Professional Documents
Culture Documents
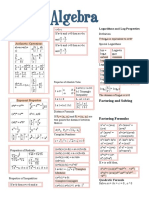
Algebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & Facts
Uploaded by
alisaqiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & Facts
Uploaded by
alisaqiCopyright:
Available Formats
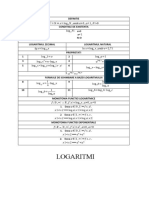
Logarithms and Log Properties
Definition
y = log b x is equivalent to x = b y
Algebra Cheat Sheet
Basic Properties & Facts
Properties of Inequalities
If a < b then a + c < b + c and a - c < b - c
Arithmetic Operations
b ab
a =
c c
ab + ac = a ( b + c )
a
a
b =
c
bc
a b
<
c c
a b
If a < b and c < 0 then ac > bc and >
c c
If a < b and c > 0 then ac < bc and
a
ac
=
b b
c
a c ad + bc
+ =
b d
bd
a c ad - bc
- =
b d
bd
a-b b-a
=
c-d d -c
a+b a b
= +
c
c c
a
b ad
=
c bc
d
ab + ac
= b + c, a 0
a
Properties of Absolute Value
if a 0
a
a =
if a < 0
-a
a 0
-a = a
a +b a + b
Exponent Properties
an
1
= a n -m = m -n
am
a
a na m = a n+ m
(a )
n m
( ab )
a
-n
= a nm
a 0 = 1, a 0
n
=a b
1
= n
a
a
b
-n
bn
b
= = n
a
a
n
m
a =a
m n
1
n
a = nm a
( ) = (a )
a = a
Properties of Radicals
Complex Numbers
i = -1
1
m
1
m
i = -1
-a = i a, a 0
( a + bi ) + ( c + di ) = a + c + ( b + d ) i
( a + bi ) - ( c + di ) = a - c + ( b - d ) i
( a + bi )( c + di ) = ac - bd + ( ad + bc ) i
( a + bi )( a - bi ) = a 2 + b2
ab = a b
a + bi = a + b
a na
=
b nb
( a + bi ) = a - bi Complex Conjugate
2
( a + bi )( a + bi ) = a + bi
a n = a , if n is odd
a n = a , if n is even
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
) = r log
x
log b = log b x - logb y
y
The domain of log b x is x > 0
Quadratic Formula
Solve ax 2 + bx + c = 0 , a 0
x 2 + 2ax + a 2 = ( x + a )
x 2 - 2 ax + a 2 = ( x - a )
-b b 2 - 4 ac
2a
If b 2 - 4ac > 0 - Two real unequal solns.
If b 2 - 4ac = 0 - Repeated real solution.
If b 2 - 4ac < 0 - Two complex solutions.
x=
x 2 + ( a + b ) x + ab = ( x + a )( x + b )
x3 - a 3 = ( x - a ) ( x2 + ax + a 2 )
b logb x = x
Factoring Formulas
x 2 - a 2 = ( x + a )( x - a )
d ( P1 , P2 ) =
+ ( y2 - y1 )
log b ( xy ) = log b x + logb y
log x = log 10 x common log
where e = 2.718281828K
x3 + 3ax 2 + 3a 2 x + a 3 = ( x + a )
log b ( x
Special Logarithms
ln x = log e x
natural log
Distance Formula
If P1 = ( x1, y1 ) and P2 = ( x2 , y2 ) are two
points the distance between them is
a
a
= n
b
b
1
n
=a
a-n
n n
Triangle Inequality
( x2 - x1 )
log b b x = x
Example
log 5 125 = 3 because 53 = 125
Factoring and Solving
a
a
=
b
b
ab = a b
Logarithm Properties
log b b = 1
log b 1 = 0
Complex Modulus
x3 - 3ax2 + 3a 2 x - a 3 = ( x - a )
Square Root Property
If x2 = p then x = p
x3 + a 3 = ( x + a ) ( x2 - ax + a 2 )
Absolute Value Equations/Inequalities
If b is a positive number
p =b
p = - b or p = b
x 2 n - a 2 n = ( x n - a n )( x n + a n )
If n is odd then,
x n - a n = ( x - a ) ( x n-1 + ax n -2 + L + a n -1 )
xn + an
= ( x + a)( x
n -1
- ax
n -2
2 n -3
+a x
-L + a
n -1
-b < p < b
p >b
p < - b or
p>b
Completing the Square
(4) Factor the left side
Solve 2 x 2 - 6 x - 10 = 0
(1) Divide by the coefficient of the x
x 2 - 3x - 5 = 0
(2) Move the constant to the other side.
x 2 - 3x = 5
(3) Take half the coefficient of x, square
it and add it to both sides
2
9 29
3
3
x 2 - 3x + - = 5 + - = 5 + =
4 4
2
2
2005 Paul Dawkins
p <b
3
29
x- =
2
4
(5) Use Square Root Property
3
29
29
x- =
=
2
4
2
(6) Solve for x
3
29
x=
2
2
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
2005 Paul Dawkins
Functions and Graphs
Constant Function
y = a or
f ( x) = a
Graph is a horizontal line passing
through the point ( 0, a ) .
The graph is a parabola that opens right
if a > 0 or left if a < 0 and has a vertex
b
b
at g - , - .
2a 2a
Line/Linear Function
y = mx + b or f ( x ) = mx + b
Graph is a line with point ( 0,b ) and
slope m.
Circle
2
2
( x - h) + ( y - k ) = r2
Graph is a circle with radius r and center
( h, k ) .
Slope
Slope of the line containing the two
points ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) is
y2 - y1 rise
=
x2 - x1 run
Slope intercept form
The equation of the line with slope m
and y-intercept ( 0,b ) is
y = mx + b
Point Slope form
The equation of the line with slope m
and passing through the point ( x1 , y1 ) is
m=
y = y1 + m ( x - x1 )
( x - h)
f ( x) = a ( x - h) + k
2
The graph is a parabola that opens up if
a > 0 or down if a < 0 and has a vertex
at ( h, k ) .
Parabola/Quadratic Function
y = ax 2 + bx + c f ( x ) = ax 2 + bx + c
The graph is a parabola that opens up if
a > 0 or down if a < 0 and has a vertex
b
b
at - , f - .
2a 2a
( y - k)
+
=1
a2
b2
Graph is an ellipse with center ( h, k )
with vertices a units right/left from the
center and vertices b units up/down from
the center.
( x - h)
(y -k)
( y - k)
=1
( x - h) = 1
b2
a2
Graph is a hyperbola that opens up and
down, has a center at ( h, k ) , vertices b
units up/down from the center and
asymptotes that pass through center with
b
slope .
a
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
Division by zero is undefined!
-32 9
-32 = -9 ,
(x
(x
2 3
x5
a
a a
+
b+c b c
1
x -2 + x-3
x2 + x3
( x + a)
x2 + a2 x + a
( x + a)
( -3)
= 9 Watch parenthesis!
= x2 x2 x 2 = x6
( x + a)
x2 + a 2
x+a
2 3
1
1
1 1
=
+ =2
2 1+ 1 1 1
A more complex version of the previous
error.
a + bx a bx
bx
= +
=1+
a
a a
a
Beware of incorrect canceling!
- a ( x - 1) = - ax + a
Make sure you distribute the -!
a + bx
1 + bx
a
x+ a
x n + a n and
2 ( x + 1) ( 2 x + 2 )
( 2x + 2)
a
b
Graph is a hyperbola that opens left and
right, has a center at ( h, k ) , vertices a
units left/right of center and asymptotes
b
that pass through center with slope .
a
Hyperbola
2
Reason/Correct/Justification/Example
2
2
0 and 2
0
0
x+a
x+n a
= ( x + a )( x + a ) = x 2 + 2 ax + a 2
5 = 25 = 3 2 + 4 2 3 2 + 4 2 = 3 + 4 = 7
See previous error.
More general versions of previous three
errors.
2 ( x + 1) = 2 ( x2 + 2 x + 1) = 2 x 2 + 4 x + 2
2
Hyperbola
2
Error
- a ( x - 1) - ax - a
Ellipse
Parabola/Quadratic Function
y = a ( x - h) + k
Common Algebraic Errors
Parabola/Quadratic Function
x = ay2 + by + c g ( y ) = ay2 + by + c
2005 Paul Dawkins
2 ( x + 1)
( 2x + 2)
= 4 x2 + 8x + 4
Square first then distribute!
See the previous example. You can not
factor out a constant if there is a power on
the parethesis!
1
- x2 + a2 - x2 + a2
a
ab
b c
c
a
ac
b
c
b
- x2 + a2 = ( - x2 + a2 )2
Now see the previous error.
a
1
a
a c ac
= = =
b b 1 b b
c c
a a
b = b = a 1 = a
c
c b c bc
1
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
2005 Paul Dawkins
You might also like
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Logarithm Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLogarithm Cheat SheetM J Rhoades82% (11)
- Trig Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat SheetDino97% (77)
- Calculus Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesCalculus Cheat SheetDino99% (75)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesAlgebra Cheat Sheet ReducedAli NaqviNo ratings yet
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionFrom EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionNo ratings yet
- Complete Algebra Calculus Laplace Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesComplete Algebra Calculus Laplace Cheat SheetJeremy100% (3)
- Algebra: Basic Properties & FactsDocument2 pagesAlgebra: Basic Properties & FactsJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Summary NotesDocument3 pagesAdditional Mathematics Summary NotesDavid Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Formulae CheatsheetDocument36 pagesFormulae CheatsheetMalathiVeluNo ratings yet
- Math RecitationDocument31 pagesMath RecitationGadiel SouzaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat SheetLiona NdayNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970From EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNo ratings yet
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDocument17 pagesEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebradeenaNo ratings yet
- Logarithm Properties With Examples PDFDocument2 pagesLogarithm Properties With Examples PDFgoserunner100% (2)
- Calculus For The Life Sciences Modelling The Dynamics of Life PDFDocument800 pagesCalculus For The Life Sciences Modelling The Dynamics of Life PDFNarsilium nq100% (5)
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Document11 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4THINES REVI100% (12)
- LOGARITMIDocument1 pageLOGARITMIAndreea Ioana AnutiNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules For Algebra & Logarithmic Functions: Quadratic Formula: ExampleDocument3 pagesBasic Rules For Algebra & Logarithmic Functions: Quadratic Formula: ExampleAdrian Roderick NavasNo ratings yet
- Home Test-03 - LogarithmDocument4 pagesHome Test-03 - LogarithmSrinibas DasNo ratings yet
- EO101 Foundations Wk1 Pt2 Fractions Reading Answers S1920Document6 pagesEO101 Foundations Wk1 Pt2 Fractions Reading Answers S1920extramailm2No ratings yet
- Exponents/Logs/Complex NumbersDocument2 pagesExponents/Logs/Complex Numbersmishi19No ratings yet
- UNIT # 02 PART-1:: Exercise - 01 Check Your GraspDocument6 pagesUNIT # 02 PART-1:: Exercise - 01 Check Your GraspKaushal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Definitions & Results of MathsDocument92 pagesDefinitions & Results of MathsdjbhutadaNo ratings yet
- Thomas Calculus Early Transcendentals Fifteenth Edition Joel Hass All ChapterDocument67 pagesThomas Calculus Early Transcendentals Fifteenth Edition Joel Hass All Chapterramona.evans546100% (6)
- Year 11 MathsDocument19 pagesYear 11 MathsSyed HasanNo ratings yet
- 109 SummarydddDocument8 pages109 Summarydddstfirstfir stlastlaNo ratings yet
- Mac OS X Terminal Commands ListDocument5 pagesMac OS X Terminal Commands ListDino100% (29)
- Client Questionnaire For Web DevelopersDocument1 pageClient Questionnaire For Web DevelopersDino89% (9)
- Bioshock ArtbookDocument78 pagesBioshock ArtbookDino92% (24)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Complete Hip-Hop Radio Station Listing (USA)Document4 pagesComplete Hip-Hop Radio Station Listing (USA)Dino99% (192)
- Production Efficiency Worksheet TemplateDocument2 pagesProduction Efficiency Worksheet TemplateDino100% (10)
- Business Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesBusiness Plan TemplateDino98% (470)
- Performance and Behavioral InterviewingDocument40 pagesPerformance and Behavioral InterviewingDino100% (7)
- MA206 Midterm IDocument2 pagesMA206 Midterm ISanjoy BrahmaNo ratings yet
- Complex DerivativesDocument16 pagesComplex DerivativesKofi Appiah-DanquahNo ratings yet
- IX-Maths-Exponents and Logarithm-Niraj Keshri (Final)Document9 pagesIX-Maths-Exponents and Logarithm-Niraj Keshri (Final)Aditya ParuiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Integration by Parts & Algebraic SubstitutionDocument19 pagesLesson 8 Integration by Parts & Algebraic SubstitutionMarvin James JaoNo ratings yet
- Courses of Study - MALDocument12 pagesCourses of Study - MALAbhishek Singh100% (1)
- Notes - Calculus II - Taylor SeriesDocument10 pagesNotes - Calculus II - Taylor Seriest_rajith1179No ratings yet
- 8-6 Law of Sines and Cosines (Presentation)Document16 pages8-6 Law of Sines and Cosines (Presentation)Sandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - Binomial SeriesDocument3 pagesCalculus II - Binomial SeriesDahanyakage WickramathungaNo ratings yet
- A Comment On Methods To Deal With Divergent Series and IntegralsDocument14 pagesA Comment On Methods To Deal With Divergent Series and Integralseljose1234100% (2)
- Chapter - 3 - Differentiation - of - Transcendental - Functions - PDF Filename UTF-8''Chapter 3 - Differentiation of Transcendental Functions PDFDocument5 pagesChapter - 3 - Differentiation - of - Transcendental - Functions - PDF Filename UTF-8''Chapter 3 - Differentiation of Transcendental Functions PDFchicken nuggetsNo ratings yet
- Winitzki - Approximation To Error FunctionDocument3 pagesWinitzki - Approximation To Error Functionwinitzki100% (1)
- Numerical Series: 7. Solved ProblemsDocument22 pagesNumerical Series: 7. Solved ProblemsMarian LupulescuNo ratings yet
- Logarithms Practice: Created by T. MadasDocument22 pagesLogarithms Practice: Created by T. MadasLoriana AndreiNo ratings yet
- Math 112 Module 10 Derivative of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument30 pagesMath 112 Module 10 Derivative of Trigonometric Functionspangcheat pubgNo ratings yet
- Hints and Solution Binomial Theorem UyhgQkhDocument69 pagesHints and Solution Binomial Theorem UyhgQkhRøyal Sujal SinhaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 4.1-4.4 - NO CALC: Find The Value of The Trig Function IndicatedDocument2 pagesPractice Test 4.1-4.4 - NO CALC: Find The Value of The Trig Function Indicatedrust accNo ratings yet
- Trignometry and Complex Numbers Importent Questions List For Diploma Holders PDFDocument5 pagesTrignometry and Complex Numbers Importent Questions List For Diploma Holders PDFSivaramakrishna NallajarlaNo ratings yet
- Physics 152 (Final) Formula Sheet Fall 2021Document2 pagesPhysics 152 (Final) Formula Sheet Fall 2021emily gNo ratings yet
- Radicals and Rational ExponentsDocument2 pagesRadicals and Rational ExponentsGhasem KhanNo ratings yet
- Laplace and Fourier Table PDFDocument1 pageLaplace and Fourier Table PDFafiqNo ratings yet
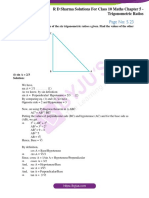
- RD Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 5 Trigonometric Ratios Exercise 5.1 PDFDocument28 pagesRD Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 5 Trigonometric Ratios Exercise 5.1 PDFJay RajputNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.3 - Formula - Laplace TransformDocument3 pagesChapter 3.3 - Formula - Laplace TransformEncik MaaNo ratings yet
- Assignment MATH2001 ModIIIDocument1 pageAssignment MATH2001 ModIIIBarshan RoyNo ratings yet
- ComplexDocument35 pagesComplexKetso MolapoNo ratings yet
- B.tech MDU Syllabus (CSE)Document83 pagesB.tech MDU Syllabus (CSE)Prakshi JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Fourier Series)Document10 pagesChapter 4 (Fourier Series)EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Frobenius ExamplesDocument3 pagesFrobenius ExamplespoozarNo ratings yet
- SL 2.8-2.10 Exponents and LogarithmsDocument26 pagesSL 2.8-2.10 Exponents and LogarithmsZeynep Aysu İskenderNo ratings yet
- Math12-1 - Lesson 3 - Trigonometric Functions of AnglesDocument12 pagesMath12-1 - Lesson 3 - Trigonometric Functions of AnglesKobe MartinezNo ratings yet
- 三角函数定理Document21 pages三角函数定理Jonathan HookNo ratings yet
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Math-ish: Finding Creativity, Diversity, and Meaning in MathematicsFrom EverandMath-ish: Finding Creativity, Diversity, and Meaning in MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Classroom-Ready Number Talks for Third, Fourth and Fifth Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Math Activities that Promote Conceptual Understanding and Computational FluencyFrom EverandClassroom-Ready Number Talks for Third, Fourth and Fifth Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Math Activities that Promote Conceptual Understanding and Computational FluencyNo ratings yet