Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
digger_scOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
digger_scCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability Cheat Sheet
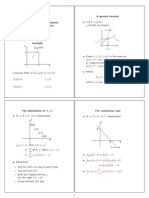
• P (Ac ) = 1 − P (A)
• P (A ∪ B) = P (A) + P (B) if A, B do not overlap.
• P (A ∩ B) = P (A)P (B) if A, B are independent.
• E(aX + bY + c) = aEX + bEY + c
• Eg(X) 6= g(EX) unless g(·) is a linear function
• V ar(X) = E(X − EX)2 = E(X)2 − (EX)2
• E(XY ) = (EX)(EY ) if X, Y are independent.
• V ar(X + Y ) = V ar(X) + V ar(Y ) if X, Y are independent.
• V ar(X + Y ) = V ar(X) + V ar(Y ) + 2cov(X, Y )
• V ar(aX + c) = a2 V ar(X)
• If X, Y independent =⇒ g(X), h(Y ) also independent.
• CDF P (X ≤ t) = F (t) = FX (t)
dF (t)
• density f (t) = dt
• EX = xfX (x)dx = xdF (x)
R R
• Eg(X) = g(x)dF (x)
R
• Central Limit Theorem: Suppose X1 , X2 , . . . Xn , . . . are independent
with a distribution F (x). Let EX = µ and V ar(X) = σ 2 . If 0 < σ 2 < ∞
then (in terms of distribution) for large n
√ √ n
1X
n(X̄ − µ) = n[ Xi − µ] ≈ N (0, σ 2 )
n i=1
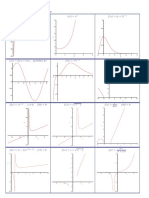
Plus the table for “Brand name distrbution/random variables”. (include
all mean, variance, etc.)
Plus the map of how the different random variables are connected.
You might also like
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Expectation: Definition Expected Value of A Random Variable X Is DefinedDocument15 pagesExpectation: Definition Expected Value of A Random Variable X Is DefinedLibyaFlowerNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Equations: 8.1 D'Alembert's SolutionDocument10 pagesHyperbolic Equations: 8.1 D'Alembert's Solutionrohit singhNo ratings yet
- M5A42 Applied Stochastic Processes Problem Sheet 1 Solutions Term 1 2010-2011Document8 pagesM5A42 Applied Stochastic Processes Problem Sheet 1 Solutions Term 1 2010-2011paradoxNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesHomework 3 SolutionsislayerNo ratings yet
- STOR 435 Formula Sheet: BasicsDocument3 pagesSTOR 435 Formula Sheet: BasicsEricQianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4TrevorNo ratings yet
- STAT2011 2017 Exam Formulae PDFDocument3 pagesSTAT2011 2017 Exam Formulae PDFeccentricftw4No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Fall 2023Document12 pagesLecture 3 - Fall 2023tarunya724No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Fall 2023Document13 pagesLecture 3 - Fall 2023tarunya724No ratings yet
- Stats3 Topic NotesDocument4 pagesStats3 Topic NotesSneha KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Calculus Reference (SparkCharts)Document2 pagesCalculus Reference (SparkCharts)www_webb100% (1)
- Mit6 041f10 l11Document3 pagesMit6 041f10 l11api-246008426No ratings yet
- Mem 601 L 3Document43 pagesMem 601 L 3Naji HayderNo ratings yet
- Interpolation and Approximation TheoryDocument15 pagesInterpolation and Approximation TheoryFaisal RahmanNo ratings yet
- Math556 07 InequalitiesDocument7 pagesMath556 07 InequalitiesFrankie HuangNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2008-10-31. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2008-10-31. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Nonlife Actuarial Models: Claim-Severity DistributionDocument62 pagesNonlife Actuarial Models: Claim-Severity Distributionvoikien01No ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaeMahatama Sharan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Structural ElementsDocument33 pagesStructural ElementsvamshiNo ratings yet
- Exercises and Answers To Chapter 1Document35 pagesExercises and Answers To Chapter 1norman camarenaNo ratings yet
- Distribusi SeragamDocument7 pagesDistribusi Seragamherlina balangsawangNo ratings yet
- Unit-II. 21mab101t - Calculus and Linear Algebra 2023-2024pptxDocument84 pagesUnit-II. 21mab101t - Calculus and Linear Algebra 2023-2024pptxsampathjogipusala123No ratings yet
