0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views1 pageDeep Excavation Risk Management
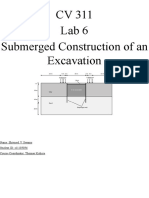
Excessive wall deflection during deep excavation can cause damage to nearby foundations and underground utilities through induced movements and surface settlement cracking. Lowering the groundwater table increases consolidation settlement in soft clay soils due to higher effective stress. Observational approach during deep excavation involves checking design adequacy, anticipating problems, modifying design if needed, optimizing design, making contingency plans, and avoiding delays.
Uploaded by
Hoang An TranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views1 pageDeep Excavation Risk Management
Excessive wall deflection during deep excavation can cause damage to nearby foundations and underground utilities through induced movements and surface settlement cracking. Lowering the groundwater table increases consolidation settlement in soft clay soils due to higher effective stress. Observational approach during deep excavation involves checking design adequacy, anticipating problems, modifying design if needed, optimizing design, making contingency plans, and avoiding delays.
Uploaded by
Hoang An TranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd