Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inserted Through A Catheter To The Heart
Inserted Through A Catheter To The Heart
Uploaded by
andrzej36Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inserted Through A Catheter To The Heart
Inserted Through A Catheter To The Heart
Uploaded by
andrzej36Copyright:
Available Formats
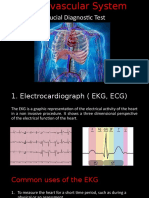
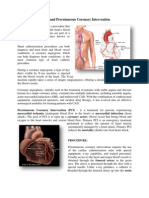
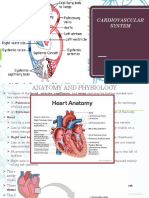
Angiography is imaging of the blood vessels and chambers of the heart after an iodine substance is inserted through a catheter
to the heart. Digital subtraction angiography ( DSA ) is a two-step imaging process described in Chapter 6. Magnetic resonance angiography is the imaging of the flow of blood through vessels. Arteriography is the imaging of arteries usually in the brain (usually to detect blockages). Arthrography is the imaging of joints after injection of an iodine substance. Cholangiography is an examination of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Cholecystography is an image taken after an iodine substance is swallowed and it reaches the gallbladder and bile ducts. Hysterosalpingography is imaging of the fallopian tubes after injection of a contrast medium containing iodine. Myelography is imaging of the spinal cord to examine disks and check for anomalies. Pyelography is the imaging of the renal pelvis and urinary tract. Venography is the imaging of any vein after injection of a contrast medium. Lymphangiography is imaging of the lymphatic vessels.
You might also like
- Types of Biomedical InstrumentsDocument12 pagesTypes of Biomedical Instrumentsgzb0120% (2)
- A Research: Perpetual Help College of Manila V.Conception ST., Sampaloc, Manila Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument8 pagesA Research: Perpetual Help College of Manila V.Conception ST., Sampaloc, Manila Bachelor of Science in NursingRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument5 pagesScriptKelly SisonNo ratings yet
- Clinical ApplicationDocument1 pageClinical ApplicationBrianne Jose FlorendoNo ratings yet
- AngiographyDocument15 pagesAngiographyCrystal AdnalacNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Neck Carotids Heart Aorta Chest Pulmonary Kidneys Gastrointestinal LimbsDocument8 pagesX-Ray Neck Carotids Heart Aorta Chest Pulmonary Kidneys Gastrointestinal Limbsfanofchips_noodles1No ratings yet
- Date 12 Oct 2023Document6 pagesDate 12 Oct 2023mughallaiba901No ratings yet
- AngiographyDocument3 pagesAngiographySai SridharNo ratings yet
- AngiographyDocument1 pageAngiographyMaftei NicusorNo ratings yet
- Anil AngiographyDocument7 pagesAnil AngiographyBikash SubediNo ratings yet
- UnchDocument2 pagesUnchAgung FittNo ratings yet
- Vascular Imaging EquipmentsDocument50 pagesVascular Imaging EquipmentsRohit nikam0% (1)
- CARDIAC Invasive Procedures FinalDocument19 pagesCARDIAC Invasive Procedures FinalSimran JosanNo ratings yet
- Intravascular Ultrasound Technique: An Alternate To Coronary Angiography (Super Simplified Edition)Document13 pagesIntravascular Ultrasound Technique: An Alternate To Coronary Angiography (Super Simplified Edition)Taanish Kumaar100% (1)
- Heart Procedures GlossaryDocument2 pagesHeart Procedures Glossary姜華No ratings yet
- The Renal Problems in X-Ray Based Imaging Techniques Using Lodinated Radiographic Contrast AgentsDocument16 pagesThe Renal Problems in X-Ray Based Imaging Techniques Using Lodinated Radiographic Contrast AgentsdenokkosasiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AngiographyDocument9 pagesCerebral AngiographyVincent LopezNo ratings yet
- Angiography: Study of Blood Vessels, by The Use of Contrast To Make TheDocument21 pagesAngiography: Study of Blood Vessels, by The Use of Contrast To Make TheFarhanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestsDocument5 pagesDiagnostic TestsDUEÑAS, MARIELNo ratings yet
- Syll. Paper 1Document49 pagesSyll. Paper 1Sruthi SruthiNo ratings yet
- Labs 1Document1 pageLabs 1hahahaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System TestDocument28 pagesCardiovascular System TestEla Angela RumapeaNo ratings yet
- Angiography and ArteriographyDocument46 pagesAngiography and ArteriographyAddisu Amare Zena 18BML0104No ratings yet
- Activity 1: Body Structure Function Abnormal Condition Diagnostic Procedure/InterventionDocument1 pageActivity 1: Body Structure Function Abnormal Condition Diagnostic Procedure/InterventionHitagi CrabNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography PDFDocument4 pagesEchocardiography PDFDualaut AndiNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular-AccidentDocument42 pagesCerebrovascular-AccidentPrisHee YhaRz SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Instrumental MethodDocument24 pagesInstrumental Methodzerish0208No ratings yet
- Angiography AssignmentDocument7 pagesAngiography AssignmentHuzzain EshuNo ratings yet
- Angiographic ProceduresDocument26 pagesAngiographic ProceduresJane Garcia100% (1)
- Baroreceptorii Sinocarotidieni Şi Aortici Sunt Stimulaţi de Modificările PresiuniiDocument4 pagesBaroreceptorii Sinocarotidieni Şi Aortici Sunt Stimulaţi de Modificările PresiuniiLabontu IustinaNo ratings yet
- Different DiagnosticDocument26 pagesDifferent DiagnosticDanica Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2Andell JagarnathNo ratings yet
- Neuro DiagnosisDocument47 pagesNeuro DiagnosissanjivdasNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemghghDocument23 pagesThe Urinary SystemghghJennibeb AmilNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused WithDocument3 pagesEchocardiography: Not To Be Confused Withgreathari1998No ratings yet
