Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report Synopsis Ashish Maglev
Uploaded by
Ashish GuptaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Report Synopsis Ashish Maglev
Uploaded by
Ashish GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
A
SYNOPSIS ON
MAGNETICALY LEVITATED TRAINS (MAGLEV)
SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENT FOR THE AWARD OF THE DEGREE
OF
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY
IN
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Submitted to:Lokesh Sharma (Seminar Coordinator)
Submitted to:K.K.Bhargava (HOD of ECE Dept.)
Submitted by:Ashish Kumar Gupta 08EMTEC016 (ECE)
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
Maharishi Arvind
INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY,JAIPUR
RAJASTHAN TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, KOTA 2011-2012
INTRODUCTION MAGNETIC LEVITATION Magnetic levitation, maglev, or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended above another object with no support other than magnetic field .The electromagnetic force is used to counteract the effects of the gravitational force.
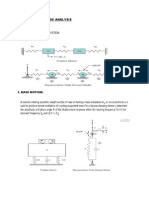
A substance which is diamagnetic repels a magnetic field. All materials have diamagnetic properties, but the effect is very weak, and usually overcome by the object's paramagnetic or ferromagnetic properties, which act in the opposite manner. Any material in which the diamagnetic component is strongest will be repelled by a magnet, though this force is not usually very large. Diamagnetic levitation can be used to levitate very light pieces of pyrolytic graphite or bismuth above a moderately strong permanent magnet. As water is predominantly diamagnetic, this technique has been used to levitate water droplets. Magnetically Levitated Trains (MAGLEV) The principal of a Magnet train is that floats on a magnetic field and is propelled by a linear induction motor. They follow guidance tracks with magnets. These trains are often referred to as Magnetically Levitated a train which is abbreviated to Maglev. Although maglev don't use steel wheel on steel rail usually associated with trains, the dictionary definition of a train is a long line of vehicles traveling in the same direction - it is a train.
A super high-speed transport system with a non-adhesive drive system that is independent of wheel-and-rail frictional forces has been a long-standing dream of railway engineers. Maglev, a combination of superconducting magnets and linear motor technology, realizes super high-speed running, safety, reliability, low environmental impact and minimum maintenance TECHNOLOGY AND WORKING OF MAGLEV TRAINS Basically the construction of the maglev train depends on 3 different working forces. They are, LEVITATION FORCE PROPULSION FORCE LATERAL GUIDING FORCE MAGLEV METHODS Repulsion between like poles of permanent magnets or electromagnets. Repulsion between a magnet and a metallic conductor induced by relative motion. Repulsion between a metallic conductor and an AC electromagnet. Repulsion between a magnetic field and a diamagnetic substance. Repulsion between a magnet and a superconductor. Attraction between unlike poles of permanent magnets or electromagnets. Attraction between the open core of an electromagnetic solenoid and a piece of iron or a magnet. Attraction between a permanent magnet or electromagnet and a piece of iron. Attraction between an electromagnet and a piece of iron or a magnet, with sensors and active control of the current to the electromagnet used to maintain some distance between them. Repulsion between an electromagnet and a magnet, with sensors and active control of the current to the electromagnet used to maintain some distance between them.
You might also like
- Physics Final (Cheat Sheet) With ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhysics Final (Cheat Sheet) With ProblemsRSlipkov97% (97)
- RMC Plant Calibration ReportDocument5 pagesRMC Plant Calibration ReportRakesh Para83% (12)
- Maglev ReportDocument31 pagesMaglev ReportLitika Sachdeva100% (1)
- Hydraulic Powered Crane with ElectromagnetDocument9 pagesHydraulic Powered Crane with ElectromagnetMichaela ViajarNo ratings yet
- MAGLEV - Magnetic Levitation TechnologyDocument25 pagesMAGLEV - Magnetic Levitation TechnologyAyanBiswas22No ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Modern Optics, Five-Volume Set, Volume 1-5Document2,285 pagesEncyclopedia of Modern Optics, Five-Volume Set, Volume 1-5Abdul Rehman AzmatNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument35 pagesSeminar Reportamalcyriac2108No ratings yet
- Maglev Trains: Rajamah EndriDocument9 pagesMaglev Trains: Rajamah EndrikudupudinageshNo ratings yet
- Driving Without Wheels: An Overview of Magnetic Levitation TechnologyDocument14 pagesDriving Without Wheels: An Overview of Magnetic Levitation TechnologySurya VamshiNo ratings yet
- Seminar ML FinalDocument10 pagesSeminar ML Finalmitaliswagh2002No ratings yet
