Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heredity Summative
Uploaded by
Rosalie Tilos Orito0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
245 views2 pagesHeredity summative
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHeredity summative
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
245 views2 pagesHeredity Summative
Uploaded by
Rosalie Tilos OritoHeredity summative
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
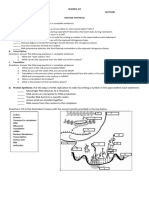
Valencia National High School
Bong-ao, Valencia, Negros Oriental
Part I
Science 10 Summative Assessment in Heredity
Direction: Answer the following questions.
Write your answer in your separate answer
sheet.
For nos. 29-32
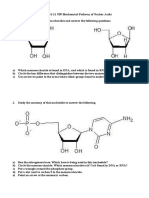
Look at the four DNA sequences of bases below.
For nos. 1-12
The sequence of bases in one DNA strand is given
below. Identify the complementary sequence of
bases in other strand of DNA.
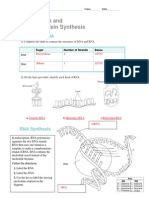
For nos. 13- 24
Show how the DNA code translate into RNA code
by placing the sequence of bases of the DNA and
RNA side by side.
How does each of these errors change the DNA
sequence? What do you call these changes?
RNA
______________________________________
For nos. 25-28
Each combination of three nitrogenous bases on
the mRNA molecule is codon, a three letter code
for a specific amino acid. Use the table below to
identify the specific amino acid for each mRNA
codon.
Part II Multiple Choice:
Direction: Choose the letter of the correct answer:
33. During translation, the tRNA sequence of
nucleotides arranged linearly is _______.
a. T C G T C C G T C T A G
b. A A U G C C A G U G G U
c. A G C A G G C A G A U C
d. U C G U C C G U C U A G
34. An exception to the central dogma is _______.
A. the infection of a virus by a bacteriophage.
B. the ability of some viruses to transfer
information from RNA to DNA.
C. the expression of different genes during
different stages of development.
D. the translation of the codon into the anticodon
of tRNA.
35. If transcribed into an mRNA, what would be
the resulting strand?
a. U U A C G G U C A C C A
b. A G C A G G A G A T C
c. A G C A G G C A G A U C
d. T C G T C C G T C T A G
36. For which amino acid is GGA a codon?
A. Lysine
C. Leucine
B. Valine
D. Glycine
37. All organisms are mostly the same in ______.
A. the proteins they make on their ribosomes.
B. how their proteins catalyze chemical reactions.
C. the size of their genes.
D. the molecular biology of their genes.
38. For which amino acid is AAA a codon?
A. Lysine
C. Leucine
B. Valine
D. Threonine
39. If this strand is replicated, which of the
following is the complementary strand that is
produced?
a. T C G T C C G T C T A G
b. A G C A G G C A G G G T
c. T T A C G G T C A C C A
d. U C G U C C U C U A G A
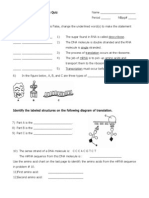
For items 40- 45 SEQUENCE
Sequence the following steps in protein
synthesis from first to last (1-6).
___40. Transcription
___41. tRNA amino acid units link to mRNA
___42. Amino acid separate from tRNA
___43. Polypeptide chain assembled
___44. mRNA links to ribosome
___45. Stop codon encountered in mRNA
Given the list of amino acids, determine the
sequence of bases in the codon of the mRNA
that codes for these amino acids. Use the table
for the Genetic Code (see table in no. 3).
46. Methionine
51. Asparagine
47. Leucine
52. Valine
48. Arginine
53. Glycine
49. Threonine
54. Aspartic acid
50. Lysine
55. Glutamic acid
Fill in the blanks.
Each combinations of nitrogen bases on the
mRNA molecule is a codon, which is a three letter
code for a specific amino acid. The table shows
the mRNA codon for each amino acid. Use the
Genetic Code Table (see table in no. 3) to answer
the questions.
56. The codon for tryptophan is ______________.
57. For leucine, there are _______ different
codons.
