Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Factoring
Uploaded by
Joy Cabato Bayno0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageFactoring is the reverse process of multiplication where a number or polynomial is written as a product of two or more factors. There are two main methods for factorizing polynomials - common monomial factoring and grouping terms. Common monomial factoring involves finding the greatest common factor of all terms and dividing each term by the GCF. Grouping terms groups the first two terms together and last two terms together before applying common monomial factoring.
Original Description:
Introduction to Factoring
Original Title
Introduction to Factoring
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFactoring is the reverse process of multiplication where a number or polynomial is written as a product of two or more factors. There are two main methods for factorizing polynomials - common monomial factoring and grouping terms. Common monomial factoring involves finding the greatest common factor of all terms and dividing each term by the GCF. Grouping terms groups the first two terms together and last two terms together before applying common monomial factoring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageIntroduction To Factoring
Uploaded by
Joy Cabato BaynoFactoring is the reverse process of multiplication where a number or polynomial is written as a product of two or more factors. There are two main methods for factorizing polynomials - common monomial factoring and grouping terms. Common monomial factoring involves finding the greatest common factor of all terms and dividing each term by the GCF. Grouping terms groups the first two terms together and last two terms together before applying common monomial factoring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
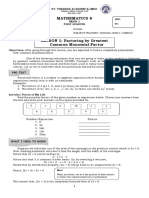
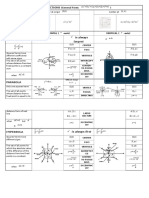
INTRODUCTION TO FACTORING
Factoring is the reverse process of multiplication.
When a number or polynomial is factored, it is written as a product of
two or more factors.
Factoring completely: A polynomial is factored completely if each of
its factors can no longer be expressed as a product of two other
polynomials of lower degree and that the coefficients have no
common factor.
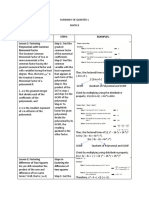
Methods of Factorizing Polynomials:
A. Common Monomial Factoring
Steps:
1. Find the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of the terms in the polynomial.
This is the first factor.
2. Divide each term by the GCF to get the other factor.
Ex: a.
b.
c.
3 x+3 y =3 ( x + y )
2
6 x+ 3 x =3 x ( 2 )+ 3 x ( x ) =3 x ( 2+ x )
( 5 x3 ) ( x y )+ 2 x ( x y )=( x y ) ( 5 x3+2 x ) =( x y ) (7 x3)
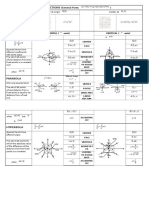
B. Grouping Terms
Steps:
1. Group the first two terms together and the last two terms together.
2. Apply common monomial factoring.
Ex: a.
b.
5 x2 3 x +5 xy3 y= x ( 5 x3 ) + y ( 5 x3 )=( 5 x3 ) ( x+ y )
6 ah2h6 ak + 2k =2 ( 3 ahh3 ak + k )=2 [ h ( 3 a1 ) k (3 a1) ]
2 ( 3 a1 ) (hk )
c.
5 x2 y5 x 2+ xyx+ y1=5 x 2 ( y1 ) + x ( y1 )+ ( y 1 )
( y1 ) (5 x 2+ x +1)
MATH 8
INTRODUCTION TO FACTORING
Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- Grade 8 - Factoring-PolynomialsDocument16 pagesGrade 8 - Factoring-PolynomialsTasyo LCruz Jr.No ratings yet
- Let's Review Regents: Algebra II Revised EditionFrom EverandLet's Review Regents: Algebra II Revised EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mon Monomial FactoringDocument32 pagesMon Monomial FactoringLANCE ANTHONY ABALLANo ratings yet
- HESI A2 Math Practice Tests: HESI A2 Nursing Entrance Exam Math Study GuideFrom EverandHESI A2 Math Practice Tests: HESI A2 Nursing Entrance Exam Math Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Practice Test in StatisticsDocument3 pagesPractice Test in StatisticsJoy Cabato Bayno100% (1)
- MATH 7 ReviewerDocument6 pagesMATH 7 ReviewerJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 1, Week 1 To 2 - Module 1.1Document46 pagesMathematics: Quarter 1, Week 1 To 2 - Module 1.1sheemz092650% (2)
- Math 8 - FactoringDocument26 pagesMath 8 - FactoringPaul John Mariano AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Revalidated MATH GR8 QTR1 MODULE 1 20 PagesDocument20 pagesRevalidated MATH GR8 QTR1 MODULE 1 20 PagesChiara CristiNo ratings yet
- Common Monomial FactoringDocument19 pagesCommon Monomial FactoringThe Gangsters Sisters100% (1)
- Factoring Completely: A Polynomial Is Factored Completely If Each ofDocument2 pagesFactoring Completely: A Polynomial Is Factored Completely If Each ofBliss JullienneNo ratings yet
- 8math Q1 Day 1Document9 pages8math Q1 Day 1adelfa.montesNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials (Common Monomial)Document19 pagesFactoring Polynomials (Common Monomial)Kim RebucasNo ratings yet
- Multiplying and Dividing Rational Algebraic ExpressionsDocument55 pagesMultiplying and Dividing Rational Algebraic ExpressionsEden Mae Sagadraca TabliagoNo ratings yet
- Section 5 (PreCalculus)Document12 pagesSection 5 (PreCalculus)Rodrigo ValdecantosNo ratings yet
- Math8-Week1 (1stquarter) HannahDocument3 pagesMath8-Week1 (1stquarter) HannahHannah Jane ClerigoNo ratings yet
- Factoring Review Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesFactoring Review Worksheet PDFGloria García-Mata100% (1)
- Math GR8 Common Monomial FactorDocument42 pagesMath GR8 Common Monomial FactormamaineejannNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8.1 - Common Monomial FactorsDocument7 pagesChapter 8.1 - Common Monomial FactorsJoy Masipag-SeminianoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Multiplying Rational Algebraic Expression What I KnowDocument23 pagesLesson 1: Multiplying Rational Algebraic Expression What I KnowHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter PPT (G8)Document109 pages1st Quarter PPT (G8)DaveXxGamerXxDragonNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials With Common Monomial FactorDocument31 pagesFactoring Polynomials With Common Monomial FactorShawn MikeNo ratings yet
- Factoring by GroupingDocument2 pagesFactoring by GroupingLazaro Larry Martin SorisNo ratings yet
- Factoring: Math 8 Teacher Jervy Josiah D. BayangDocument23 pagesFactoring: Math 8 Teacher Jervy Josiah D. BayangFatima Nicole BaladadNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Math LessonDocument1 pageGrade 8 Math LessonRendelaite DanaoNo ratings yet
- Alg 2 Factoring ReviewDocument7 pagesAlg 2 Factoring Reviewapi-261379705No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Math Q1 M1Document10 pagesGrade 8 Math Q1 M1Renny Romero LuzadaNo ratings yet
- Common Monomial Factorin GDocument1 pageCommon Monomial Factorin GJedelyn RoyNo ratings yet
- Activity 1. Factor - CommonDocument5 pagesActivity 1. Factor - CommonJohair BalindongNo ratings yet
- Factoring ReviewDocument7 pagesFactoring Reviewapi-261379705No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 1ADocument7 pagesMathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 1AEdward Lorenz TabligaNo ratings yet
- Factoring PolynomialsDocument22 pagesFactoring PolynomialsEden Mae Sagadraca TabliagoNo ratings yet
- Factors of PolynomialsDocument49 pagesFactors of PolynomialsHeatblastNo ratings yet
- Ang Lakas Ay Daig NG ParaanDocument5 pagesAng Lakas Ay Daig NG ParaanCarylle MarasiganNo ratings yet
- 3simple Factors of PolynomialsDocument28 pages3simple Factors of PolynomialsEve Krystel Baya - MamugayNo ratings yet
- Module - Grade 8 MathsDocument14 pagesModule - Grade 8 MathsJohn Mark Hermedilla50% (6)
- Department of Education: Activity Sheets in Mathematics 8 1st QuarterDocument57 pagesDepartment of Education: Activity Sheets in Mathematics 8 1st QuarterRenalyn MirandaNo ratings yet
- Math 8-Q1-L1-Factoring by The Greatest Common FactorDocument22 pagesMath 8-Q1-L1-Factoring by The Greatest Common FactorPearl De CastroNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Summarized ModuleDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Summarized ModuleIsrael MarquezNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Unit 1 Lesson 5 Power PointDocument35 pagesMath 8 Unit 1 Lesson 5 Power Pointmary joy buliagNo ratings yet
- FactoringDocument55 pagesFactoringCalvin LabialNo ratings yet
- Q1 - 1.1 - Common Monomial FactorDocument18 pagesQ1 - 1.1 - Common Monomial FactorErika Lloren Luyun-GaliaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 8 Q1-M1 PDFDocument18 pagesMathematics 8 Q1-M1 PDFMay Ann GodezanoNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 1 2 SLK 1Document31 pagesQ1 Week 1 2 SLK 1Aileen Joyce EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Factoring Out Oct. 11Document20 pagesFactoring Out Oct. 11kayleighdanielle17No ratings yet
- 13.2 Factorizing by GroupingDocument7 pages13.2 Factorizing by Groupingroudydaher98No ratings yet
- College Algebra Tutorial 7: Factoring PolynomialsDocument27 pagesCollege Algebra Tutorial 7: Factoring Polynomialssalman saeedNo ratings yet
- 1.Factoring-Greatest Common Monomial FactorDocument16 pages1.Factoring-Greatest Common Monomial FactorChelle Tadeo De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- AbcdDocument14 pagesAbcdGerald Lorenzo DomingoNo ratings yet
- Algebraic FractionsDocument4 pagesAlgebraic FractionsFocasan Rence-TeNo ratings yet
- Factoring Perfect Square TrinomialsDocument52 pagesFactoring Perfect Square TrinomialsEden Mae Sagadraca TabliagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Factoring Polynomials: MSJC San Jacinto CampusDocument59 pagesIntroduction To Factoring Polynomials: MSJC San Jacinto Campusmayonaissedelight smoothieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Part 1Document18 pagesLesson 4 Part 1Satvin SinghNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Asha Babbar TGT - Maths KV Tagore GardenDocument25 pagesPresented By-Asha Babbar TGT - Maths KV Tagore GardenVibhu GoelNo ratings yet
- Math 101 Unit 2 Lesson 1Document11 pagesMath 101 Unit 2 Lesson 1Paul John PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Can You Still Remember?: Direction: Determine The Product. Show Your SolutionDocument12 pagesCan You Still Remember?: Direction: Determine The Product. Show Your SolutionErika Lloren Luyun-GaliaNo ratings yet
- Factoring - Common Monomial FactorDocument18 pagesFactoring - Common Monomial FactorJessalyn De VillaNo ratings yet
- Common Monomial FactorDocument31 pagesCommon Monomial FactorErika Lloren Luyun-Galia100% (1)
- PolynomialsDocument54 pagesPolynomialsGimar Alingig ReyesNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Module MR. BACCAYDocument44 pagesGrade 8 Module MR. BACCAYMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Quarter 1Document31 pagesSummary of Quarter 1Lilacx ButterflyNo ratings yet
- FactoringDocument7 pagesFactoringHannah FaithNo ratings yet
- SportsDocument2 pagesSportsJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Citizenship Advancement Training: What Is Cadt? (Deped Order No. 35 S. 2003)Document6 pagesCitizenship Advancement Training: What Is Cadt? (Deped Order No. 35 S. 2003)Joy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- List of DemeritsDocument1 pageList of DemeritsJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Military Courtesy: Rules in Rendering Hand SaluteDocument1 pageMilitary Courtesy: Rules in Rendering Hand SaluteJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- List of DemeritsDocument1 pageList of DemeritsJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Measures of SpreadDocument4 pagesMeasures of SpreadJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- List of DemeritsDocument1 pageList of DemeritsJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Citizenship Advancement Training: What Is Cadt? (Deped Order No. 35 S. 2003)Document6 pagesCitizenship Advancement Training: What Is Cadt? (Deped Order No. 35 S. 2003)Joy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - I. Find The Unknown AnglesDocument2 pagesNAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - I. Find The Unknown AnglesJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- A Review of Basic Concepts in Geometry and AlgebraDocument20 pagesA Review of Basic Concepts in Geometry and AlgebraJoy Cabato Bayno100% (2)
- Military Courtesy: Rules in Rendering Hand SaluteDocument1 pageMilitary Courtesy: Rules in Rendering Hand SaluteJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Rules of Exponents For MultiplicationDocument1 pageRules of Exponents For MultiplicationJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- List of DemeritsDocument1 pageList of DemeritsJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Ellipse WorksheetDocument2 pagesEllipse WorksheetJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Stat ActivityDocument2 pagesStat ActivityJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesConic SectionsJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle-Stat TermsDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle-Stat TermsJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Stat ActivityDocument2 pagesStat ActivityJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Stat ActivityDocument2 pagesStat ActivityJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Stat ActivityDocument1 pageStat ActivityJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- RF and CF QuizDocument1 pageRF and CF QuizJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- RF and CF QuizDocument1 pageRF and CF QuizJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle-Stat TermsDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle-Stat TermsJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- RF and CF QuizDocument1 pageRF and CF QuizJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Elective 8 (Statistics) SQ#1 (3 QTR), SY 2016-2017Document1 pageElective 8 (Statistics) SQ#1 (3 QTR), SY 2016-2017Joy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- RF and CF QuizDocument1 pageRF and CF QuizJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Bingo CardDocument1 pageBingo CardJoy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections Circle: + + Center at Origin (0,0) Center at (H, K)Document2 pagesConic Sections Circle: + + Center at Origin (0,0) Center at (H, K)Joy Cabato BaynoNo ratings yet