Professional Documents
Culture Documents
W7-State and Non-State Institutions (Q2-M1) Notes
W7-State and Non-State Institutions (Q2-M1) Notes
Uploaded by
xdgninety9Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
W7-State and Non-State Institutions (Q2-M1) Notes
W7-State and Non-State Institutions (Q2-M1) Notes
Uploaded by
xdgninety9Copyright:
Available Formats
Group 3 Economic Institutions:
SSDate: March 12, 2024
Purpose: Satisfy basic needs, influence societal complexity.
Level and Subject: Grade 11 UCSP Definition: Enduring organizations handling economic dilemmas.
Topic: Understanding Culture Society, and Politics. Forms of Redistribution and Exchange:
State and Non-State Institution.
Week number: WEEK 7
1. Reciprocity: is the exchange of goods or services with an expectation of something in
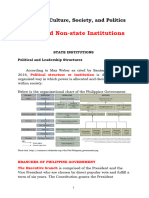
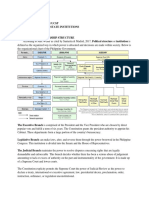
Philippine Government Structure: return.
Types:
Executive Branch:
•President and Vice President elected for six years. Generalized Reciprocity (1.1):
•President appoints Cabinet members, forming a significant part of the bureaucracy. Definition: Equal exchange between socially equal parties.
Example: Muslim groom's dowry to a bride.
Legislative Branch:
•Comprises the Senate and the House of Representatives. Balanced Reciprocity (1.2):
•Holds the power to make, alter, and reverse laws through the Philippine Congress. Definition: Expecting something back, not necessarily immediately.
Example: Eldest child's graduation support for siblings.
Judicial Branch:
•Supreme Court and lower courts. Negative Reciprocity (1.3):
•Resolves disputes on legally demandable and enforceable rights. Definition: Deceptive transaction for maximum gain, minimal payment.
•Empowered with Judicial Review. Example: Business deals with unknown individuals.
Types of Authority: 2. Redistribution:
•Central authority oversees storage, counting, and distribution of community-produced
1. Traditional Authority goods.
•Power based on long-standing cultural patterns.
2. Rational-Legal Authority (Bureaucratic) 3. Market Exchange:
•Power legitimized by rules and regulation •Transactions governed by supply and demand.
3. Charismatic Authority •Involves money for goods or services.
•Power based on extraordinary personal skills.
Non-State Institutions:
1. Banks:
• Commercial/Retail: Manage deposits, loans.
• Investment: Buys and resells shares.
2. Insurance Companies
• Offer policies directly or through employers.
3. Corporations:
•Legal entity distinct from owners, with rights to contracts, loans, etc.
4. Cooperatives:
•Jointly owned enterprises for mutual benefit.
Trade Unions:
Worker groups pursuing goals like better pay and safety standards.
Transnational Advocacy Groups:
Influence decisions across borders.
Development Agencies:
Aid economic growth, focusing on the poor.
International Organizations:
INGOs transcend borders for common causes.
IGOs based on treaties, with formal structures (e.g., UN peacekeeping forces).
You might also like
- A Ritual of Freemasonry PDFDocument312 pagesA Ritual of Freemasonry PDFLuis HenriqueNo ratings yet
- State and Non-State InstitutionDocument25 pagesState and Non-State InstitutionJangelli Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Gates PetitionforDissolutionDocument5 pagesGates PetitionforDissolutionErin FuchsNo ratings yet
- UCSP NotesDocument4 pagesUCSP NotesRandolph Aj Ballesteros UgaddanNo ratings yet
- GMA Network Inc., V. NTC GR 192128 September 13, 2017 Case DigestDocument3 pagesGMA Network Inc., V. NTC GR 192128 September 13, 2017 Case Digestbeingme2No ratings yet
- Schools Division of Parañaque City Humanities and Social Sciences Understanding Culture, Society and Politics Second QuarterDocument7 pagesSchools Division of Parañaque City Humanities and Social Sciences Understanding Culture, Society and Politics Second QuarterAlyssa SolidumNo ratings yet
- Memorial of RespondentDocument13 pagesMemorial of Respondentarvind100% (2)
- Class 10 History Timeline Shobhit NirwanDocument19 pagesClass 10 History Timeline Shobhit Nirwanrakesh singh80% (5)
- UCSP Q2 Module1 Part2Document12 pagesUCSP Q2 Module1 Part2Amanda FlowerNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Q2 Module-1-7Document28 pagesUcsp Q2 Module-1-7Rose DiNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 1ST Semester UcspDocument16 pagesQuarter 2 1ST Semester Ucspschool.eunicepaculbaNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Subject For Elementary 3rd Grade Civics GovernmentDocument40 pagesSocial Studies Subject For Elementary 3rd Grade Civics GovernmentMax LiaraNo ratings yet