58. The codon GAU is for __________________.
59-60. In a stop codon, if the second base is G,
the first and third bases are _______ and
________.
You might also like
- DNA Methods in Food Safety: Molecular Typing of Foodborne and Waterborne Bacterial PathogensFrom EverandDNA Methods in Food Safety: Molecular Typing of Foodborne and Waterborne Bacterial PathogensNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetMercy Jade CaysidoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet: ST ND RD TH THDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet: ST ND RD TH THMoonNo ratings yet
- Protien Synthesis TestDocument2 pagesProtien Synthesis TestAnna Grace Lobigas RanocoNo ratings yet
- Translation Notes SheetDocument5 pagesTranslation Notes SheetKelsey BakerNo ratings yet
- CH 29Document10 pagesCH 29VamNo ratings yet
- Long Test As Level Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesLong Test As Level Nucleic AcidPrisky Jofan SimbarNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation Practice WorksheetDocument4 pagesTranscription and Translation Practice Worksheetsmith joeNo ratings yet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Practice WorksheetDocument4 pagesDNA Protein Synthesis Practice WorksheetAmbrielle WhiteNo ratings yet
- CH Test BDocument4 pagesCH Test BTahfeel -- GamingNo ratings yet
- Transcription Translations HandoutDocument13 pagesTranscription Translations HandoutMedina Zahic100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- Bio 111 Final Exam Fall05Document21 pagesBio 111 Final Exam Fall05Zeshan AslamNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisJoshua MarianoNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Study Guide KeyDocument5 pagesCH 13 Study Guide Keyi_wana_readNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma Module For Grade 10 ScienceDocument3 pagesCentral Dogma Module For Grade 10 ScienceJan Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Gene FunctionDocument5 pagesGene FunctionJon Hosmer0% (1)
- CH 7 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsDocument20 pagesCH 7 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsRokia GhariebNo ratings yet
- DNA RAN Prot Syn Web PracticeDocument11 pagesDNA RAN Prot Syn Web PracticeTimothy MacdonaldNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 WorkhsheetDocument5 pagesLecture 8 Workhsheetrobet12No ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Problem SetDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Problem SetEMMA FACCIONo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 RNA Test NAME Abdullah Alabdullah CLASS 9A DATEDocument7 pagesChapter 13 RNA Test NAME Abdullah Alabdullah CLASS 9A DATEAbdullah AlabdullahNo ratings yet
- MCQ MolecularDocument11 pagesMCQ MolecularMahmOod Gh100% (2)
- D0795090 C13 L02 Lesson Review Workbook ADocument4 pagesD0795090 C13 L02 Lesson Review Workbook AE ZenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Gene Expression From Gene To ProteinDocument18 pagesChapter 17 Gene Expression From Gene To Protein蔡旻珊100% (1)
- Gene To Protein, Part 2Document10 pagesGene To Protein, Part 2shiyiNo ratings yet
- Pyq Cbse 2021-1-2Document19 pagesPyq Cbse 2021-1-2Yuvraj MehtaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - 2ND Summative TestDocument2 pagesScience 10 - 2ND Summative Testalmira villarealNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-4 Week-5Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-4 Week-5Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis QuizDocument6 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis QuizJeremy Guggenheim100% (2)
- DNA To Protein Worksheet: Directions: Below Are Five (5) Different DNA SequencesDocument2 pagesDNA To Protein Worksheet: Directions: Below Are Five (5) Different DNA SequencesJuju Zenemij0% (2)
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Problems KEYDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Problems KEYnona wayne dela peña100% (1)
- Review Bell ringer-DNA - RNA-Relication-Protein Synthesis April 12thDocument12 pagesReview Bell ringer-DNA - RNA-Relication-Protein Synthesis April 12thBreanna MooreNo ratings yet
- DNA RNA: Basis of ComparisonDocument3 pagesDNA RNA: Basis of ComparisonMa. Lourdes CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Rna Test Name Class DateDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Rna Test Name Class DateAbdullah AlabdullahNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 SummativeDocument1 pageGrade 10 SummativeZaifel PacillosNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q3 Week4 MELC07 ASP Aceret, Dan Manayon Dan ManayoN AceretDocument10 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q3 Week4 MELC07 ASP Aceret, Dan Manayon Dan ManayoN AceretChristian Mart SoncioNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 5 ExamDocument13 pagesAP Biology Unit 5 ExamLana Sage CummingsNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis GizmoDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis GizmomInd prOceSsNo ratings yet