- Exam - 2013 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2013 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Discrete Probability Distribution Chapter3Document47 pagesDiscrete Probability Distribution Chapter3TARA NATH POUDELNo ratings yet
- Story SheetDocument2 pagesStory SheetEd ZNo ratings yet
- The Area of The SurfaceDocument5 pagesThe Area of The SurfaceThùy Dung TrầnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document45 pagesChapter 5api-3729261No ratings yet
- 2022 2023midtermDocument3 pages2022 2023midtermCyber AlphaNo ratings yet
- Mat CeroDocument17 pagesMat CeroYuber CcoaNo ratings yet
- MIT14 381F13 Lec1 PDFDocument8 pagesMIT14 381F13 Lec1 PDFDevendraReddyPoreddyNo ratings yet
- Class03 8Document2 pagesClass03 8Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- 1 More Dispersion: Weston Barger June 30, 2016Document6 pages1 More Dispersion: Weston Barger June 30, 2016ranvNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability TheoryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Probability TheoryarjunvenugopalacharyNo ratings yet
- Taper Rod FEM LongDocument25 pagesTaper Rod FEM LonglapuNo ratings yet
- HW 092603Document5 pagesHW 092603Aaron LeãoNo ratings yet
- Convolutions Involving The Exponential Function and The Exponential IntegralDocument9 pagesConvolutions Involving The Exponential Function and The Exponential IntegralSajid Mahmud SejanNo ratings yet
- Unit-II. 21mab101t - Calculus and Linear Algebra 2023-2024pptxDocument84 pagesUnit-II. 21mab101t - Calculus and Linear Algebra 2023-2024pptxhisameer0026No ratings yet
- CSC413 A2Document3 pagesCSC413 A2Ian QuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Particle Size AnalysisDocument13 pagesChapter 1. Particle Size AnalysisKhan AaghaNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus - Solutions 1: 1. in Each Case, S Is The Shaded Region, Excluding Any Hatched Lines/curves. (A) (B)Document7 pagesVector Calculus - Solutions 1: 1. in Each Case, S Is The Shaded Region, Excluding Any Hatched Lines/curves. (A) (B)Zohiab ZafarNo ratings yet
- Llistafuncions Figures c1 PlanouDocument1 pageLlistafuncions Figures c1 PlanoualberttauleraNo ratings yet
- Answers To Final-2021Document9 pagesAnswers To Final-2021Enes ErtenNo ratings yet
- Lecture DMDocument11 pagesLecture DMHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stats 100A Hw5Document2 pagesStats 100A Hw5Billy BobNo ratings yet
- Differentiation RevisionDocument4 pagesDifferentiation RevisionMyureshwaranNo ratings yet
- Review1 PDFDocument22 pagesReview1 PDFdNo ratings yet
- Functions With Several VariablesDocument36 pagesFunctions With Several VariablesBlackBunny103No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledAdrian CulicăNo ratings yet
- Integrals Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesIntegrals Cheat SheetFrostDevs GTNo ratings yet
- Distributions and Normal Random VariablesDocument8 pagesDistributions and Normal Random Variablesaurelio.fdezNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Probability Theory - Formula SheetDocument13 pagesProbability Theory - Formula SheettommielombartsNo ratings yet
- Existence of Positive Solutions of Nonlinear Fractional Differential EquationsDocument9 pagesExistence of Positive Solutions of Nonlinear Fractional Differential EquationsBoutiara AbdellatifNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Probability & Random Variable Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesProbability & Random Variable Cheat SheetadkinsblNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics AssignmentDocument10 pagesFluid Mechanics AssignmentabhijeetNo ratings yet
- Probability Unit 4Document32 pagesProbability Unit 4Sayli KomurlekarNo ratings yet
- Probability & RV Lec 11 & 12Document58 pagesProbability & RV Lec 11 & 12areebarajpoot0453879No ratings yet
