Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BATTERIES
Uploaded by
Line Pestaño0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views14 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views14 pagesBATTERIES
Uploaded by
Line PestañoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
BATTERIES
• Batteries are the most common power source for basic
handheld devices to large scale industrial applications. A
battery can be defined as; it is a combination of one or more
electrochemical cells that are capable of converting stored
chemical energy into electrical energy.
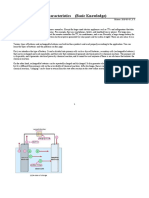
Working Principle
• A battery is a device, which consists of a various voltaic cells.
Each voltaic cell consists of two half cells connected in series
by a conductive electrolyte holding anions and cat ions. One
half-cell includes electrolyte and the electrode to which
anions move, i.e. the anode or negative electrode; the other
half-cell includes electrolyte and the electrode to which cat
ions move, i.e. the cathode or positive electrode.
2 Types of Batteries
• 1) Primary Batteries:
• As the name indicates these batteries are meant for single usage.
Once these batteries are used they cannot be recharged as the
devices are not easily reversible and active materials may not return
to their original forms. Battery manufacturers recommend against
recharge of primary cells.
• Some of the examples for the disposable batteries are the normal AA,
AAA batteries which we use in wall clocks, television remote etc.
Other name for these batteries is disposable batteries.
• 2) Secondary Batteries:
• Secondary batteries are also called as rechargeable batteries. These
batteries can be used and recharges simultaneously. They are usually
assembled with active materials with active in the discharged state.
Rechargeable batteries are recharged by applying electric current,
which reverses the chemical reactions that occur during discharge.
Chargers are devices which supply the required current.
• Some examples for these rechargeable batteries are the batteries
used in mobile phones, MP3 players etc. Devices such as hearing aids
and wristwatches use miniature cells and in places such as telephone
exchanges or computer data centre’s, larger batteries are used.
Types of Secondary (rechargeable)
Batteries:
• SMF Battery:
• SMF is a sealed maintenance free battery, designed to offer reliable,
consistent and low maintenance power for UPS applications. These
batteries can be subject to deep cycle applications and minimum
maintenance in rural and power deficit areas. These batteries are
available from 12V.
• Lithium (Li) Battery:
• We all use it in portable devices such as cell phone, a laptop computer
or a power tool. The lithium battery has been one of the greatest
achievements in portable power in the last decade; with use of
lithium batteries we have been able to shift from black and white
mobile to color mobiles with additional features like GPS, email alerts
etc. These are the high energy density potential devices for higher
capacities. And relatively low self-discharge batteries. Also Special
cells can provide very high current to applications such as power
tools.
• Nickel Cadmium (Nicd) Battery:
• The Nickel Cadmium batteries have the advantage of being recharged
many times and possess a relatively constant potential during
discharge and have more electrical and physical withstanding
capacity. This battery uses nickel oxide for cathode, a cadmium
compound for anode and potassium hydroxide solution as its
electrolyte.
• Lead Acid Battery:
• Lead Acid batteries are widely used in automobiles, inverters, backup
power systems etc. Unlike tubular and maintenance free batteries,
Lead Acid batteries require proper care and maintenance to prolong
its life. The Lead Acid battery consists of a series of plates kept
immersed in sulphuric acid solution. The plates have grids on which
the active material is attached. The plates are divided into positive
and negative plates. The positive plates hold pure lead as the active
material while lead oxide is attached on the negative plates.
Working of Lithium – Ion Battery
• Lithium –Ion batteries are now popular in majority of electronic
portable devices like Mobile phone, Laptop, Digital Camera, etc due to
their long lasting power efficiency. These are the most popular
rechargeable batteries with advantages like best energy density,
negligible charge loss and no memory effect. Li-Ion battery uses
Lithium ions as the charge carriers which move from the negative
electrode to the positive electrode during discharge and back when
charging. During charging, the external current from the charger
applies an over voltage than that in the battery. This forces the
current to pass in the reverse direction from the positive to the
negative electrode where the lithium ions get embedded in the
porous electrode material through a process called Intercalation. The
Li- Ions pass through the non aqueous electrolyte and a separator
diaphragm. The electrode material is intercalated lithium compound.
