Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design of Staircase PDF
Uploaded by
karthikaswiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Staircase PDF
Uploaded by
karthikaswiCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Staircase | RCC Structures | Civil Engineering Projects
Page 2 of 7
Bonds in Brickwork | Building Construction Building Materials | Use of Carbonnegative Cement in Building Construction Calculation of loads for Foundation Design | Structural Design Calculations for Overhead Water tank | Building Construction Capitalized Value and Year's Purchase | Property Valuation System Causes of Foundation Damage and Retrofitting | Settlement in the ground Causes of Foundation Damage | Moisture Classification of Cracks | Treatment of Cracks in a Building Column Bases | Design of Steel Structures Concept of Fire Zoning | National Building Code Conduits | Building Construction Construction of Earth Tunnels | Building Construction Continuous Beams | Design of RCC Structures Deconstructivism | Walt Disney Concert Hall Defects in Construction | Building Materials used in Construction Design Methods for Singly reinforced Sections Design of Doubly reinforced sections | Numerical example Design of Singly reinforced sections | Design Method 2 Design of Staircase | RCC Structures Design procedure for designing doubly reinforced section Determining stresses in Steel and Concrete | Doubly reinforced Sections Development in Structural Systems in Postmodernist Period Development of Surface Active Structure system Development of Suspended Structures | Structural Systems Differences between Working stress method and Limit state method Dormer Window | Architectural Construction Drainage and Dewatering | Building Construction Example of the Design of Shear reinforcement in a beam Factors causing damage to the building | Failures in Buildings Failures in Buildings | Important Construction Materials Fly ash Bricks | Building Materials and Construction Foundation Damage and Retrofitting Guide to Construction of Terrace Garden | RCC Construction Guide to design of Doubly reinforced Sections | Civil Engineering Guide to Design of RCC Columns Guide to Design of Shear Reinforcement in a beam
Dog Legged Stair In this article, we will discuss different types of staircases and study the RCC design of a dog-legged staircase
Stairs
Stairs consist of steps arranged in a series for purpose of giving access to different floors of a building. Since a stair is often the only means of communication between the various floors of a building, the location of the stair requires good and careful consideration. In a residential house, the staircase may be provided near the main entrance. In a public building, the stairs must be from the main entrance itself and located centrally, to provide quick accessibility to the principal apartments. All staircases should be adequately lighted and properly ventilated. Various types of Staircases Straight stairs Dog-legged stairs Open newel stair Geometrical stair
RCC design of a Dog-legged staircase
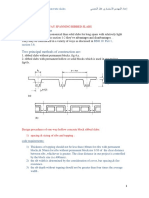
In this type of staircase, the succeeding flights rise in opposite directions. The two flights in plan are not separated by a well. A landing is provided corresponding to the level at which the direction of the flight changes. Design of Dog-legged Stairs Based on the direction along which a stair slab span, the stairs maybe classified into the following two types. 1. Stairs spanning horizontally 2. Stairs spanning vertically Stairs spanning horizontally
http://www.civilprojectsonline.com/building-construction/design-of-stairs-rcc-structures/
15-Jan-13
Design of Staircase | RCC Structures | Civil Engineering Projects
Page 3 of 7
