0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views34 pages04 - Center of Gravity
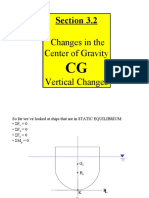
1) The center of gravity (CG) of an object is the point where its entire weight is considered to act. It can be calculated as the sum of the moments of individual masses about an axis divided by the total mass.
2) The vertical center of gravity (VCG) or KG is the height of the CG above the keel, while the longitudinal center of gravity (LCG) is the distance of the CG forward or aft of amidships.
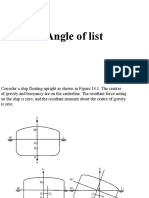
3) Adding or removing mass, or moving existing mass on a ship, causes the ship's CG to shift in the direction of the added/removed/moved mass by an amount proportional to the mass and distance of movement divided by the ship's
Uploaded by
Goldy26Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views34 pages04 - Center of Gravity
1) The center of gravity (CG) of an object is the point where its entire weight is considered to act. It can be calculated as the sum of the moments of individual masses about an axis divided by the total mass.
2) The vertical center of gravity (VCG) or KG is the height of the CG above the keel, while the longitudinal center of gravity (LCG) is the distance of the CG forward or aft of amidships.
3) Adding or removing mass, or moving existing mass on a ship, causes the ship's CG to shift in the direction of the added/removed/moved mass by an amount proportional to the mass and distance of movement divided by the ship's
Uploaded by
Goldy26Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd