Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ex 3 2 FSC Part2 Ver214
Uploaded by
adnanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ex 3 2 FSC Part2 Ver214
Uploaded by
adnanCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 3.
2 (Solutions)
MathCity.org
Calculus and Analytic Geometry, MATHEMATICS 12
Merging man and maths
Available online @ http://www.mathcity.org, Version: 2.1.4
Theorem on Anti-Derivatives
i) cf ( x)dx = c f ( x)dx where c is constant.
ii)
[ f ( x) g ( x)] dx = f ( x)dx g ( x)dx
n
x dx =
x n +1
n +1
1
x + 1 dx = x x 2 + 1 dx
= x 2 + x dx
= x 2 dx + x dx
3
where n 1
1
dx = dx (here x 0 )
x
d
1
ln x =
Since
dx
x
1
Therefore dx = ln x + c
x
Note: Since log of zero and negative numbers
does not exist therefore in above formula mod
assure that we are taking a log of +ive quantity.
1
Important Integral
n +1
n
d
Since
ax + b ) = (n + 1) ( ax + b ) a
(
dx
Taking integral
n +1
n
d
dx ( ax + b ) dx = (n + 1) ( ax + b ) a dx
n +1
n
( ax + b ) = (n + 1) a ( ax + b ) dx
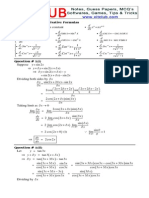
Question # 1(i)
2
2
3x 2 x + 1 dx = 3 x dx 2 xdx + dx
x 2 +1
x1+1
2
+ x+c
2 +1
1+1
x3
x2
= 3 2 + x + c
3
2
= x3 x 2 + x + c
= 3
( ax + b )
( 2 x + 3)
x
x
+
+c
1
1
+1 +1
2
2
3
2
1
2
x
x
+
+c
3
1
2
2
dx
( 2 x + 3) 2
=
+1
1 + 1 2
2
+c
( 2 x + 3) 2 + c
=
3 2
2
3
1
= ( 2 x + 3) 2 + c
3
1
2
1
+1
2
n +1
(n + 1) a
1
2
= x dx + x dx
1
+1
2
( ax + b )
dx =
Question # 1(iv)
Question # 1(ii)
1
12
1
2
x
+
dx
=
x
+
x
dx
1
2
+1
x2
x1+1
x 2 x2
=
+
+c =
+ +c
3
1+1
5
2
+1
2
2
5
2
1
= x 2 + x2 + c
5
2
If n = 1 then
1
2 32
x + 2 x 2 + c Ans.
3
Question # 1(iii)
Important Integral
d n +1
Since
x = ( n + 1) x n
dx
Taking integral w.r.t x
d n +1
n
dx x dx = ( n + 1) x dx
x n +1 = ( n + 1) x n dx
Page 130
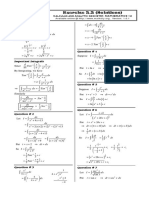
Question # 1(v)
x + 1 dx = ( x ) 2 + 2 x + 1 dx
1
= x + 2 ( x ) 2 + 1 dx
= x dx + 2 ( x ) 2 dx + dx
FSc-II / Ex- 3.2 - 2
1
2
1
=
+
d
1
1
= 2 2 + 2 d
+1
x1+1
x2
=
+2
+ x+c
1+1
1
+1
2
3
x2
x2
= +2
+ x+c
2
3
2
3
2
x
4x
+
+ x+c
2
3
Question # 1(vi)
2
1
1
x x dx = x + x 2 dx
1
= xdx + dx 2 dx
x
2
x
=
+ ln x 2 x + c
2
(1 x )
( y)
( y + 1) dy
y
3
2
1
2
y
y
y
y
+
+c =
+
+c
1
1
3
1
+1 +1
2
2
2
2
3
1
2
= y2 + 2y2 + c
3
Question # 1(ix)
d =
+c
2
1 2 x + x
dx
x
1 2 x
x
=
+
dx
x
x
x
1
1
= x 2 2 + x 2 dx
+1
x2
x2
=
3 +
+c
1
3
2
2
1
2 3
= 2 x 2 2 x + x 2 + c Ans
3
1
+1
2
1
+1
= y 2 dy + y 2 dy
1
+1
2
1
2
x 2
x2
=
2x +
+c
1
1
+1
+1
2
2
1
y
12
1
2
=
y
+
y
=
+
dy
dy
y
y
2 +
+c
dx =
Question # 1(viii)
y ( y + 1)
y dy
dy =
1
+1
2
Now do yourself.
3
2
2 +
1
+1
2
Question # 1(x)
y ( y + 1)
1
+1
2
1
2
= 2 + 2 2 + c Ans
3
= 3 x1 2 dx + 2 x 1 2 dx
+1
3
2
Question # 1(vii)
3x + 2
3x + 2
x dx = x1 2 dx
3x
2
= 1 2 + 1 2 dx
x
x
12
= 3 x + 2 x 1 2 dx
2 +1
d
Important Integral
d ax
We know
e = a eax
dx
Taking integral
d ax
ax
dx e dx = a e dx
e ax = a eax dx
e ax
e dx = a
Also note that
ax
( ax + b )
e dx =
e( ax +b )
a
Question # 1(xi)
e2 x e x
e2 x + e x
dx
=
ex
e x + e x dx
= e x + 1 dx
FSc-II / Ex- 3.2 - 3
= e x dx + dx
= ex + x + c
Ans
Question # 2(i)
dx
x+a + x+b
dx
x+a x+b
=
x+a + x+b x+a x+b
x+a x+b
=
dx
x+a xb
=
=
( x + a)
1
2
Question # 2(iii)
dx
x+a + x
dx
x+a x
=
x+a + x x+a x
x+a x
=
dx
x+ax
1
=
=
1
2
( x + b)
dx
a b
1
1
1
2 dx ( x + b ) 2 dx
x
+
a
(
)
a b
3
3
2
2 ( x + b ) 2 + c Ans.
x
+
a
(
)
3( a b)
Important Integral
d
1
Since
Tan 1 x =
dx
1 + x2
d
1
Also
Cot 1 x =
dx
1 + x2
1
Therefore
dx = Tan 1 x or Cot 1 x
2
1+ x
1
Similarly
dx = Sin 1 x or Cos 1 x
2
1 x
1
1
1
x x 2 1 dx = Sec x or Csc x
1
2
1 + x 1 x2
1 x 2
+
dx
1
1
1
2 dx ( x ) 2 dx
x
+
a
(
)
3
3
2
2 x 2 + c Ans.
x
+
a
(
)
3a
Question # 2(iv)
3
( a 2x)
3
2
dx =
( a 2x)2
+1
3 + 1 2
2 ( )
+c
(a 2x)2
=
5 2
2 ( )
Question # 2(ii)
1 x2
1 + x 2 dx
2
= 1 +
dx
1 + x2
1
= dx + 2
dx
1 + x2
= x + 2Tan 1 x + c
1
1
+1
2
2
x
+
a
x
(
)
(
)
1
+c
a
1
1
+1
2 + 1
2
3
3
2
2
+
x
a
x
(
)
(
)
1
+c
3
3
a
2
2
1
1
+1
x + b)2
(
1 ( x + a )2
=
+c
1
a b 1
1
1
+
+
2
2
3
3
1 ( x + a )2 ( x + b)2
=
+c
3
a b 3
2
2
( x + a)2 ( x)2
+c
5
( a 2x)2 + c
=
5
Question # 2(v)
x 3
(1 + e )
ex
dx =
(1 + 3e
+ 3e 2 x + e3 x
ex
) dx
1 3e x 3e 2 x e3 x
= x + x + x + x
e
e
e
e
= e x + 3 + 3e x + e2 x dx
dx
2x
e
e
+ 3 x + 3e x +
+c
1
2
1
= e x + 3x + 3e x + e2 x + c
2
=
FSc-II / Ex- 3.2 - 4
Important Integrals
d
We know
cos ax = a sin ax
dx
Taking integral
d
dx cos ax dx = a sin ax dx
cos ax = a sin ax dx
sin ax dx =
cos ax
a
d
sin ax = a cos ax
dx
sin ax
cos ax dx =
a
Similarly
tan ax
2
sec ax dx = a
d
1
ln f ( x) =
f ( x)
dx
f ( x)
Taking integral
f ( x)
ln f ( x) =
dx
f ( x)
Also
f ( x)
dx = ln f ( x) + c
f ( x)
Put f ( x) = ln x f ( x) =
cot ax
cosec ax dx = a
sec ax
sec ax tan ax dx = a
csc ax
a
Also note that
cos ( ax + b )
a
sin ( ax + b )
and so on.
cos ( ax + b ) dx =
a
sin ( ax + b ) dx =
Question # 2(vi)
cos(a + b) x
+c
a+b
Question # 2(vii)
1 cos 2x dx
1 cos 2 x
= 2sin x dx
sin x =
2
= 2 sin x dx = 2 ( cos x ) + c
2
; n 1
Question # 2(viii)
1
Let I = ln x dx
x
sin(a + b) x dx =
i.e.
