Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 P2
Chapter 9 P2
Uploaded by
08hakimiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9 P2
Chapter 9 P2
Uploaded by
08hakimiCopyright:
Available Formats
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
CHAPTER 9: ELECTRONIC
9.1 CRO
1. Question 4: Melaka 09
Diagram 4.1 shows a deflecting
cathode rays tube
(a) The function of the filament is to
heat the cathode and releases
electrons on its surface
(i) Name the process mention in (a)
(ii) Explain why a very high voltage
of 3000 V is used in Diagram 4.1
........................................................
(iii) State the energy changes
experience by the electrons
from anode to the screen
..
(b) The voltage between the cathode
and anode is 3000 V. The charge
of an electron is 1.6 x 10
-19
Calculate the kinetic energy
possesses by an electron as it
reaches the anode.
[2 marks]
Diagram 4.1 shows a deflecting
The function of the filament is to
heat the cathode and releases
Name the process mention in (a)
[1 mark]
Explain why a very high voltage
of 3000 V is used in Diagram 4.1
........................................................
[1 mark]
State the energy changes
experience by the electrons
from anode to the screen.
..
[1 mark]
The voltage between the cathode
and anode is 3000 V. The charge
19
C.
Calculate the kinetic energy
possesses by an electron as it
[2 marks]
(c)(i) 1000 V power supply is
connected to the top and lower
plates. The top plate is connected
to the positive terminal and the
lower plate is connected
negative terminal. Sketch the
path of the cathode rays in
Diagram 4.2.
(c)(ii) From the answer in (c)(i), state
one characteristic of cathode
rays.
..
2. Question 4: Kedah 08
Diagram 4.1 shows the structure of a
cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO)
(a) State the process involved in
producing electron from electrode
X.
..........................................................
(c)(i) 1000 V power supply is
connected to the top and lower
plate is connected
to the positive terminal and the
lower plate is connected to the
negative terminal. Sketch the
path of the cathode rays in
[1 mark]
From the answer in (c)(i), state
one characteristic of cathode
..
[1 mark]
Question 4: Kedah 08
Diagram 4.1 shows the structure of a
cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO)
State the process involved in
producing electron from electrode
..........................................................
[1 mark]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(b) Describe the type of motion of the
electron moving from
(i) Y to Z
...........................................
(ii) Z to the screen
....................................................
(c) A student uses the CRO to study
the output voltage from a bicycle
dynamo. Diagram 4.2 shows the
trace on the screen and the
settings of the CRO.
(i) State the type of current
produced by the dynamo.
.......................................................
(ii) Determine the frequency of
output voltage of the dynamo.
[2 marks]
(iii)Sketch the new trace in Diagram
4.3 if the time-based setting is
set at 0.01 s/div.
Describe the type of motion of the
....................................................
[1 mark]
....................................................
[1 mark]
A student uses the CRO to study
the output voltage from a bicycle
Diagram 4.2 shows the
trace on the screen and the
State the type of current
produced by the dynamo.
.......................................................
[1 mark]
Determine the frequency of the
output voltage of the dynamo.
[2 marks]
Sketch the new trace in Diagram
based setting is
9.2 SEMIICONDUCTOR
3. Question 6: MRSM 08
(a) Diagram 6.1 shows a waveform on
the screen of a cathode ray
oscilloscope that is connected
across R. Diagram 6.2 shows
how an electric component Q is
connected to the circuit.
Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.2
(i) Tick (x) the correct answer
in the box provided. The
input power supply is
Diagram 6.1 is connected to..
......... alternating current
........ direct current
(ii) What is the function of
component Q in Diagram
6.2?
..................................................
(iii) Draw the waveform produced
on the screen in Diagram 6.2
Question 6: MRSM 08
Diagram 6.1 shows a waveform on
screen of a cathode ray
oscilloscope that is connected
across R. Diagram 6.2 shows
how an electric component Q is
connected to the circuit.
Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.2
Tick (x) the correct answer
in the box provided. The
input power supply is
Diagram 6.1 is connected to..
......... alternating current
........ direct current
[1 mark]
What is the function of
component Q in Diagram
..................................................
[1 mark]
Draw the waveform produced
n in Diagram 6.2
[1 mark]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(iv) Compare the waveforms in
Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2.
Name the process involved
in Diagram 6.2
..................................................
[1 mark]
(b) Name the component Q in
Diagram 6.2.
.....................................................
[1 mark]
(c) Component Q is made from a
semiconductor material. One
type of semiconductor is the n-
type. Explain how the n-type
semiconductor is produced.
........................................................
.......................................................
[2 marks]
4. Question 6: SBP 08
Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2 shows
two diodes A and B, two bulbs P and Q
are connected to a dry cell with two
different arrangements.
Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.2
(a) Based on Diagram 6.1 and
Diagram 6.2,
(i) compare the connection of
diodes to the terminal of
the dry cell.
..............................................
[1 mark]
(ii) compare the lighting of the
bulbs.
................................................
[1 mark]
(iii) Relate the connection of
diodes to the terminal of
the dry cell with the lighting
of the bulbs.
...............................................
[1 mark]
(b) (i) Draw the arrangement of
four diodes and suitable
power supply in the space
given in Diagram 6.3 that
can be used to produce full
wave rectifier circuit.
[3 marks]
To
CRO
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(iii) Draw the wave form of full
wave rectification
[1 mark]
(iv) Name an electronic
component that can be
used to smooth the
current produced.
.............................................
[1 mark]
5. Question 7: Teknik 07
Impurities are added to a pure
semiconductor to increase its
conductivity in a process known as
doping.
(a) (i) State what is meant by
semiconductor?
.......................................................
.......................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain why certain
semiconductors are known as
n-type semiconductors?
......................................................
......................................................
......................................................
[2 marks]
(b) A diode comprises of n and p-type
semiconductors joined together.
Diagram 7.1 shows an a.c. supply
connected to a resistor and a
diode.
Diagram 7.1
(i) State the effect of fitting the
diode in the circuit to the current
flows
.........................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) On Diagram 7.2, sketch graphs to
show the variation of the a.c.
supply voltage and the output
voltage with time.
DIAGRAM 7.2
[2 marks]
a.c. supply voltage
.
time
Output voltage
time
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(iii) Describe how the output
voltage can be further
improved to get a pure and
smoothened d.c. voltage.
.....................................................
.....................................................
.....................................................
.....................................................
[4
9.3 TRANSISTOR
6. Question 4: Kedah 07
Diagram 4.1 shows the use of a
transistor in a circuit.
Diagram 4.1
(a) Name the type of transistor used.
.............................................................
(b) The transistor is switched on when
the base voltage V
2
2 V.
(i) Write an equation to show the
relationship between I
B
,
I
E
.
.............................................................
Describe how the output
voltage can be further
improved to get a pure and
smoothened d.c. voltage.
.....................................................
.....................................................
.....................................................
.....................................................
[4 marks]
Diagram 4.1 shows the use of a
Name the type of transistor used.
..........................
[1 mark]
(b) The transistor is switched on when
Write an equation to show the
, I
C
and
.............................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) Calculate the minimum value of
R
2
when the transistor is
switched on.
(c) The resistor R
2
is then replaced
with a light dependent resistor
which has a high resistance whe
is dark.
(i) Explain whether the bulb will
light up during the day.
.............................................................
.............................................................
(ii) Besides being used as a switch,
state one other use of a
transistor.
........................................................
7. Question 6: Trengganu 07
Diagram 6.1 shows a circuit to
investigate the working principle
transistor.
The rheostat R is adjusted to get a set
of data of the microammeter reading ,
I
1
and the miliammeter reading, I
Diagram 6.1
Calculate the minimum value of
when the transistor is
[2 marks]
is then replaced
with a light dependent resistor
which has a high resistance when it
Explain whether the bulb will
light up during the day.
.............................................................
.............................................................
[2 marks]
Besides being used as a switch,
state one other use of a
..............................
[1 mark]
Question 6: Trengganu 07
Diagram 6.1 shows a circuit to
investigate the working principle of a
The rheostat R is adjusted to get a set
of data of the microammeter reading ,
and the miliammeter reading, I
2.
Diagram 6.1
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
Table 6 shows the reading of I
I
1
/A I
2
/mA
0.0 0.0
0.5 0.2
1.0 0.4
1.5 0.6
2.0 0.8
2.5 1.0
Table 6
(a) Name the current
(i) I
1
: ..........................................
(ii) I
2
: ..........................................
(b) Using Table 6, state two
observations about the value of I
and I
2
..........................................................
..........................................................
[ 2
(c) Based on your answer in (b) state
the function a transistor.
........................................................
[ 1
(d) The battery P is removed and
replaced by two resistors.
(i) Complete the circuit in
Diagram 6.2 to ensure the
transistor workable without
battery P.
Table 6 shows the reading of I
1
and I
2.
: ..........................................
[1 mark ]
..........................................
[1 mark]
observations about the value of I
1
..........................................................
..........................................................
[ 2 marks ]
Based on your answer in (b) state
........................................................
[ 1 mark ]
The battery P is removed and
replaced by two resistors.
Complete the circuit in
Diagram 6.2 to ensure the
transistor workable without
(ii) State the function of the two
resistors.
............................................
8. Question 7: Johor 08
Diagram 7.1 shows a semiconductor
transistor.
(a)(i) Name the type of the
.
(a)(ii) Transistor has three terminals
connected to the emitter, base
and collector. Label the emitter,
base and collector in Diagram
7.1
[ 2 marks ]
State the function of the two
..................................................
[ 1 mark ]
Question 7: Johor 08
Diagram 7.1 shows a semiconductor
Name the type of the transistor.
.
[1 mark]
(a)(ii) Transistor has three terminals
connected to the emitter, base
and collector. Label the emitter,
base and collector in Diagram
[1 mark]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(b) Diagram 7.2 shows a transistor
circuit.
When the sliding contact X is at the 0
V end of the potentiometer,
(i) is there any current flow
through the base and emitter
circuit?
..................................................
(ii) is there any current flow
through the base and emitter
circuit?
(iii) If the sliding contact X were
raised from 0 V end to the 3 V
end of the potentiometer,
what happened to the bulb?
Explain your answer
[2 marks]
(c) Diagram 7.3 shows a transistor is
used to light up during the day.
Diagram 7.2 shows a transistor
contact X is at the 0
is there any current flow
through the base and emitter
..................................................
[1 mark]
is there any current flow
through the base and emitter
[1 mark]
the sliding contact X were
raised from 0 V end to the 3 V
potentiometer,
what happened to the bulb?
[2 marks]
Diagram 7.3 shows a transistor is
used to light up during the day.
(i) Suggest a modification to light
up the lamp at night.
.
A student replaced lamp L with a lamp
labeled 240 V 24 W in Diagram 7.3.
(ii) The bulb is not light up.
Why the lamp is not light up?
.
.
(iii) An electrical component is
connected to the output
transistor so that the lamp is
light up. Name the electrical
component and state the
functions.
.
.
9. Question 7: SBP 07
Diagram 7.1 shows a transistor circuit
with a bulb L.
Diagram 7.1
(a) Name the type of transistor shown
in Diagram 7.1.
............................................................
modification to light
up the lamp at night.
.
[1 mark]
A student replaced lamp L with a lamp
labeled 240 V 24 W in Diagram 7.3.
The bulb is not light up.
Why the lamp is not light up?
.
.
[2 marks]
electrical component is
connected to the output
the lamp is
Name the electrical
component and state the
.
.
[2 marks]
Question 7: SBP 07
Diagram 7.1 shows a transistor circuit
Diagram 7.1
Name the type of transistor shown
............................................................
[1 mark]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(b) Based on Diagram 7.1:
(i) What is the potential difference
across point X and point Z?
.............................................................
(ii) What is the total resistance
between point X and point Z?
..................................................................
(iii) Using the answers from (b)(i)
and b(ii), calculate the potential
difference
[2
(c) State what will happen to the
lamp,L, if the base-emitter
potential difference, V
BE
is 2
volts? Explain your answer.
..........................................................
..........................................................
..........................................................
[2
(d) Without adding any new
component to Diagram 7.1, what
modification is needed so that the
opposite situation than the one in
7(c) occur at lamp L.
..........................................................
(e) An automatic fire alarm is needed
to emit sound in case of fire.
Suggest two modifications that
have to be made to the circuit in
Diagram 7.1 by replacing the
components with suitable
electronic components.
..........................................................
..............................................
..........................................................
[2
What is the potential difference
across point X and point Z?
.............................................................
[1 mark]
What is the total resistance
between point X and point Z?
.................
[1 mark]
Using the answers from (b)(i)
and b(ii), calculate the potential
[2 marks]
State what will happen to the
emitter
is 2
volts? Explain your answer.
..........................................................
..........................................................
..........................................................
[2 marks]
agram 7.1, what
modification is needed so that the
opposite situation than the one in
..........................................................
[1 mark]
An automatic fire alarm is needed
fire.
Suggest two modifications that
have to be made to the circuit in
Diagram 7.1 by replacing the
components with suitable
..........................................................
..........................................................
..........................................................
[2 marks]
10. Question 8: Negeri 9 08
Diagram 8 shows a transistor circuit.
The circuit is used to automatically
switch on the bulb at night.
(a)(i) Name component Q.
........................................................
(a)(ii) State two functions of
component Q?
........................................................
(d) What is the function of resistor
R?
.......................................
(c)(i) What happens to potential
difference V
P
at night? Explain.
........................................................
........................................................
(c)(ii) Explain why the bulb is lighted
up at night?
........................................................
........................................................
(d) Bulb M is labelled 240 V, 60 W
starts to light up when V
V and the resistance of resistor
P is 10 k. Determine the
maximum resistance of resistor
S.
Question 8: Negeri 9 08
Diagram 8 shows a transistor circuit.
The circuit is used to automatically
switch on the bulb at night.
Name component Q.
........................................................
[1 mark]
State two functions of
........................................................
[2 marks]
What is the function of resistor
.........................................................
[1 mark]
(c)(i) What happens to potential
at night? Explain.
........................................................
........................................................
[2 marks]
Explain why the bulb is lighted
........................................................
........................................................
[2 marks]
Bulb M is labelled 240 V, 60 W
starts to light up when V
P
is 2.0
ance of resistor
. Determine the
maximum resistance of resistor
[2 marks]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(e) What happens to the bulb
when it is connected directly to
the transistor circuit without
using the relay switch. Explain
why.
.....................................................
.....................................................
[2 marks]
11. Question 8: Melaka 08
Diagram 8.1 shows four electrical
circuits with identical electrical
components.
The electrical circuits consist o
transistor , a bulb, a light dependent
resistor, LDR, two resistors, R
and battery as a power supply.
(a) What is meant by power?
..........................................................
[1 mark]
(b) Based on Diagram 8.1, state the
suitable characteristic of the
arrangement position of the
electrical components of the
circuit to use as an automatic
switch.
(i) Resistor, R
2
..........................................................
Reason
.........................................................
[2 marks]
What happens to the bulb
when it is connected directly to
the transistor circuit without
using the relay switch. Explain
.....................................................
.....................................................
[2 marks]
Diagram 8.1 shows four electrical
identical electrical
The electrical circuits consist of a
transistor , a bulb, a light dependent
resistor, LDR, two resistors, R
1
and R
2
power supply.
What is meant by power?
..........................................................
[1 mark]
(b) Based on Diagram 8.1, state the
suitable characteristic of the
arrangement position of the
electrical components of the
to use as an automatic
..........................................................
.........................................................
(ii) Resistor R
1
and light dependent
resistor, LDR
...........................................................
Reason
...........................................................
(iii) Collector terminal of the transistor
to the battery
......................................
Reason
...........................................................
(c) Based on the answers in 8(b), state
one suitable circuit in Diagram 8
to be use as an automatic switch.
.
............................................................
(d) The circuit in 8(c) is used as an
automatic switch. State the
application of the circuit.
...........................................................
(e) Diagram 8.2 show a circuit
transistor used as an amplifier.
The transistor is on when the
voltage across Y and Z is 1 V.
light dependent
...........................................................
...........................................................
[2 marks]
(iii) Collector terminal of the transistor
...........................................................
...........................................................
[2 marks]
Based on the answers in 8(b), state
one suitable circuit in Diagram 8
an automatic switch.
............................................................
[ 1 mark]
(d) The circuit in 8(c) is used as an
automatic switch. State the
ion of the circuit.
...........................................................
[ 1 mark]
(e) Diagram 8.2 show a circuit
transistor used as an amplifier.
The transistor is on when the
voltage across Y and Z is 1 V.
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
When the potential difference
accross Yand Z is 1 V;
(i) What is the potential
difference between X and Y?
[ 1 mark]
(ii) Calculate the maximum
resistance of the rheostat for
the transistor to switch on?
[2 marks]
12. Question 8: Kelantan 09
(a) Diagram 8.1 shows a relay used in
an electrical circuit.
(i) What is the function of a
relay?
..................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain what will happen
when an electric current flow
in the main circuit?
..................................................
..................................................
[2 marks]
(b) Diagram 8.2 shows a circuit
consists of an automatic switch
using a relay to switch on a street
light at night.
(i) Name the component labeled
Q.
..................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) State the main characteristic
for component Q.
..................................................
[1 mark]
(iii) Explain how the component
Q light up the street light.
..................................................
.................................................
.................................................
[3 marks]
(c) Diagram 8.3 shows a simple
tsunami control system used to
detect an earthquake and
eruption volcano at the sea bed
which will produced tsunami.
The circuit consists of vibration
sensor, V, and waves temperature
sensor, T, athe sea bed. The vibration
and increase in temperature detected
will produce signals whichl will be
sent to a logic gate and then to the
tsunami operation detector room
through the transmitter.
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
Keys:
Vibration sensor,V:
With vibration: Logic 1
Without vibration : Logic 0
Water temperature sensor, T:
High temperature: Logic 1
Low temperature: Logic 0
Output S:
Radar is activated : Logic 1
Radar is deactivated: Logic 0
Tsunami will occur when there is a
vibration or change of high
temperature at the sea bed.
Table 8 is a truth table which shows
the operation of the logic gate in the
tsunami control system.
V T S
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
(i) Using the keys given,
complete Table 8.
[2 marks]
(ii) Name the logic gate in the
circuit in Diagram 8.3
..................................................
[1 marks]
(iii) In the space below, draw the
logic gate symbol in (c)(ii)
[1 mark]
9.4 LOGIC GATES
13. Question 1: Melaka 07
Diagram 1 shows a logic circuit
consisting of get logic C, D and E. X is
the output operation of gate logic D.
(a) Name gates logic C and D.
