Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guysue
Uploaded by
Dylan RogersCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guysue
Uploaded by
Dylan RogersCopyright:
Available Formats
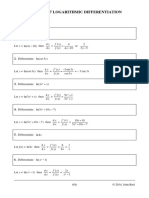
1. x3 – 2x2 – 3x + 6 5.
36x4 + 11x2 +1
Group into two terms Expand 11x2 and assume the difference of
= (x3 – 2x2) – (3x-6) missing terms
Factor out common terms = 36x4 – 6x3+6x3+6x2 – x2 + x – x –x –1
= x2(x-2) – 3 (x–2) Use commutative basis and group into
Factor out x –2 here terms
= (x–2) (x2–3) = (36x4–6x3+6x2)+(6x3–x2+x)+(6x2–x–1)
Factor out common terms
2. 4m3 – 4m – 3m2 + 3 = 6x2 (6x2–x+1)+ x(6x2 –x+1)+(6x2 –x+1)
Group into two terms Factor out 6x2 – x + 1
= (4m3 – 4m) – (3m2-3) = (6x2 – x + 1) (6x2 + x + 1)
Factor out common terms
= 4m (m2 – 1) – 3 (m2 – 1) 6. x4 + 4
Factor out m2 –1 Assume the Difference of 4x2 to get
= (m2 – 1) (4m – 3) perfect squares
Factor m2 – 1 using difference of squares = x4 + 4x2 – 4x2 + 4
= (m+1) (m–1) (4m – 3) Use commutative laws and Group into
two terms
3. 8x3 – y3 – 6x + 3y = (x2 +4x2 + 4) – (4x2)
Group into two terms Factor 4x4 + 4x2 + 4 using Difference of
= (8x3 – y3) – (6x –3y) squares
Factor 8x3-y3 using difference of cubes x3 (x2)2 x x2
x3 (2x)3 x 2x y3 (2)2 y 2
y3 (y)3 y y 2xy 2(x2)(2)
Factor out common terms from 6x – 3y = (x+2)2 – (4x2)
= (2x – y) (4x2 + 2xy + y2) – 3 (2x –y) Turn 4x2 into (2x)2 to use Difference of
Factor out 2x –y squares
= (2x –y) [(4x2 + 2xy + y2) – 3)] = (x2 + 2)2 – (2x)2
= (2x –y) (4x2 + 2xy + y2 – 3) x x2+2 y 2x
= [(x +2)+2x] [(x +2) –2x)
2 2
4. 16x2 + 8xy + y2 – z2 – 10z – 25
=(x2+2+2x) (x2+2–2x)
Group into two terms
= (16x2 + 8xy + y2) – (z2 + 10z + 25)
Factor two terms using Perfect Trinomial
x2 (4x)2 x 4x x2 (z)2 x z
y2 (y) y
2 y y 2 (5) y
2 25
2xy 2(4x)(y) 8xy 2xy 2(z)(5) 10z
= (4x + y) 2 – (z+5)2
Factor using Difference of squares
=[(4x + y) + (z+5)] [(4x+y) – (z+5)]
= (4x + y + z +5) (4x + y – z –5)
You might also like
- Polynomials and Polynomial EquationDocument7 pagesPolynomials and Polynomial EquationDionel RizoNo ratings yet
- P.4 Factoring Polynomials: Factor Each Expression (Means Factor COMPLETELY) A. 6x - 4x (3x) - (2) 2x (3x - 2)Document4 pagesP.4 Factoring Polynomials: Factor Each Expression (Means Factor COMPLETELY) A. 6x - 4x (3x) - (2) 2x (3x - 2)Ismail Medhat SalahNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions and InequalitiesRevisedDocument57 pagesQuadratic Functions and InequalitiesRevisedShawnNo ratings yet
- Soluciones Polinomios: Descomposición Factorial: Matemáticas 3º Eso - ÁlgebraDocument2 pagesSoluciones Polinomios: Descomposición Factorial: Matemáticas 3º Eso - ÁlgebraInes Maria Lanza DominguezNo ratings yet
- Special Products and FactoringDocument41 pagesSpecial Products and FactoringLYNDON MENDIOLANo ratings yet
- 4orca Share Media1664099245129 6979738120242220226Document5 pages4orca Share Media1664099245129 6979738120242220226Angelo GranadaNo ratings yet
- TurÍa de DerivadasDocument3 pagesTurÍa de DerivadasGerson DueñasNo ratings yet
- Expanding bracketsDocument2 pagesExpanding bracketsstovbik.anastasiyaNo ratings yet
- DERIVATIVES_SOLUTIONSDocument2 pagesDERIVATIVES_SOLUTIONSMayaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1Document2 pagesTarea 1Alejandro LapoNo ratings yet
- F X) F (X) X X X: Tarea 1Document2 pagesF X) F (X) X X X: Tarea 1Alejandro LapoNo ratings yet
- Actividad Aprendizaje 2 Matematicas IiDocument12 pagesActividad Aprendizaje 2 Matematicas IiKaren Lorena Botonero IssaNo ratings yet
- TurÍa de DerivadasDocument2 pagesTurÍa de Derivadasnathalia_06201No ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions 1C: y 3xy (3y + 4x)Document2 pagesAlgebraic Expressions 1C: y 3xy (3y + 4x)AnnaNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb p1 Ex1c PDFDocument2 pagesAlevelsb p1 Ex1c PDFSri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb p1 Ex1c PDFDocument2 pagesAlevelsb p1 Ex1c PDFThis AccountNo ratings yet
- alevelsb_p1_ex1cDocument2 pagesalevelsb_p1_ex1cm2dsplashNo ratings yet
- FACTORINGDocument62 pagesFACTORINGGojira916No ratings yet
