Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food Processing Technology - Separation Processes
Uploaded by
Anonymous0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views25 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views25 pagesFood Processing Technology - Separation Processes
Uploaded by
AnonymousCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
Separation processes
Food Processing Technology Unit V
Part 2
Distillation and Extraction
Separations in Food Processing
Separations are vital to all areas of the
food processing industry.
Types of separation process in food
industry
1. Distillation
2. Extraction
3. Washing
4. Filtration
5. Sedimentation
6. Sieving
7. Centrifugation
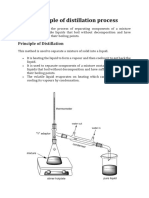
1. Distillation
Principle:
Distillation is a method of separation which
depends on there being a difference in
composition between a liquid mixture and
the vapour formed from it.
This difference in composition develops if
the different components of the mixture
have different vapor pressures or volatilities.
Types Of Distillation
Batch Distillation
Flash Distillation
Continuous Distillation with
Rectification
Rectification with Stripping
Steam Distillation
Vacuum Distillation
Batch Distillation
Batch distillation are commonly used for small
capacity operations of 100-500 litres.
It is extensively used in food processing for
desolventization of the solvent from an
extracted mixture.
As the name (batch) indicates that all the
contents are fed into the distillation still which
is heated by means of steam. The mixture boils,
and the vapours start generating.
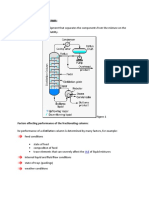
Continuous Distillation with Rectification
In a rectification processing, the vapours and
liquid pass in a cascade of stages so that they
are brought into intimate contact.
In the process of contact, the less volatiles in
vapour stream are exchanged with the more
volatiles in the liquid stream.
They exchange both mass & heat, and they
reach equilibrium.
STEAM DISTILLATION
It is one of the most convenient methods to distil
volatile components(which are heat sensitive and are
insoluble in steam/water) from non-volatile
components at a temperature which is much less than
the boiling point of the volatile component.
It is extensively used to distil the volatile oils from the
spices like clover, ginger, garlic or cardamom.
Steam distillation set-up.
Vacuum Distillation
This will reduce the boiling temperature of the
mixture, and hence , distillation can be carried
out at a temperature much less than normal b.p
of mixture .
It is particularly useful for those components
which are heat sensitive, and may degrade if
they are heated upto the b.p of mixture.
Applications of Distillation in Food
Processing
Brewery industry
Solvent recovery
Extraction of essential oil
2. EXTRACTION
Principle:
Extraction uses the property of solubility to transfer a
solute from one phase to another. In order to perform
an extraction, the solute must have a higher solubility
in the second phase than in the original. In general,
very nonpolar solutes will partition into an organic
phase, while very polar solutes will partition into an
aqueous phase. The choice of phases will depend on
the solute of interest.
Extraction operations can be
subdivided into-
>solid-liquid extraction
>liquid-liquid extraction
Factors Affecting Extraction
Concentration difference,
Area of contact
Solubility of the solute in the solvent,
Viscosity of the solvent
Diffusivity of the solvent into the solid matrix
Temperature of extraction
degree of agitation to improve eddy
diffusivity.
Extraction Equipment
Batch Continuous
Single Multi Single Multi
Stage Stage Stage Stage
Soxhlet Hildebrandt Bollman
Batch
type extractor extractor
extractor
extractor
Advantages of batch extractor
It is simple in operation ,easy in maintenance and
flexible in utilization(i.e same vessel can be use for
different extraction processes) .
Demerit: Generally in
batch processing, the
throughputs are low , and is
restricted to one ton batch.
