that the charger can withstand between the primary and secondary. The general product is 3000V,
the time is 60S, and the leakage current is 5mA.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 22
Test Items
It is done when launch any new model with
the device it will be packed. To check the
fast charging and other key function of
Match With charger like charging time etc.
Device
It is appearance inspection of Cosmetic Functional Test With
Loader
Loader is a device which can
show output voltage, current
charger with 30cm distance & 800-
1200 lux light.
and Visual and power of charger.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 23
Test Items
1.High
temperature To determine the effect of time ,
8. Constant storage test humidity and temperature, under
temperature 2.Low storage conditions, for thermally
and humidity temperature activated failure mechanisms of
test storage test charger.
• High temperature storage test
• Low temperature storage test
• Temperature impact test
it used to determine the 3.Temperature • High temperature Operation
corrosive resistance of
charger AC pins with
7. Salt spray
test Environmental impact test •
•
Low temperature Operation
Temperature rise test
environment conditions.
test • Constant temperature
and humidity test
4. High
6.Temperature
temperature
rise test 5.Low
Operation
temperature
Operation
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 24
Test Items
The purpose of vibration tests is to
evaluate the effect caused on component
parts by vibration in a specified frequency
range.
Wire interface lifting & body 9.Interface
tensile used to test the life of lifting test 1.Vibration
wire or USB cable. Tumble test and drop test are critical to
& Wire Test
evaluate a product ability to survive the
body tensile 2.Tumble test many bumps and scrapes, it will
test
experience in its life cycle with an end-
It is a test that applies high user.
voltage to assets to 8. HIPOT Test
determine the adequacy of (High Potential
the electrical insulation to test)
withstand voltage transients
and make sure the insulation
Key 3.Drop test
is not marginal performance
Flame test used to test the
7. Flame
test
test
charger housing material.
4. USB plug Bend & sway test used to test
and pull test the life of wire or USB cable.
It is the process of testing a device's
resistance to electrostatic discharge. 6.Esd test
5. Surge test
ESD occurs when two electrically
charged objects contact each other, are The surge test finds shorts and
involved in an electrical short or suffer a insulation weaknesses in coils, windings
dielectric breakdown, resulting in a and transformers
sudden flow of electricity.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 25
In High voltage test applied more than
Test Items
450V for different timing. Its purpose to
know the high voltage sustainability in
charger at user end.
1.Constant high
Tumble test basically used to
During rainy weather customer voltage till dead
control the handling failure in
used charger so we put the the charger at user end, we
2.Tumble test till
charger with 90% humidity for 3- 7.High checked it to know the maximum
dead
4 hours & test the charger humidity test sustainability till fail. We test it
function to know the failure till dead double or more cycles till dead.
sustainability.
TTD Test
(Test till dead) drop test also used to
control the handling failure
6.High 3.Drop test in the charger at user end,
temperature till dead we checked it to know the
In summer season temperature with load test maximum dropping height
reached more than 45˚c in India till dead sustainability till fail.
& customer use charger with
this temperature so we tested 4.Voltage
the charger with load in 70˚c fluctuation till
temperature to know the dead In rural area have AC supply
charger sustainability with this fluctuation in India so we tested
condition it to know the failure at
maximum voltage fluctuation in
charger.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 26
Certification & Marking
Class 2: These appliances are double insulated, have no
grounding requirements for it. This type of electrical
appliances has a high degree of safety and can be used
for appliances that come into contact with human skin.
Indoor Use: This icon indicates that the product is
intended for indoor use.
WEEE: WEEE stands for Waste Electrical and Electronic
Equipment. It is a directive in the European Union that designates
safe and responsible collection, recycling and recovery procedures
for all types of electronic waste.
BIS Logo: Considering how harmful a charger can be for the final
consumer, BIS standards have been introduced to ensure
conformance with Indian safety standards.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 27
Common failure of Charger
1-Fuse burn
It mainly caused by the high AC voltage applied in charger.