- SOL Regla de La Cadena. Recta Tangente y Recta NormalDocument14 pagesSOL Regla de La Cadena. Recta Tangente y Recta NormalJavier Alejandro Manrique CatalanNo ratings yet
- 1polynomialsand Rational ExpressionsDocument52 pages1polynomialsand Rational ExpressionsNiño Bhoy FloresNo ratings yet
- Diff 2 Terms..SquarebinomialDocument5 pagesDiff 2 Terms..SquarebinomialCeleste CelestineNo ratings yet
- Zeros of Polynomial FunctionsDocument11 pagesZeros of Polynomial FunctionsRhoda LuisNo ratings yet
- ANSWER: (3x + 4y - 2) (3x - 4y - 2)Document21 pagesANSWER: (3x + 4y - 2) (3x - 4y - 2)Desmond MunisNo ratings yet
- Estudiante 4 YesicaDocument3 pagesEstudiante 4 YesicaBRAYAN YESID BURGOS VILLAMILNo ratings yet
- UEM Sol To Exerc Chap 057Document9 pagesUEM Sol To Exerc Chap 057janvincentcentinoNo ratings yet
- F (X) 3 X X: 1) Usando La Ecuación Dada para El Limite Cuando H Tiende A CeroDocument3 pagesF (X) 3 X X: 1) Usando La Ecuación Dada para El Limite Cuando H Tiende A Ceroviviana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Calculo AngelDocument3 pagesCalculo Angelviviana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Dominio de FuncionDocument2 pagesEjercicios Dominio de Funcionordnael perez pujolsNo ratings yet
- TALLER No 7Document16 pagesTALLER No 7angie_varela8511No ratings yet
- Explicación Propiedades Derivada 01Document6 pagesExplicación Propiedades Derivada 01Omar FuentesbustilloNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions-NotesDocument4 pagesAlgebraic Expressions-NotesaceranobarNo ratings yet
- Exercise#4 1Document7 pagesExercise#4 1Masood AlamNo ratings yet
- Maths IIT-JEE Best Approach' (MC SIR) Fundamental of MathematicsDocument7 pagesMaths IIT-JEE Best Approach' (MC SIR) Fundamental of MathematicsHARSHITA CAN DANCENo ratings yet
- Dasgal 3.5Document2 pagesDasgal 3.5renchindorj_md3753No ratings yet
- Calculo de DerivadasDocument5 pagesCalculo de Derivadasemmanuel mirandaNo ratings yet
- LOGARITHMS AND FUNCTIONS CLASS EXERCISEDocument6 pagesLOGARITHMS AND FUNCTIONS CLASS EXERCISEVarun GargNo ratings yet
- Taller Teorema de DerivadasDocument2 pagesTaller Teorema de DerivadasAyarithNo ratings yet
- CP Algebra 2 Unit 2-1: Factoring and Solving Quadratics Worksheet PacketDocument59 pagesCP Algebra 2 Unit 2-1: Factoring and Solving Quadratics Worksheet PacketShibly SadikNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Sec 2 Express Mid-Year Revision 2: X X X XDocument7 pagesSolutions To Sec 2 Express Mid-Year Revision 2: X X X Xlow_jacksonNo ratings yet
- Zadatak 5.: Deriviraj Sljede Ce Funkcije: 2 3Document2 pagesZadatak 5.: Deriviraj Sljede Ce Funkcije: 2 3MayaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of functions including radicals and fractionsDocument2 pagesDerivatives of functions including radicals and fractionsMayaNo ratings yet
- Matemática I/ 2009: Material de Apoyo Preparado para El CursoDocument3 pagesMatemática I/ 2009: Material de Apoyo Preparado para El CursoBeverly RaxNo ratings yet
- Piboon ChomsombatDocument7 pagesPiboon ChomsombatJarukit Jr JunjiewchaiNo ratings yet
- Homework Questions 5 - Factor Theorem: (C2-1.5a) NameDocument1 pageHomework Questions 5 - Factor Theorem: (C2-1.5a) Nameiwan60No ratings yet
- Análisis Matemático Grupo 15: Trabajo Práctico 1Document5 pagesAnálisis Matemático Grupo 15: Trabajo Práctico 1Eva Natalia Sosa Van SoestNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 Module 1 Week 1Document12 pagesGRADE 8 Module 1 Week 1Aileene Joy Blanco AlonzoNo ratings yet
- 1078 Basic Algebra Questions: Factoring, Expanding, and SimplifyingDocument18 pages1078 Basic Algebra Questions: Factoring, Expanding, and SimplifyingRonaldo ManaoatNo ratings yet
- MATH113 Calculus 1 Trigonometric DerivativesDocument9 pagesMATH113 Calculus 1 Trigonometric DerivativesANGEL ALBERTNo ratings yet
- M2 Mixed 20221230Document5 pagesM2 Mixed 20221230penfly koNo ratings yet
- Algebraic expressions and rational functionsDocument14 pagesAlgebraic expressions and rational functionsJennifer CruzNo ratings yet
- Turunan Fungsi AljabarDocument1 pageTurunan Fungsi AljabarKholid RamadanaNo ratings yet