- MAGLEV TRAIN TECHDocument17 pagesMAGLEV TRAIN TECHMartin AntoNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Levitation: An Efficient Transportation System in 40 CharactersDocument12 pagesMagnetic Levitation: An Efficient Transportation System in 40 CharacterstirumalarajNo ratings yet
- MaglevDocument23 pagesMaglevSneha NagaruruNo ratings yet
- Maglev Train Propulsion and Levitation SystemsDocument10 pagesMaglev Train Propulsion and Levitation SystemsammuNo ratings yet
- Levitation EMS EDLDocument38 pagesLevitation EMS EDLhemanth sai kumar giduturiNo ratings yet
- 44driving Without Wheels Flying Without Wings (Magn LevitDocument12 pages44driving Without Wheels Flying Without Wings (Magn LevitArimilli SricharanNo ratings yet
- Levitation and Maglev Train Work ProcessDocument5 pagesLevitation and Maglev Train Work Processrobinislam2002khanNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument28 pagesSeminar ReportMohammed Abdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Fig. 1.1-An Example of Wireless Power TransmissionDocument18 pagesChapter - 1: Fig. 1.1-An Example of Wireless Power TransmissionjasminetsoNo ratings yet
- Project Paper Maglev FinalDocument26 pagesProject Paper Maglev Finaljp2002sonuNo ratings yet
- Maglev Train Seminar: Principles, Benefits & ApplicationsDocument19 pagesMaglev Train Seminar: Principles, Benefits & ApplicationsVaibhav KantNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Levitating TrainsDocument8 pagesMagnetic Levitating TrainsArindomNo ratings yet
- Review of Maglev Train Technologies-Seminar SubhuDocument13 pagesReview of Maglev Train Technologies-Seminar Subhurich2subhu2009No ratings yet
- One Axis Controlled Super Conducting Magnetic Levitation SystemDocument21 pagesOne Axis Controlled Super Conducting Magnetic Levitation SystemClassic PrintersNo ratings yet
- Levitation: "Driving Without Wheels Made Possible"Document15 pagesLevitation: "Driving Without Wheels Made Possible"Firoz KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Overview of Magnetic Levitation (MAGLEV) Train SystemDocument6 pagesIntroduction & Overview of Magnetic Levitation (MAGLEV) Train SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Magnetic LevitationDocument26 pagesMagnetic LevitationSalil Sharma100% (1)
- MODERN SUSPENSION SYSTEM: MAGNETIC LEVITATIONDocument17 pagesMODERN SUSPENSION SYSTEM: MAGNETIC LEVITATIONreenaNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum: Maglev TrainsDocument6 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum: Maglev Trainschethan rNo ratings yet
- Magnetism PresentationDocument8 pagesMagnetism PresentationKareem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Paper On Magnetic LevitationDocument13 pagesPaper On Magnetic LevitationAshutosh Agrawal100% (7)
- "Driving Without Wheels, Flying Without Wings": (Magnetic Levitation)Document15 pages"Driving Without Wheels, Flying Without Wings": (Magnetic Levitation)Boreda RahulNo ratings yet
- A Technical Seminar Presentation: Magnetically Levitated Trains (Maglev)Document19 pagesA Technical Seminar Presentation: Magnetically Levitated Trains (Maglev)Lav AroraNo ratings yet
- Maglev Train: Magnetic Levitation and Types of Maglev TrainsDocument7 pagesMaglev Train: Magnetic Levitation and Types of Maglev TrainsGaneshNo ratings yet
- Driving Without WheelsDocument14 pagesDriving Without WheelsSen AnushaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits ExplainedDocument7 pagesMagnetic Circuits ExplainedAngel RamonesNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Leviation: MaglevDocument27 pagesMagnetic Leviation: MaglevAjay Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- GoTriangle's Report On EMIDocument27 pagesGoTriangle's Report On EMIthedukechronicleNo ratings yet
- Experimental Verification and Electromagnetic Analysis For Force Performance of Levitation and Guidance Electromagnet in Semi-High-Speed Maglev TrainDocument1 pageExperimental Verification and Electromagnetic Analysis For Force Performance of Levitation and Guidance Electromagnet in Semi-High-Speed Maglev TrainManuel DíazNo ratings yet
- Manglev: GuidewaysDocument7 pagesManglev: GuidewaysSaumya KharyaNo ratings yet
- Nalanda: Institute of Technology (Nit)Document23 pagesNalanda: Institute of Technology (Nit)RAGHU RAGHUNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On MaglevDocument14 pagesA Seminar On MaglevuttamNo ratings yet
- Anilal PRTDocument16 pagesAnilal PRTAmal JithNo ratings yet
- Paper Presented at Youth Conference On Magnetic Levitation TechnologyDocument8 pagesPaper Presented at Youth Conference On Magnetic Levitation TechnologyFaisal EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Maglev Technology's Future PotentialDocument26 pagesMaglev Technology's Future PotentialSatwik ShridharNo ratings yet
- Magnetic LevitationDocument21 pagesMagnetic LevitationSaurabh AnandNo ratings yet
- Magnetic LevitationDocument16 pagesMagnetic LevitationPrabhat PatelNo ratings yet
- EMT - Assingment (Electromagnatic Floater)Document10 pagesEMT - Assingment (Electromagnatic Floater)Iqbal Haziq AzmiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic LevitationDocument4 pagesMagnetic Levitationtowfiqeee0% (1)
- Magnetic Levitation ProjectDocument5 pagesMagnetic Levitation ProjectnimishNo ratings yet