2-Input capacitor leakage
It mainly caused by the high AC voltage applied in charger more
than capacitor specifictions.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 28
Common failure of Charger
3-IC burn
It mainly caused by the high AC voltage applied in charger.
4-Water damage
It mainly caused by some liquid inserted into charger &
component got short by liquid.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 29
Common failure of Charger
5-BD Functional fail
when the fuse got burn by high voltage & high voltage applied in
Bridge rectifier then rectifier function got fail.
6-Charger intermittent problem
It mainly caused micro 5pins bend or wire ng connections.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 30
Common failure of Charger
7-PCBA Track damage
it mainly caused by dropping of charger from more height.
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS 31
Thank You !
www.transsion.com
Copyright © TRANSSION HOLDINGS
You might also like
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- Report On Power SupplyDocument14 pagesReport On Power SupplyBhavesh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 02A Lesson Proper For Week 7Document9 pages02A Lesson Proper For Week 7Maxela CastroNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Direction Control Using Power TriacDocument7 pagesDC Motor Direction Control Using Power TriacAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument3 pagesPower SupplyJane AlamoNo ratings yet
- Lic Report 14 - 4 Final2Document12 pagesLic Report 14 - 4 Final2Harshvardhan MishraNo ratings yet
- Electric CalDocument20 pagesElectric CalRisky RiyanshNo ratings yet
- Substation EquipmentsDocument106 pagesSubstation EquipmentsChetansharma2048100% (1)
- BS en Iso 16474-3-2013Document28 pagesBS en Iso 16474-3-2013AlineMeirelesNo ratings yet
- Q2 M2 Octet-Rule-And-Lewis-StructureDocument18 pagesQ2 M2 Octet-Rule-And-Lewis-StructureElysha Mae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Adh-2000 Manual de OpracionDocument48 pagesAdh-2000 Manual de OpracionCarlos MenaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Code Lock Using One TransistorDocument18 pagesElectronics Code Lock Using One TransistorAnonymous TvXDUWDaol50% (2)
- Self Switching Power SupplyDocument20 pagesSelf Switching Power SupplyPutra Purechk TokyoNo ratings yet
- Uppcl Training ReportDocument18 pagesUppcl Training Reportnidhi100% (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Design of RDF Refuse Fired Boilers B&W - BR1657 - !998Document8 pagesDesign of RDF Refuse Fired Boilers B&W - BR1657 - !998pawanumarji1No ratings yet
- Nonlinear PDEs With Applications PDFDocument486 pagesNonlinear PDEs With Applications PDFAidan Holwerda100% (1)
- Sinha Power Plant QuestionDocument14 pagesSinha Power Plant QuestionRaihanNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 Wind0.02Document25 pagesAss 2 Wind0.02Šämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDC Power Supplyweaam raedNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDC Power Supplyweaam raedNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 WindDocument10 pagesAss 2 WindŠämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Eng NaderDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- Power Supply 1Document9 pagesPower Supply 1mohammed almaswaryNo ratings yet
- Security Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1Document30 pagesSecurity Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1DebashishParida100% (1)
- 1.power Electronics Circuits Lecture 01 - IntroductionDocument24 pages1.power Electronics Circuits Lecture 01 - Introductionandreasmagaka11No ratings yet
- Pneumatic Based Punching MachineDocument45 pagesPneumatic Based Punching Machineraja100% (3)
- KMT#4Document5 pagesKMT#4RomanHerreraNo ratings yet
- Kenji RDocument9 pagesKenji RKenji R. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Electronics Question Bank Class 11Document2 pagesElectronics Question Bank Class 11Parth KakayeNo ratings yet