(i) C: ........................
(ii) D: .......................
[2 marks]
(b) (i) State the logic gate of logic
gate E.
.....................................................
[1 mark]
(iii) In the box below, tick x the
correct output for X.
1001 _____
1110 _____
1011 _____ [1 mark]
14. Question 3: Johor 2007
Diagram 3.1 shows the symbol for a
NAND gate.
(a) State the basic logic gates that
form the NAND gate.
.
............................................................
[1 mark]
A
B
C
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(b) NAND get can be used to make
other types of gate as shown in
Diagram 3.2 and Diagram 3.3.
(i) Write a truth table for get in
Diagram 3.2.
[1 mark]
(ii) Write a truth table for get in
Diagram 3.3.
[2 marks]
(iii)Decide what type of gate is
equivalent to get in Diagram 3.2
and Diagram 3.3.
Diagram 3.2:
..........................................................
Diagram 3.3:
..........................................................
[2 marks]
15. Question 4: MRSM 07
Figure 4 shows a circuit which
consists of several logic gates.
(a)(i) Name the logic gates labelled P
and Q.
P: ...................... Q:....................
[2 marks]
(a)(ii) State the function of logic gate
X.
........................................................
[1 mark]
(b)(i) Based on Figure 4, complete the
Truth table below.
Input Output
A B C
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
[3 marks]
(b)(ii) Draw the symbol of the logic
gate which is equivalent to
output C.
[1 mark]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
16. Question 5: MRSM 09
Diagram 5.1 shows an electronic
system used to switch on a security
light outside a house.
(a) Name the type of logic gate
which receives input A.
(b) Based on Diagram 5.1, complete
the following sentences about
input A, B and C by ticking the
mark (x) in the correct bracket.
(i) If the surrounding is dark
Input A will be
And so input B will be
[2 marks]
(ii) If a person is detected,
input C will be
(c) The security light should be
switched on if a person is
detected when it is dark. Name
the type of logic gate which
should be used in the box
marked Logic Gate X.
........................................................
(d) Diagram 5.2 shows a
combination of three logic
gates.
electronic
system used to switch on a security
Name the type of logic gate
Based on Diagram 5.1, complete
the following sentences about
input A, B and C by ticking the
mark (x) in the correct bracket.
the surrounding is dark
And so input B will be
[2 marks]
If a person is detected,
[1 mark]
The security light should be
switched on if a person is
detected when it is dark. Name
the type of logic gate which
be used in the box
........................................................
[1 mark]
combination of three logic
Construct a truth table for the gate
combination shown in Diagram 5.2.
17. Johor 09
Diagram 6 shows a circuit used as a
safety system in a house.
(a) Name logic gate R.
......................................................
(b) Using two switches, two dry
cells and a bulb, draw a circuit
that equivalent to logic gate S.
(c) The truth table represents the
logic gate in the Diagram 6
above.
A B
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
(c)(i) Complete the truth table above.
Construct a truth table for the gate
combination shown in Diagram 5.2.
[2 marks]
Diagram 6 shows a circuit used as a
safety system in a house.
Name logic gate R.
......................................................
[1 mark]
Using two switches, two dry
cells and a bulb, draw a circuit
that equivalent to logic gate S.
The truth table represents the
logic gate in the Diagram 6
L M
(c)(i) Complete the truth table above.
[2 marks]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(c)(ii) What happens to the door and
the gate when the main switch is
closed?
........................................................
........................................................
[2 marks]
(c)(iii) State two methods to open the
door and the gate
simultaneously. [2 marks]
.......................................................
....................................................
18. Question 7: Perak 07
Diagram 7.1 shows a circuit that turns
on a water pump.
Diagram 7.1
When the output from the NOR gate is
high, the water pump is on. The soil
contacts are buried in the soil near the
plants. When the soil dries the logic
state of input B changes from high
(logic 1) to low (logic 0).
(a) (i) Explain why the logic state of
input B is low when the soil is
dry.
.......................................................
What happens to the door and
the gate when the main switch is
........................................................
........................................................
[2 marks]
State two methods to open the
[2 marks]
.....................
....................................................
Diagram 7.1 shows a circuit that turns
When the output from the NOR gate is
high, the water pump is on. The soil
buried in the soil near the
plants. When the soil dries the logic
state of input B changes from high
Explain why the logic state of
input B is low when the soil is
.......................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain why the logic state of
input A is low when it is dark
and high when it is bright.
....................................................
........................................................
(b) Complete the truth table for the
NOR gate.
Input A Input B
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
(c) The water pump is on. State
(i) The logic levels of
input B and output Q.
Input A :
Input B :
Output Q : .
(ii) The light level (dark or
bright) and the soil
condition (wet or dry).
Light level:
Soil condition :
19. Question 8: Trengganu 09
Diagram 8.1 shows an automatic
parking barrier for any vehicle enter
parking lots. The parking
automatically rises up when a
sufficient amount of coin is slotted in a
machine or an applicable electronic
card is touched to the detector.
Explain why the logic state of
input A is low when it is dark
and high when it is bright.
........................................................
........................................................
[2 marks]
Complete the truth table for the
Output Q
The water pump is on. State
The logic levels of input A,
input B and output Q.
Input A :
Input B :
Output Q : .
[3 marks]
The light level (dark or
bright) and the soil
ondition (wet or dry).
Light level:
Soil condition :
[2 marks]
Question 8: Trengganu 09
Diagram 8.1 shows an automatic
parking barrier for any vehicle enter
parking lots. The parking barriers
automatically rises up when a
sufficient amount of coin is slotted in a
machine or an applicable electronic
card is touched to the detector.
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
Diagram 8.2 shows the circuit used in
the automatic parking barrier.
(a) Name the electronic component
X.
........................................................
(b) What is the potential different
across the electronic card
detector when the potential
different across resistor S is
4 V?
........................................................
(c) The electronic component Y is
connected to an electric motor
to lift up the automatic barrier
240 V a.c is supplied to the
motor.
(i) Name the electronic
component Y.
..................................................
Diagram 8.2 shows the circuit used in
Name the electronic component
........................................................
[1 mark]
What is the potential different
across the electronic card
detector when the potential
different across resistor S is
........................................................
[1 mark]
The electronic component Y is
connected to an electric motor
to lift up the automatic barrier.
a.c is supplied to the
Name the electronic
..................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain why the
component Y is used?
..................................................
(d) The following truth table shows
the operation of a logic gate in
the circuit in Diagram 8.2.
Input P
Electronic
card
detector
Input
voltage
at P
Coin
detector
No No
No Yes
Yes No
Yes Yes
Key:
An applicable electronic card is
touched:
High input voltage at P
An inapplicable electronic card is
touched:
Low input voltage at P
A sufficient amount of coin slotted in
High input voltage at Q Logic 1
An insufficient amount of coin is
slotted in:
Low input voltage at Q Logic 0
(i) Using the given key,
complete the truth table
above
(ii) Name the logic gate in the
circuit in Diagram 12.2.
.................................................
(iii) Draw the symbol of the logic
gate in (d)(ii)
Explain why the electronic
component Y is used?
..................................................
[1 mark]
The following truth table shows
the operation of a logic gate in
the circuit in Diagram 8.2.
Input Q Output
R
Coin
detector
Input
voltage
at Q
An applicable electronic card is
at P Logic 1
An inapplicable electronic card is
ge at P Logic 0
A sufficient amount of coin slotted in:
High input voltage at Q Logic 1
An insufficient amount of coin is
Low input voltage at Q Logic 0
Using the given key,
complete the truth table
[4 marks]
logic gate in the
circuit in Diagram 12.2.
.................................................
[1 mark]
Draw the symbol of the logic
[1 mark]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
(e) Using two switches, two dry
cells and a bulb draw a circuit
that equivalent to logic gate in
d(iii)
[2 marks]
20. Understanding: Johor 07
A semiconductor diode is made from
combination of an n-type
semiconductor and p-type
semiconductor.
(a) Explain how an n-type
semiconductor is produce.
[2 marks]
Diagram 12.1 and 12.2 shows a circuit
consisting of a diode and a bulb.
(a) Based on Diagram 12.1 and
Diagram 12.2, which bulb will
light up?
[1 mark]
(b) Explain how the bulb will light
up.
[3 marks]
Draw a circuit to produce full-wave
rectification and show the input
Voltage and the output voltage wave
forms.
Explain why a capacitor is connected
in the Diagram 12.3 and how it
functions.
21. Making decision: Johor 07
You are required to set up a battery
charge for your hand phone by using
lower a.c input voltage as in Diagram
12.3 and in Table 12.1.
Ratio
N
1
:N
2
Type of
transformer
core
Diode
arrange-
ment
100
80
60
40
20
Solid copper
core
Laminated
copper core
Solid soft
iron core
Laminated
soft iron
core
Half-wave
rectification
Full wave
rectification
Table 12.1
Study the information in Diagram 12.3
and Table 12.1 determine:
(i) the number of turns in the
primary coil and the
secondary coil of the
transformer and justify your
choice.
(ii) the type of core you will use
in the transformer and justify
your choice.
(iii) the diode arrangement you
will use and justify your
choice.
[6 marks]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
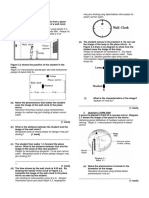
22. Section B: Trengganu 09
Diagram 10.1 and 10.2 show the
deflections of a cathode ray in a
deflection tube.
Diagram 10.1
Diagram 10.2
(a) What is the meaning of cathode
ray?
(b) Using Diagram 10.1 and
Diagram 10.2,
(i) State the charge of the
cathode ray
(ii) Compare the voltage of EHT
connected to the metal plate
and the deflection of the
cathode ray.
[2 marks]
(c) State the relationship between
(i) The voltage of EHT and the
strength of the electric field
between the metal plates.
Section B: Trengganu 09
Diagram 10.1 and 10.2 show the
deflections of a cathode ray in a
of cathode
[1 mark]
Using Diagram 10.1 and
State the charge of the
[1 mark]
Compare the voltage of EHT
connected to the metal plate
and the deflection of the
[2 marks]
State the relationship between
voltage of EHT and the
strength of the electric field
between the metal plates.
[1 mark]
(ii) The strength of the electric
field between the metal
plates and the deflection of
the cathode ray.
(d) Diagram 10.3 shows a shadow is
formed on fluroscent scree
the Maltese cross tube.
Diagram 10.3
Explain how the shadow is
formed on the fluorescent
screen?
(e) Maltese cross tube in Diagram
10.3 is not suitable for
measuring the frequency of the
sound waves. Suggest
modification that can be made
to the Maltese cros tube in
Diagram 10.3 to transform it into
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope that
can measure the frequency of
the sound waes.
In your suggestion, state the
components that are used and their
function based on the following
aspects:
- the electron gun
- the deflection system
The strength of the electric
field between the metal
plates and the deflection of
the cathode ray.
[1 mark]
Diagram 10.3 shows a shadow is
formed on fluroscent screen of
the Maltese cross tube.
Diagram 10.3
Explain how the shadow is
formed on the fluorescent
[4 marks]
Maltese cross tube in Diagram
10.3 is not suitable for
measuring the frequency of the
sound waves. Suggest
modification that can be made
the Maltese cros tube in
Diagram 10.3 to transform it into
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope that
can measure the frequency of
In your suggestion, state the
components that are used and their
function based on the following
the deflection system
[10 marks]
FIZIKMOZAC 2010
You might also like
- Pattern C5 Vectors - SM025 - 2019 2020Document17 pagesPattern C5 Vectors - SM025 - 2019 2020NUR BATRISYIA AMALYANo ratings yet
- 2006 MRSM With AnswerDocument70 pages2006 MRSM With AnswerccffyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document5 pagesTutorial 8Aina AqilahNo ratings yet
- Pre-UPS1 SP015 (Copy) : Please Answer All Questions in 30 MinutesDocument11 pagesPre-UPS1 SP015 (Copy) : Please Answer All Questions in 30 MinutesWAN NUR ALEEYA TASNIM BINTI WAN MOHAMED HAZMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Question Score A Chapter 1Document14 pagesQuestion Score A Chapter 1Dee -AdilaNo ratings yet
- Kedah-Answer Physics-Trial SPM 2007Document17 pagesKedah-Answer Physics-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmoza67% (3)
- 6 ElectrochemistryDocument24 pages6 ElectrochemistryMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Pre PSPM Computer Science Subject (Sc015) Kolej Matrikulasi Labuan (2019/2020)Document8 pagesPre PSPM Computer Science Subject (Sc015) Kolej Matrikulasi Labuan (2019/2020)Veshal RameshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 3 AnswerDocument7 pagesChemistry Paper 3 AnswerMohd Hafiez67% (6)
- Essay QuestionDocument4 pagesEssay QuestionVilasini RajaramNo ratings yet
- Bab 07 - ElektrikDocument39 pagesBab 07 - ElektrikAl Nazuris100% (2)
- 2022 Pahang - Jerantut Chemistry K3Document5 pages2022 Pahang - Jerantut Chemistry K3Anand KaneshNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Experiment ListDocument17 pagesBiology Form 5 Experiment ListLin Fadzlin0% (3)
- Chemistry SkemaMara2009Document13 pagesChemistry SkemaMara2009spm_victim2010No ratings yet
- SPM Trial 2012 Physics A PerakDocument17 pagesSPM Trial 2012 Physics A PerakwaichongNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 3Document46 pagesForm 5 Chapter 3qq23571% (7)
- 3A Chemical Formulae and Equations-AnswerDocument11 pages3A Chemical Formulae and Equations-AnswerWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Paper 1 2016Document35 pagesSPM Chemistry Paper 1 2016azharsarahNo ratings yet
- Module Physics Paper 3 Section B Experiments (Form 4 &form 5) With Analysis SPM QuestionsDocument38 pagesModule Physics Paper 3 Section B Experiments (Form 4 &form 5) With Analysis SPM QuestionsEncikMohdNNo ratings yet
- 2 Heat of PrecipitationDocument22 pages2 Heat of PrecipitationSyawal AnizamNo ratings yet
- Latihan Empirical FormulaDocument11 pagesLatihan Empirical FormulaRusdi Chodeng100% (1)
- Kertas 2 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2011Document12 pagesKertas 2 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2011Muhamad FarisNo ratings yet
- F5 KSSM Tutorial 1.1 (Force and Motion Ii)Document13 pagesF5 KSSM Tutorial 1.1 (Force and Motion Ii)Alia Qistina Mara KasmedeeNo ratings yet
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K2 No SkemaDocument36 pagesTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K2 No SkemaCikgu Faizal83% (6)
- SBP-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-TRIAL SPM 2009Document15 pagesSBP-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-TRIAL SPM 2009kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Asid, Bes Dan GaramDocument6 pagesAsid, Bes Dan GaramTENGKU AHMAD NAQIUDDIN BIN TENGKU NADZUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- SOALAN STRUKTUR Form 5Document9 pagesSOALAN STRUKTUR Form 5Willey TaluanNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Bio-Score Bab 1 (Form 5)Document45 pagesJawapan Bio-Score Bab 1 (Form 5)azamsensei94% (32)
- Koleksi Trial 2017 Paper 123Document176 pagesKoleksi Trial 2017 Paper 123shahidaNo ratings yet
- (A) Define (I) Electric Field.: Physics Paper 2 Sf026/2 PSPM Semester 2 Session 2015/2016 1Document13 pages(A) Define (I) Electric Field.: Physics Paper 2 Sf026/2 PSPM Semester 2 Session 2015/2016 1Voon Chen WeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Answer)Document17 pagesChapter 2 (Answer)najibahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Form 4 Chapter 4Document5 pagesChemistry Notes Form 4 Chapter 4lenovosubaNo ratings yet
- PMTLDocument314 pagesPMTLRahoul Chicharito RooneyNo ratings yet
- Trial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 Skema PDFDocument16 pagesTrial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 Skema PDFamadkacakNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 PPT T4 SPM 2017Document19 pagesKertas 2 PPT T4 SPM 2017Mastura Hussin0% (1)
- Experiment 4Document5 pagesExperiment 4Nur ShazieyahNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 5 Chapter 5Document22 pagesPhysics Form 5 Chapter 5Charlene87% (15)
- Marking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Document21 pagesMarking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Physics SPM 2003Document4 pagesPhysics SPM 2003Joanne Cheah100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Light Paper 2 SPMDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Light Paper 2 SPMN.NityainiNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document44 pagesPaper 2ayydenNo ratings yet
- Smart Notes - f4 Chapter 5 WavesDocument9 pagesSmart Notes - f4 Chapter 5 WavesJenjen StNo ratings yet
- Modul Galus Chem 2014Document83 pagesModul Galus Chem 2014Juni Farhana100% (2)
- Latihan Bab 3Document12 pagesLatihan Bab 3Hasnah GhaniNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Bab 1-Bab 5Document15 pagesJawapan Bab 1-Bab 5Nurul AzuwinNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Kimia JPNDocument86 pagesModul Cemerlang Kimia JPNA9951983% (6)
- 6 Displacement of Halogen From Its Halide SolutionDocument9 pages6 Displacement of Halogen From Its Halide SolutionJedidah JongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 P2Document29 pagesChapter 9 P2Hafizasharin OthmanNo ratings yet
- Group Discussion G Group Discussion HDocument5 pagesGroup Discussion G Group Discussion HMohd Afiffi BaharuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 P2Document20 pagesChapter 7 P2Amelia SuidNo ratings yet
- Structure Questions: 1. SPM 2013: QUESTION 3Document22 pagesStructure Questions: 1. SPM 2013: QUESTION 3Cart KartikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 P2Document20 pagesChapter 7 P2siewkiemNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 7 QPDocument16 pagesElectric Circuits 7 QPChong Xue ErNo ratings yet
- Module Electronic 2020Document22 pagesModule Electronic 2020Cart KartikaNo ratings yet
- MRSM08P2SAQ8: Structured Question: (Force On Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field)Document10 pagesMRSM08P2SAQ8: Structured Question: (Force On Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field)ChewLee TanNo ratings yet
- Structured Question 8 - 1Document8 pagesStructured Question 8 - 1ChewLee TanNo ratings yet
- 4 7 3InducedPotentialTransformersandtheNatGrid PDFDocument69 pages4 7 3InducedPotentialTransformersandtheNatGrid PDFlNo ratings yet
- Module ElectronicsDocument20 pagesModule ElectronicsCart KartikaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities WorksheetDocument10 pagesElectrical Quantities WorksheetMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- 1.electricity p2 Organized CompleteDocument53 pages1.electricity p2 Organized CompletedfsdfNo ratings yet