Professional Documents
Culture Documents
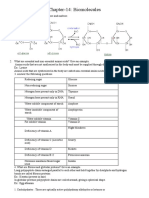
What Happens When D-Glucose Is Treated With The Following Reagents? HI (Ii) Bromine Water (Iii) HNO
Uploaded by
Anishka SainiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Happens When D-Glucose Is Treated With The Following Reagents? HI (Ii) Bromine Water (Iii) HNO
Uploaded by
Anishka SainiCopyright:
Available Formats
BIO MOLECULES By Ajeet Chaudhary
Q1) Which type of linkage is present in-
(a) Oligosaccharides(Di and Tri----) and Polysaccharides,
(b) Polypeptides (Proteins)
(c) Nucleic Acids (Polynucleotides)
Ans) a) Glycosidic linkage, b) Peptide linkage, c) Phosphodiester linkage
Q2) What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents?
(i) HI (ii) Bromine water (iii) HNO3
Ans) (i)
(ii)
(iii)
Q 3) Enumerate the reactions of D-glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
OR
Write any two limitations of open chain structure of D-glucose.
Ans) a) It is unable to react with 2,4-DNP and NaHSO3.
b) Its pentaacetate does not react with hydroxylamine(NH2OH).
Q4) What are anomers?
Ans) These are the isomers which differ in their configuration at C-1 of cyclic D-glucose. Ex: α- and β –D-
glucose.
Q5) Draw the Haworth (pyranose) structure of α- and β –D-glucose.
Ans)
Q6) What is glycosidic linkage?
Ans) The linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage.
Q7) Name the monomer(monosaccharides) unit of the following-
OR
What are the products obtained on hydrolysis of the following:
(a) Sucrose (d) Starch
(b) Maltose (e) Cellulose
1
(c) Lactose (f) Glycogen
Page
Ans) a) Sucrose- α-D-Glucose and β-D-Fructose, b) Maltose- α-D-Glucose,
c) Lactose - β-D-Glucose and β-D-Galactose, d) Starch - α-D-Glucose,
e) Cellulose - β-D-Glucose, f) Glycogen - α-D-Glucose
Q 8) What is invert sugar?
Ans) Mixture of α-D-Glucose and β-D-Fructose which is formed by inversion of cane sugar(sucrose), is known
as invert sugar.
Q 9) What are the component of starch? How do they differ from each other?
Ans) The two components of starch are amylose and amylopectin.
Differences
Amylose Amylopectin
1. It constitutes 15-20% of 1. It constitutes 80-85% of starch.
starch.
2. It is water soluble. 2. It is insoluble in water.
3. It is linear chain of α-D- 3. It is branched chain of α-D-
Glucose. Glucose.
Q10) Why is Glycogen known as animal starch?
Ans) Glycogen is stored in animal body and its structure is similar to amylopectin , a component of starch.
Q11) What are essential and non-essential aminoacids? Give two examples of each type.
Ans)
ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS NON- ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS
1. Amino acids which cannot 1. Amino acids which can be
be synthesised in the body synthesised in the body.
and must be taken through
diet.
Ex: Valine, Lysine Ex: Glysine, Alanine
Q12) What is petide bond(Peptide linkage)?
Ans) It is an amide linkage formed between –COOH group of one amino acid and –NH2 group of the other
amino acid.
Q13) State the differences between:
(a) Fibrous and Globular Protein, (b) α-Helix and β-pleated sheet structure
(c) Primary and secondary structure of proteins
Ans a)
Fibrous Protein Globular Protein
1. These have fibre like structure. 1. These have spherical shape.
2. They are water soluble. 2. They are water insoluble.
Ex: Keratin, Myosin Ex: Insulin, Enzymes
b)
α-Helix β-pleated sheet structure
1. The polypeptide chain are 1. The polypeptide chains are stretched
right handed coiled and the out and laid side by side and held
turns are held together by together by intermolecular hydrogen
intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
bonds.
c)
Primary Struture of Protien Secndary Struture of Protien
1. The sequence in which the 1. It arises due to regular folding of the
amino acids are arranged in a plypeptide chain due to intermolecuar
protein. hydrogen bonding between the –COOH
2
and –NH2 group.
Page
Q14) What is native protein?
Ans) Pritein found in biological system with a unique three dimensional structure and biological activity is
called native protein.