Applications of extraction in food
processing:
Extraction of oils and fats
Extraction of oleoresins
Extraction of natural food colours
Extraction of caffeine
Extraction of coffee
You might also like
- Soxhlet ExtractionDocument17 pagesSoxhlet ExtractionMahe Rukh88% (8)
- Sample Problem #17Document10 pagesSample Problem #17Dozdi100% (10)
- Oils ProcessingDocument6 pagesOils ProcessingAlexNo ratings yet
- Edibls Oil and Fats TechnologyDocument20 pagesEdibls Oil and Fats TechnologyKhurram Shahzad100% (3)
- CPTDocument7 pagesCPTAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Abrar Rasool 2015-Ag-6288: MSC (Hons) Plant Breeding & Genetics 2 SemesterDocument37 pagesAbrar Rasool 2015-Ag-6288: MSC (Hons) Plant Breeding & Genetics 2 SemesterHamza Bin SajidNo ratings yet
- Lurgi Deodorizing PDFDocument6 pagesLurgi Deodorizing PDFAnonymous 6Nt20xKNo ratings yet
- CentrifugationDocument15 pagesCentrifugationPrashantSoniNo ratings yet
- Extraction: LeachingDocument2 pagesExtraction: LeachingToufik ChaabaneNo ratings yet
- Food PocessingDocument20 pagesFood PocessingPradeepNo ratings yet
- Recycling of Waste Oil, Waste Oil Manufacturer, Waste Oil Processors - Jawrawala PetroleumDocument2 pagesRecycling of Waste Oil, Waste Oil Manufacturer, Waste Oil Processors - Jawrawala PetroleumJawrawala PetroleumNo ratings yet
- PPK Bab 2Document19 pagesPPK Bab 2Renanto Pandu WirawanNo ratings yet
- Brief History of DistillationDocument17 pagesBrief History of DistillationRaheel AhmedNo ratings yet
- General Description of Industry ActivitiesDocument9 pagesGeneral Description of Industry ActivitiesCher EmNo ratings yet
- Application of Distillation & Leaching (Autosaved)Document14 pagesApplication of Distillation & Leaching (Autosaved)Saloni AryaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab 2Document9 pagesBiochem Lab 2Khadijah Ulol AzmiNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction in RefineryDocument16 pagesSolvent Extraction in RefineryFalcon CollegeRaja JangNo ratings yet
- KaranDocument13 pagesKarankaranNo ratings yet
- Fat Splitting: Fatty Acid Isolation and Glycerine RecoveryDocument41 pagesFat Splitting: Fatty Acid Isolation and Glycerine RecoveryAzhan FikriNo ratings yet
- Steam Distillation ApparatusDocument4 pagesSteam Distillation ApparatusAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Edible Oil Processing LinesDocument32 pagesEdible Oil Processing LinesOmar Moradi100% (2)
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction: Name: Suman Kumar Paul ROLL NO.: 16AG63R09 M.Tech, Food Process Engineering Iit KharagpurDocument21 pagesLiquid-Liquid Extraction: Name: Suman Kumar Paul ROLL NO.: 16AG63R09 M.Tech, Food Process Engineering Iit KharagpurDnyaneshwar GawandeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Methods of Purification of Organic Substances by Sanjit Govindraj of Class 11A1 Done On 8.12.23Document10 pagesChemistry Project Methods of Purification of Organic Substances by Sanjit Govindraj of Class 11A1 Done On 8.12.23sanjitgovind20dataNo ratings yet
- 08 - Vegetable Oil RefiningDocument39 pages08 - Vegetable Oil Refiningwaleed chNo ratings yet
- Lipase Separation Downstream ProcessDocument23 pagesLipase Separation Downstream ProcessSonia SnowvyNo ratings yet
- Oil and Fat Assignment PDFDocument21 pagesOil and Fat Assignment PDFM Asrar SidonNo ratings yet
- Distilasi Uap: Sj. Raharjo Staf Akafarma PimDocument69 pagesDistilasi Uap: Sj. Raharjo Staf Akafarma PimsjraharjoNo ratings yet
- FlashDocument28 pagesFlashArbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 NE41102 19.2.19Document57 pagesLec 2 NE41102 19.2.19NURUL SHAEERA BINTI SULAIMAN -No ratings yet
