100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote) 8K views23 pages1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics (Day 8 Solid Geometry)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
Solid Geometry 183
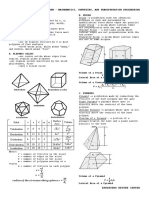
Polyhedron is a solid whose faces are plane polygons. A regular polyhedron is a
solid with all its faces identical regular polygons. There are only five regular
polyhedrons, namely
tetrahedron, hexahedron (cube), octahedron, dodecahedron
and icosahedron. These solids are also known as Platonic solids in honor of Plato
(427 348 B.C),
Polyhedron | No.of | Faces | No.of
Faces Edges
Tetrahedron 4 | Triangle | 6
Hexahedron 6 Square | 12
‘Octahedron 8 | Triangle | 12
Dodecahedron | 12 | Pentagon | 30
lcosahedron | 20 | Triangle | 30
Cube is a polyhedron with all six faces a square.
Rectangular parallelepiped is a polyhedron with all six faces a rectangle.
a
Volume of cube:
Volume of rectangular parallelepiped
vaste�184 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Surface area of cube: Surface area of rectangular parallelepiped:
oe
Prism is a polyhedron with two faces (bases) parallel and congruent and whose
remaining faces (lateral faces) are parallelograms.
Right prism is one which has its lateral faces perpendicular to the base.
Oblique prism is one which has it lateral faces not perpendicular to the base.
Truncated prism is a portion of a prism contained between the base and a plane
that is not parallel to the base.
qi
right prism
oblique prism
Volume of prism:
where:
h= altitude of prism
K = area at right section
Lateral area of prism: = lateral edge
Py = perimeter of right section
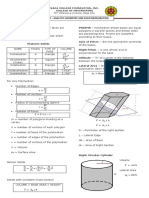
Cylinder is a solid bounded by a closed cylindrical surface and two parallel planes.�Solid Geometry 185
Volume of cylinder:
where
Webheke B = area of the base
a f h = alfitude of prism
K = area at right section
Lateral area of cylinder: = lateral edge
erimeter of right section
Pyramid is a polyhedron of which one face, called the base, is a polygon of any
number of sides and the other faces are triangles which have a common vertex.
Cone is a solid bounded by a conical surface (lateral surface) whose directrix is a
closed curve, and a plane (base) which cuts all the elements.
Gap
Volume of pyramid / cone:
where: B = area of the base
h= altitude
Frustum (of a pyramid/cone) is a portion of the pyramid / cone included between the
base and a section parallel to the base.
A> A,
Ja!
Volume of frustum of pyramid / cone:
where: R = bigger radius
= smaller radius�186 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Prismatoid is a polyhedron having for bases two polygons in parallel planes and for
lateral faces triangles or trapezoids with one side lying in one base, and the opposite
vertex or side lying in the other base of the polyhedron.
Volume of prismatoid:
This formula is known as
Prismoidal formula
‘Volume of truncated prism:
Truncated prism
‘Sphere is a solid bounded by a closed surface every point of which is equidistant
from a fixed point called center.
Volume of sphere:
Great circle
Surface area of sphere:
Area of zone:
‘A=2nRh�Solid Geometry 187
‘Spherical segment is a solid bounded by a zone and the plaries of the zone’s base.
Volume of spherical segment:
Spherical sector is a solid generated by rotating a sector of a circle about an axis
which passes through the center of the circle but which contains no point inside the
sector,
Volume of spherical sector:
where : A = area of zone
Spherical pyramid is a pyramid formed by a portion of a surface of a sphere as
base and whose elements are the edges from the vertices of the base to the center
of the sphere.
(> Volume of spherical pyramid:
where : E = spherical excess of
polygon ABCD in degrees
Spherical wedge is a portion of a sphere bounded by two half great circles and an
included arc.
Volume of spherical wedge:
aR°0
270�188 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Torus is a solid formed by revolving a circle about a line not intersecting it.
Volume of torus:
—
@/s Lateef ers tone
where : R = distance from axis to
center of generating circle
= radius of generating circle
Ellipsoid (Spheroid) is a solid formed by revolving an ellipse about its axis.