Also
csc ax cot ax dx =
n +1
[ f ( x)]
[ f ( x)] f ( x)dx = ( n + 1)
n
= 2 cos x + c
Important Formula
n +1
n d
d
f ( x)] = ( n + 1) [ f ( x)]
f ( x)
[
dx
dx
n +1
n
d
f ( x)] = ( n + 1) [ f ( x)] f ( x)
[
dx
Taking integral
n +1
n
d
dx [ f ( x)] dx = ( n + 1) [ f ( x)] f ( x)dx
n +1
n
[ f ( x)] = ( n + 1) [ f ( x)] f ( x)dx
1
x
So I = [ f ( x)] f ( x) dx
1+1
[ f ( x)]
=
+c
1+1
2
ln x )
(
=
+c
2
[ f ( x)]
=
2
+c
Question # 2(ix)
1 cos 2 x
2
sin x dx = 2 dx
1 1
= cos 2 x dx
2
2
1
1
= dx cos 2 x dx
2
2
1
1 sin 2 x
= x
+c
2
2 2
1
1
= x sin 2 x + c
2
4
Question # 3(x)
1
1 + cos x dx
1
=
dx
2 x
2 cos
2
1
x
= sec2 dx
2
2
cos 2
x 1 + cos x
=
2
2
x
x
1 tan 2
=
+ c = tan + c
2 1
2
2
Alternative
1
1
1 cos x
1 + cos x dx = 1 + cos x 1 cos x dx
1 cos x
=
dx
1 cos 2 x
FSc-II / Ex- 3.2 - 5
1 cos x
dx
sin 2 x
cos x
1
= 2 2 dx
sin x sin x
cos x
= cosec 2 x
dx
sin
x sin x
= cosec2 xdx cosec x cot x dx
=
= cot x ( cosec x ) + c
= cosec x cot x + c
So I =
= sec 2 x dx + dx
= tan x + x + c
Question # 2(xiv)
2
2
tan x dx = sec x 1 dx
= sec2 x dx dx
Question # 2(xi)
ax + b
Let I = 2
dx
ax + 2bx + c
Put f ( x) = ax 2 + 2bx + c
f ( x) = 2ax + 2b
f ( x) = 2 ( ax + b )
1 cos 2 x
dx
1 + cos 2 x
2sin 2 x
=
dx
2 cos 2 x
= tan 2 x dx = sec 2 x 1 dx
= tan x x + c
1
f ( x) = ax + b
2
1 f ( x )
2
dx
f ( x)
1
1 f ( x)
=
dx = ln f ( x) + c1
2 f ( x)
2
1
= ln ax 2 + 2bx + c + c1
2
Review
2sin cos = sin ( + ) + sin ( )
Important Integral
d
1
d
Since
( ax + b )
ln ax + b =
dx
ax + b dx
d
1
a
ln ax + b =
dx
ax + b
On Integrating
1
ln ax + b = a
dx
ax + b
ln ax + b
1
dx =
ax + b
a
The End
By mathcity.org, admin@mathcity.org
2 cos sin = sin ( + ) sin ( )
Found Error
2 cos cos = cos ( + ) + cos ( )
Tell us at
http://www.mathcity.org/error
2sin sin = cos ( + ) cos ( )
Error Analysts
1-
Question # 2(xii)
cos 3x sin 2 x dx
1
2 cos 3x sin 2 x dx
2
1
= [sin(3x + 2 x) sin(3x 2 x)] dx
2
1
= [sin 5 x sin x ] dx
2
1 cos 5 x
=
( cos x ) + c
2
5
1 cos 5 x
=
cos x + c
2 5
Question # 2(xiii)
cos 2 x 1
1 + cos 2 x dx
1 cos 2 x
2
1 + cos 2 x
2
cos x =
2
sin 2 x =
23-
Muhammad Hussnain Khadim - (20011-13)
PISH AL-HASA KSA
Asad (2014)
Mohammad Abdullah Amjad - (2014-16)
Fazaia Degree College Risalpur
Book: Exercise 3.2 (Page 130)
Calculus and Analytic Geometry Mathematic 12
Punjab Textbook Board, Lahore.