- Introduction To Special Issue On Monte Carlo Methods in StatisticsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Special Issue On Monte Carlo Methods in Statisticsdigger_scNo ratings yet
- What-Is A BilliardDocument2 pagesWhat-Is A Billiarddigger_scNo ratings yet
- What-Is A MotiveDocument3 pagesWhat-Is A Motivedigger_scNo ratings yet
- What-Is A GerbeDocument2 pagesWhat-Is A Gerbedigger_scNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Special Issue On Healthcare Modeling and SimulationDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Special Issue On Healthcare Modeling and Simulationdigger_scNo ratings yet
- The Four Meanings of Accurate To 3 PlacesDocument5 pagesThe Four Meanings of Accurate To 3 Placesdigger_scNo ratings yet
- Parametric Envelopes: 226 The Mathematical GazetteDocument4 pagesParametric Envelopes: 226 The Mathematical Gazettedigger_scNo ratings yet
- Early Work in Numerical Hydrodynamics Francis H. HarlowDocument1 pageEarly Work in Numerical Hydrodynamics Francis H. Harlowdigger_scNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Modeling of Biological SystemsDocument2 pagesQuantitative Modeling of Biological Systemsdigger_scNo ratings yet
- Integration by Parts and Infinite Series Kilmer2-0801921Document5 pagesIntegration by Parts and Infinite Series Kilmer2-0801921digger_scNo ratings yet
- Inversion in The Complex PlaneDocument2 pagesInversion in The Complex Planedigger_scNo ratings yet
- A Reading List in Inverse Problems-BiblioDocument5 pagesA Reading List in Inverse Problems-BibliotomdarelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Special Issue On Fractional Differentiation and Its ApplicationsDocument1 pageIntroduction To The Special Issue On Fractional Differentiation and Its Applicationsdigger_scNo ratings yet
- Parseval's TheoremDocument2 pagesParseval's Theoremthanque7182No ratings yet
- DIYMathematics v. ThePackage Mag.2019.15Document2 pagesDIYMathematics v. ThePackage Mag.2019.15digger_scNo ratings yet
- Resource Letter ScL-1 Scaling LawsDocument5 pagesResource Letter ScL-1 Scaling Lawsdigger_scNo ratings yet
- When Is The Sum of The First N Consecutive Odd Cubes A Square Mag.2019.62Document2 pagesWhen Is The Sum of The First N Consecutive Odd Cubes A Square Mag.2019.62digger_scNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers and Triangles Mag.2015.54Document2 pagesComplex Numbers and Triangles Mag.2015.54digger_scNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers and Triangles Mag.2015.54Document2 pagesComplex Numbers and Triangles Mag.2015.54digger_scNo ratings yet
- (Chris Doran, Anthony Lasenby) Geometric Algebra F PDFDocument6 pages(Chris Doran, Anthony Lasenby) Geometric Algebra F PDFOctavianus Julianto SamanNo ratings yet
- Probability Cheat SheetDocument1 pageProbability Cheat Sheetdigger_scNo ratings yet
- DIYMathematics v. ThePackage Mag.2019.15Document2 pagesDIYMathematics v. ThePackage Mag.2019.15digger_scNo ratings yet
- Interview Gian Carlo RotaDocument15 pagesInterview Gian Carlo Rotadigger_scNo ratings yet
- One Line ProgrammingDocument7 pagesOne Line Programmingdigger_scNo ratings yet
- One Line ProgrammingDocument7 pagesOne Line Programmingdigger_scNo ratings yet
- Sorting Single MoleculesDocument8 pagesSorting Single Moleculesdigger_scNo ratings yet
- The Magic Calculator and The Sine Addition FormulaDocument6 pagesThe Magic Calculator and The Sine Addition Formuladigger_scNo ratings yet
- A Statistics Summary-Sheet: Sampling Conditions Confidence Interval Test StatisticDocument7 pagesA Statistics Summary-Sheet: Sampling Conditions Confidence Interval Test Statisticdigger_scNo ratings yet
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsFrom EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Transform Your 6-12 Math Class: Digital Age Tools to Spark LearningFrom EverandTransform Your 6-12 Math Class: Digital Age Tools to Spark LearningNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathFrom EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)