Volume of general ellipsoid:
‘major axis
Prolate spheroid is a solid formed by Oblate spheroid is a solid formed by
revolving an ellipse about its major axis. Revolving an ellipse about its minor axis.�Solid Geometry 189
Tips:1. Lateral area is the total area of the faces of the
polyhedron excluding the bases.
2. Surface area refers to the total area of the faces of the
Polyhedron including the bases.
3. Anchor ring or Doughnut is another term for a torus,
4. Rhomboid is another term of a parallelogram.
5. Geoid is the actual shape of the earth although earth
most of the time is regarded as a spheroid or ellipsoid.
6. Cavalieri’s Theorem states that solids of equal height
have equal volume if sections parallel to and
‘equidistant trom their bases have equal area. [his is
named after Bonaventura Cavalieri (1598 - 1647)
BIB pou finow that...the Pascal’s triangle which is used to determine
the coefficient of a binomial expansion was named after the French
mathematician, philosopher and physicist Blaise Pascal but did not
claim recognition for the discovery because such triangle was first
introduced by a Chinese mathematician, Chu Shih-chieh in 1303!
Proceed to the next page for your fourth test. GOODLUCK !�190 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Time element: 2 hours & 30 minutes
se
Problem 356: ME Board October 1991
A circular piece of cardboard with a diameter of 1 m will be made into a conical,
hat 40 cm high by cutting a sector off and joining the edges to form a cone.
Determine the angle subtended by the sector removed.
A 144°
B. 148°
G. 1525,
D. 154°
Problem 357: CE Board November 1994
‘What is the area in sq. m of the zone of a spherical segment having a volume of
1470.266 cu. m if the diameter of the sphere is 30 m?
A. 465.5 m>
B. 565.5 m?
C. 665.5 m?
D. 656.5 m*
Problem 358: CE Board May 1995
A sphere having a diameter of 30 cm is cut into 2 segments. The altitude of the
first segment is 6 cm. What is the ratio of the area of the second segment to that of
the first?
A 44
B. 3:1
Gea
D232
Problem 359: CE Board November 1996
If the edge of a cube is increased by 30%, by how much is the surface area
increased?
30%
33%
60%
69%
oop>�Solid Geometry 191
Problem 360: ECE Board April 1995,
Each side of a cube is increased by 1%. By what percent is the volume of the
cube increased?
A 1.21%
B. 28%
C. 3.03%
D. 35%
Problem 361: ECE Board November 1992
Given a sphere of diameter, d. What is the percentage increase in its diameter
when the surface area increases by 21%?
A. 5%
B. 10%
C. 21%
D. 33%
Problem 362: ECE Board November 1992
Given a sphere of diameter, d. What is the percentage increase in its volume
when the surface area increases by 21%?
A. 5%
B. 10%
C. 21%
D. 33%
Problem 363: EE Board October 1991
How many times does the volume of a sphere increases if the radius is
doubled?
A. Atimes
B. 2times
C. 6times
D. 8 times
Problem 364: CE Board May 1997
A circular cone having an altitude of 9 m is divided into 2 segments having the
same vertex. If the smaller altitude is 6 m. find the ratio of the volume of the small
cone to the big cone.
0.186
0.296
0.386
0.486
9op>�192 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Problem 365: CE Board November 1997
Find the volume of a cone to be constructed from a sector having a diameter of
72cm and a central angle of 210°.
A. 12367.2 cm?
B. 13232.6 cm:
C. 13503.4 cm,
D. 14682.5 cm?
Problem 366: CE Board May 1998
Find the volume of a cone to be constructed from a sector having a diameter of
72 cm and a central angle of 150°.
533.32 cm?
6622.44 cm?
7710.82 cm?
8866.44 cm*
Som>
Problem 367: CE Board November 1996
‘A conical vessel has a height of 24 cm and a base diameter of 12 cm. It holds
water to a depth of 18 cm above its vertex. Find the volume (in cm’) of its content.
A. 188.40
B. 298.40
C. 381.70
D. 412.60
Problem 368: CE Board May 1995
‘What is the height of a right circular cone having a slant height of /10x anda
base diameter of 2x?
A. 2x
B. 3x
C. 3.317x
D. 3.162x
Problem 369: CE Board November 1995
The ratio of the volume to the lateral area of a right circular cone is 2:1. If the
altitude is 15 cm, what is the ratio of the slant height to the radius?
5:6
54
mG
5:2
pomp�Solid Geometry 193
Problem 370: CE Board November 1994
A regular triangular pyramid has an altitude of 9 m and a volume of 187.06 cu
m. What is the base edge in meters?
A 12
B. 13
Cc. 14
D. 15
Problem 371: CE Board November 1995,
The volume of the frustum of a regular triangular pyramid is 136 cu. m. The
lower base is an equilateral triangle with an edge of 9 m. The upper base is 8 m
‘above the lower base. What is the upper base edge in meters?
gom>
eee
Problem 372: EE Board April 1992,
What is the volume of a frustum of a cone whose upper base is 15 cm in
diameter and lower base 10 cm. in diameter with an altitude of 25 cm?
A. 3018.87 cm?
B. 3180.87 cm?
C. 3108.87 cm?
D. 3081.87 cm*
Problem 373: EE Board April 1993
In a portion of an electrical railway cutting, the areas of cross section taken
every 50 m are 2556, 2619, 2700, 2610 and 2484 sq. m. Find its volume.
A. 522,600 m?
B. 520,500 m>
C. 540,600 m?
D. 534,200 m*
Problem 374: ME Board April 1996
Determine the volume of a right truncated triangular prism with the following
definitions: Let the corners of the triangular base be defined by A, B and C. The
length of AB = 10 ft, BC = 9 ft. and CA =12 fl. The sides A, B and C are
Perpendicular to the triangular base and have the height of 8.6 ft, 7.1 ft. and 5.6 ft.
respectively.
413 fe
311 ft
313 ft
391 f°
pom>�194 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Problem 375: CE Board November 1995
A circular cylinder with a volume of-6.54 cu. m is circumscribed about a right
prism whose base is an equilateral triangle of side 1.25 m. What is the altitude of the
cylinder in meters?
A. 3.50
B. 3.75
c. 4.00
D. 4.25
Problem 376: CE Board May 1996
AA circular cylinder is circumscribed about a right prism having a square base
‘one meter on an edge. The volume of the cylinder is 6.283 cu.m. Find its altitude in
meters.
A. 4.00
B. 3.75
Cc. 3.50
D. 3.25
Problem 377: CE Board November 1997
The bases of a right prism is a hexagon with one’of each side equal to 6 cm,
The bases are 12 cm apart. What is the volume of the right prism?
A. 1211.6 cm?
B. 2211.7 cm?
C. 1212.5 cm>
D. 1122.4 cm*
Problem 378: EE Board April 1996
Two vertical conical tanks are joined at the vertices by a pipe. Initially the bigger
tank is full of water. The pipe valve is open to allow the water to flow to the smaller
tank until it is full. At this moment, how deep is the water in the bigger tank? The
bigger tank has a diameter of 6 ft and a height of 10 ft, the smaller tank has a
diameter of 6 ft and a height of 8 feet. Neglect the volume of water in the pipeline.
{200
{50
26
{50
poOp>
Problem 379:
‘The central angle of a spherical wedge is 1 radian. Find its volume if its radius is
1 unit.
A 28
B. 12�Solid Geometry 195
c. 3/4
D. 26
Problem 380:
A regular octahedron has an edge 2m. Find its volume (in m’).
3.77
1.88
3.22
244
gom>
Problem 381: CE Board May 1996
‘A mixture compound of equal parts of two liquids, one white and the other black,
was placed in a hemispherical bowl. The total depth of the two liquids is 6 inches.
After standing for a short time, the mixture separated, the white liquid settling below
the black. If the thickness of the segment of the black liquid is 2 inches, find the
radius of the bow in inches.
A. 7.33
B. 7.53
Cc. 7.73
D. 7.93
Problem 382: CE Board November 1996
The volume of water in a spherical tank having a diameter of 4 m is 5.236 m°.
Determine the depth of the water in the tank.
A
pop
e@aNO
Problem 383:
‘An ice cream cone is filed with ice cream and a surmounted ice cream in the
form of a hemisphere on top of the cone. if the hemispherical surface is equal to the
lateral area of the cone, find the total volume (in cubic inches) of ice cream if the
radius of the hemisphere is 1 inch and assuming the diameter of hemisphere is
‘equal to the diameter of the cone.
A. 3.45
B. 3.91
Cc. 4.12
D. 4.25�196 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Problem 384: ME Board April 1997
A cubical container that measures 2 inches on a side is tightly packed with 8
marbles and is filled with water. All 8 marbles are in contact with the walls of the
container and the adjacent marbles. All of the marbles are of the same size. What is
the volume of water in the container?
A. 0.38 in*
B. 25in°
C. 3.8in®
D. 4.2 in®
Problem 385: CE Board May 1997
The comers of a cubical block touched the closed spherical shell that encloses
it. The volume of the box is 2744 cubic cm. What volume in cubic centimeter inside
the shell is not occupied by the block?
2714.56
3714.65,
gop>
ANSWER KEY RATING
366.C 376.A
367. 377.D [_] 26-30 Topnotcher
368. 378.A
369.D 379.A [LJ 20-25 Passer
370.A 380. A ae
371.B 381.A LC) 15-19 Conditional
372. i
0-14 Failed
373.
374. a)
375.
ODrQD>OEDO
B
A
D
c
|B
D
D
.B
1. C
If FAILED, repeat the test.�SOLUTIONS TO TEST 8
SS .- Fo
ircumference of the circle
ircumference of the base of the cone
C = 2n(50) - 2n(30) = 40x
c=
40x = (50)0
oe A0e,
x
60
360° _ 144°
2
ve = @-n)
2
1470.265 = = bats) h]
1410.795 = nh?(45.- hy
1404 = 45h*— h®
h=6
A= 2nth
A = 2n(15)(6) = 565.5 m*
he = 30-6 = 24 cm. .
Ag _ 2nthy
A, 2nth,
oth
hy
= 4
6
Thus, Ao: Ay= 4:4
2
Ag _{X2
Sra ias we
=
x2 21.3% wr @
Substitute (2) in (1):
Solid Geometry 197�198 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Ay _(131m)
Ay xy
Ag = 1.69 Ay
Thus, A2 is increased by 69%.
3
Nave Ae
vs S eo
210m ar @
‘Substitute (2) in (1):
Ve = 1.0303 V1
Thus, V2 is increased by 3.03%
‘Substitute (2) in (1):
dy 121A,
4 Ay
dz = 1.14;
Thus, d2is increased by 10%
Note: In proportions, balance the resulting units on both sides
2 3
erate evs
(¥ } (s pe
Aa121A we @
‘Substitute (2) in (1):
Ne _ 1.22
Wen 20)�Solid Geometry 199
Thus, Vz is increased by 33.1%
BA (ey we
My
me2ry wz @
‘Substitute (2) in (1):
Vy (24)
YM Uh
Vo =8Vs
3 5
#-(%) het
Ve (he) hyo
364.
KEE Let: C; = circumference of the circle
C2 circumference of the base of the cone
C = length of are
229-3 /s00% 24]
2n
360°
x=21om.
have? -x?
= h=y(36) - (21 = 29.24 cm.
ve tm
4
Ve yn2nr(29. 24) = 13503.4 cm
Let: C; = circumference of the circle
Cr ircumference of the base of the cone
© = length of arc�200 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
G22C-C
20x = 2a 10
ee
2n
36| 2n
= 36 -2[ 210%
eo [210% 25]
x
x= 150m.
her? -
h= (36) — (18 = 32.726 cm.
Jaeh
3
xt 5)? (32.726) = 7710.88 cm
EEA 8y ratio & proportion:
24
18
= 4£014.5)%18)
= 381.70 cm?