• Advantages of Lithium – Ion Battery:
• Lithium Ion batteries outperform NiCd batteries and other secondary
batteries. Some of the advantages are
• Light weight compared to other batteries of similar size
• Available in different shape including Flat shape
• High open circuit voltage that increases the power transfer at low current
• Lack of memory effect.
• Very low self discharge rate of 5-10% per month. Self discharge is around
30% in NiCd and NiMh batteries.
• Eco-friendly battery without any free lithium metal
• Disadvantages of Li-Ion Battery:
• The deposits inside the electrolyte over time will inhibit the flow of
charge. This increases the internal resistance of the battery and the
cell’s capacity to deliver current gradually decreases.
• High charging and high temperature may leads to capacity loss
• When overheated, Li-Ion battery may suffer thermal run away and cell
rupture.
• Deep discharge may short circuit the Li-Ion battery. So to prevent this,
some makes have internal shut down circuitry that shut down the
battery when its voltage is above the safe level of 3 to 4.2 volts. In this
case, when the battery is not using for long time, the internal circuitry
will consume power and drain the battery below its shut down
voltage. So to charge such batteries normal chargers are not useful.
You might also like
- Seminar ReportDocument11 pagesSeminar Reporttushar20june71% (7)
- Supercapacitors 101: A home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandSupercapacitors 101: A home Inventors HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Li Ion BatteriesDocument25 pagesLi Ion BatteriesSreed Sharma K0% (1)
- The Greenock HangingsDocument5 pagesThe Greenock HangingsInverclyde Community Development Trust100% (2)
- The Road Not TakenDocument12 pagesThe Road Not TakenAnjanette De LeonNo ratings yet
- PD2017 013 PDFDocument36 pagesPD2017 013 PDFChico Hermanu BrillianNo ratings yet
- Ix-karmapa-The Chariot For Traveling The Supreme PathDocument54 pagesIx-karmapa-The Chariot For Traveling The Supreme Pathssm100% (1)
- Types of BatteriesDocument8 pagesTypes of BatteriesVaibhav AwareNo ratings yet
- Types of BatteriesDocument10 pagesTypes of BatteriesBakhshiNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument8 pagesBatteryThithiksha JNo ratings yet
- Types of Batteries PDFDocument1 pageTypes of Batteries PDFMariz Julian Pang-ao0% (1)
- Ae MaterialDocument15 pagesAe MaterialK Sruti RaniNo ratings yet
- Electrochem 6Document18 pagesElectrochem 6kangirene9705No ratings yet
- EE0007 FA4 BatteryDocument2 pagesEE0007 FA4 BatteryLance CadiangNo ratings yet
- Battery Technology: Lithium Flow BatteriesDocument14 pagesBattery Technology: Lithium Flow BatteriesdepakNo ratings yet
- Battery Technology: Lithium Ion BatteriesDocument14 pagesBattery Technology: Lithium Ion BatteriesdepakNo ratings yet
- Sunum Son HaliDocument24 pagesSunum Son HaliasdasfasdasdNo ratings yet
- Lithium Ion BatteriesDocument18 pagesLithium Ion BatteriesSu truong vanNo ratings yet
- Batteries and EarthingDocument10 pagesBatteries and EarthingRobin ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Kinds of BatteryDocument13 pagesKinds of BatteryBalbon BonbonNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument11 pagesBatteriesDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- Lithium Ion Batteries: Submitted To Prof. Dinesh Kasdekar Mits, Gwalior Submitted by Prakhar Gupta 0901ME131071Document18 pagesLithium Ion Batteries: Submitted To Prof. Dinesh Kasdekar Mits, Gwalior Submitted by Prakhar Gupta 0901ME131071Javed DhillonNo ratings yet
- Battery TechnologyDocument10 pagesBattery TechnologyArunjeet Singh RainuNo ratings yet
- Kinds of BatteryDocument32 pagesKinds of BatteryBalbon BonbonNo ratings yet
- Batteries PresentationDocument14 pagesBatteries PresentationMukhtiar HussainNo ratings yet
- Date: 17/04/2020: Outcome: - Explain Different Types of Batteries and State Its Merits and DemeritsDocument15 pagesDate: 17/04/2020: Outcome: - Explain Different Types of Batteries and State Its Merits and Demeritssrikanthislavatu7615No ratings yet