- Cardiology Laboratory TestsDocument2 pagesCardiology Laboratory TestsBeatrice SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Special Investigation in RadiographyDocument4 pagesSpecial Investigation in RadiographyYamah PrincewillNo ratings yet
- Coronary Angiogram and Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocument9 pagesCoronary Angiogram and Percutaneous Coronary Interventionellaine0024100% (2)
- Urinalysis Is The Physical, Chemical and Microscopic Analysis of Urine. in TheDocument2 pagesUrinalysis Is The Physical, Chemical and Microscopic Analysis of Urine. in TheRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Angiography 1Document8 pagesAngiography 1Mazhar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesDocument15 pagesInstrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesA A D H INo ratings yet
- Invasive and Non Invasive MonitorDocument22 pagesInvasive and Non Invasive Monitorbagya priyaNo ratings yet
- IrcerebralDocument30 pagesIrcerebralJamel MacasNo ratings yet
- Medical Ultrasound - WikipediaDocument30 pagesMedical Ultrasound - WikipedianibNo ratings yet
- Angiography: Presented By: Mulituba, Nairah DDocument9 pagesAngiography: Presented By: Mulituba, Nairah DAkazukin AineNo ratings yet
- X Rays, Ecg Routine Blood SugarDocument2 pagesX Rays, Ecg Routine Blood SugarNitin AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument22 pagesMyocardial InfarctionDeepali SansoiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PVD AND PAD WEEK 3 RN SummerDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PVD AND PAD WEEK 3 RN SummerSalvatore RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Dust inDocument7 pagesDust inlarkspor31No ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock Workup (Medscape)Document8 pagesCardiogenic Shock Workup (Medscape)Tia WasrilNo ratings yet
- What Is An UltrasoundDocument9 pagesWhat Is An UltrasoundKaren RégulesNo ratings yet
- Stroke1 130926201848 Phpapp02Document29 pagesStroke1 130926201848 Phpapp02Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- 4 3 5 Hbs AbiDocument2 pages4 3 5 Hbs Abiapi-343747642No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests: Aleth Therese L. Dacanay, MSCDocument59 pagesDiagnostic Tests: Aleth Therese L. Dacanay, MSCMikee MeladNo ratings yet
- A CNN and ResNet 50 Approach To Detect Cardiac Diseases Using ECG ImagesDocument13 pagesA CNN and ResNet 50 Approach To Detect Cardiac Diseases Using ECG ImagesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- To KaraDocument3 pagesTo Karacielot_sj26No ratings yet
- Nuclear ImagingDocument19 pagesNuclear Imagingdr.anuthomas14No ratings yet
- Angiographic ThoracalisDocument22 pagesAngiographic ThoracalisermaendahNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument36 pagesCardiovascularShield Mae BalanlayNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide to Vascular Ultrasound: Diagnosing and Understanding Vascular ConditionsFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide to Vascular Ultrasound: Diagnosing and Understanding Vascular ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Terms and Related AdjectivesDocument1 pageAnatomy Terms and Related Adjectivesandrzej36No ratings yet
- Medical History - ExerciseDocument1 pageMedical History - Exerciseandrzej36No ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument1 pageVaccinesandrzej36No ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument1 pagePassive Voiceandrzej36No ratings yet
- Herniated Disc: Spine Conditions 1Document2 pagesHerniated Disc: Spine Conditions 1andrzej36No ratings yet
- Diseases and Illnesses of The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesDiseases and Illnesses of The Respiratory Systemandrzej36No ratings yet
- Function of Digestive TractDocument1 pageFunction of Digestive Tractandrzej36No ratings yet
- Presentations: A. PreparationDocument2 pagesPresentations: A. Preparationandrzej36No ratings yet
- Common Types of Drugs: CapsuleDocument1 pageCommon Types of Drugs: Capsuleandrzej36No ratings yet
- Begin Here: Neck Pain Diagnosis Symptoms Diagnosis Self-CareDocument1 pageBegin Here: Neck Pain Diagnosis Symptoms Diagnosis Self-Careandrzej36No ratings yet
- Antibiotics GeneralGuidelinesDocument1 pageAntibiotics GeneralGuidelinesandrzej36No ratings yet
- The Practice of First Aid 1 Initial AssessmentDocument1 pageThe Practice of First Aid 1 Initial Assessmentandrzej36No ratings yet
- Sense of SmellDocument1 pageSense of Smellandrzej36No ratings yet
- EczemaDocument1 pageEczemaandrzej36No ratings yet
- Bypass SurgeryDocument1 pageBypass Surgeryandrzej36No ratings yet
- Cochlea Eustachian (Auditory) Tube External Auditory Canal (Meatus) Incus Malleus Ossicles Pharynx Pinna Semicircular Canals Stapes Temporal Bone Tympanic Membrane Vestibule Vestibulocochlear NerveDocument1 pageCochlea Eustachian (Auditory) Tube External Auditory Canal (Meatus) Incus Malleus Ossicles Pharynx Pinna Semicircular Canals Stapes Temporal Bone Tympanic Membrane Vestibule Vestibulocochlear Nerveandrzej36No ratings yet
- AffixesDocument2 pagesAffixesandrzej36No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageCirculatory Systemandrzej36No ratings yet
- 1 Passive: 1.1 Modal Verbs in The PassiveDocument1 page1 Passive: 1.1 Modal Verbs in The Passiveandrzej36No ratings yet
- 1 Present Simple v. Present ContinuousDocument1 page1 Present Simple v. Present Continuousandrzej36No ratings yet