Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Channelisation Realignment Advantages & Disadvantages
Uploaded by
Millie HappypooOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Channelisation Realignment Advantages & Disadvantages
Uploaded by
Millie HappypooCopyright:
Available Formats
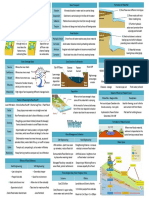
Types of Channelisation Realignment
What The straightening of the river channel
Advantages - increase the speed of the river - deepens the channel
Disadvantages - increased speed of the river after channelization may result in ooding downstream - although oods in one part of the rivers course of managed, they can still occur in another part of the river - disappearance of wetlands - affect plants and animals as their natural habitats may be destroyed
Examples Wallsea island
Re-sectioning
The widening - increases the and deepening channels of the river ability to hold channel water - increases the amount of surface runoff from the surrounding areas into the river - less friction between the water and river bed and banks
Sungei Api Api
Types of Channelisation Bank protection
What To prevent oods from occurring and to reduce soil erosion along the river banks
Advantages - increase the capacity of the river to hold water - protect the river banks from being eroded by running water
Disadvantages - the construction of dykes, revetments and gabions causes sediments to accumulate behind these structures
Examples - China, dykes have been built for centuries in the lower course of the Yellow River - In some countries, concrete structures like gabions and revetments are built along a river channel - Chao Phraya River, Thailand
Planting vegetation
Protect river banks against erosion as the roots of trees and other plants hold the soil together rmly
- slows down the rate of surface runoff - reduces the amount of eroded sediments being transported into the river - the channel does not become shallower
- ecosystems Pasir Ris Park, may be Singapore destroyed - excessive shade prevents sunlight from reaching the river bed, killing aquatic plants and affecting aquatic food chains
You might also like
- River EngineeringDocument23 pagesRiver EngineeringPinky Rose Alfaro GreganaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics: Type of Erosion: Features:: Upper CourseDocument6 pagesCharacteristics: Type of Erosion: Features:: Upper CourseSabine NgNo ratings yet
- River Channel ManagementDocument4 pagesRiver Channel ManagementPeiyan Lim100% (1)
- (Notes) ChannelisationDocument2 pages(Notes) ChannelisationZeneonNo ratings yet
- 2 2riversDocument12 pages2 2riversLK chanellNo ratings yet
- River Management StrategiesDocument6 pagesRiver Management Strategiesveronicatwy1239100% (2)
- RiversDocument5 pagesRiversRebekah BastiaanNo ratings yet
- Mind Map On Human Activities On RiverDocument1 pageMind Map On Human Activities On RiverMalia DamitNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Streambank ProtectionDocument6 pagesGuidelines For Streambank Protectionabhinaya pyakurelNo ratings yet
- River TrainingDocument21 pagesRiver TrainingBhaskar Jyoti NathNo ratings yet
- Presentation Handout 2Document3 pagesPresentation Handout 2Marco Gharaibeh LandwehrNo ratings yet
- River NavigationDocument7 pagesRiver NavigationKenneth MadroñalNo ratings yet
- River Navigation GuideDocument7 pagesRiver Navigation GuideIntan MadiaaNo ratings yet
- Flooding 6 Solutions To FloodingPresentation TranscriptDocument4 pagesFlooding 6 Solutions To FloodingPresentation TranscriptRazvanNo ratings yet
- River Navigation Christian BaldoDocument12 pagesRiver Navigation Christian BaldoChristian BaldoNo ratings yet
- Marine & Costal HazardDocument2 pagesMarine & Costal HazardKelvsNo ratings yet
- 1992Q2Document3 pages1992Q2Iris LamNo ratings yet
- Dams and TunnelsDocument99 pagesDams and TunnelsVicente ScottNo ratings yet
- 8 AnsDocument2 pages8 AnsManpreet singhNo ratings yet
- River Management StrategiesDocument2 pagesRiver Management StrategiesNorman PhuaNo ratings yet
- Lesson5 Water Uses Energy ProductionDocument3 pagesLesson5 Water Uses Energy ProductionVALENTINA MÓNACONo ratings yet
- Geog LearningDocument2 pagesGeog LearningJason YeungNo ratings yet
- Hydro EnvironmentDocument51 pagesHydro EnvironmentHammad JamesNo ratings yet