Q15) Define denaturation. OR When is a protein said to be denaturated? OR What is the effect of
denaturation on protein?
Ans) When the secondery and tertiary structure of proteins is destroyed due to change in p H and
temperature, it looses its biological actyivity. Such a protein is called denatured protein.
Q16) How are vitamins classified? Explain with example.
Ans) Vitamins are classified on the basis of their solubility in water and fat.
(i) Fat soluble vitamins: Vitamins which are soluble in fat and oils but insoluble in water.
Ex: Vitamin A, D , E , K
(ii) Water soluble vitamins: Vitamins which are soluble in water.
Ex: Vitamin B and C
Q17) What are the products obtained on complete hydrolysis of nucleic acids?
Ans) Pentose sugar, Phosphoric acid and nitrogeneous bases.
Q18) What is the difference between :
(a) Nucleoside and Nucleotide
(b) DNA and RNA
Ans) (a)
NUCLEOSIDE NUCLEOTIDE
1. It constitutes of a pentose sugar and 1. It constitutes of a pentose sugar,
nitrogenous base. Phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base.
(b)
DNA RNA
1. It contains deoxyribose sugar. It contains ribose sugar.
2. It contains thymine along with It contains uracil along with adenine, cytosine
adenine, cytosine and guanine. and guanine.
3. It is responsible for maintaining It is responsible for protein synthesis.
heredity transformation.
4. It has a double helical structure. It is single stranded.
Q19) Which type of bonds holds a DNA double helix together?
Ans) Intramolecular hydrogen bond.
Q20) What are zwitter ions?
Ans) The dipolar molecules ( internal salt) which have both positive and negative part.
Ex: Glycine NH3+CH2COO- , Sulphanilllic acid
Q21) Why vitamin C cannot be stored in our body?
Ans) Vitamin C being soluble in water is excreted out through urine from the body.
Q22) Name the type of bonding which stabilize α-helix structure in proteins?
Ans) Hydrogen bonding
Q23) Name the naturally occurring amino acid which is not optically active?
Ans) Glycine
Q24) Name the carbohydrate used as storage molecule to store energy in animals?
Ans) Glycogen( animal starch)
Q25) Name an oil soluble vitamin which is a powerful antioxidant. Give its one natural source.
Ans) Vitamin E. Its source is almond oil and wheat.
Q26) Wrtie the name of deficiency disease of amino acids?
Ans) Kwashiorkor ( Disbalance of water in a particular part of our body)
3
###########################################CAS############################################
Page
You might also like
- Biomolecules Question Bank (Subjective)Document10 pagesBiomolecules Question Bank (Subjective)Rajendra SahaNo ratings yet
- XII Biomolecules OrganizedDocument9 pagesXII Biomolecules OrganizedKazi afroz SultanNo ratings yet
- 12 Qa-BiomoleculesDocument6 pages12 Qa-BiomoleculesSUMIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument7 pagesBIOMOLECULESMasum AhmedNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 BiomoleculesVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula Chapter14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesChemistry Formula Chapter14 BiomoleculesAnup GoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Biomolecules Worksheet Answers Set 4Document9 pagesChapter 14 Biomolecules Worksheet Answers Set 4kyomuhendobright4No ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESSDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESScse.220840131017No ratings yet
- 14 BiomoleculesDocument5 pages14 BiomoleculesForzen flamesNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry Practice Sheet Unit 14: BIOMOLECULESDocument4 pages12th Chemistry Practice Sheet Unit 14: BIOMOLECULESGLOBAL XNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules of LifeDocument9 pagesBiomolecules of LifeAbhishek PantheeNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument19 pagesBIOMOLECULESarviindkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ch4 BiochemistryDocument6 pagesCh4 BiochemistryMohamed Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules ImpDocument22 pagesBiomolecules ImpmrdaddydaddaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Biology 101 Answer MemoDocument18 pagesTutorial 3 - Biology 101 Answer MemoKaizer NdoloNo ratings yet
- Carbs LehningerDocument9 pagesCarbs LehningerElla BangalanNo ratings yet
- BCH 214 Tutorial 2 2013 Memo & QuesDocument6 pagesBCH 214 Tutorial 2 2013 Memo & QuesvictorNo ratings yet
- Question Bank With Solution Biochemistry PDFDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank With Solution Biochemistry PDFKiran SharmaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 BiomoleculesPrsprabakar 1977No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument29 pagesBiomoleculeswavodak821No ratings yet