- Load Inverter Solar Panel: Chapter ThreeDocument13 pagesLoad Inverter Solar Panel: Chapter ThreeMakesh MäKzNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of DC Power SupplyDocument2 pagesBlock Diagram of DC Power Supplybess.sangabriel17No ratings yet
- Stator: Excitation Transformers Are Use To Magnetize Generators andDocument8 pagesStator: Excitation Transformers Are Use To Magnetize Generators andMian UsmanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Sub StationDocument14 pagesElectrical Sub StationDAYA LAHARE100% (1)
- Industrial Training at Uppcl: 132 KV, Naini Complex Allahabad BY Amit Kumar YadavDocument12 pagesIndustrial Training at Uppcl: 132 KV, Naini Complex Allahabad BY Amit Kumar YadavBhagwati PrasadNo ratings yet
- Stator: Excitation Transformers Are Use To Magnetize Generators andDocument7 pagesStator: Excitation Transformers Are Use To Magnetize Generators andMian UsmanNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Protection in DC Low Voltage System: Matrix Institute of Technology, Eee, Cheekatimamidi 1Document64 pagesShort Circuit Protection in DC Low Voltage System: Matrix Institute of Technology, Eee, Cheekatimamidi 1Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Inverters and Applications Requirements of The Final ReportDocument5 pagesInverters and Applications Requirements of The Final ReportHuỳnh BảoNo ratings yet
- Power SuppliesDocument4 pagesPower SuppliesShaheer TariqNo ratings yet
- Rotor: Excitation Transformers Are Use To Magnetize Generators andDocument8 pagesRotor: Excitation Transformers Are Use To Magnetize Generators andMian UsmanNo ratings yet
- BETA 1313 (Assignment)Document3 pagesBETA 1313 (Assignment)Sepi Itu IndahNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument2 pagesDC Regulated Power Supplysean ballocanagNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document2 pagesExercise 3mike ocayNo ratings yet
- Learner's Module in Technology and Livelihood Education 10 Electronics Product Assembly and Servicing (EPAS)Document8 pagesLearner's Module in Technology and Livelihood Education 10 Electronics Product Assembly and Servicing (EPAS)Chard VascoNo ratings yet
- Final Naeem WaqasDocument14 pagesFinal Naeem WaqasNaeem AliNo ratings yet
- Automatic Phase ChangerDocument25 pagesAutomatic Phase ChangerChellakaruppasamyNo ratings yet
- Slip Ring: Ring Can Be Used in Any Electromechanical System That Requires RotationDocument8 pagesSlip Ring: Ring Can Be Used in Any Electromechanical System That Requires RotationMian UsmanNo ratings yet
- Project PaperDocument8 pagesProject PaperSuRaJ BroNo ratings yet
- Project Load Protector Final 22Document42 pagesProject Load Protector Final 22virendkumarNo ratings yet
- Single PhasingDocument41 pagesSingle PhasingdiljithNo ratings yet
- For Training - June 2015Document59 pagesFor Training - June 2015Lionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 (Power Supply) : Name: Amelinda Azalia Savira Class: EK-3ADocument6 pagesTopic 6 (Power Supply) : Name: Amelinda Azalia Savira Class: EK-3Avira amelindaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Instrument TransformersDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Instrument TransformersAbdul'Azeez Stanley IgweNo ratings yet
- 26 Most Asked Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers With PDF CompressedDocument7 pages26 Most Asked Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers With PDF CompressedAishwarya0% (1)
- Z-Source Inverter For UPS Application: R.Senthilkumar, R.Bharanikumar, Jovitha JeromDocument5 pagesZ-Source Inverter For UPS Application: R.Senthilkumar, R.Bharanikumar, Jovitha Jeromnikhil naniNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection-2Document49 pagesPower System Protection-2IsaacNo ratings yet
- List of ComponentsDocument13 pagesList of ComponentsBenita AgbagwaraNo ratings yet
- BSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) : A Presentation OnDocument25 pagesBSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) : A Presentation OnMahesh Kumar NigamNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1.1 The Principle of WindmillDocument22 pagesChapter-1: 1.1.1 The Principle of WindmillVijay BavikattiNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument21 pagesPower SupplyAkashi SeijuroNo ratings yet
- PSCO CHapter 1Document70 pagesPSCO CHapter 1tebelayhabitamu12No ratings yet
- IE Mod 01 PowerSupplyDocument25 pagesIE Mod 01 PowerSupplyRy AnNo ratings yet
- CSE Stream Case Study and Innovative - 3 IA PDFDocument3 pagesCSE Stream Case Study and Innovative - 3 IA PDFarindam samantaNo ratings yet
- P7 - H20 094 Kaeuflin PaperDocument8 pagesP7 - H20 094 Kaeuflin PaperRahul ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 4 Important Methods of Ground Resistance TestingDocument5 pages4 Important Methods of Ground Resistance TestingAbdul Mohid SheikhNo ratings yet
- Light Energy Sound EnergyDocument1 pageLight Energy Sound EnergykenNo ratings yet
- Electrochlorination System Equipment Data Sheet: Project C77-SKE-PCO File Nr. C77-E-406Document3 pagesElectrochlorination System Equipment Data Sheet: Project C77-SKE-PCO File Nr. C77-E-406Ediquio GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Zbd30kce TFDDocument6 pagesZbd30kce TFDarpac tecnologiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes-1 - Magnetic & DielectricsDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Notes-1 - Magnetic & Dielectricsaman bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Vx-8xx3-xxx-5-x Series VB-8xx3 SeriesDocument36 pagesVx-8xx3-xxx-5-x Series VB-8xx3 SeriesNATHANNo ratings yet
- Sudah, 2002 - Bin Blender Case StudyDocument12 pagesSudah, 2002 - Bin Blender Case StudyDayane VeríssimoNo ratings yet
- Doesthe Sun Transfer Heat Science Experiment Adobe ReaderDocument3 pagesDoesthe Sun Transfer Heat Science Experiment Adobe ReaderSurbhi MainiNo ratings yet
- Reading Materials - Week4 1Document34 pagesReading Materials - Week4 1ivy loraine enriquezNo ratings yet
- F 434 - 93 R97 - Rjqznc05m1i5nwDocument3 pagesF 434 - 93 R97 - Rjqznc05m1i5nwMorched TounsiNo ratings yet
- JSPM 5200 Instructional ManualDocument5 pagesJSPM 5200 Instructional Manualmajid khan yousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Week6 Unsymmetricalfault 160318151132Document57 pagesWeek6 Unsymmetricalfault 160318151132Hardik MachNo ratings yet
- Flat Ride Problems and Solutions in VehicleDocument8 pagesFlat Ride Problems and Solutions in Vehiclelakshmanakumarr@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NumericalsDocument36 pagesChapter 2 NumericalsAASHISH KATUWALNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Engineering Technology in A C & I R: FCD 20603 (Heating and Cooling Load) TitleDocument7 pagesBachelor of Engineering Technology in A C & I R: FCD 20603 (Heating and Cooling Load) TitleYuzzyne ZainolNo ratings yet
- SSC Je Ce 2016 1Document57 pagesSSC Je Ce 2016 1ezradural99No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 v1Document4 pagesTutorial 3 v1ir_yusriNo ratings yet
- Philippines My Beloved (Rough Translation by Lara)Document4 pagesPhilippines My Beloved (Rough Translation by Lara)ARLENE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Force Analysis: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument48 pagesForce Analysis: Department of Mechanical EngineeringRamaswamy SubbiahNo ratings yet
- Compaction of Soils 2013Document9 pagesCompaction of Soils 2013Nature NatureNo ratings yet
- CRTAG - CRTAG-1 - Product ReportDocument2 pagesCRTAG - CRTAG-1 - Product ReportMohammed EmamNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet 2 Bernoulli's EquationDocument5 pagesLab Sheet 2 Bernoulli's EquationEmmanuel EasterNo ratings yet
- Creep and Shrinkage - KhouryDocument12 pagesCreep and Shrinkage - KhouryMouhaNo ratings yet