Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical and Chemical Digestion
Uploaded by
snehashreemohanty390 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 pagesMechanical and Chemical Digestion
Uploaded by
snehashreemohanty39Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
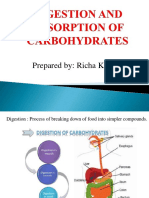
Mechanical and chemical digestion
Digestion is defined as the process by
which food is broken down into simple
chemical substances with the help of
enzymes , that can be absorbed and used
as nutrients by the body.
Digestive process is accomplished by
mechanical and enzymatic break down of
food into simple chemical compounds.
CARBOHYDRATES:-
Human diet contains 3 types of
carbohydrates.
1. Polysaccharides: Glycogen, amylose
and amylopectin.
2. Disaccharides:Sucrose(Glu + Fructose)
Lactose(Glu + Galsctose)
3. Monosacharides: Glucose and Fructose.
Cellulose is plant origin.
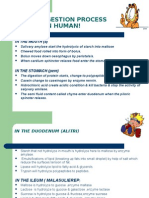
Digestion of carbohydrate in Mouth:
Mechanical Digestion:Chewing and mastication.
Chemical Digestion: Most of the carbohydrates
are in polysaccharide form.
Starch ---------Maltose + Dextrin.
[ptyalin/ salivary amylase]
Digestion of carbohydrate in Stomach:
Mechanical Digestion: Peristalsis
{It is alternative contraction and relaxation of
circular and longitudinal muscle that produces
the wave of contraction due to which the food
passes along the lumen of alimentary canal }
Chemical Digestion: Food may remain in
the fundus without becoming mixed with gastric
juice. During This period digestion by salivary
amylase from the salivary gland may continue in
the stomach for as long as 1 hour.
(stomach has no direct involvement in digestion of carbohydrate)
In Small Intestine:
The activity of salivary amylase is destroyed
as it come in contact with Acidic PH of stomach.
Duodenum is the initial part of the small
intestine. It receives the secretion from pancreas
and liver.
Amylolytic enzymes in the small intestine are
derived from pancreatic juice and sucus entericus.
The pancreatic amylase act on glycogen and
starch [Maltase,Sucrase,Lactase,Dextrinase]
Starch & Glycogen + Amylase ----Maltose &
dextrin.
DIGESTION BY INTESTINAL JUICES;
The following changes occurs due to
the action of enzymes of intestinal juice
(sucus entericus)
Lactose—Lactase- Glucose+Galactose.
Sucrose---SucraseGlucose + Fructose
Maltose---MaltaseGlucose + Glucose
Dextrin----Dextrinase-Glucose.
DIGESTION OF PROTEIN.
Food stuffs containing protein are
Meat, Fish, Egg, and milk, Wheat, Soya
bean ,Oats and various types of pulses
Enzymes responsible for protein
digestion are called proteolytic enzymes.
No digestion of protein occurs in the
buccal cavity due to lack of proteolytic
enzymes in Saliva.
Digestion in Stomach;-
presence of food in stomach stimulates the
secretion of gastric juice by the cells of
mucosa layer. The cells like mucous
secreting neck cells , Oxyntic cells and
peptic cells/chief cells/parietal cells
secretes mucous, HCL and various
enzymes respectively. They act on various
kinds of protein.
Pepsinogen----HCL- Active pepsin.
Prorennin---HCL--Active Rennin
Protein—Pepsin-Proteoses+Peptones+A.A
Caseinogen(soluble milk protein)-----
Rennin & Ca--- Ca paracaseinate(Curd)
Pepsin is most effective in the acidic
environment of the stomach. Pepsin is
secreted in its inactive form called
pepsinogen.
DIGESTION IN SMALL INTESTINE;
Chyme entering the small intestine
contains partially digested carbohydrate,
protein, and lipids. The completion of the
digestion of carbohydrate, protein and lipid
is aided by pancreatic juice, bile juice and
intestinal juice in the small intestine.
Pancreatic juice contains two
nucleases like Ribonucleases, and
deoxyribonucleases.
Trypsinogen---Enterokinase- Active trypsin
Chymotrypsinogen---Trypsin- ActiveChymotrypsin
Peptone, Proteoses, peptones--- Trypsin,
chymotrypsin- Polypeptide + Aminoacids.
DIGESTION OF FAT;
Lipids are mostly consumed in the
form of neutral fats, which are also known
as triglycerides, each molecule is composed
of a glycerol nucleus and three fatty acids .
Dietary fats are classified into Saturated and
unsaturated fats.
Mouth has no role in the digestion of
fat. In the stomach the enzyme lipase split
triglycerides.
Lipids----Gastric lipase- F.Acids + Glycerol
Chyme entering the small intestine
contains partially digested carbohydrate,
protein, fat .Digestion of all food stuffs
completed in the small intestine in the
presence of pancreatic juice , bile and
intestinal juice.
The most important enzyme for
digestion of the triglyceride is pancreatic
lipase, present in the pancreatic secreted
by the pancreas in to the small intestine.
Triglycerides are broken down by
pancreatic lipase into fatty acids and
monoglycerides.
You might also like
- Small Intestine and PancreasDocument52 pagesSmall Intestine and PancreasLutfi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition Chapt 1 2022Document59 pagesBasic Nutrition Chapt 1 2022a.joshuaNo ratings yet
- Digestion & AbsorptionDocument18 pagesDigestion & AbsorptionDoghouseNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument10 pagesBiochemWaseem Abbas ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates, Proteins and FatsDocument45 pagesDigestive System: Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates, Proteins and FatshiNo ratings yet
- Unit-V: Animal Physiology. 2Document5 pagesUnit-V: Animal Physiology. 2Sachikanta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument33 pagesDigestive SystemSatyabrat DuttaNo ratings yet
- Digestion of Starch in Human Body 1Document12 pagesDigestion of Starch in Human Body 1rbkavin10No ratings yet
- Digestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionDocument26 pagesDigestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionTemz HlubyNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Richa KhatiwadaDocument10 pagesPrepared By: Richa KhatiwadaSabiha TabassumNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewDocument117 pagesGastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewFatima Syed100% (3)
- The Digestive System Final 1Document34 pagesThe Digestive System Final 1Jam DabalosNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of CarbohydratesDocument28 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Carbohydratesshakila786No ratings yet
- Digestive GlandDocument22 pagesDigestive GlandMalinus TorquatusNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption - 101328Document10 pagesDigestion and Absorption - 101328Emmanuel IshiomaNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Document41 pagesDigestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Divya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Digestive and Absorption Process of Dietary-Sunarti-Biochemistry (2015)Document36 pagesBiochemical Digestive and Absorption Process of Dietary-Sunarti-Biochemistry (2015)nayanikatesalonikaNo ratings yet
- Food DigestionDocument36 pagesFood Digestionthiruchelvam1No ratings yet
- 1.biochemistry of Digestive SystemDocument55 pages1.biochemistry of Digestive SystemNor Izhharuddin Zainy60% (10)
- Salivary SecretionDocument10 pagesSalivary SecretionMahadi Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- Really Final Discussion of Group 6Document16 pagesReally Final Discussion of Group 6Nicole Hershley RequieroNo ratings yet
- Assimilation and Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesAssimilation and Digestive Systemridwan88% (8)
- 15 Digestive System: Give The Function and Mechanism of Secretion of Salivary Juice?Document24 pages15 Digestive System: Give The Function and Mechanism of Secretion of Salivary Juice?Bhavin ChangelaNo ratings yet