EGEM By Pythagorean theorem:
(Ax) =n? +x?
10x Pat eis idx
369.�Solid Geometry 201
sir
a
|
0
nia
(Base Area)h
v abe sina]
Et
3|2
Note: 0 = 60°, since equilateral triangle.
187.06 3} Fever" ©)
x= 12m.
Era)
wz @
Note: 0 = 60", since equilateral triangle.
AS tof sin60°
A= 36.074 w@
Ae 400? sin60°
A2=0433K ar ©
Substitute (2) & (8) in (1):
195 Sos 074 +.0.433x? + (36. 074) 0.43052) |
0.625 = 35.074 + 0.433 x" + 3.897 x
x + 9x-36 =0
(x-3)(x+12)=0
x= 3m.
= By tAa RAs] wr @
Avs ar? = (5)? = 250
Ag= miz’ = x(7.5)° = 56.250
‘Substitute Ay and Ag in (1):
Ve 2 bss 4+ 58.25n + (25n66.257)|
V.= 3108.87 cm®�202 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
Note: Since the areas being cut is at the same distance, then the given
solid is a prismatoid. And since there are 5 different areas being cut
then, this is equivalent to 2 prismatoids.
v 5A, + 44m +2)
v= Ue lpsse +4(2619) +2700] "0° [2700 + 4(2610) + 2484]
6
V = 522,600 m?
+b+o_9+12+10
2 2
A=/s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
A= 15.5(15.5-9)(15.5 — 12)(15.5— 10)
A= 44.039 ft
374. 15.5
375. = 120°
By cosine law:
EGR d= (1) +O" =1.4142m
Re
v= Zan
6.283 =7(1.4142)*h
h=4m.�Solid Geometry 203
Note: A= area of one base
b= length of each side of the base
nb?
4tane
360° _ 360°
= Se + 30° =
zn 26) Fat
Substitute:
2
Az 6 _ 93.53 om?
4tan30°
V=An b=6 em
V = 93.53(12) = 1122.4 cm?
Let: Vj = total volume of the bigger tank
V2 = total volume of the smaller tank
V = volume left in the bigger tank
= att), * er eoye 2
Ms : A - 72 (9) (10) = 94.247 ft
1] nd,? X 2 e
eee =75:
4 f hs 77 © (8) = 75.398 ft
VEVi—V2
V = 94.247 — 75.398 = 18.849 ft
By ratio and proportion:
Mio (a) -
vi\h
94.247 _(10)°
18.849 \h field
h= 9200 ft.
volume of the wedge
jolume of the sphere
By ratio and proportion:
GI
2n 0
vs Me (a/ainto
Qn On�204 1001 Solved Problems in Engineering Mathematics by Tiong & Rojas
:
v= 40% 2 conte
he a?- Wa? = V2
Let: y volume of the octahedron
= [3 ere] =3.77 m?
Let: Ve = volume of the black mixture :
Vw = volume of the white mixture vz
ur @
Vr=Ve+Ww ir @
‘Substitute (2) in (1):
By inspection:
het
Let: Ac = surface area of the cone
‘Au = surface area of the hemisphere
Vr = total volume
Vc = volume of the cone�Solid Geometry 205
Vu = volume of the hemisphere r
Ay
Renny
Re eaeaeieseF
ees
Ms
havi? — A L ed L
n= er Re
Vr= Ve + Va ¥
ot 1/4
= fren S oe]
=(* 4n
= (3) 732)+ =?
Vr = 3.91 in®
Let: r= radius of each marble
‘Vw = volume of water inside the cube
Ve = volume of the cube
‘Vu = volume of each marble
4r=x=2
r=05in.
w= Ve~ 8Vu
= 00? a[ 440"
ww=@y'-0[ 41097 ]=20 0°
Let: V = volume inside the sphere but outside the box
Vs = volume of the sphere
solume of the box
d= 3(14)? = 24.24 cm.
r= 12.12em.
V=Vs- Ve
es = 4 3
= Grr? - 2744 = 5 a(12.12)° 2744
V = 4713.555 cm?