Fluid Flow Measurement Lab
Object:
To investigate typical methods of measuring the discharge of an essentially
incompressible fluid. (LOs: 1,2)
To verify the application of Steady Flow Energy Equation and the
Bernoullis Equation by experimental results. (LOs: 1,2)
Due Date: ________________
Weighting: 4% of laboratory practicals
Late rule: It is applied as a penalty
Type: Group assignment
Submission details: Submit soft copy onto Moodle as well as hard copy to the
Tutor
Figure 1: Fluid flow measurement apparatus
EN7917
�Apparatus:
Fluid Flow measurement apparatus using a Venturi meter, an Orifice plate
meter and a rotameter and a gravimetric hydraulics bench (fig. 1 &2)
Figure 2: Fluid flow measurement apparatus and hydraulics bench of our Fluid Lab
Procedure:
1. Connect the supply hose from the gravimetric hydraulics bench to the inlet
of the Venturi meter and secure with a hose clip. Connect a hose to the
control valve outlet and direct its free end into the bench-weigh tank
2. Close the main valve fully then open it about a 1/3. Switch on the bench and
slowly open the bench valve until water starts to flow. Allow the flow
measurement apparatus to fill with water then open the bench valve fully,
and then close the main Flow Measurement valve. Couple the hand pump to
the purge valve and pump down until all the manometers read approximately
330 mm. Dislodge any entrapped air from the manometers by gentle tapping
with the fingers. Check that the tube ferrules and the top manifold are free
from water blockage, which will suppress the manometer level.
3. Open the apparatus valve until the rotameter shows a reading of
approximately 40mm. When a steady flow is maintained measure the flow
EN7917
�with the gravimetric Hydraulics bench. During this period, record the
readings of the manometers, the venture and the orifice plate in Table 1.
Figure 3: The rotameter
4. Repeat this procedure for five equidistant values of rotameter readings up to
the point in which the maximum pressure values can be recorded from the
manometer
Results:
In the form of tables, graphs, etc . (LOs: 1,2)
Enter results into table 1. (Best to set this up in an excel spread sheet format
if possible, or use the table provided) . (LOs: 1,2)
Produce a Rotameter calibration chart by plotting the Rotameter readings vs.
the mass flow rates from the weighing tank. . (LOs: 1,2)
Calculation (LOs: 1,2)
Show one full set of calculations.
Refer to the theory and calculation sheet
Comments and Conclusions (LOs: 1,2)
Comment on:
Compare the Cd values for the venturi and the orifice meter with tabulated
values.
Compare and comment on the three types of flow measurement devices used
in this experiment with regards to accuracy, ease of use, size and head loss
requirements.
EN7917
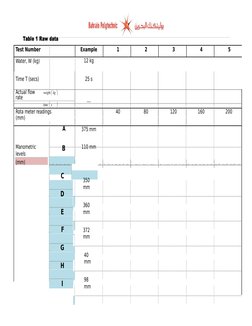
�Table 1 Raw data
Test Number
Example
Water, W (kg)
12 kg
Time T (secs)
25 s
Actual flow
rate
40
80
120
160
200
weight kg
time s
0.480 kg/s
Rota meter readings
(mm)
Manometric
levels
(mm)
375 mm
110 mm
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
350
mm
360
mm
372
mm
40
mm
98
mm
�8
8
72m
m
m
m
EN79
17
�Table 2: Calculation of CD values for the venturi and the orifice plate
Test Number
Example
2
For
venturi
(A-B)
0.265 m
Flow rate = (0.962*dp0.5) (kg/s)
0.495 m
Dp across
venture
Actual
.970
CD value for venture =
therotical
For Orifice
Plate
Dp across
orifice
Upstream velocity
(52mm)
(E-F)
0.332 m
Mass flowrate
.2260
m/s
1000 Area
Down stream velocity (20mm) Mass
flowrate
1000 Area
v2
Kinetic head in
Kinetic head out
.002603 m
2g
v2
CD value for
orifice =
1.5279 m/s
.1190 m
2g
(KH out KHin )
dp
.592
�EN79
17
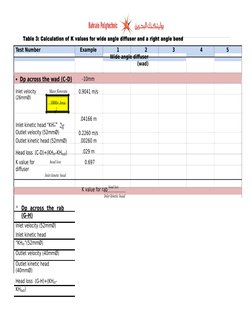
�Table 3: Calculation of K values for wide angle diffuser and a right angle bend
Test Number
Example
Dp across the wad (C-D)
Inlet velocity
(26mm)
Mass flowrate
1
2
Wide angle diffuser
(wad)
-10mm
0.9041 m/s
1000 Area
v2
.04166 m
Inlet kinetic head KHin 2g
Outlet velocity (52mm)
Outlet kinetic head (52mm)
0.2260 m/s
.00260 m
Head loss (C-D)+(KHin-KHout)
.029 m
K value for
diffuser
head loss
0.697
Inlet kinetic head
K value for rab
head loss
Inlet kinetic head
Dp across the rab
(G-H)
Inlet velocity (52mm)
Inlet kinetic head
KHin(52mm)
Outlet velocity (40mm)
Outlet kinetic head
(40mm)
Head loss (G-H)+(KHinKHout)
�Right angle bend rab
10mm
.0226 m/s
.0026 m
.3820 m/s
.00728 m
.00532 m
2.05
EN79
17