Guide to Design of Simple Beam | Design of Steel Structures Guide to Design of Simply Supported Slabs | Design of RCC Structures Guide to design of Singly reinforced beams | Solved examples Guide to designing a Rolled Steel Beam Guide to Doubly Reinforced RCC Beam Design Guide to Foundation Design | Column Footings Guide to Repair and Maintenance of Buildings Guide to repair and waterproofing of Jack Arch Concrete Roof Guide to the Construction of Sunken Slabs | RCC Construction Hollow Block Partitions | Terracotta Partitions Hollow Cement Block Partitions Importance of Home Insurance Policies | Prevention from Future Damages Interview with Architect Javed Kachchhi | Construction Site Inspection Introduction to Design of RCC Structures Introduction to the calculation of the loads | Building Construction Is it possible to construct an Earthquakeproof building? Lantern Light | Architectural element of Roof lighting Major causes of Cracks in Buildings | Building Construction Market Value, Book Value, Capital Cost | Property Valuation System Metal Lath Partitions | Metal Partitions Methods of Structural Design | Design of Steel Structures Methods to calculate Property Depreciation | Building Costing and Estimation Moment Distribution Method | Civil Engineering Moment of Resistance | Design of Singly reinforced Sections Moment of Resistance | Doubly reinforced Sections Neutral Axis Solved Example | Doubly reinforced Sections New material trends, Aesthetics and Lighting Techniques New trends in the Color schemes and Materials of Design Numerical example 2 | Singly reinforced Sections Numerical Examples | Moment of Resistance Calculations Plate Girders | Structural Steel Components Practical Problems related to Construction on Site | Building Construction Prefabricated Construction and Lightweight building systems Recession cannot stop the boom in Construction Industry
These stairs are supported at each side by walls. Stringer beams or at one side by wall or at the other side by a beam. Loads Dead load of a step = x T x R x 25 Dead load of waist slab = b x t x 25 Live load = LL (KN/m ) Floor finish = assume 0.5 KN/m Stairs spanning Longitudinally In this, stairs spanning longitudinally, the beam is supported ay top and at the bottom of flights. Loads Self weight of a step = 1 x R/2 x 25 Self weight of waist slab = 1 x t x 25 Self weight of plan = 1 x t x 25[(R + T )/T] Live load = LL (KN/m ) Floor finish = assume 0.5 KN/m For the efficient design of an RCC stair, we have to first analyse the various loads that are going to be imposed on the stair. The load calculations will help us determine, how much strength is required to carry the load. The strength bearing capacity of a staircase is determined on the amount of steel and concrete used. The ratio of steel to concrete has to be as per standards. Steel in the staircase will take the tension imposed on it and the concrete takes up the compression. These are the essential steps that are to be followed for the RCC Stair Design.
2 2 2 2
Civil Engineering Projects Archives and Search
Related posts: 1. Column Bases | Design of Steel Structures Column bases are structural elements used in the design of
steel structures to transfer the column load to the footings. Types of Column bases Slab base Gusseted base Slab Base...
2. Methods of Structural Design | Design of Steel Structures Structural design is the science of studying the
Mechanics of a structure. Designing the skeleton of a building determines the real strength of the structure. If the structure is externally... This entry was posted on May 18, 2010, 6:12 pm and is filed under Building Construction. You can follow any responses to this entry through RSS 2.0. You can leave a response, or trackback from your own site.
COMMENTS (29)
TRACKBACKS (1)
RELATED POSTS
#1 by Narayan on November 29, 2010 - 3:44 am
give the genral thumb rule for designing of structural element& u have give great information of designing of slab,staircase.
#2 by s.thiru on December 30, 2010 - 11:52 pm
your RCC theory very good
http://www.civilprojectsonline.com/building-construction/design-of-stairs-rcc-structures/
15-Jan-13
You might also like
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Finite Element Analysis and Design of Steel and Steel–Concrete Composite BridgesFrom EverandFinite Element Analysis and Design of Steel and Steel–Concrete Composite BridgesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- Staircase DesignDocument7 pagesStaircase DesignLee Tin YanNo ratings yet
- Staircase DesignDocument45 pagesStaircase DesignHenRy Ngu 旭67% (3)
- Design of Cantilever Retaining WallDocument13 pagesDesign of Cantilever Retaining WallHARSHARAN100% (1)
- Example 1 - Staircase Design PDFDocument2 pagesExample 1 - Staircase Design PDFHaziq Senin80% (5)
- Design of Dog Legged StaircaseDocument2 pagesDesign of Dog Legged Staircasekhalidq_1850% (2)
- Design Recommendations For Steel Deck Floor SlabsDocument32 pagesDesign Recommendations For Steel Deck Floor Slabswayzane100% (1)
- RectangularTanks PCADocument61 pagesRectangularTanks PCAvictorcivNo ratings yet
- RCC RampDocument4 pagesRCC Ramphemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- Stair Cases DesignDocument19 pagesStair Cases DesignWrishad Zia93% (14)
- Helical Stair - CalculationDocument5 pagesHelical Stair - CalculationLalima Chatterjee67% (6)
- Design Example-Beam Compact SectionDocument13 pagesDesign Example-Beam Compact SectionManoj RautNo ratings yet
- Column Design As Per BS 8110-1:1997: PHK/JSNDocument16 pagesColumn Design As Per BS 8110-1:1997: PHK/JSNJennifer Tang100% (2)
- Example 1 ': σ σ on faces near water face) on faces away σ water faceDocument4 pagesExample 1 ': σ σ on faces near water face) on faces away σ water faceyenebeb tarikuNo ratings yet
- Design Shear Resistance (Beams EC2)Document2 pagesDesign Shear Resistance (Beams EC2)dhanya1995No ratings yet
- 4.2.3 Design of Eccentric Welded Connections (IIIDocument10 pages4.2.3 Design of Eccentric Welded Connections (IIIyadoleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - House DesignDocument18 pagesLecture 4 - House Designkkhan_451062No ratings yet
- Ribbed Slabs: Design ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesRibbed Slabs: Design ConsiderationsAwadNo ratings yet
- Design Chapter StaircaseDocument4 pagesDesign Chapter StaircaseAsish Seeboo100% (1)
- Preliminary Design of Steel StructuresDocument17 pagesPreliminary Design of Steel StructuresAltayeb Yassin100% (5)
- Steel Staircase DesignDocument6 pagesSteel Staircase Designserafini75% (4)
- Two Way Slab AnalysisDocument58 pagesTwo Way Slab AnalysisBaloch Khan100% (1)
- Design of StaircaseDocument28 pagesDesign of Staircasesirfmein82% (11)
- Load Distribution of Slab To BeamsDocument9 pagesLoad Distribution of Slab To BeamsBala Subramanian100% (5)
- Rafter Foundation CalculationsDocument8 pagesRafter Foundation CalculationstsapoutshisNo ratings yet
- Design & Detailing of Retaining WallsDocument26 pagesDesign & Detailing of Retaining Wallsnaveenpnaidu1100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Beams Curved in Plan FinalDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Beams Curved in Plan Finalyosef gemessa100% (1)
- Design Steps of One Way Slab (RCC)Document7 pagesDesign Steps of One Way Slab (RCC)Saurav_Shrestha93% (30)
- RCC71 Stair Flight & Landing - SingleDocument4 pagesRCC71 Stair Flight & Landing - SingleCioabla BogdanNo ratings yet
- ES - Swiming Pool CalculationDocument2 pagesES - Swiming Pool CalculationprabhuNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing Design PDFDocument2 pagesCombined Footing Design PDFRenee100% (1)
- Composite Slab DesignDocument6 pagesComposite Slab DesignFranklyn GenoveNo ratings yet
- Retaining Walls - Design To BS - CODEDocument11 pagesRetaining Walls - Design To BS - CODEAnonymous xUo6UrNo ratings yet
- Water TankDocument40 pagesWater TankAdil MansuriNo ratings yet
- Corbel Excel Sheet WorksDocument5 pagesCorbel Excel Sheet WorksIbrahim A.LNo ratings yet
- Single RC Staircase DesignDocument4 pagesSingle RC Staircase Designezarul fitri100% (4)
- Calculation of Loads For Column and Foundation DesignDocument2 pagesCalculation of Loads For Column and Foundation DesignMandar Nadgaundi100% (1)
- Strap #1: Design AssumptionsDocument27 pagesStrap #1: Design AssumptionsLeanna Abdul Wahab100% (4)
- Design of BeamDocument17 pagesDesign of BeamAbhinav Chowdary100% (2)
- Circular Column DesignDocument10 pagesCircular Column DesignVasanthapragash Nadarajha100% (1)
- Slab Design ExampleDocument5 pagesSlab Design ExamplejacksonNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Detailing and Construc PDFDocument40 pagesStructural Design Detailing and Construc PDFIbnuyusoff77No ratings yet
- Design Procedure For ColumnDocument102 pagesDesign Procedure For ColumnPerarasan M100% (2)
- Weller's Chart Methode - Inizial SizeDocument3 pagesWeller's Chart Methode - Inizial SizenobodicNo ratings yet
- Labone Office Complex Structural Design Report Rev 01 PDFDocument99 pagesLabone Office Complex Structural Design Report Rev 01 PDFBoris Escubio100% (1)
- Thumb Rules For Designing A Column Layout - Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering ProjectsDocument6 pagesThumb Rules For Designing A Column Layout - Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering ProjectsThulasi Raman Kowsigan0% (1)
- StaircaseDocument7 pagesStaircasemcadsriNo ratings yet
- BMT-S4-RCC Structures Class - 02june2021Document56 pagesBMT-S4-RCC Structures Class - 02june2021aishNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document15 pagesLecture 1araloxNo ratings yet
- Staircase DesignDocument3 pagesStaircase DesignDeep DebnathNo ratings yet
- Concrete Structures, R.C Design &project Design IIDocument73 pagesConcrete Structures, R.C Design &project Design IINtawuyirusha AloysNo ratings yet
- GR-5 HirengDocument64 pagesGR-5 HirengMarizia MrlddNo ratings yet
- Civil Mini Project DivyaKamathDocument63 pagesCivil Mini Project DivyaKamathJanaki Vamaraju100% (1)
- Beam SlabDocument66 pagesBeam Slabmadkik100% (1)
- 1 & 2 Introduction To DesignDocument56 pages1 & 2 Introduction To DesignSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- RCC Structures StairDocument31 pagesRCC Structures Staira_j_sanyal259No ratings yet
- Concrete Frame BuildingsDocument100 pagesConcrete Frame BuildingsNuwantha UduwageNo ratings yet
- SAFE DESIGN AGAINST COLLAPSE & DETAILING (Seminar)Document85 pagesSAFE DESIGN AGAINST COLLAPSE & DETAILING (Seminar)Tasbirul HussainNo ratings yet
- RCC Building Design Guide - Structural Design For BuildingsDocument3 pagesRCC Building Design Guide - Structural Design For BuildingsMalik Nazim ChannarNo ratings yet
- TC PDFDocument18 pagesTC PDFkarthikaswiNo ratings yet
- PDF Tamil RulesDocument117 pagesPDF Tamil RulesPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- FIDIC - 10 Things To KnowDocument7 pagesFIDIC - 10 Things To KnowSheron AnushkeNo ratings yet
- Conversion PDFDocument3 pagesConversion PDFkarthikaswiNo ratings yet
- Depriciation PDFDocument9 pagesDepriciation PDFkarthikaswiNo ratings yet
- Hindu TraditionsDocument119 pagesHindu TraditionsMohana Sundaram Ma Ni100% (8)
- Tamil Ramayanam - .PDF & Word Free Ebooks DownloadDocument305 pagesTamil Ramayanam - .PDF & Word Free Ebooks Downloadrajkum01100% (1)
- Understanding Construction Contracts PDFDocument39 pagesUnderstanding Construction Contracts PDFkarthikaswiNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis PDFDocument32 pagesCost Analysis PDFkarthikaswiNo ratings yet
- RCC Beam DesignDocument3 pagesRCC Beam Designjakeer767% (3)
- Labor Cost Code PDFDocument5 pagesLabor Cost Code PDFkarthikaswiNo ratings yet
- Swami VivekaanandhaDocument57 pagesSwami VivekaanandhakarthikaswiNo ratings yet
- Concrete BasicsDocument56 pagesConcrete Basicsengcecbepc100% (6)
- CCC CCESampleExamDocument24 pagesCCC CCESampleExamapi-3842704100% (1)
- Planning - CCS Guide PDFDocument133 pagesPlanning - CCS Guide PDFkarthikaswi100% (2)
- White WoodDocument12 pagesWhite WoodkarthikaswiNo ratings yet
- Piles DesignDocument12 pagesPiles Designn_sasanNo ratings yet
- Devaram 1Document150 pagesDevaram 1lathapriya123No ratings yet
