Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sains Form 3 - CHAPTER 1
Sains Form 3 - CHAPTER 1
Uploaded by
Encik F YusuffOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sains Form 3 - CHAPTER 1
Sains Form 3 - CHAPTER 1
Uploaded by
Encik F YusuffCopyright:
Available Formats
1
CHAPTER 1: RESPIRATION
1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism
Breathing is a physical process in which air is inhaled or taken in and exhaled or given out by
a living body.
Air enters the nose through both nostrils. The walls of the nostrils are lined with hairs to trap
dust particles in the air.
From the nostrils, air enters the nasal cavity. The nasal cavity secretes mucus to trap bacteria
and other foreign particles in the inhaled air.
From the nasal cavity, air enters the trachea.
The trachea does not collapse because it is kept open by rings of cartilage. These cartilage
rings are C-shaped.
The trachea branches into a left bronchus and a right bronchus. Each bronchus goes into a
lung.
Each bronchus then branches into smaller tubes called bronchioles.
These tubes end in many tiny air sacs called alveoli.
The alveoli are surrounded by blood capillaries.
Gaseous exchange takes place in the lungs by diffusion.
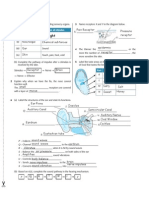
The pathway of air flowing into our lungs is as follows:
Nostril nasal
cavity
pharynx trachea
bronchi bronchioles
alveoli
2
Comparison between inhalation and exhalation mechanisms
Inhalation
Part Involved
Exhalation
Contracts External intercostal muscle Relaxes
Relaxes Internal intercostal muscle Contracts
Moves upwards and
outwards
Movement of ribs Moves downwards and
inwards
Contracts, moves
downwards and flattens
Diaphragm Relaxes and curves
upwards
Increases Volume of thoracic cavity Decreases
Decreases Air pressure in the
thoracic cavity
Increases
Air is inhaled into the
lungs
Air movement Air in the lungs is forced
out
1.2 Transport of Oxygen In The Human Body
The air that enters the lungs fills up the alveoli.
Oxygen from the air then diffuses into the blood capillaries.
It combines with the haemoblobin in the red blood cells to form oxyhaemoglobin.
Oxygen + haemoglobin oxyhaemoglobin
The blood carries the oxygen in the form of oxyhaemoglobin to all parts of the body.
When the oxygenated blood reaches tissues or cells that do not have enough oxygen, the
oxyhaemoglobin breaks down and releases the oxygen.
The oxygen diffuses through the capillaries into the cells.
Adaptation of the alveoli for efficient gas exchange
1. Large surface area
2. Very thin walls
3. Moist inner surface
4. Surrounded by a network of blood capillaries
3
1.3 T he Important of A Healthy Respiratory System
Substances harmful to the respiratory system
Chemical Substances Harmful effect on the respiratory system
a. Nicotine Causes illnesses like bronchitis, throat cancer and
lung cancer
b. Tobacco tar Blackens the lungs
Lung cancer
kills cells in the air passages and the lungs
increases production of mucus and phlegm in the
lungs
c. Carcinogen Stimulates the growth of cancer cells, causing
lung cancer and throat cancer
d. Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen
dioxide
Damages the breathing channel and lungs
e. Carbon monoxide prevents haemoglobin from transporting oxygen
around the body
causes a lack of oxygen in our body which may lead
to headaches, brain damage or even death
f. Forest fire and open burning
(Haze)
Irritates the respiratory system, causing respiratory
disorders such as asthma
g. Burning plastic material
(Hydrogen chloride, ammonia
and hydrogen cyanide)
Corrodes the breathing channel
4
Diseases of the respiratory system
Diseases Symptoms
a. Lung emphysema
the abnormal growth of the cells lining the fine air
vessels in the lungs which block the air vessels.
the alveoli swell and burst
shortness of breath
the feeling of pain while breathing
tiredness
b. Bronchitis
is the inflammation of the bronchi caused by tar and
the irritants in cigarette smoke
continuous coughing(smokers
cough)
constant breathlessness
sleeplessness
c. Lung cancer
unusual cell growths in the lungs
carcinogen is the cause of cancer
regular coughing
blood in the sputum
feeling of pain while breathing
d. Asthma
is caused by the inflammation of the breathing
channel
breathing channel suddenly becomes narrow causing
difficulty in breathing
very sensitive to certain allergens
shortness of breath
wheezing
excessive coughing
e. Influenza
is caused by viruses which attack the mucus
membranes in the respiratory system
blocked noses, teary eyes, giddiness
headaches, aches in the limbs
coughs and fever
f. Pneumonia
is caused by bacteria, viruses and chemical
substances
trachea and alveolus are attacked by bacteria and
viruses
lungs are filled with pus and fluid
chest pains
coughs and fever
g. Tuberculosis
is caused by bacterial infection (Mycobacterium
tuberculosis)
prolonged coughs and spits out
blood in the end stages
You might also like
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1-10Document16 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1-10Nur Atiah Daud57% (7)
- Exercise Chapter 2 Physics Form 4Document4 pagesExercise Chapter 2 Physics Form 4afiqiman8950% (2)
- Basic Life Support 2020Document69 pagesBasic Life Support 2020vidyashetty007100% (2)
- CO-pgm14 EDocument8 pagesCO-pgm14 EAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDocument5 pagesF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Document14 pagesTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanNo ratings yet
- FORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversityDocument15 pagesFORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversitySyahrul100% (11)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2Document31 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 2rosya100% (5)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- Photosynthesis Notes - BiologyDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes - Biologythe lillyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Birth AsphyxiaDocument14 pagesPathophysiology of Birth AsphyxiaEduardo Rios DuboisNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument18 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionAutumn JJ100% (3)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 5Document62 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 5qq23585% (41)
- Nutrition Notes Science Form 2Document9 pagesNutrition Notes Science Form 2Veloo Gunasagaran100% (3)
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemOyrik Mukhopadhyay100% (1)
- Form 3 Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 3 Chapter 10naza977575% (4)
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Ck OoiNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of MetalsDocument11 pagesForm 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of Metalsgrace_lo_1100% (1)
- Mid Term Form 1 2004Document13 pagesMid Term Form 1 2004Ct HusnaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science NoteDocument16 pagesForm 2 Science NoteMyName Tiff94% (16)
- Respiration Form 3Document21 pagesRespiration Form 3Chin Kok SoonNo ratings yet
- Form 3 ScienceDocument10 pagesForm 3 ScienceCK100% (1)
- Respiration Form 3Document21 pagesRespiration Form 3P.m. KaruNo ratings yet
- Model Pt3Document30 pagesModel Pt3Sean Larson100% (4)
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument15 pagesBlood Circulation and Transportqas1727No ratings yet
- PT3 Science PMR HighlightsdDocument14 pagesPT3 Science PMR HighlightsdAnonymous bwVxI8Y8W100% (3)
- Form 3 Science Chapter 1Document9 pagesForm 3 Science Chapter 1Mohamad Harith100% (1)
- P 2Document7 pagesP 2qq235100% (3)
- Year 5 Science:HeatDocument7 pagesYear 5 Science:HeatRaj King50% (2)
- SPM Biology NotesDocument32 pagesSPM Biology NotesAin Fza0% (1)
- Science Answer Scheme Paper 1 and 2 Form1 09Document6 pagesScience Answer Scheme Paper 1 and 2 Form1 09azmijaaffarNo ratings yet
- Biology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2Document13 pagesBiology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2SanjeefKumrIINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 QuestionDocument9 pagesChapter 3 QuestionShila KaurNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4Document95 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 4Eric Chew100% (1)
- Biology Form 4: Chapter 7 - RespirationDocument3 pagesBiology Form 4: Chapter 7 - RespirationGerard Selvaraj100% (1)
- Nutrition - Energy Value in FoodDocument15 pagesNutrition - Energy Value in FoodZurainy Md IsaNo ratings yet
- Pt3 Science Seminar ModuleDocument28 pagesPt3 Science Seminar ModuleSuntharan Muniandy100% (5)
- Biology SPM Hots Questions & Answers (2020)Document9 pagesBiology SPM Hots Questions & Answers (2020)Sushi Emilia100% (1)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 6Document9 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 6Syazwani Radzi100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDocument39 pagesChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideMuhd Rifaie RodzilNo ratings yet
- Science F3 RespirationDocument3 pagesScience F3 RespirationSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 4 Variety of Resources On EarthDocument5 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 4 Variety of Resources On EarthSyahrul100% (1)
- SPM Form 4 Notes Introduction To ChemistryDocument1 pageSPM Form 4 Notes Introduction To ChemistryMimie Yasmin KamalNo ratings yet
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocument16 pagesPMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science, Chapter 1Document47 pagesForm 3 Science, Chapter 1qq23586% (56)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 3 - Excretion PDFDocument2 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 3 - Excretion PDFFarah Sofea Razali57% (7)
- CHAPTER 1 Form 4 BIOLOGY SPMDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 1 Form 4 BIOLOGY SPMCrescentiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Document9 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Steven Wong50% (2)
- Chapter 1: Respiration: 1.1 Human Breathing MechanismDocument7 pagesChapter 1: Respiration: 1.1 Human Breathing Mechanismsufi_sobariah8044No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemArjunNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Lecture1Document43 pagesRespiratory Lecture1Angel CepedaNo ratings yet
- Human Breathing MechanismDocument5 pagesHuman Breathing MechanismAngsNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 3: Science Form 3Document27 pagesSains Tingkatan 3: Science Form 3Nadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 9Document23 pagesRespiratory System 9scaythereignNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemMotiourNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument36 pagesBiologymaleeha shahzadNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideDocument22 pagesRespiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Respiratory SysteDocument5 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory SysteMohd FirdausNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Chapter 1Document25 pagesForm 3 Science Chapter 1Mukilan MurugasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismWindy SanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesRespiratory SystemLulaNo ratings yet
- Hole'S Human Anatomy and Physiology: Powerpoint Lecture Outlines To AccompanyDocument52 pagesHole'S Human Anatomy and Physiology: Powerpoint Lecture Outlines To AccompanyEllen LiberaceNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem Pernafasan - Id.enDocument7 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem Pernafasan - Id.enCindy Ari SantiNo ratings yet
- General Introduction: Respiration Takes Place in Four StagesDocument4 pagesGeneral Introduction: Respiration Takes Place in Four Stagesriskyy1No ratings yet
- Macmillan Publishers LTD 2002 63 This Page May Be Photocopied For Use in ClassDocument2 pagesMacmillan Publishers LTD 2002 63 This Page May Be Photocopied For Use in ClassAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- IPA Place and Manner of Articulation 1Document33 pagesIPA Place and Manner of Articulation 1Autumn JJNo ratings yet
- Clock Worksheet 1: Write The TimeDocument2 pagesClock Worksheet 1: Write The TimeAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- Discussing Dating: Blind DatesDocument2 pagesDiscussing Dating: Blind DatesAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- Word Problem Worksheet 4Document1 pageWord Problem Worksheet 4Autumn JJNo ratings yet
- Word Problem Worksheet 5Document1 pageWord Problem Worksheet 5Autumn JJNo ratings yet
- Word Problem Worksheet 2Document1 pageWord Problem Worksheet 2Autumn JJNo ratings yet
- Word Problem Worksheet 1Document1 pageWord Problem Worksheet 1Autumn JJNo ratings yet
- Word Problem Worksheet 3Document1 pageWord Problem Worksheet 3Autumn JJNo ratings yet
- Few Essential Ways That Will Help To Prevent PollutionDocument1 pageFew Essential Ways That Will Help To Prevent PollutionAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- Talk No 2 Does The Bible Say That Some Will Never Be SavedDocument2 pagesTalk No 2 Does The Bible Say That Some Will Never Be SavedAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- Thank You For Your Understanding of My Decision To Leave The Company, and All Your Support. I Wish You All The Best For Your Continued SuccessDocument1 pageThank You For Your Understanding of My Decision To Leave The Company, and All Your Support. I Wish You All The Best For Your Continued SuccessAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- 1 Corinthians 9Document2 pages1 Corinthians 9Autumn JJNo ratings yet
- The Railway Children (Short Summary)Document2 pagesThe Railway Children (Short Summary)Autumn JJ100% (1)
- Aaron - Ways in Which Aaron Was A Good Example For ChristiansDocument2 pagesAaron - Ways in Which Aaron Was A Good Example For ChristiansAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- Title: There Is No Bible Record of Adams Keeping A SabbathDocument2 pagesTitle: There Is No Bible Record of Adams Keeping A SabbathAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of God's NameDocument1 pageThe Meaning of God's NameAutumn JJNo ratings yet
- Talk No 2Document4 pagesTalk No 2Autumn JJNo ratings yet
- Emergency Ab Osce 2017Document22 pagesEmergency Ab Osce 2017Alwaallh MohammedNo ratings yet
- Toate Bolile CardiovasculareDocument6 pagesToate Bolile CardiovasculareAnca CopreanNo ratings yet
- L1 - SyncopeDocument5 pagesL1 - SyncopeMuthukumaranNo ratings yet
- Conn's Syndrome in A Male Adult With Uncontrolled Hypertension A Case ReportDocument2 pagesConn's Syndrome in A Male Adult With Uncontrolled Hypertension A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- DrowningDocument9 pagesDrowningCarlos Alberto Torres LópezNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region XI Division of Davao CityDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region XI Division of Davao CityCYNTHIA GALEONNo ratings yet
- ElectrocitoDocument17 pagesElectrocitobachiusach2008No ratings yet
- Biochemistry BC Ii: Lecture On GlycolysisDocument17 pagesBiochemistry BC Ii: Lecture On GlycolysisMusonda MulengaNo ratings yet
- Amboss - Cradiac CycleDocument18 pagesAmboss - Cradiac CycleAllysahNo ratings yet
- EngresearchpaperDocument12 pagesEngresearchpaperapi-488128601No ratings yet
- InhalDocument33 pagesInhallupeNo ratings yet
- Conduction of The HeartDocument1 pageConduction of The HeartPearlyn John BrittoNo ratings yet
- Transport Mecha Wps Office 1Document17 pagesTransport Mecha Wps Office 1Gelu SyNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Submitted For The Completion Of: (Declared As Deemed University Under Section 3 of The UGC Act, 1956)Document120 pagesDissertation Submitted For The Completion Of: (Declared As Deemed University Under Section 3 of The UGC Act, 1956)venkata karthikNo ratings yet
- 7 Principles of Exercise and Sport TrainingDocument2 pages7 Principles of Exercise and Sport TrainingSheikh MohdNo ratings yet
- Ruminant Nutrition Nutrient Partitioning in LactationDocument24 pagesRuminant Nutrition Nutrient Partitioning in Lactationamritnam satyadasNo ratings yet
- Zoology 4Document18 pagesZoology 4danishNo ratings yet
- Ketosis and KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesKetosis and KetoacidosisRajalakshmi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Managing Stress Through Physical ActivityDocument6 pagesManaging Stress Through Physical ActivityNiña Joyce AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Homeostasis MSDocument4 pages5.1 Homeostasis MSMareeb ShahNo ratings yet
- IJGMP - RV Function Assessment Pre and Post PTMC in Patients With Severe - AutosavedDocument8 pagesIJGMP - RV Function Assessment Pre and Post PTMC in Patients With Severe - AutosavedImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid CompartmentsDocument26 pagesBody Fluid CompartmentsShameena KnNo ratings yet
- Dabl Educational TrustMonitors For Self-Measurement of Blood Pressure (SBPM)Document1 pageDabl Educational TrustMonitors For Self-Measurement of Blood Pressure (SBPM)iranbengoaNo ratings yet
- BOTANY FIRST PAPER (Plant Morphology and Anatomy)Document4 pagesBOTANY FIRST PAPER (Plant Morphology and Anatomy)GuruKPO100% (2)
- PaCO2 and End-Tidal PCO2Document3 pagesPaCO2 and End-Tidal PCO2phobicmdNo ratings yet
- Biolevox HA TENDON Extended PresentationDocument32 pagesBiolevox HA TENDON Extended PresentationABUBAKER ZANBOUZINo ratings yet