- DigestDocument84 pagesDigestBella FebrianNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of ProteinsDocument14 pagesHydrolysis of Proteinsanmol kohliNo ratings yet
- Digestion SlideDocument18 pagesDigestion SlideezebelluciNo ratings yet
- Digestive Hormones and EnzymesDocument2 pagesDigestive Hormones and EnzymesTiannaNo ratings yet
- Essay PlanDocument3 pagesEssay PlanSherbet SpenceNo ratings yet
- Role of Digestive EnzymesDocument8 pagesRole of Digestive EnzymesvasaviNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of GitDocument33 pagesAnatomy of GitOnuora DeraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Gastro Intestinal Tract Corrected Work 1Document33 pagesAnatomy of Gastro Intestinal Tract Corrected Work 1Onuora DeraNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 WK 3 NoteDocument5 pagesYr 10 WK 3 Notesedrick ocheNo ratings yet
- Human & Social Biology 4th FormDocument23 pagesHuman & Social Biology 4th Formhedasdudh100% (1)
- BIOCHEM DigestionDocument53 pagesBIOCHEM DigestionAngelika Perez CunanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NutritionDocument20 pagesChapter 2 NutritionAzie Nurul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Physiology of DigestionDocument23 pagesPhysiology of DigestionLàXsun ShrèsthàNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pencernaan (Digestion System)Document28 pagesSistem Pencernaan (Digestion System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaNo ratings yet
- Digestion of Food (PS)Document12 pagesDigestion of Food (PS)Pragya SahooNo ratings yet
- Updated Presentation Note - 082207Document3 pagesUpdated Presentation Note - 082207Joshua AladenikaNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument21 pagesDigestionAndersonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Nutrition in MammalsDocument25 pagesChapter-6 Nutrition in MammalsRaeed FarshidNo ratings yet
- KlingDocument4 pagesKlingKlingot Mc DigheelsNo ratings yet
- Nutritiondiettherapy Lectureprelimstomidterm 191112061026Document138 pagesNutritiondiettherapy Lectureprelimstomidterm 191112061026Augustine chandigaNo ratings yet
- The Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinDocument64 pagesThe Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinSayhidoen CepexNo ratings yet
- Note On Digestion of Protein 2021Document11 pagesNote On Digestion of Protein 2021Charity NwaogbeNo ratings yet
- (Gastrointestinal Function) Analysis Report Card: Actual Testing ResultsDocument2 pages(Gastrointestinal Function) Analysis Report Card: Actual Testing ResultsShashikanth RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment Mammalian Physiology: Topic:-Mechanism of Digestion ForDocument6 pagesAssignment Mammalian Physiology: Topic:-Mechanism of Digestion ForRajkamal SarmaNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Heces CompletoDocument10 pagesAnalisis de Heces CompletoIvonne SVNo ratings yet
- Pencernaan Dan Absorbsi Ys New 201Document50 pagesPencernaan Dan Absorbsi Ys New 201wizaiswantiNo ratings yet
- Digestion: Hsslive - in Rajini A.P, HSST Zoology, Govt. Aphss Elappully, PalakkadDocument11 pagesDigestion: Hsslive - in Rajini A.P, HSST Zoology, Govt. Aphss Elappully, PalakkadShan RomioNo ratings yet
- Updated Presentation Note - 091343Document3 pagesUpdated Presentation Note - 091343Joshua AladenikaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PhysiologyDocument38 pagesDigestive System PhysiologyJessa Marie CaparasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Day 2 - Small Intestine (Cont') : Part One: The DuodenumDocument5 pagesAnatomy - Day 2 - Small Intestine (Cont') : Part One: The DuodenumRobert MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Handouts - CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesHandouts - CarbohydratesJerrold CruzNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption 10Document42 pagesDigestion and Absorption 10Pranjul MishraNo ratings yet
- Digestive/Endocrine Answer KeyDocument10 pagesDigestive/Endocrine Answer KeykmulqsNo ratings yet
- How I Cured My Chronic Back Pain in 48Hours: with Best Herbal Medicines, Diets Plan, Aromatherapy…and Many Others That Give Quick and Permanent Relief of Back PainFrom EverandHow I Cured My Chronic Back Pain in 48Hours: with Best Herbal Medicines, Diets Plan, Aromatherapy…and Many Others That Give Quick and Permanent Relief of Back PainNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Clinical Records DatasetDocument14 pagesHeart Failure Clinical Records Datasetpanca saputraNo ratings yet
- 1 Sensory MemoryDocument8 pages1 Sensory MemoryViệt Dũng Trần NguyễnNo ratings yet
- ABC Model and Floral Evolution: ReviewDocument7 pagesABC Model and Floral Evolution: ReviewHairunisa FebrianiNo ratings yet
- CBC Reviewer Anaphy LabDocument9 pagesCBC Reviewer Anaphy LabARVINE JUSTINE CORPUZNo ratings yet
- Embryology ObgDocument36 pagesEmbryology ObgsamrusangaliNo ratings yet
- Floating Leaf Disk Assay For Apes Final 2019 AprilDocument11 pagesFloating Leaf Disk Assay For Apes Final 2019 AprilJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NeoplasiaDocument24 pagesChapter 6 Neoplasiahenna patelNo ratings yet
- Strigo FungiDocument3 pagesStrigo FungiMarc AmnésiaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Phytochemical Profiling of Clerodendrum InfortunatumDocument10 pagesComparative Phytochemical Profiling of Clerodendrum Infortunatumupendra1616No ratings yet
- Facial Nerve MCQDocument4 pagesFacial Nerve MCQIqbal Syed100% (1)
- External Ventricular Drainage PDFDocument2 pagesExternal Ventricular Drainage PDFBarbara100% (1)
- PHIL-IRI-ENGLISH Screening TestDocument4 pagesPHIL-IRI-ENGLISH Screening Testjmar almazanNo ratings yet
- Kidney Structure (14.1.3) EdExcel A Level Biology Revision Notes 2022Document2 pagesKidney Structure (14.1.3) EdExcel A Level Biology Revision Notes 2022Steven FieldsNo ratings yet
- Total LaryngectomyDocument15 pagesTotal LaryngectomyKumaran Bagavathi RagavanNo ratings yet
- Dewey: DecimalDocument888 pagesDewey: Decimalpratiik pyakurelNo ratings yet
- From Li ZhongziDocument4 pagesFrom Li ZhongziRadhakrishnan KasthuriNo ratings yet
- What Is Documentation For Head To Toe AssessmentDocument5 pagesWhat Is Documentation For Head To Toe Assessment155jennyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology MidwiferyDocument108 pagesAn Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology MidwiferyGayuh Kartika100% (3)
- Bandha Yoga. Tips and TechniquesDocument26 pagesBandha Yoga. Tips and TechniquesTatjana Good100% (6)
- 4Document130 pages4Upender BhatiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Physical EducationDocument43 pagesMCQ Physical EducationDr Tilak Raj MeenaNo ratings yet
- Cat Muscles and O.I.A.: Body Region Muscle Origin Insertion ActionDocument5 pagesCat Muscles and O.I.A.: Body Region Muscle Origin Insertion ActioneumarasiganNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Biliary-Type Abdominal Pain: Bertha Van Der DijsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Biliary-Type Abdominal Pain: Bertha Van Der DijsDina RuslinaNo ratings yet
- Biological (Met)Document52 pagesBiological (Met)SirLhitz B. UmaliNo ratings yet
- 1998 - Copper and Zinc in Inflammatory and Degenerative DiseasesDocument198 pages1998 - Copper and Zinc in Inflammatory and Degenerative DiseasesvmarinelliNo ratings yet
- 24 Cerebral Blood FlowDocument31 pages24 Cerebral Blood FlowZuhaib Ahmed100% (1)
- Slave Breakers 2Document167 pagesSlave Breakers 2kjmama100% (1)
- Brooke Cybel TanateDocument5 pagesBrooke Cybel TanateEbenezer Manguerra Diala Gube Jr.No ratings yet
- Pacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingDocument57 pagesPacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingAhmad Khalil Ahmad Al-SadiNo ratings yet
- Higher Cortical Functions and Basis of LanguageDocument78 pagesHigher Cortical Functions and Basis of Languagelovelots1234No ratings yet