- FEV Unit - 5Document13 pagesFEV Unit - 5Sai SiDNo ratings yet
- Assignmnet 2 FINALDocument10 pagesAssignmnet 2 FINALPiyush AneejwalNo ratings yet
- The 2020 Lithium-Ion Battery Guide - The Easy DIY Guide To Building Your Own Battery Packs (Lithium Ion Battery Book Book 1)Document101 pagesThe 2020 Lithium-Ion Battery Guide - The Easy DIY Guide To Building Your Own Battery Packs (Lithium Ion Battery Book Book 1)Hangar Graus75% (4)
- Battery: Vijayanandh RDocument24 pagesBattery: Vijayanandh RVijayanandh RNo ratings yet
- Optimizing BatteryDocument8 pagesOptimizing BatteryLGM NightNo ratings yet
- Battery Types and CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesBattery Types and CharacteristicsWai HinNo ratings yet
- AEN Chapter-4 NotesDocument102 pagesAEN Chapter-4 Notesashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- Battery TopologiesDocument37 pagesBattery TopologiesDhanush KNo ratings yet
- Categories and Types of Batteries: Main ArticleDocument3 pagesCategories and Types of Batteries: Main ArticleJdlgNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 4 - Automobile Electronics and Electrical SystemsDocument125 pagesChapter No. 4 - Automobile Electronics and Electrical Systemsashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- Cells & Batteries: Kavin DhanapalDocument8 pagesCells & Batteries: Kavin DhanapalKaveen DNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument30 pagesBatteriessunamisurendar123No ratings yet
- Battery System PPT 1Document32 pagesBattery System PPT 1TitusNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument9 pagesBatteryMaria CamiLa Roxanne ViernesNo ratings yet
- Lithium Ion Batteries: (Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Document17 pagesLithium Ion Batteries: (Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering)TesterNo ratings yet
- Battery TechnologyDocument59 pagesBattery TechnologySuneet Khurana0% (1)
- Lead Acid BatteryDocument7 pagesLead Acid BatteryMateti Madhu100% (1)
- What Is A Battery?Document5 pagesWhat Is A Battery?Geric Anton CapreNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Battery TechnologyDocument25 pagesUNIT-2 Battery TechnologyVasudev GuptaNo ratings yet
- Batteries Introduction PDFDocument30 pagesBatteries Introduction PDFarthur dena-enNo ratings yet
- Energy StorageDocument5 pagesEnergy StorageRaghav V BhatNo ratings yet
- Electric VehicleDocument33 pagesElectric VehicleJatin Goel100% (1)
- Q1 Types of Battery StorageDocument4 pagesQ1 Types of Battery StorageTanisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells: BatteriesDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Cells: BatteriesMae TadaNo ratings yet
- 3.220 Notes (Opt.) - Electrochemical CellsDocument16 pages3.220 Notes (Opt.) - Electrochemical CellsAngel MariaNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle TechnologyDocument27 pagesElectric Vehicle TechnologyB BASAVAPRABHUNo ratings yet
- Types of BatteryDocument22 pagesTypes of BatteryAppidi Sai Sushrith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lithium Ion BatteryDocument14 pagesLithium Ion BatteryomshaktisbNo ratings yet
- Solid State Batteries - Vinayak J. PatilDocument16 pagesSolid State Batteries - Vinayak J. Patilvinayaksavant9119No ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument11 pagesSeminar ReportAnkit GulumkarNo ratings yet
- Lithium Ion CellDocument13 pagesLithium Ion CellAjani SavariauNo ratings yet
- Types of Battery TechDocument7 pagesTypes of Battery TechAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Lithium Ion Battery NotesDocument4 pagesLithium Ion Battery NotesloioNo ratings yet
- Lithium-Polymer Usb Rechargeable BatteryDocument7 pagesLithium-Polymer Usb Rechargeable BatteryIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Lithium Ion BatteryDocument25 pagesLithium Ion BatterydepakNo ratings yet