- Magnetic levitation methods for stable levitationDocument7 pagesMagnetic levitation methods for stable levitationImad SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Comparision and Cost Analysis of Different Maglev TechnologiesDocument7 pagesComparision and Cost Analysis of Different Maglev TechnologiesseenNo ratings yet
- Maglev TrainDocument8 pagesMaglev TrainPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- Maglev Paper PresentationDocument12 pagesMaglev Paper Presentationaditya_kumar_me100% (1)
- Revolution in Wireless Electricity: The Rise of WiTricity TechnologyDocument31 pagesRevolution in Wireless Electricity: The Rise of WiTricity TechnologyvenkatakartheekNo ratings yet
- General Relativistic Galvano-Gravitomagnetic Effect in Current Carrying ConductorsDocument8 pagesGeneral Relativistic Galvano-Gravitomagnetic Effect in Current Carrying ConductorsCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Maglev Trains: Magnetic Levitation Technology ExplainedDocument17 pagesMaglev Trains: Magnetic Levitation Technology ExplainedrituNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop Transportation System AnalysisDocument2 pagesHyperloop Transportation System AnalysisNmg KumarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Levitation Research PapersDocument7 pagesMagnetic Levitation Research Papersqzetcsuhf100% (1)
- Driving Without Wheels, Flying Without WingsDocument18 pagesDriving Without Wheels, Flying Without Wingsaditya_kumar_me100% (1)
- Basics of Semiconductor Lasers: Semiconductor Optoelectronics (Farhan Rana, Cornell University)Document20 pagesBasics of Semiconductor Lasers: Semiconductor Optoelectronics (Farhan Rana, Cornell University)vj.krlambaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus Lecture-wise Breakup for PHYSICS-1 (15B11PH111Document2 pagesDetailed Syllabus Lecture-wise Breakup for PHYSICS-1 (15B11PH111Swapnil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Jones Matrix Method For Predicting and Optimizing The Optical ModulationDocument7 pagesJones Matrix Method For Predicting and Optimizing The Optical ModulationStephany SantosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1.: N C DK DWDocument10 pagesAssignment 1.: N C DK DWjuNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document2 pagesQuiz 3C G-CNo ratings yet
- Test: Light and Optics: True/FalseDocument12 pagesTest: Light and Optics: True/FalseMeeta DeviNo ratings yet
- Matter-Waves Trap: What Is Physics?Document29 pagesMatter-Waves Trap: What Is Physics?Mashi RosliNo ratings yet
- Ch.9 Circular MotionDocument10 pagesCh.9 Circular MotionJoanne Aga EslavaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum and ReflectionDocument49 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum and ReflectionInanNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Light NotesDocument5 pagesClass 7 Light Noteschotu bhanuNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Response Analysis: I. Two Mass Spring SystemDocument5 pagesHarmonic Response Analysis: I. Two Mass Spring SystemDinesh_Tadkapa_62No ratings yet
- OM-5 Operating Microscope Versatile Affordable QualityDocument5 pagesOM-5 Operating Microscope Versatile Affordable QualityMohammad A. BawtagNo ratings yet
- Fiber Bragg Grating - WikipediaDocument5 pagesFiber Bragg Grating - WikipediaNeelabh MaheshNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Cheat Sheet With ProblemsDocument3 pagesPhysics Final Cheat Sheet With ProblemsLeiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Magnetic CircuitsDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Magnetic Circuitssharad kumarNo ratings yet
- RVR JC College of Engineering Question Bank 1Document2 pagesRVR JC College of Engineering Question Bank 1MOHAMMED AFZALNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Transmission Lines Part 1Document32 pagesCH 7 Transmission Lines Part 1Ashraf YusofNo ratings yet
- Q.2. Srlu W3 G10Document6 pagesQ.2. Srlu W3 G10Pamela IndosoNo ratings yet
- Digital Image FundamentalsDocument48 pagesDigital Image FundamentalsVishwanath Narayanan100% (1)
- Samboan National High School Science ExamDocument3 pagesSamboan National High School Science ExamDexter JaducanaNo ratings yet
- 4th Attenuation and DispersionDocument45 pages4th Attenuation and DispersionSahmi Abdulqahar NizoriNo ratings yet
- Metal CarbonylsDocument17 pagesMetal CarbonylsJim Livingston100% (3)
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) ConceptsDocument1 pageScanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) ConceptsRangoli SaxenaNo ratings yet
- m42 Mount Spiral - Carl Zeiss Jena Biometar 80mm f2 CompletteDocument30 pagesm42 Mount Spiral - Carl Zeiss Jena Biometar 80mm f2 ComplettesigaweNo ratings yet
- 4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDFDocument1 page4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDFRudzi Udzi100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument40 pagesPhysicsSanjiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanics (Physics Paper 1 B.SC I (For CORRECTION)Document126 pagesMechanics (Physics Paper 1 B.SC I (For CORRECTION)GuruKPO100% (4)