- 9 Flood Control, L-5,6Document10 pages9 Flood Control, L-5,6Qushik Ahmed ApuNo ratings yet
- Waterlogging and Lined Canals GuideDocument6 pagesWaterlogging and Lined Canals GuideShainee Delle PalmeraNo ratings yet
- Formation of Oxbow Lakes: A Concise GuideDocument10 pagesFormation of Oxbow Lakes: A Concise GuideSandy SaddlerNo ratings yet
- DAMSANDRESERVOIRSDocument8 pagesDAMSANDRESERVOIRSAhmed ElwanyNo ratings yet
- Dam and Their Role: Sub By-Jay Suman 6Th Sem CUJ1/1/2012/IMBA/8Document16 pagesDam and Their Role: Sub By-Jay Suman 6Th Sem CUJ1/1/2012/IMBA/8Bhaskar BhushanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Freshwater Resources: Natural Systems, Human Impacts, and ConservationDocument6 pagesChapter 15: Freshwater Resources: Natural Systems, Human Impacts, and ConservationEva WuNo ratings yet
- Seepage Through Dams (CHAPTER 1)Document3 pagesSeepage Through Dams (CHAPTER 1)Kimberly Shawn Nicole SantosNo ratings yet
- Seepage Through Dams: Reporters: Padua, Lyster Keith M. Veraces, John Paolo ADocument31 pagesSeepage Through Dams: Reporters: Padua, Lyster Keith M. Veraces, John Paolo ANiña Lyn BaladjayNo ratings yet
- Fluvial Erosion Processes ExplainedDocument20 pagesFluvial Erosion Processes ExplainedPARAN, DIOSCURANo ratings yet
- Environmental Impacts of Large Dams: African Examples - International RiversDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Impacts of Large Dams: African Examples - International RiversjayNo ratings yet
- Suggestions To Solve World Big FloodDocument4 pagesSuggestions To Solve World Big FloodPei Fen KuanNo ratings yet
- Study of Optimizing Techniques of Reservoir OperationDocument8 pagesStudy of Optimizing Techniques of Reservoir OperationRobert AguedoNo ratings yet
- Flood control and river training works guideDocument7 pagesFlood control and river training works guideLance ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- DRE-12 Ch-1 Dam Introduction 28-8-2012Document48 pagesDRE-12 Ch-1 Dam Introduction 28-8-2012Ali Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic AnalysisDocument49 pagesHydrologic AnalysissawadnoemishaneNo ratings yet
- 2011.11.16 EmbankmentDocument1 page2011.11.16 EmbankmentJagdish RoyNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Dam and Its RoleDocument28 pagesSeminar On Dam and Its RoleSourabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Revision Teams 2023Document53 pagesPaper 1 Revision Teams 2023alfiepetersdenisonNo ratings yet
- Design Grass Swales for Stormwater ConveyanceDocument10 pagesDesign Grass Swales for Stormwater Conveyancesyafiq najwanNo ratings yet
- Creating forest sector solutions handbookDocument63 pagesCreating forest sector solutions handbookDhany100% (1)
- Dams and BarragesDocument3 pagesDams and BarragesTariq Ahmed0% (1)
- Pond Construction RequirementsDocument63 pagesPond Construction RequirementsOnuoha Cyprain-AnthonyNo ratings yet
- RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATIONDocument19 pagesRESERVOIR SEDIMENTATIONAhmed BalahNo ratings yet
- HARVESTING FLOOD WATERS WITH WEIRSDocument8 pagesHARVESTING FLOOD WATERS WITH WEIRSKiscodep KiscodepNo ratings yet
- Selection CriteriaDocument4 pagesSelection CriteriamaizurahNo ratings yet
- Man's Impact On CoastlinesDocument35 pagesMan's Impact On CoastlinesLaura-Lee DownesNo ratings yet
- Delta 3Document8 pagesDelta 3Azad SamiNo ratings yet
- Delta: Wetlands: It Is Defined As A Transitional Area Between Terrestrial and Aquatic EcoDocument8 pagesDelta: Wetlands: It Is Defined As A Transitional Area Between Terrestrial and Aquatic EcoMohAmmAd sAmiNo ratings yet
- Channel ModificationsDocument3 pagesChannel ModificationsSubhajitNo ratings yet
- Flood MitigationDocument16 pagesFlood MitigationatienzavinamarieNo ratings yet
- DeltasDocument37 pagesDeltasmulkikimulNo ratings yet
- Floods and DeltasDocument18 pagesFloods and DeltasThe Equinox DudeNo ratings yet
- Dams and ReservoirsDocument8 pagesDams and ReservoirsAbdullah AL QahtaniNo ratings yet
- Aquaculture Engineering Site SelectionDocument113 pagesAquaculture Engineering Site SelectionKarieDetoreTolonesNo ratings yet
- Dam and Reservoir EngineeringDocument800 pagesDam and Reservoir Engineeringnongvanden2100% (8)
- Design Consideration 1Document2 pagesDesign Consideration 1wheniwanttologinNo ratings yet