Edition: May 2013.
Made by: Atiq ur Rehman (Atiq@MathCity.org)
Available online at http://www.MathCity.org in
PDF Format (Picture format to view online).
Page Setup used A4.
Updated: September 18, 2015.
You might also like
- Integral Calculus by Arihant B016Document27 pagesIntegral Calculus by Arihant B016Luis Anderson60% (5)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Indefinite IntegrationDocument24 pagesIndefinite IntegrationAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Magic of Definite IntegralDocument88 pagesMagic of Definite IntegralsagarNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- 9 Integrals PDFDocument19 pages9 Integrals PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- X Class Calculus SolutionDocument20 pagesX Class Calculus SolutionSamhithaReddyNo ratings yet
- M 4u IntegrationDocument14 pagesM 4u IntegrationTrungVo369No ratings yet
- Integration Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesIntegration Cheat Sheetjiebo100% (1)
- Answers Are You Ready For CalculusDocument6 pagesAnswers Are You Ready For CalculusKevin HsiehNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- CalA - 6 - 2 PDFDocument8 pagesCalA - 6 - 2 PDFGeorge Leon RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics: For CAPEDocument11 pagesPure Mathematics: For CAPERonaldoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.3 (Solutions) : y X X XDocument6 pagesExercise 2.3 (Solutions) : y X X XFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.7 (Solutions) : y X X X XDocument9 pagesExercise 2.7 (Solutions) : y X X X XFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- FSc-II Math Ex 2.4 SolutionsDocument7 pagesFSc-II Math Ex 2.4 SolutionsOsamaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bab-I & Bab IiDocument28 pagesTugas Bab-I & Bab IiblackzmillianNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2Document4 pagesMathematics 2Boon Khai ChienNo ratings yet
- Ex 2 5 FSC Part2Document12 pagesEx 2 5 FSC Part2Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Calculus exercise solutions with integralsDocument4 pagesCalculus exercise solutions with integralsadnanNo ratings yet
- MatematicasDocument9 pagesMatematicasYoel Lopez MejiasNo ratings yet
- 1 1 U X X 1 U 1 U 1 U: I. Integración Por Cambio de Variable Problema 1Document13 pages1 1 U X X 1 U 1 U 1 U: I. Integración Por Cambio de Variable Problema 1FernandoFloresNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument8 pagesIntegralthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Ex 2 6 FSC Part2Document12 pagesEx 2 6 FSC Part2Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- MÉTODOS DE INTEGRACIÓNDocument6 pagesMÉTODOS DE INTEGRACIÓNFernandoFloresNo ratings yet
- 2010 DHS Paper 1solDocument10 pages2010 DHS Paper 1solnothingtodo1992No ratings yet
- Avaliações 2009-1 - GabaritoDocument13 pagesAvaliações 2009-1 - GabaritoEduardobelloNo ratings yet
- Integration: Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8Document16 pagesIntegration: Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8Raja KushwahNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module Tests AnswersDocument28 pagesUnit 2 Module Tests AnswersashtigosineNo ratings yet
- Solutions: S - 1 5 Mathematics-III (May-2012, Set-2) JNTU-KakinadaDocument10 pagesSolutions: S - 1 5 Mathematics-III (May-2012, Set-2) JNTU-KakinadaSri DNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 Sar Tun Abdul RazakDocument4 pages2014 2 Sar Tun Abdul RazakMasytah YazidNo ratings yet
- Maths integrals and formulasDocument24 pagesMaths integrals and formulashem_33jackNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Lecture Notes Section 5.1 1 of 6: y X YeDocument6 pagesCalc 2 Lecture Notes Section 5.1 1 of 6: y X Yemasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Las integrales están correctamente resueltas aplicando el método de integración por fracciones parciales (caso IIDocument9 pagesLas integrales están correctamente resueltas aplicando el método de integración por fracciones parciales (caso IIDahirNo ratings yet
- 09 04 Second Order Derivatives PDFDocument19 pages09 04 Second Order Derivatives PDFSri DNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture Week 2 - Morning ClassDocument24 pagesOnline Lecture Week 2 - Morning ClasszamkNo ratings yet
- Section G: Integer Answer Type: X FX F XDocument10 pagesSection G: Integer Answer Type: X FX F XsatwiksmNo ratings yet
- M 4u Integration FatmuscleDocument14 pagesM 4u Integration Fatmuscleapi-36563676No ratings yet
- Limits & Derivatives Worksheet SOLUTIONS Math 1100-005 01/26/06Document4 pagesLimits & Derivatives Worksheet SOLUTIONS Math 1100-005 01/26/06vaibhav544No ratings yet
- E (1 X) DX e (1 X) DX Edx Xedx: Exercise - 8 (F)Document14 pagesE (1 X) DX e (1 X) DX Edx Xedx: Exercise - 8 (F)Javaji SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Additional Calculus Problems 3 - Integration and Differential Equations SolutionsDocument3 pagesAdditional Calculus Problems 3 - Integration and Differential Equations SolutionsNicholas TehNo ratings yet
- E.D. Reducibles A Variable SeparableDocument14 pagesE.D. Reducibles A Variable Separableelvis_3343No ratings yet
- bbmp1103 Sem 2Document13 pagesbbmp1103 Sem 2irisardellaNo ratings yet
- Leep 207Document27 pagesLeep 207Koyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- IntegralsDocument27 pagesIntegralssudersanaviswanathanNo ratings yet
- Chiclayo - Perú Trabajo 01 Análisis Matemático IIDocument11 pagesChiclayo - Perú Trabajo 01 Análisis Matemático IIMonika Stefany Samillan ZapataNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)Document2 pagesExercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)sohail2798No ratings yet
- Continuity and Differentiability: Chapter - 5Document3 pagesContinuity and Differentiability: Chapter - 5pardeepbthNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.2 (Solutions) : ProofDocument12 pagesExercise 8.2 (Solutions) : ProofFaizan Awan FeziNo ratings yet
- 2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 SolutionsDocument9 pages2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 Solutionsvincesee85No ratings yet
- Calc FormulasDocument2 pagesCalc FormulasratansrikanthNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument27 pagesIntegralesKevin DgoNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integration QnsDocument7 pagesIndefinite Integration QnsLokesh Kumar100% (1)
- 30 Diffrentiation Part 1 of 1dddddddddddddDocument18 pages30 Diffrentiation Part 1 of 1dddddddddddddVishal VjNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 8 FSC Part2Document4 pagesEx 3 8 FSC Part2Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 4 FSC Part2Document8 pagesEx 3 4 FSC Part2Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ex 6 5 FSC Part2 Ver 2 0 0Document9 pagesEx 6 5 FSC Part2 Ver 2 0 0adnanNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 8 FSC Part2Document4 pagesEx 3 8 FSC Part2Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 4 FSC Part2Document8 pagesEx 3 4 FSC Part2Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ex 5 3 FSC Part2 (Handwritten)Document22 pagesEx 5 3 FSC Part2 (Handwritten)adnanNo ratings yet
- Ex 7 2 FSC Part2 Ver 2 3Document4 pagesEx 7 2 FSC Part2 Ver 2 3adnanNo ratings yet
- Ex 6 9 FSC Part2Document26 pagesEx 6 9 FSC Part2adnanNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 4 FSC Part2Document8 pagesEx 3 4 FSC Part2Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5.3 (Solutions) : Merging Man and MathsDocument6 pagesExercise 5.3 (Solutions) : Merging Man and MathsadnanNo ratings yet
- Calculus exercise solutions with integralsDocument4 pagesCalculus exercise solutions with integralsadnanNo ratings yet
- Ex 7 2 FSC Part2 Ver 2 3Document4 pagesEx 7 2 FSC Part2 Ver 2 3adnanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)Document2 pagesExercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)sohail2798No ratings yet
- Exercise 6.3 (Solutions) : Consider A Circle With Centre at Origin and Radius R - . Differentiating W.R.TDocument3 pagesExercise 6.3 (Solutions) : Consider A Circle With Centre at Origin and Radius R - . Differentiating W.R.TadnanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)Document2 pagesExercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)sohail2798No ratings yet
- MathCity Exercise 6.7 Solutions Calculus Analytic GeometryDocument8 pagesMathCity Exercise 6.7 Solutions Calculus Analytic GeometryadnanNo ratings yet