Professional Documents
Culture Documents
By: Jhon Añez: Aritmética Desigualdades Radicales Potenciación
Uploaded by
Jhon D'LozxoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
By: Jhon Añez: Aritmética Desigualdades Radicales Potenciación
Uploaded by
Jhon D'LozxoCopyright:
Available Formats
Math for Dummies
By: Jhon Añez
Aritmética Desigualdades Radicales Potenciación
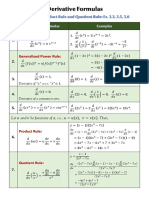
1) 𝑎(𝑏 + 𝑐) = 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑎𝑐 ≥ (𝑀𝑎𝑦𝑜𝑟 𝑜 𝑖𝑔𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑞𝑢𝑒 … ) 𝑛 𝑛 𝑛 0
√𝑎 . √𝑏 = √𝑎 ∙ 𝑏 𝑎 =1
𝑎 𝑐 𝑎𝑐 ≤ (𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑜𝑟 𝑜 𝑖𝑔𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑞𝑢𝑒 … )
2) ∙ =
𝑏 𝑑 𝑏𝑑 > (𝑀𝑎𝑦𝑜𝑟 𝑞𝑢𝑒 … ) 𝑛 𝑎𝑛 ∙ 𝑎𝑚 = 𝑎𝑚+𝑛
𝑎 𝑐 𝑎𝑑 + 𝑏𝑐 < (𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑜𝑟 𝑞𝑢𝑒 … ) √𝑎 𝑎 𝑛
3) + = 𝑛 = √
𝑏 𝑑 𝑏𝑑 ≫ (𝑀𝑢𝑐ℎ𝑜 𝑚𝑎𝑦𝑜𝑟 𝑞𝑢𝑒 … ) √𝑏 𝑏 𝑎𝑛
𝑎/𝑏 𝑎 𝑑 ≪ (𝑀𝑢𝑐ℎ𝑜 𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑜𝑟 𝑞𝑢𝑒 … ) = 𝑎𝑛−𝑚
4) 𝑐/𝑑 = 𝑏 ∙ 𝑐 𝑎𝑚
𝑛 𝑚 𝑚
𝑛
𝑎±𝑏 𝑎 𝑏
Completación de Cuadrados
√𝑎𝑚 = ( √𝑎) = 𝑎𝑛 1
5) = ±
𝑐 𝑐 𝑐 = 𝑎−𝑛 → 𝑎 ≠ 0
si 𝒂 ≠ 𝟎 entonces: 𝑎𝑛
6) (𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑐 + 𝑑) =
𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 = 𝑎𝒖2 + 𝑲 𝑚 𝑛
√ √𝑎 = 𝑚 . 𝑛
𝑎𝑐 + 𝑎𝑑 + 𝑏𝑐 + 𝑏𝑑
𝑏 𝑏2
√𝑎 𝑎 𝑛 𝑎𝑛
𝒖=𝑥+( ) → 𝑲=𝑐− ( ) = 𝑛
2𝑎 4𝑎 𝑏 𝑏
Logaritmos Logaritmo Neperiano Productos Notables
𝑦 = log 𝑎 𝑥 ↔ 𝑥 = 𝑎 𝑦 𝑦 = ln(𝑥) ↔ 𝑥 = 𝑒 𝑦 (𝑎 + 𝑏) ∙ (𝑎 − 𝑏) = 𝑎2 − 𝑏 2
log 𝑎 1 = 0 𝑙𝑛( 1) = 0 (𝑎 + 𝑏)2 = 𝑎2 + 2𝑎 ∙ 𝑏 + 𝑏 2
log 𝑎 𝑎 = 1
ln( 𝑒) = 1 (𝑎 − 𝑏)2 = 𝑎2 − 2𝑎 ∙ 𝑏 + 𝑏 2
log 𝑎 (𝐴 ∙ 𝐵) = log 𝑎 𝐴 + log 𝑎 𝐵
𝐴 𝑙𝑛(𝐴 ∙ 𝐵) = ln(𝐴) + 𝑙𝑛( 𝐵) (𝑎 + 𝑏)3 = 𝑎3 + 3𝑎2 ∙ 𝑏 + 3𝑎 ∙ 𝑏 2 + 𝑏 3
log 𝑎 ( ) = log 𝑎 𝐴 − log 𝑎 𝐵 𝐴
𝐵 (𝑎 − 𝑏)3 = 𝑎3 − 3𝑎2 ∙ 𝑏 + 3𝑎 ∙ 𝑏 2 − 𝑏 3
𝑙𝑛 ( ) = 𝑙𝑛( 𝐴) − 𝑙𝑛( 𝐵)
log 𝑎 𝐴𝑛 = 𝑛. log 𝑎 𝐴 𝐵 (𝑥 + 𝑎)(𝑥 + 𝑏) = 𝑥 2 + (𝑎 + 𝑏)𝑥 + 𝑎 ∙ 𝑏
log 𝑏 𝑥 𝑛
𝑙𝑛( 𝐴 ) = 𝑛. 𝑙𝑛(𝐴)
log 𝑎 𝑥 = (𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎2 − 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 ) = 𝑎3 + 𝑏 3
log 𝑏 𝑎 1 𝑙𝑛( 𝑥)
𝑛
1 log 𝑎 𝑥 𝑙𝑛( √𝑥 ) = 𝑙𝑛( 𝑥) = (𝑎 − 𝑏)(𝑎2 + 𝑎 ∙ 𝑏 + 𝑏 2 ) = 𝑎3 − 𝑏 3
𝑛
log 𝑎 √𝑥 = log 𝑎 𝑥 = 𝑛 𝑛
𝑛 𝑛 Triangulo de Pascal
log𝑎 (𝑥) 𝑒 𝑙𝑛(𝑥) = 𝑥
𝑎 =𝑥
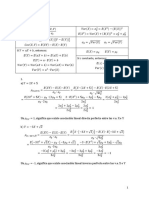
Identidades Trigonométricas
𝑠𝑒𝑛2 (𝑥) = 1 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠 2 (𝑥) 1
𝑠𝑒𝑐 𝑛 (𝑥) =
𝑐𝑜𝑠 2 (𝑥) = 1 − 𝑠𝑒𝑛2 (𝑥) 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑛 (𝑥)
1
𝑡𝑔2 (𝑥) = 𝑠𝑒𝑐 2 (𝑥) − 1 𝑐𝑠𝑐 𝑛 (𝑥) =
𝑠𝑒𝑛𝑛 (𝑥)
2 (𝑥) 2 (𝑥)
𝑠𝑒𝑐 = 𝑡𝑔 +1
𝑐𝑠𝑐 2 (𝑥) = 𝑐𝑡𝑔2 (𝑥) + 1 1
𝑐𝑡𝑔𝑛 (𝑥) = Factorización
1 − cos(2𝑥) 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑛 (𝑥) 𝑎2 − 𝑏 2 = (𝑎 − 𝑏)(𝑎 + 𝑏)
2 (𝑥)
𝑠𝑒𝑛
2 sin(2𝑥) = 2 sin(𝑥) cos(𝑥)