- Reviewers AllDocument55 pagesReviewers Allmarckyaurelio09No ratings yet
- DocxDocument11 pagesDocxLaarni EcalnirNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document38 pagesWeek 7segundogideon719No ratings yet
- Module 1 State and NonstateDocument14 pagesModule 1 State and Nonstatejoesuman05No ratings yet
- Ucsp - Q2 - Module 1 7 No ActivitiesDocument22 pagesUcsp - Q2 - Module 1 7 No Activitiesangelamlc0106No ratings yet
- Q2 Lesson 1 State and Non State InstitutionsDocument5 pagesQ2 Lesson 1 State and Non State InstitutionsShareena OrielNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module 7Document50 pagesUCSP Module 7pneuma.elcanoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics: Second QuarterDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics: Second QuarterEDRIAN MEDINANo ratings yet
- UcspDocument5 pagesUcspalejandroleaharneeNo ratings yet
- FORMS FUNCTIONS OF STATE and Noon StateDocument3 pagesFORMS FUNCTIONS OF STATE and Noon StateIvy LunaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 State and Non State InstitutionsDocument32 pagesLesson 7 State and Non State Institutionsjaticohazyl9No ratings yet
- LasagnaDocument39 pagesLasagnaRutvik ShahNo ratings yet
- Forms and Functions of State and Non-StateDocument37 pagesForms and Functions of State and Non-Stateapril rancesNo ratings yet
- UCSP RevieweeDocument5 pagesUCSP RevieweeBhea Mariel CaipangNo ratings yet
- Iop 2608 B - Long-QuestionsDocument17 pagesIop 2608 B - Long-QuestionsNelani GreeffNo ratings yet
- Economic InstitutionsDocument25 pagesEconomic InstitutionsMs. Rica Mae LajatoNo ratings yet
- SCHOOLDocument20 pagesSCHOOLPrincess Mae AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment: EntrepreneurshipDocument6 pagesIndividual Assignment: EntrepreneurshipLê Huy HoàngNo ratings yet
- Hand Outs Political Organization and Economic OrganizationDocument6 pagesHand Outs Political Organization and Economic OrganizationJane AlmanzorNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Q4 W1-2Document26 pagesUcsp Q4 W1-2AJ AguilarNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module 7Document39 pagesUCSP Module 7jomari.rafael001No ratings yet
- Ucsp State and Non State InstitutionsDocument9 pagesUcsp State and Non State InstitutionsliankishmartinezNo ratings yet
- PPG - Humss 11Document52 pagesPPG - Humss 11danyellafrancois385No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 CSP InstitutionsDocument38 pagesLesson 6 CSP Institutionsangelamorales0995No ratings yet
- State & Non State InstitutionsDocument37 pagesState & Non State InstitutionsCaesar AmigoNo ratings yet
- Social Contract 2 (15 May 09)Document9 pagesSocial Contract 2 (15 May 09)Jacob HaroldNo ratings yet
- PP - (Common) U-1, 2 & 3Document35 pagesPP - (Common) U-1, 2 & 3yemanemiesho26No ratings yet
- International Business Is Defined As A Business (Or Firm) That Engages in International (CrossDocument5 pagesInternational Business Is Defined As A Business (Or Firm) That Engages in International (CrossjpNo ratings yet
- Notes State and Non State Institutions ReportingDocument4 pagesNotes State and Non State Institutions Reportingxdgninety9No ratings yet
- W03 - Accounting and EnvironmentDocument36 pagesW03 - Accounting and EnvironmentHera KristianaNo ratings yet
- EXAM Constitutional LAW 1Document6 pagesEXAM Constitutional LAW 1Dann JOCKERNo ratings yet
- Forms and Functions of State InstitutionsDocument48 pagesForms and Functions of State InstitutionsJohn Milen Garvida FabiNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 7 UcspDocument134 pagesQuarter 1 Week 7 UcspNameNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 1Document7 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 1Lynlee Bebs T. ClavicillasNo ratings yet
- Q2 Ucsp ReviewerDocument4 pagesQ2 Ucsp ReviewerTiffany Ross PortesNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Q4Document11 pagesUcsp Q4Mary Mae RemeticadoNo ratings yet
- DEFINITIONDocument2 pagesDEFINITIONBorson NafisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 International Dispute Resolution ProcessDocument22 pagesLecture 2 International Dispute Resolution ProcessMominNo ratings yet
- TuitioDocument12 pagesTuitioJhoanna R. RegachueloNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Week 1 LessonDocument2 pagesUcsp Week 1 Lessonbless HamiNo ratings yet
- Oblicon 1Document6 pagesOblicon 1Charlotte AlcomendasNo ratings yet
- W03 - Acct and EnvironmentDocument18 pagesW03 - Acct and EnvironmentMarsha Sabrina LillahNo ratings yet
- Big Picture C UlobDocument6 pagesBig Picture C UlobAnvi Rose CuyosNo ratings yet
- State Non State InstitutionDocument29 pagesState Non State Institutionpim pimNo ratings yet
- UNDERSTANDING CULTURE SOCIETY and POLITICS q2 Week4Document3 pagesUNDERSTANDING CULTURE SOCIETY and POLITICS q2 Week4Jay CabalgadaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Reporter 1Document6 pagesQ2 Reporter 1Charles Dexter SuanNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Reporting Group 1Document16 pagesUcsp Reporting Group 1Kevin SantosNo ratings yet
- Prefinal Lesson 1Document4 pagesPrefinal Lesson 1Jose Manuel AmbitoNo ratings yet
- FM3 Jan.20 2020 Student Handout1Document10 pagesFM3 Jan.20 2020 Student Handout1Frenzy PicasalesNo ratings yet
- Poli 1100Document20 pagesPoli 1100Kyle NadlerNo ratings yet
- Hand Outs For 2nd Quarter UcspDocument15 pagesHand Outs For 2nd Quarter UcspdianamarietonacaoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Christian University: Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (G 12) W 9 MAY 4-8, 2020Document7 pagesPhilippine Christian University: Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (G 12) W 9 MAY 4-8, 2020Adrian DoblasNo ratings yet
- The Partnership AgreementDocument4 pagesThe Partnership AgreementMelisa FatiNo ratings yet
- DeepikaDocument1 pageDeepikachanduazad8808No ratings yet
- xaxbshZBLb1lnizdKQJiTw PDFDocument2 pagesxaxbshZBLb1lnizdKQJiTw PDFshreveporttimesNo ratings yet
- Crimpro Consolidated Cases For DigestsDocument6 pagesCrimpro Consolidated Cases For DigestsClarisse-joan GarmaNo ratings yet
- Wajeeha Ashraf and Sultan HaidarDocument11 pagesWajeeha Ashraf and Sultan HaidarSultan HaidarNo ratings yet
- Esdc Emp5519Document16 pagesEsdc Emp5519Manan MughalNo ratings yet
- Chapter One:: Prepared by Md. Sagar Rana Lecturer Banking and Insurance University of RajshahiDocument15 pagesChapter One:: Prepared by Md. Sagar Rana Lecturer Banking and Insurance University of RajshahiMd Daud HossianNo ratings yet
- Chantilly DocumentDocument5 pagesChantilly DocumentAlbNo ratings yet
- Taxation Matters Relating To Securities and DerivativesDocument60 pagesTaxation Matters Relating To Securities and DerivativesAnjali JainNo ratings yet
- LSE Fellow JD 2023Document2 pagesLSE Fellow JD 2023Vidhi BubnaNo ratings yet
- Niramaya EngDocument24 pagesNiramaya Engashwanitayal83488No ratings yet
- Portia For and Against: The Merchant of Venice Is "About" Judgment, Redemption and Mercy TheDocument20 pagesPortia For and Against: The Merchant of Venice Is "About" Judgment, Redemption and Mercy TheFalkin AXNo ratings yet
- Arroyo V People GR 220598Document116 pagesArroyo V People GR 220598Fatzie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Test 6 at Paper 5 (Chapter 1 To 5 Procurement of Goods) : CorrectDocument19 pagesTest 6 at Paper 5 (Chapter 1 To 5 Procurement of Goods) : CorrectANURAG SINGHNo ratings yet
- Ra-043144 - Nurse - Koronadal City - 5-2023 Rev1Document22 pagesRa-043144 - Nurse - Koronadal City - 5-2023 Rev1kazel DantesNo ratings yet
- Letter of Bid - Financial PartDocument2 pagesLetter of Bid - Financial PartRabiul IslamNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Damages With DefinitionDocument4 pagesKinds of Damages With DefinitionTenten ConanNo ratings yet
- HealthSouth Inc An Instructional Case ExDocument13 pagesHealthSouth Inc An Instructional Case Exgayan vijerathneNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument42 pagesFrench RevolutionHurmull ZurmlofNo ratings yet
- Benevolent Fund Grant Scholarship FormDocument2 pagesBenevolent Fund Grant Scholarship FormLareeb MoeenNo ratings yet
- 8/11/2014 HTTPS://WWW - Irctc.Co - In/Eticketing/Printticket - JSF?PNR 6332719847 B 11-Aug-2014 0Document1 page8/11/2014 HTTPS://WWW - Irctc.Co - In/Eticketing/Printticket - JSF?PNR 6332719847 B 11-Aug-2014 0దూర్వాసుల శ్రీనివాస్No ratings yet
- CSBL - MEPF Tender Volume-1Document79 pagesCSBL - MEPF Tender Volume-1Rakib HasanNo ratings yet
- Economics Topic Guide Taxation and RevenueDocument55 pagesEconomics Topic Guide Taxation and RevenueAndreea BalicaNo ratings yet
- J. Johnson TranscriptDocument101 pagesJ. Johnson TranscriptDaily KosNo ratings yet
- Valmonte v. Belmonte (Finish)Document9 pagesValmonte v. Belmonte (Finish)MJ AlsuaNo ratings yet