- Biology National MDCAT FLP # 1Document22 pagesBiology National MDCAT FLP # 1Salam FatimaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemry Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument22 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemry Chapter 14 BiomoleculesfailurewasteworthlessNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Lesson Plan For AbsenteesDocument4 pagesBiomolecules Lesson Plan For AbsenteesGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio ImpDocument10 pagesBio Implinngeshwar BNo ratings yet
- Xii CH14 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesXii CH14 BiomoleculesKrish KambojNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Revision BookletDocument71 pagesBiological Molecules Revision Bookletmanikandanv.18No ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument14 pagesBio MoleculesAmbesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules NotesDocument14 pagesBiomolecules NotesbrovinsbrovinNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument4 pagesBio Moleculestimepass CreationNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Important PointsDocument25 pagesBiomolecules: Important PointsPankaj MishraNo ratings yet
- 2019 Chapter5 Carbohydrates Students PDFDocument32 pages2019 Chapter5 Carbohydrates Students PDFyoNo ratings yet
- Unit Test-1 - Chemical Basis of LifeDocument9 pagesUnit Test-1 - Chemical Basis of LifeMighty Warrior GSRNo ratings yet
- BVOPT-102 General BiochemistryDocument14 pagesBVOPT-102 General BiochemistryManisha khanNo ratings yet
- Unit-14 Biomolecules Mini 2023Document5 pagesUnit-14 Biomolecules Mini 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH14 Biomolecules 01Document5 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH14 Biomolecules 01AditiNo ratings yet
- (H2) CI1.2 - Biomolecules (Carboh)Document24 pages(H2) CI1.2 - Biomolecules (Carboh)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 10 QP BiomoleculeDocument5 pages10 QP BiomoleculePREM SINGHNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument18 pagesBiomoleculesKrish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Past PapersDocument2 pagesBiomolecules Past Papersharshiiiii352No ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 4 BioDocument9 pagesTutorial Chapter 4 BioZunnurain AmniNo ratings yet
- Biology Holiday PackageDocument7 pagesBiology Holiday PackagechogoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 - Biomolecules Important Questions 2022-23Document22 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 - Biomolecules Important Questions 2022-23Archanaa PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Quiz of General BiologyDocument35 pagesQuiz of General Biologyhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 ch9 Class 11Document4 pagesWorksheet 9 ch9 Class 11akilapaul17682No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Biomolecules)Document6 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Biomolecules)SivakumarNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Unit F212 Molecules, Biodiversity, Food and HealthDocument34 pagesAS Biology Unit F212 Molecules, Biodiversity, Food and HealthTravisJohn-JohnsonReadNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Anil HssliveDocument2 pagesBiomolecules Anil HssliveMathew YoyakkyNo ratings yet
- As OCR Biology Notes Unit 2Document34 pagesAs OCR Biology Notes Unit 2Jawwad Lnd KhanNo ratings yet
- Bimenyimana Bio ExercisesDocument119 pagesBimenyimana Bio Exercisesmunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Amino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Document2 pagesAmino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Noviemae TuandaNo ratings yet
- Bio Mole CuleDocument13 pagesBio Mole CuleaayanNo ratings yet
- Unit 14..Document6 pagesUnit 14..7.7.harshitpatelNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument16 pagesBiological MoleculesThandeka NcubeNo ratings yet
- Biology 1st Year T-2Document2 pagesBiology 1st Year T-2Amir HabibNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules AssignmentDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules AssignmentTanu BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice 2013 09 25 1 8Document8 pagesMultiple Choice 2013 09 25 1 8mimtabolismNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates and LipidsJasmin RIshel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument14 pagesBiomoleculesnadeemmessi30No ratings yet
- 16 - Chapter 6 PDFDocument33 pages16 - Chapter 6 PDFAnishka SainiNo ratings yet
- R v. BedingfieldDocument50 pagesR v. BedingfieldPuja NairNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To The Project: 1.1 Unicitral Model Law On IcaDocument10 pages1.introduction To The Project: 1.1 Unicitral Model Law On IcaAnishka SainiNo ratings yet
- 2 1927 PDFDocument8 pages2 1927 PDFAnishka SainiNo ratings yet
- Chanul BioDocument1 pageChanul BioAnishka SainiNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: BiochemistryDocument10 pagesGluconeogenesis: BiochemistryManila Med100% (1)
- Bioinfo Exp 7Document5 pagesBioinfo Exp 7navneetNo ratings yet
- Alteration of Host Cell Behavior by PathogensDocument7 pagesAlteration of Host Cell Behavior by PathogensAbhijit SatpatiNo ratings yet
- rối loạn lipid máu PDFDocument107 pagesrối loạn lipid máu PDFNguyễn MaiNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Action Revision NotesDocument2 pagesEnzyme Action Revision Notessohailnoreen5062No ratings yet
- Vitaminsfinal 150515162131 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument52 pagesVitaminsfinal 150515162131 Lva1 App6892 PDFkrishna upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Signaling PathwaysDocument6 pagesSignaling PathwaysBELLA NISANo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Lipid MetabolismDocument45 pagesChapter 21 Lipid MetabolismWaad MajidNo ratings yet
- PPP QuestionsDocument3 pagesPPP QuestionsHarun MohamedNo ratings yet
- Articulo, Proteinas en La Maduración de La CarneDocument9 pagesArticulo, Proteinas en La Maduración de La CarneLinda Margarita Alcala BoteroNo ratings yet
- Enzyme PPTDocument20 pagesEnzyme PPTJames ReiterNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics Questions and Answers: 2 Year Undergraduates-Biology 2018-2019Document8 pagesEnzyme Kinetics Questions and Answers: 2 Year Undergraduates-Biology 2018-2019Emmanuel JoyNo ratings yet
- Protein FoldingDocument9 pagesProtein FoldingAyush ZalaNo ratings yet
- Bio Materials - Physics and ChemistryDocument502 pagesBio Materials - Physics and ChemistryJosé RamírezNo ratings yet
- Ketogenesis PDFDocument36 pagesKetogenesis PDFDinda KbulahNo ratings yet
- CH1131 Biomolecular Engrg Lipid Metabolism To Coordination Summary 2013Document4 pagesCH1131 Biomolecular Engrg Lipid Metabolism To Coordination Summary 2013Nhân TrầnNo ratings yet
- EC Thesis 08052019Document206 pagesEC Thesis 08052019Jose EduardoNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton EngDocument7 pagesCytoskeleton EngTha Joon Lautner MatsuyamaNo ratings yet
- What Is HyperlipidemiaDocument9 pagesWhat Is Hyperlipidemiaichanara100% (2)
- LipidsDocument53 pagesLipidsGlen Mangali100% (1)
- SCOP and CATH DatabaseDocument22 pagesSCOP and CATH DatabaseAishwarya Dharan100% (3)
- Glycogen MetabolismDocument11 pagesGlycogen MetabolismShruti MishraNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Oils and FatsDocument36 pagesUNIT III Oils and FatsShubham WarseNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 2Document6 pagesPractice Exam 2John SmithNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question On CytokinesDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Question On CytokinesRimsha Naveed100% (1)
- CH 101 CH 21 Lecture Notes LipidsDocument6 pagesCH 101 CH 21 Lecture Notes Lipidskishan kunwarNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PresDocument14 pagesEnzymes PresSaeed Ahmad Zeb100% (1)
- Module 8: Food Chemistry, Nutrition, and Traditional Foods: Food: Any Substances That Can Be MetabolizedDocument36 pagesModule 8: Food Chemistry, Nutrition, and Traditional Foods: Food: Any Substances That Can Be Metabolizedhmce kalyaniNo ratings yet
- Nilai GiziDocument3 pagesNilai GiziDwi Rendiani SeptaNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Recipe: Perfectly Rawsome Vip MembershipDocument4 pagesSupplemental Recipe: Perfectly Rawsome Vip MembershipGaby BegetNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Applied Geochemistry: Advances in Mineral Exploration TechniquesFrom EverandApplied Geochemistry: Advances in Mineral Exploration TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Dust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesFrom EverandDust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesNo ratings yet
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Practical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationFrom EverandPractical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationNo ratings yet
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The Unfortunate Truth About Vaccines: Exposing the Vaccine OrthodoxyFrom EverandThe Unfortunate Truth About Vaccines: Exposing the Vaccine OrthodoxyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Long Hard Road: The Lithium-Ion Battery and the Electric CarFrom EverandLong Hard Road: The Lithium-Ion Battery and the Electric CarRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNo ratings yet