- MLB 110 MLS M 1920 02 (1) Molecular ExamsDocument15 pagesMLB 110 MLS M 1920 02 (1) Molecular Examsmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Molecular Bio Quiz 1 04.01.2019Document6 pagesMolecular Bio Quiz 1 04.01.2019Sean ChoNo ratings yet
- Biology A Level, MCQ Problem Sets, Protein Synthesis, Dna and RnaDocument5 pagesBiology A Level, MCQ Problem Sets, Protein Synthesis, Dna and RnaAcep AbdullahNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein - Transcription and TranslationDocument11 pagesFrom Gene To Protein - Transcription and TranslationELOISA N. CASANENo ratings yet
- Pretest 10Document5 pagesPretest 10Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 10 MutationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Grade 10 MutationPatricia100% (3)
- Worksheet 2 Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument11 pagesWorksheet 2 Central Dogma of Molecular Biologykoreaneminem2No ratings yet
- SEHH2231-22 T09 Biochemical Pathway of Nucleic Acid Exercise (Question)Document6 pagesSEHH2231-22 T09 Biochemical Pathway of Nucleic Acid Exercise (Question)Brian Chi Yan Cheng 鄭智仁No ratings yet
- CodonDocument22 pagesCodonDipanshi shahNo ratings yet
- Human Genetic Inheritance LabDocument5 pagesHuman Genetic Inheritance LabAntonov MikalisNo ratings yet
- Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 1St Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesGenetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 1St Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFPhilipHoustoncamy100% (12)
- Test Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis Eleventh EditionDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis Eleventh Editiondaonhatc2ddrq100% (27)
- DNA QuizDocument5 pagesDNA QuizMARO BGNo ratings yet
- Timothy Harris - Translation Worksheet - 2449410Document2 pagesTimothy Harris - Translation Worksheet - 2449410India PerezNo ratings yet
- C Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Document14 pagesC Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Daisy Soriano Prestoza100% (1)
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Document11 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT)GraceEstoleCalo100% (1)
- DNA SamplexDocument6 pagesDNA SamplexNelica RotoniNo ratings yet
- 12 Review WSDocument11 pages12 Review WSJASON WILLSNo ratings yet
- Transcription Translation Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesTranscription Translation Practice Worksheetapi-2619420100% (1)
- 2014Document14 pages2014Samuel RobertsNo ratings yet
- Biosc1940 Molecular Biology Midterm Exam 1: Multiple Choice (2 Pts Each) - Circle One Answer For EachDocument10 pagesBiosc1940 Molecular Biology Midterm Exam 1: Multiple Choice (2 Pts Each) - Circle One Answer For EachMohamed MounirNo ratings yet
- Types of HazardsDocument2 pagesTypes of HazardsRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- SalerioDocument28 pagesSalerioRizqaFebrilianyNo ratings yet
- How Much Can We Perceive With Sixth SenseDocument5 pagesHow Much Can We Perceive With Sixth SenseRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- 3007Document4 pages3007Lgutierrez Yu RiNo ratings yet
- 10 Basic Tips in Preparation For Let ExainationDocument4 pages10 Basic Tips in Preparation For Let ExainationMarciano Ken HermieNo ratings yet
- Print Least LearnedDocument4 pagesPrint Least LearnedRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Diom / Phrase Meaning Example SentenceDocument4 pagesDiom / Phrase Meaning Example SentenceRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Class Observation Guide SHSDocument1 pageClass Observation Guide SHSRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Chap 13practestDocument6 pagesChap 13practestPau PastorNo ratings yet
- Chap 13practestDocument6 pagesChap 13practestPau PastorNo ratings yet
- Cost and Return AnalysisDocument1 pageCost and Return AnalysisRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Chap 13practestDocument6 pagesChap 13practestPau PastorNo ratings yet
- Maintaining PPEDocument6 pagesMaintaining PPERosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Land ClearingDocument6 pagesLand ClearingRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Terminologies: Kinship Terminology Systems of Consanguinity and Affinity of The Human FamilyDocument2 pagesTerminologies: Kinship Terminology Systems of Consanguinity and Affinity of The Human FamilyRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Production CostDocument19 pagesWorksheet Production CostRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- BicyclesDocument6 pagesBicyclesRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- History of TheoriesDocument4 pagesHistory of TheoriesRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Social: A Group Portrait of A Mother, Son and Daughter On Glass,, C. 250 ADDocument2 pagesSocial: A Group Portrait of A Mother, Son and Daughter On Glass,, C. 250 ADRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Farm Tools UsesDocument5 pagesFarm Tools UsesRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Types of Kinship: PatrilinealDocument1 pageTypes of Kinship: PatrilinealRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Degrees of KinshipDocument2 pagesDegrees of KinshipRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Family RolesDocument4 pagesFamily RolesRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Types of FamilyDocument4 pagesTypes of FamilyRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Species: List of Rosa SpeciesDocument1 pageSpecies: List of Rosa SpeciesRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- O. Henry Greenwich Village: and Other Stories. Set inDocument1 pageO. Henry Greenwich Village: and Other Stories. Set inRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Rose UsesDocument5 pagesRose UsesRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- FamilyDocument1 pageFamilyRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Perennial Flowering Plant Genus Rosaceae Species Cultivars Prickles Asia Europe North America Africa Cultivars HybridsDocument1 pagePerennial Flowering Plant Genus Rosaceae Species Cultivars Prickles Asia Europe North America Africa Cultivars HybridsMarjorie RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- The Da Vinci Code: The Lost Symbol Is A 2009 Novel Written by American WriterDocument1 pageThe Da Vinci Code: The Lost Symbol Is A 2009 Novel Written by American WriterRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Millon's TestDocument4 pagesMillon's TestSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- S1 2021 414622 AbstractDocument1 pageS1 2021 414622 AbstractNaufalika DzahabiyyaNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis 2Document2 pagesGluconeogenesis 2Nikhitha NunnaNo ratings yet
- Classification of ProteinsDocument6 pagesClassification of ProteinsAlexia Mary Solei BacolodNo ratings yet
- Lac and TRP OperonDocument8 pagesLac and TRP OperonShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Cell Final ExamDocument8 pagesCell Final ExamJorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Protien-Synthesis Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesProtien-Synthesis Lesson PlanHAIDEE VASQUEZNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Ayunie ZulkeflyNo ratings yet
- BF3 2 Lesson 2021 PDFDocument37 pagesBF3 2 Lesson 2021 PDFrajeshNo ratings yet
- 2.1 BiochemistryDocument19 pages2.1 BiochemistryPaul Darrel MenesesNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Genomes: Organization, Regulation, and Evolution: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument66 pagesEukaryotic Genomes: Organization, Regulation, and Evolution: Powerpoint Lectures Forxo_simpledreamNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules L4Document69 pagesBiomolecules L4rhansari1616No ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 4 Qualitative Protein AnalysesDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 4 Qualitative Protein AnalysesErikaJoillePatayonNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Worksheet 2 KeyDocument6 pagesAmino Acid Worksheet 2 KeyCARL JAMES SIMONNo ratings yet
- Booklet The Structures of LifeDocument66 pagesBooklet The Structures of LifeIrving EuanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Pierce Amino Acid Standard H Using Vanquish FlexDocument1 pageAnalysis of Pierce Amino Acid Standard H Using Vanquish FlexAlexander Nieto VelaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Written ReportDocument28 pagesNucleic Acid Written ReportCatnikimco100% (1)
- Book ProblemsDocument27 pagesBook Problemsعلي محمد عبد العال عبد اللهNo ratings yet
- AA Protein EnzymeDocument64 pagesAA Protein EnzymeNash DeniegaNo ratings yet
- Protein Isolation and Characterization of Nestle Non - Fat MilkDocument4 pagesProtein Isolation and Characterization of Nestle Non - Fat MilkcelineNo ratings yet
- 1995 - Davies Et Al. - Structures of Oligosaccharide-Bound Forms of The Endoglucanase V From Humicola Insolens at 1.9 Å ResolutionDocument11 pages1995 - Davies Et Al. - Structures of Oligosaccharide-Bound Forms of The Endoglucanase V From Humicola Insolens at 1.9 Å ResolutionYOTIN JUPRASONGNo ratings yet
- Enzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesDocument34 pagesEnzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesPromise EncinaresNo ratings yet
- DNA TranslastionDocument2 pagesDNA TranslastionJoySe Merrera ÜNo ratings yet
- Week 1 cb1131 NotesDocument24 pagesWeek 1 cb1131 NotesTanisha ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument32 pagesAmino AcidsWakjira GemedaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 - ProblemsDocument6 pagesCH 7 - ProblemsKhris Griffis100% (4)
- Infographic - CRISPR - Cas9Document3 pagesInfographic - CRISPR - Cas9felipe duarteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Transcription and Post Transcription ModificationsDocument73 pagesLecture 4 - Transcription and Post Transcription ModificationskibzwanjikuNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritancePriyanshu ShivamNo ratings yet
- Protein - Structures and FunctionsDocument33 pagesProtein - Structures and FunctionsGracentya AninNo ratings yet