- Speiseoel - Engl Edible Oil WestfaliaDocument28 pagesSpeiseoel - Engl Edible Oil WestfaliaLTE002No ratings yet
- Industrial Application of Distillation ColumnDocument6 pagesIndustrial Application of Distillation Columnkumarsachin3801No ratings yet
- AGE09 - N - Lesson 13 - LContentDocument10 pagesAGE09 - N - Lesson 13 - LContentalwaysremembering14No ratings yet
- Techniques For Extraction of Essential Oils From PlantsDocument3 pagesTechniques For Extraction of Essential Oils From PlantsRahman SuyadiNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument8 pagesDistillationDr_GSNo ratings yet
- The HyLubeDocument4 pagesThe HyLubeZahoor Hussain RanaNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Technology PDFDocument27 pagesFatty Acid Technology PDFmuzammil iqbalNo ratings yet
- Kellen S 2007Document14 pagesKellen S 2007JUNIORNo ratings yet
- Distillation Basics: Dharmsinh Desai UniversityDocument20 pagesDistillation Basics: Dharmsinh Desai UniversityGilles DakouriNo ratings yet
- Unit Four - PhagnosyExtraction TechniquesDocument74 pagesUnit Four - PhagnosyExtraction TechniquesMulugeta TesfayNo ratings yet
- RefineryDocument41 pagesRefineryawad awadNo ratings yet
- Oilandfat IVDocument28 pagesOilandfat IVARATHI PMPMNo ratings yet
- Microbial Biofuels IIDocument42 pagesMicrobial Biofuels IITaraNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Anas SaleemDocument21 pagesPresented By: Anas SaleemAnas Saleem100% (2)
- Solvent Extraction PresentationDocument5 pagesSolvent Extraction PresentationBartwell TazvingaNo ratings yet
- Modern Method of Extraction of Crude DrugsDocument13 pagesModern Method of Extraction of Crude Drugsamama khanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering 20-12-19Document8 pagesChemical Engineering 20-12-19levineNo ratings yet
- Method of ExtractionDocument21 pagesMethod of ExtractionTim WongNo ratings yet
- Edible Oil Processing - Alkali RefiningDocument8 pagesEdible Oil Processing - Alkali RefiningKard SamndNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2aravinthNo ratings yet
- good-MUCLecture 2022 123148640Document16 pagesgood-MUCLecture 2022 123148640baburao01803No ratings yet
- Solvents Used in Liquid-Liquid ExtractionDocument3 pagesSolvents Used in Liquid-Liquid ExtractionJohn Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Divoflow 185 enDocument2 pagesDivoflow 185 enHau SinâuđaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Fat and OilDocument46 pagesUnit 5 Fat and OilLoh JiayeeNo ratings yet
- Top Edible Oil ProductionDocument16 pagesTop Edible Oil Productionabelteshale2244No ratings yet
- Extraction and Formulation of Perfume From LemongrassDocument5 pagesExtraction and Formulation of Perfume From LemongrassMartina Stan100% (1)
- Mr. Daramola AsssignmentDocument2 pagesMr. Daramola AsssignmentVictorNo ratings yet
- Eclr 02Document9 pagesEclr 02Nayanathara PilapitiyaNo ratings yet
- Distillation (Part 2) : (DR.) Mirza Salman BaigDocument31 pagesDistillation (Part 2) : (DR.) Mirza Salman BaigSrđan TufegdžićNo ratings yet
- BioethanolDocument29 pagesBioethanolVikas JanuNo ratings yet
- Evaporators SugarDocument28 pagesEvaporators SugarAnkur KoulNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Hidrokuinon Pada Krim Pemutih Racikan Yang Beredar Di Pasar Tengah Bandar Lampung Secara Kromatografi Lapis Tipis (KLT)Document8 pagesIdentifikasi Hidrokuinon Pada Krim Pemutih Racikan Yang Beredar Di Pasar Tengah Bandar Lampung Secara Kromatografi Lapis Tipis (KLT)Chandra YuniantoNo ratings yet