- AEE - Automotive Electrical and ElectronicsDocument78 pagesAEE - Automotive Electrical and ElectronicsKarthik BabuNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Battery: Submitted By:Pragildas CK Electrical & Electronics Engineering S5 JDT Islam Polytechnic CollegeDocument17 pagesSolid-State Battery: Submitted By:Pragildas CK Electrical & Electronics Engineering S5 JDT Islam Polytechnic CollegefayizkozhikodeNo ratings yet
- A Designers Guide To Lithium Battery Charging - DigiKeyDocument4 pagesA Designers Guide To Lithium Battery Charging - DigiKeySuresh BabuNo ratings yet
- LESSON EXEMPLAR in ENGLISHDocument4 pagesLESSON EXEMPLAR in ENGLISHFelices Christy C. CorderoNo ratings yet
- GST Compensation CessDocument2 pagesGST Compensation CessPalak JioNo ratings yet
- From St. Francis To Dante-Translations From The Chronicle of The Franciscan Salimbene, 1221-1288Document489 pagesFrom St. Francis To Dante-Translations From The Chronicle of The Franciscan Salimbene, 1221-1288Jake SalNo ratings yet
- 6to Present Continuous AllDocument1 page6to Present Continuous AllEliana VogtNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document3 pagesLab Report 2Shah jalalNo ratings yet
- DM Plan Manda Upazila Noagaon District - English Version-2014Document104 pagesDM Plan Manda Upazila Noagaon District - English Version-2014CDMP BangladeshNo ratings yet
- Regulations ON Academic Matters: Tezpur UniversityDocument21 pagesRegulations ON Academic Matters: Tezpur UniversitybishalNo ratings yet
- Ankit Pathak: Business AnalystDocument3 pagesAnkit Pathak: Business AnalystBibhuPrakashDasNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses RevisionDocument1 pagePresent Tenses RevisionJasmina LatinovicNo ratings yet
- Profit Loss Account TemplateDocument4 pagesProfit Loss Account TemplatesnehaNo ratings yet
- Current Logk VkbaDocument8 pagesCurrent Logk Vkba21muhammad ilham thabariNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5 ppspNOTESDocument29 pagesUNIT-5 ppspNOTESEverbloom EverbloomNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant MaintenanceDocument7 pagesTypes of Plant MaintenanceTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNo ratings yet
- U59cbu5f97u897fu5c71u5bb4u904au8a18-U6307u5b9au6587u8a00u7d93u5178u7cbeu7de8u53c3u8003u7b54u6848.docx - 1 10 (Document1 pageU59cbu5f97u897fu5c71u5bb4u904au8a18-U6307u5b9au6587u8a00u7d93u5178u7cbeu7de8u53c3u8003u7b54u6848.docx - 1 10 (Yo YuuiNo ratings yet
- Tourism in India: Service Sector: Case StudyDocument16 pagesTourism in India: Service Sector: Case StudyManish Hemant DatarNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Transferable Skills Dalam PembelajaraDocument12 pagesPengembangan Transferable Skills Dalam PembelajaraKesat RiyanNo ratings yet
- Technical Support Questions and Answers: How Do I Access Commseciress?Document3 pagesTechnical Support Questions and Answers: How Do I Access Commseciress?goviperumal_33237245No ratings yet
- LY Adverbs Combined ListDocument1 pageLY Adverbs Combined ListcarmencrisanNo ratings yet
- Milkfish Tilapia TunaDocument5 pagesMilkfish Tilapia Tunatonbar000No ratings yet
- Human Rights RapDocument4 pagesHuman Rights Rapapi-264123803No ratings yet
- Occlusal Considerations in Implant Therapy Clinical Guidelines With Biomechanical Rationale PDFDocument10 pagesOcclusal Considerations in Implant Therapy Clinical Guidelines With Biomechanical Rationale PDFSoares MirandaNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICABLEDocument6 pagesCOMMUNICABLEAngeline TaghapNo ratings yet
- DMSO (A.k.a. Dimethylsulfoxide) by Ron Kennedy, M.D., Santa Rosa, CADocument8 pagesDMSO (A.k.a. Dimethylsulfoxide) by Ron Kennedy, M.D., Santa Rosa, CAprioris100% (8)
- Understanding: Sexual HarassmentDocument8 pagesUnderstanding: Sexual HarassmentAlex TwahirwaNo ratings yet
- Background: The Islamic World of Academy of ScienceDocument5 pagesBackground: The Islamic World of Academy of ScienceNusrat MaqboolNo ratings yet
- Illustrating Arithmetic Sequence: For MATHEMATICS Grade 10 Quarter 1/week 1.bDocument11 pagesIllustrating Arithmetic Sequence: For MATHEMATICS Grade 10 Quarter 1/week 1.bVenice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet