Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical Work Formula
Uploaded by
vikass0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
387 views4 pagesMechanical Work Formula
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMechanical Work Formula
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
387 views4 pagesMechanical Work Formula
Uploaded by
vikassMechanical Work Formula
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
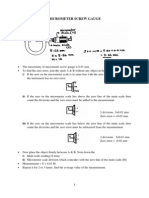
Worked example 3.
3
What is the potential energy of a 10kg mass:
a. 100m above the surface of the earth
b. at the bottom of a vertical mine shaft 1000m deep.
Solution
a)
b)
Back to the top
Kinetic energy
Kinetic energy may be described as energy due to motion.
The kinetic energy of a body may be defined as the amount of work it can do before
being brought to rest.
For example when a hammer is used to knock in a nail, work is done on the nail by
the hammer and hence the hammer must have possessed energy.
Only linear motion will be considered here.
Back to the top
Formulae for kinetic energy
Let a body of mass m moving with speed v be brought to rest with uniform
deceleration by a constant force F over a distance s.
Using Equation 1.4
And work done is given by
The force is F = ma so
Thus the kinetic energy is given by
Equation 3.4
Back to the top
Kinetic energy and work done
When a body with mass m has its speed increased from u to v in a distance s by a
constant force F which produces an acceleration a, then from Equation 1.3 we know
multiplying this by m give an expression of the increase in kinetic energy (the
difference in kinetic energy at the end and the start)
Thus since F = ma
but also we know
So the relationship between kinetic energy can be summed up as
Work done by forces acting on a body = change of kinetic energy in the body
Equation 3.5
This is sometimes known as the work-energy theorem.
You might also like
- Light Prism Pandathe Test2 Question PaperDocument4 pagesLight Prism Pandathe Test2 Question Paperboltu100% (1)
- Magnetic Braking System Report - 2nd Year ProjectDocument11 pagesMagnetic Braking System Report - 2nd Year Projectfransisca rumendeNo ratings yet
- EDEXCEL MODEL PHYSICS ANSWERS 1995-2001 (04-Oct-10)Document265 pagesEDEXCEL MODEL PHYSICS ANSWERS 1995-2001 (04-Oct-10)Radiant ree100% (1)
- Problem Solving: Dr. Saima Shabbir, MSE, ISTDocument15 pagesProblem Solving: Dr. Saima Shabbir, MSE, ISTOsama Aadil SaadiNo ratings yet
- Ec6304 Electronic Circuits-I OldDocument204 pagesEc6304 Electronic Circuits-I OldVijayakumar SNo ratings yet
- 5 Work, Energy and PowerDocument39 pages5 Work, Energy and PowerGeanelle BonilloNo ratings yet
- DifferencesDocument3 pagesDifferenceschhabra navdeep100% (1)
- Topic 2: KinematicsDocument129 pagesTopic 2: KinematicsWee Chee Lim100% (1)
- 5.1 ElectronDocument53 pages5.1 ElectronFarish MikhaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Conservation of Energy and MomentumDocument40 pagesChapter 7 - Conservation of Energy and Momentumascd_msvuNo ratings yet
- CH 23 Thermal Questions - KEYDocument3 pagesCH 23 Thermal Questions - KEYShe DilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 ElectronicsDocument107 pagesChapter 21 ElectronicsPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- 2014 Electrical Systems-StudentDocument53 pages2014 Electrical Systems-StudentKim TaehyungNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionzaira_rq3551No ratings yet
- WorkEnergy P2Document26 pagesWorkEnergy P2dhairya gandhi100% (1)
- Electricity NOTES-physics-SCIENCE SECONDARY CHECKPOINTDocument11 pagesElectricity NOTES-physics-SCIENCE SECONDARY CHECKPOINTsusan hiraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - Sound WavesDocument4 pagesIGCSE - Sound WavesUsman SirNo ratings yet
- Motor EffectDocument3 pagesMotor EffectRaj ChandaranaNo ratings yet
- Physics A-Level ExperimentsDocument15 pagesPhysics A-Level ExperimentsmariostevNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument55 pagesForces and MotionTreeicicles100% (3)
- Physics Paper 6 QA CardsDocument17 pagesPhysics Paper 6 QA CardsSmr Only100% (5)
- Conservation of Energy QuizDocument2 pagesConservation of Energy QuizJay Noma RamosNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Review Worksheet With AnswersDocument2 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion Review Worksheet With AnswersVicious core100% (1)
- Momentum QPDocument6 pagesMomentum QPXandws -IOS tips and trick and gamingNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Chapter 6 PDFDocument17 pagesIGCSE Physics Chapter 6 PDFtasmiah100% (2)
- Micrometer Screw GaugeDocument5 pagesMicrometer Screw Gaugepraphul4uNo ratings yet
- Applications of Physics Part 1Document11 pagesApplications of Physics Part 1Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Work, Energy, PowerDocument57 pagesChapter 06 Work, Energy, PowerPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion QuestionsDocument4 pagesLaws of Motion QuestionsRajesh DeyNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document22 pagesTopic 3ChaudhryAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Common Questions IGCSE Physics - Version 1Document3 pagesCommon Questions IGCSE Physics - Version 1RidwanAbrarNo ratings yet
- Physics 1Document150 pagesPhysics 1omletpao100% (1)
- Turning Effect and Deformation Questions p2Document39 pagesTurning Effect and Deformation Questions p2Arko SahaNo ratings yet
- Turning Effects of Forces PDFDocument6 pagesTurning Effects of Forces PDFMazharul SamiNo ratings yet
- 0417 m17 QP 31Document8 pages0417 m17 QP 31Popi MastroianniNo ratings yet
- Answers To IGCSE Physics Revision Q's 26-01-2013Document5 pagesAnswers To IGCSE Physics Revision Q's 26-01-2013Yaw Kean HuatNo ratings yet
- 4003 Physics Section Revision Guide-1Document31 pages4003 Physics Section Revision Guide-1Noel MakambaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Waves WorksheetDocument1 pageProperties of Waves WorksheetHùng Võ HoàngNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics CheatsheetDocument11 pagesO Level Physics Cheatsheetkoh_tian_2No ratings yet
- Grade 11 İb PhysicsDocument1 pageGrade 11 İb PhysicsKemal OzturkNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Magnetic TorqueDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Magnetic TorquePathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- A Level PhysicsDocument28 pagesA Level PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- Energetics (Thermochemistry) : Page 1 of 12Document12 pagesEnergetics (Thermochemistry) : Page 1 of 12MBOTAKE Lawson100% (1)
- Student Exploration: Circuit Builder: Rebecca Rodriguez 5/7/2021Document4 pagesStudent Exploration: Circuit Builder: Rebecca Rodriguez 5/7/2021Rebecca RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Igcse 13 Forces&MovementDocument26 pagesIgcse 13 Forces&MovementHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Coloumb's Law LectureDocument69 pagesColoumb's Law LectureArslan Kiani100% (1)
- Modul Electricity 2019Document24 pagesModul Electricity 2019Cart Kartika100% (7)
- EIM Electrical Tools Winstonjun N. TuliaoDocument57 pagesEIM Electrical Tools Winstonjun N. Tuliaowinstonjun n. TuliaoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentkunalNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics ATP ReferencesDocument4 pagesO Level Physics ATP ReferencesHassan Ali BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (Unit: Ii) : One Mark QuestionsDocument13 pagesCurrent Electricity (Unit: Ii) : One Mark Questionsmechanical_lecturer100% (1)
- Physics PressureDocument35 pagesPhysics Pressuresai yadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 F2 Stars and GalaxiesDocument35 pagesChapter 11 F2 Stars and GalaxiesBernardNo ratings yet
- Ding Thethe Effects of A ForceDocument18 pagesDing Thethe Effects of A Forcenik mohamad solehinNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankFrom EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- BJT TRDocument6 pagesBJT TRvikassNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Work FormulaDocument4 pagesMechanical Work FormulavikassNo ratings yet
- Electrical FormulaDocument4 pagesElectrical FormulavikassNo ratings yet
- Electronics FormulaDocument2 pagesElectronics FormulavikassNo ratings yet
- Fisica Potencial ElectricoDocument14 pagesFisica Potencial Electricovaca16100% (13)
- Effect of Hand Rim Diameter On Manual Wheelchair Propulsion Using Mechanical Energy and Power Flow AnalysisDocument9 pagesEffect of Hand Rim Diameter On Manual Wheelchair Propulsion Using Mechanical Energy and Power Flow AnalysisavalosheNo ratings yet
- @StudyTime - Channel 09 - Work, Energy, Power (TH)Document12 pages@StudyTime - Channel 09 - Work, Energy, Power (TH)Legendary MathematicianNo ratings yet
- Week 4 General Physics 2Document7 pagesWeek 4 General Physics 2Pamela GalveNo ratings yet
- Test Bank 7Document20 pagesTest Bank 7LukeLi100% (1)
- Emrs Physics SyllabusDocument4 pagesEmrs Physics SyllabusNscience freakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEMohd Khairul Anuar100% (4)
- Aits CRT-2 Jee Main SolutionDocument22 pagesAits CRT-2 Jee Main SolutionVarri Demudu BabuNo ratings yet
- Dual Degree Syllabus 20180703 PDFDocument96 pagesDual Degree Syllabus 20180703 PDFmeerNo ratings yet
- Linear Kinetics of Human Movement - Part 3: Basic Biomechanics, 4 Edition Susan J. HallDocument19 pagesLinear Kinetics of Human Movement - Part 3: Basic Biomechanics, 4 Edition Susan J. HallSandeep BadigantiNo ratings yet
- As MechanicsDocument57 pagesAs MechanicsIkram KhanNo ratings yet
- 70 Vector 3d Part 3 of 6 PDFDocument6 pages70 Vector 3d Part 3 of 6 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument12 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapacitanceGagan DesaiNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes (Midterm 2)Document21 pagesPhysics Notes (Midterm 2)William StewartNo ratings yet
- Physics-I (Quarter-I)Document2 pagesPhysics-I (Quarter-I)Qais KaisraniNo ratings yet
- WPE SheetDocument47 pagesWPE SheetAmit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics (Set - A)Document7 pagesClass 11 Physics (Set - A)Teri MeriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Problem Solving ReviewerDocument6 pagesMathematics Problem Solving ReviewerhanselNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies DYSMEDrb222 PDFDocument7 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies DYSMEDrb222 PDFMichael PadillaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and PotentialDocument39 pagesKinetic and PotentialKrisha PoloanNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusDr Abhijeet GangulyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PPT 02Document94 pagesChapter 2 PPT 02No NameNo ratings yet
- Apdx4 PDFDocument2 pagesApdx4 PDFlotannaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Energy Conservation: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesExperiment 3 Energy Conservation: Learning Outcomes翁绍棠No ratings yet
- Ps 1Document2 pagesPs 1Ram Balaji100% (1)
- 1st PU Physics Model QP 3 PDFDocument6 pages1st PU Physics Model QP 3 PDFPrasad C M100% (2)
- Forces and MotionDocument150 pagesForces and MotionAz MYNo ratings yet
- MIT8 01SC Problems11 SolnDocument13 pagesMIT8 01SC Problems11 Solnडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माNo ratings yet
- KE and PE PDFDocument13 pagesKE and PE PDFiiAikkoiiNo ratings yet
- 8.5 Final Review Key PDFDocument4 pages8.5 Final Review Key PDFAlex VongNo ratings yet