𝑎3 − 𝑏 3 = (𝑎 − 𝑏)(𝑎2 + 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 )
1 + cos(2𝑥) cos(2𝑥) = 2 sin(𝑥) cos(𝑥)
𝑐𝑜𝑠 2 (𝑥) 𝑎4 − 𝑏 4 = (𝑎 − 𝑏)(𝑎3 + 𝑎2 𝑏 + 𝑎𝑏 2 + 𝑏 3 )
2
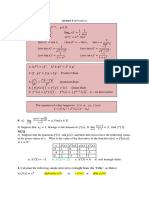
Intervalos Trigonometría Formula Cuadrática
Intervalo Abierto: (𝑎, 𝑏) si 𝑎 ≠ 0 y 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 = 0,
Intervalo Cerrado: [𝑎, 𝑏] 𝐶𝑂 𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝑂 𝐶𝐴 𝐻𝐼𝑃 𝐻𝐼𝑃 entonces:
⋯ ⋯ ⋯ ⋯ ⋯
Intervalo Semi-Abierto: (𝑎, 𝑏] 𝐻𝐼𝑃 𝐻𝐼𝑃 𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝑂 𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝑂
Intervalo I: ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ −𝑏 ± √𝑏 2 − 4𝑎𝑐
𝑠𝑒𝑛 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑡𝑎𝑔 𝑐𝑡𝑔 𝑠𝑒𝑐 𝑐𝑠𝑐 𝑥=
(𝑎, ∞+ ); (−∞, 𝑏); (−∞, ∞+ ) 2𝑎
Valores de las funciones trigonométricas de los ángulos notables → 𝜋 = 180°
En radianes En grados 𝑠𝑒𝑛 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑡𝑎𝑔
0° 0 1 0
1 √3 √3
𝜋/6 30°
2 2 3
𝜋/4 45° √2 √2 1
2 2
√3 1
𝜋/3 60° √3
2 2
𝜋/2 90° 1 0 +∞
√3 1
2𝜋/3 120° − −√3
2 2
√2 √2
3𝜋/4 135° − −1
2 2
1 √3 √3
5𝜋/6 150° − −
2 2 3
𝜋 180° 0 −1 0
1 √3 √3
7𝜋/6 210° − −
2 2 3
5𝜋/4 225° √2 √2 1
− −
2 2
√3 1
4𝜋/3 240° − − √3
2 2
3𝜋/2 270° −1 0 −∞
√3 1
5𝜋/3 300° − −√3
2 2
√2 √2
7𝜋/4 315° − −1
2 2
1 √3 √3
11𝜋/6 330° − −
2 2 3
2𝜋 360° 0 1 0
You might also like
- Formula Sheet - EM1 - EM2Document12 pagesFormula Sheet - EM1 - EM2Ziyang XieNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Math Formulas SummaryDocument25 pagesMath Formulas SummaryEduard Joseph Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Super HojaDocument3 pagesSuper HojaWilfriSegundoIzquierdoNo ratings yet
- Formulário Cálculo DiferencialDocument1 pageFormulário Cálculo DiferencialmsbambirraNo ratings yet
- SUPER HOJA CHEATSHEETDocument2 pagesSUPER HOJA CHEATSHEETasdsdadNo ratings yet
- Super HojaDocument2 pagesSuper HojaKyara MolinaNo ratings yet
- Super Hoja 1Document2 pagesSuper Hoja 1Daniel Diaz CastilloNo ratings yet
- SUPER HOJA FORMULASDocument2 pagesSUPER HOJA FORMULASYUNIOR ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Formulario Pre..Document7 pagesFormulario Pre..MILTON ANABI SAIWANo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Formula SpecDocument33 pagesPure Mathematics Formula SpecSubaproNo ratings yet
- Derivative FormulasDocument3 pagesDerivative FormulasGul sher BalochNo ratings yet
- Formulario LaPlaceDocument1 pageFormulario LaPlaceandres.castellonNo ratings yet
- Formulario Cálculo Diferencial: Leyes de Los Exponentes Logaritmos Razones TrigonométricasDocument1 pageFormulario Cálculo Diferencial: Leyes de Los Exponentes Logaritmos Razones TrigonométricasJoel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics: Revision Worksheet - 1Document9 pagesPure Mathematics: Revision Worksheet - 1Halal BoiNo ratings yet
- Formulario+de+Matemática+Básica+ +Profe+IsmarDocument1 pageFormulario+de+Matemática+Básica+ +Profe+IsmarmjaNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Integrales InmediatasDocument2 pagesTabla de Integrales Inmediatasjose robertoNo ratings yet
- Successive Differentiation NewDocument21 pagesSuccessive Differentiation NewgcwrhbyzgfNo ratings yet
- Notes - Fourier Series in (-π,π)Document35 pagesNotes - Fourier Series in (-π,π)vu1f2122093No ratings yet
- Formulario de Álgebra - Matemóvil PDFDocument2 pagesFormulario de Álgebra - Matemóvil PDFEliane De Souza ZangNo ratings yet
- 597 - Correction TD Fonction CirculaireDocument4 pages597 - Correction TD Fonction CirculaireToxic DEVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SolutionsDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Solutionshappy062733No ratings yet
- Notes - Fourier Series in (0,2l)Document20 pagesNotes - Fourier Series in (0,2l)vu1f2122093No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 SolutionsDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Solutionshappy062733No ratings yet
- FrmulasClculoIntegral PDFDocument1 pageFrmulasClculoIntegral PDFRicardo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas Cálculo IntegralDocument1 pageFórmulas Cálculo IntegralRicardo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Power Series and TheoremsDocument4 pagesPower Series and TheoremsYen, Charles Enzeih CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Must Knows BasicsDocument2 pagesMathematical Must Knows BasicsKrish KannanNo ratings yet
- Universidad José Carlos MariáteguiDocument4 pagesUniversidad José Carlos MariáteguitreisythaisRNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formulas and IdentitiesDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Formulas and IdentitiesFelipe RetamalNo ratings yet
- Quick Math ReviewDocument9 pagesQuick Math ReviewRC Rech CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Fourier Series in (0,2π)Document39 pagesNotes - Fourier Series in (0,2π)vu1f2122093No ratings yet
- Tarea Derivadas Funciones Trigonometricas David Portilla Saltos Ing Gregorio CoelloDocument6 pagesTarea Derivadas Funciones Trigonometricas David Portilla Saltos Ing Gregorio CoelloDavid PortillaNo ratings yet
- U of T Scarborough MATA33H3 Calculus for Management II Winter 2018 Final ExamDocument37 pagesU of T Scarborough MATA33H3 Calculus for Management II Winter 2018 Final ExamAissatou FallNo ratings yet
- Limite de Funcții: A. Limita Funcției PolinomialeDocument6 pagesLimite de Funcții: A. Limita Funcției PolinomialeJohnBossNo ratings yet