- Ce 5 Sem Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC) Structures Jun 2017Document2 pagesCe 5 Sem Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC) Structures Jun 2017Monika jainNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 21-Aug-2021 inDocument15 pagesAdobe Scan 21-Aug-2021 inKishan SirohiNo ratings yet
- Construction EngineeringDocument138 pagesConstruction EngineeringMohamed987No ratings yet
- Gleneagles Community Centre - Case Study - NaturallywoodDocument12 pagesGleneagles Community Centre - Case Study - NaturallywoodMohamad HafizudinNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Fidder PillarDocument16 pagesPengenalan Fidder PillaracademicNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Brick Works - Code of Practice (First Revision)Document2 pagesIndian Standard: Brick Works - Code of Practice (First Revision)Sathish Elangovan0% (1)
- Staifix CoDocument32 pagesStaifix CoAnna BarthaNo ratings yet
- Long Form Specification For Structural Glazed TileDocument13 pagesLong Form Specification For Structural Glazed TileElgin ButlerNo ratings yet
- Confined MasonryDocument41 pagesConfined Masonryvijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Tile Works Reyes EstimatesDocument4 pagesTile Works Reyes EstimatesVicent John ParedesNo ratings yet
- Material Science: CompositesDocument1 pageMaterial Science: CompositesRollysa MelaniasariNo ratings yet
- 4 Classification of BuildingsDocument37 pages4 Classification of BuildingsFrancis LNo ratings yet
- Torsional Behavior of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete BeamsDocument7 pagesTorsional Behavior of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete BeamssokamantyNo ratings yet
- Acid Sulfate SoilsDocument31 pagesAcid Sulfate SoilsBernard ShuenNo ratings yet
- Original Adventures Reincarnated 6 Temple of Elemental Evil - Volume 2Document356 pagesOriginal Adventures Reincarnated 6 Temple of Elemental Evil - Volume 2Valdir Barbosa100% (8)
- Nitocote Primer SealerDocument2 pagesNitocote Primer SealerVJ QatarNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Technology in Action Complete 16th Edition Evans PDF Full ChapterDocument35 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Technology in Action Complete 16th Edition Evans PDF Full Chaptertannery.eurusp0p2b6100% (20)
- MyDocument61 pagesMynvnrev0% (1)
- Spesifikasi Material Uraian Keterangan BahanDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi Material Uraian Keterangan BahanfauziNo ratings yet
- Affection Plan1686126827109Document1 pageAffection Plan1686126827109Jamshed AlamNo ratings yet
- Dragon Age RPG One-Shot - Unwelcome Guests - Adventure Outline and StatsDocument13 pagesDragon Age RPG One-Shot - Unwelcome Guests - Adventure Outline and StatsIan MarinhoNo ratings yet
- Seminar Presentation PPT On Reactive Powder Concrete Civil EngineeringDocument39 pagesSeminar Presentation PPT On Reactive Powder Concrete Civil Engineeringshreekanth bapatNo ratings yet
- TDS Consol 71 EpDocument4 pagesTDS Consol 71 EpPEP GUDANGNo ratings yet
- Tcsq11305r0 CmuDocument24 pagesTcsq11305r0 CmuAJEC IndiaNo ratings yet
- THK Base Isolation Catalog Technical Book PDFDocument20 pagesTHK Base Isolation Catalog Technical Book PDFChee Soon LeeNo ratings yet
- 30-Second Architecture - The 50 Most Signicant Principles and Styles in Architecture, Each Explained in Half A MinuteDocument239 pages30-Second Architecture - The 50 Most Signicant Principles and Styles in Architecture, Each Explained in Half A MinutesiesmannNo ratings yet
- Flowtite GRP Pipe and Fittings: InstallationDocument8 pagesFlowtite GRP Pipe and Fittings: InstallationMohammed khaleelNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages in AAC BlocksDocument3 pagesDisadvantages in AAC BlocksGaurav JainNo ratings yet
- AMF-65 AMS RFT Partnership Range - CULT PDFDocument46 pagesAMF-65 AMS RFT Partnership Range - CULT PDFShafeek AhamedNo ratings yet
- Build 139 29 Build Right Bottom Plate AnchorsDocument2 pagesBuild 139 29 Build Right Bottom Plate AnchorsIonFlorentaNo ratings yet