- Batch Distillation Quiz Number 1Document6 pagesBatch Distillation Quiz Number 1PRINCESS DIANNE DUG-ANo ratings yet
- Take Home Quiz DestilasiDocument2 pagesTake Home Quiz DestilasiLutherJericoNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Synthesis and Shortcut Design of Separation Processes Using Residue Curve Maps - A ReviewDocument18 pagesHeuristic Synthesis and Shortcut Design of Separation Processes Using Residue Curve Maps - A ReviewFDNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 pageGujarat Technological UniversityPatel DhruvilNo ratings yet
- Cake Filters: - by Aatreyee GuhaDocument16 pagesCake Filters: - by Aatreyee GuhamotilalNo ratings yet
- Problems For Distillation Column Sequencing - Tutorial - 3Document4 pagesProblems For Distillation Column Sequencing - Tutorial - 3eelya93No ratings yet
- CHEM 212 - Distillation LabDocument15 pagesCHEM 212 - Distillation LabkristaNo ratings yet
- CH306 Mass Transfer Operations - IIDocument2 pagesCH306 Mass Transfer Operations - IIVish Vishwas0% (1)
- DistillationDocument4 pagesDistillationArvind SinghNo ratings yet
- ,scientific Writing (Review)Document14 pages,scientific Writing (Review)Raviraj MalaniNo ratings yet
- Chromatographic Separations PDFDocument90 pagesChromatographic Separations PDFAishah SamNo ratings yet
- Bio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 10/05/2018Document18 pagesBio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 10/05/2018Atif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 (2023) PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment-2 (2023) PDFKhairul AmrinzzNo ratings yet
- Basic Chromatography Notes 1Document27 pagesBasic Chromatography Notes 1Aufa InsyirahNo ratings yet
- Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Operating Data NormalizationDocument74 pagesReverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Operating Data NormalizationShark1971No ratings yet
- Wa0015 PDFDocument43 pagesWa0015 PDFEstherNo ratings yet
- Craft Whiskey DistillingDocument13 pagesCraft Whiskey Distillinggauzz_erNo ratings yet
- Factors Effecting Performance of The Fractionating ColumnDocument4 pagesFactors Effecting Performance of The Fractionating ColumnHasieb Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Purification SystemDocument2 pagesChoosing The Right Purification SystemYoosu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Separation SystemDocument98 pagesSeparation SystemprocesspipingdesignNo ratings yet
- Filtration Experiment: Unit OperationDocument12 pagesFiltration Experiment: Unit OperationHelin HassanNo ratings yet
- Filter ListDocument170 pagesFilter ListpranayNo ratings yet
- Design of Packed Column (Materi Ajar OPB 18 Mei 2020)Document52 pagesDesign of Packed Column (Materi Ajar OPB 18 Mei 2020)Nafilah Insan BestariNo ratings yet
- Composition of Methanol-Water Batch Distillation: Prepared By: Jason Hixson Don Scott Michael Hickey September 20, 2005Document28 pagesComposition of Methanol-Water Batch Distillation: Prepared By: Jason Hixson Don Scott Michael Hickey September 20, 2005bakhtyar21No ratings yet
- Desalination of Sea WaterDocument12 pagesDesalination of Sea WateraparnaNo ratings yet
- Catalogue CSM PDFDocument4 pagesCatalogue CSM PDFFran IgledominguezNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment ForecastingDocument10 pagesWater Treatment Forecastingvaldi sNo ratings yet
- Chemical Separation and Chromatographic Methods Chem 458Document37 pagesChemical Separation and Chromatographic Methods Chem 458Krishanarju VenkatesanNo ratings yet