- Limite de Funcții: A. Limita Funcției PolinomialeDocument6 pagesLimite de Funcții: A. Limita Funcției PolinomialeJohnBossNo ratings yet
- Calculus Taylor Polynomial ApproximationsDocument4 pagesCalculus Taylor Polynomial ApproximationsSuman BhurtelNo ratings yet
- Calcular Las Primeras Derivadas ParcialesDocument4 pagesCalcular Las Primeras Derivadas ParcialesBert RTGNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Quick ReviewDocument7 pagesMathematics Quick ReviewRC Rech CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Calculo Diferencial Derivadas de FuncionesDocument6 pagesCalculo Diferencial Derivadas de FuncionesrobertoNo ratings yet
- Fourier TC Vs 4Document33 pagesFourier TC Vs 4Daniel MedauraNo ratings yet
- Calculo 2.tarea 1Document9 pagesCalculo 2.tarea 1DIANA LEYVA HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- FORMULARIODocument2 pagesFORMULARIOpriscila vargasNo ratings yet
- SMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 Answer SchemeDocument5 pagesSMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 Answer SchemeZurainiNo ratings yet
- 04 - HW Derivatives ProblemsDocument3 pages04 - HW Derivatives ProblemsMaxNo ratings yet
- Upto Mid-TermDocument39 pagesUpto Mid-TermSourav DeNo ratings yet
- Tarea2 EnriqueMartinezMuñozDocument7 pagesTarea2 EnriqueMartinezMuñozEnrique Martinez MuñozNo ratings yet
- Harolds Taylor Series Cheat Sheet 2022Document8 pagesHarolds Taylor Series Cheat Sheet 2022MagedNo ratings yet
- Formulae ListDocument6 pagesFormulae ListRISHABH JAINNo ratings yet
- Notes Method of Undetermined Coefficients M.U.C.Document6 pagesNotes Method of Undetermined Coefficients M.U.C.Ghabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Math For FunDocument4 pagesMath For FunFrederick MarsNo ratings yet
- Solución Practico 10Document9 pagesSolución Practico 10Catalina TroncosoNo ratings yet
- Identidades NEH @mathphyrickrezDocument3 pagesIdentidades NEH @mathphyrickrezFelipe Leyva HaroNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet晓春王No ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales - Puntos de LaplaceDocument7 pagesEcuaciones Diferenciales - Puntos de LaplaceJuan Pablo Ramirez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas Matemática IIIDocument1 pageFórmulas Matemática IIIMelvin SermeñoNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: FormularioDocument10 pagesUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de México: FormularioLuis Mauricio Aguilar MunguíaNo ratings yet
- Presentador: M. en C. José Manuel Rosales Guzmán 13/07/2021Document1 pagePresentador: M. en C. José Manuel Rosales Guzmán 13/07/2021José Manuel Rosales GuzmánNo ratings yet