- S S S 2 Fur Maths 1ST Term E-Note 2017Document56 pagesS S S 2 Fur Maths 1ST Term E-Note 2017palmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- Taller de Derivadas.Document7 pagesTaller de Derivadas.Alejandra VeraNo ratings yet
- Factorization Formula Cheat SheetDocument30 pagesFactorization Formula Cheat SheetaadiNo ratings yet
- Enma 101 Exam 1-6 3Document21 pagesEnma 101 Exam 1-6 3Aquino EricNo ratings yet
- Calculating derivatives of functionsDocument3 pagesCalculating derivatives of functionsLaura Gómez CardonaNo ratings yet
- Aporte 3 Tarea 3 DerivadasDocument3 pagesAporte 3 Tarea 3 DerivadasLaura Gómez CardonaNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Graphs (1) : Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument4 pagesAlgebra and Graphs (1) : Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationteezkangNo ratings yet
- Taller Segundo CorteDocument19 pagesTaller Segundo Corter daNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- UNDERSTANDING CULTURE p3Document3 pagesUNDERSTANDING CULTURE p3Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- UNDERSTANDING CULTURE p2Document3 pagesUNDERSTANDING CULTURE p2Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Religion in The Age of Globalization SecularizationDocument3 pagesReligion in The Age of Globalization SecularizationDylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics: (Summary of Lessons)Document4 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics: (Summary of Lessons)Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Placement Reviewer 4Document3 pagesPlacement Reviewer 4Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- UNDERSTANDING CULTURE p4Document3 pagesUNDERSTANDING CULTURE p4Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Placement Reviewer 2Document3 pagesPlacement Reviewer 2Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Acne From DoctorDocument7 pagesAcne From DoctorDylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Placement Reviewer 5Document3 pagesPlacement Reviewer 5Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Placement Reviewer 3Document3 pagesPlacement Reviewer 3Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Secondary EducationDocument2 pagesBachelor of Secondary EducationDylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Spanish GroupDocument42 pagesSpanish GroupDylan RogersNo ratings yet
- PE Curriculum: Physical Education Learning Outcomes FrameworkDocument5 pagesPE Curriculum: Physical Education Learning Outcomes FrameworkGina GregorioNo ratings yet
- Physics problem set on relative velocityDocument1 pagePhysics problem set on relative velocityDylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Defining GlobalizationupdatedDocument51 pagesChapter 1 Defining GlobalizationupdatedKarma Akabane92% (24)
- Upload For Download 1Document1 pageUpload For Download 1Dylan RogersNo ratings yet
- GuysueDocument1 pageGuysueDylan RogersNo ratings yet
- UploaaaaaadDocument3 pagesUploaaaaaadDylan RogersNo ratings yet
- Modern Math in Real LifeDocument16 pagesModern Math in Real LifeRachel PetersNo ratings yet
- List of Square Numbers at Math - ToolsDocument39 pagesList of Square Numbers at Math - ToolsVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Square RootsDocument17 pagesSquare RootsKkhushi GanacharyaNo ratings yet
- Géomancie (Compilation)Document11 pagesGéomancie (Compilation)John PittNo ratings yet
- Approximating Square RootsDocument7 pagesApproximating Square RootsBradAnkneyNo ratings yet
- CG'QMD / ) 0Flqmd: Series and SequenceDocument11 pagesCG'QMD / ) 0Flqmd: Series and Sequencemuna100% (1)
- 10 - Chapter 4Document40 pages10 - Chapter 4Aldin Jr Legaspi GragedaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Mathematics Worksheet - Cubes and Cube RootsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 8 Mathematics Worksheet - Cubes and Cube RootsISHAAN GOYAL100% (1)
- Ifa TableDocument4 pagesIfa Tablecapelo30100% (2)
- Mathsgenie - Co.uk Mathsgenie - Co.uk Please Do Not Write On This SheetDocument1 pageMathsgenie - Co.uk Mathsgenie - Co.uk Please Do Not Write On This SheetYousif Jamal Al Naqbi 12BENo ratings yet
- J176 + 2401 Is Equal: Directions Against Correct Answer: (Bank P0. 2003)Document8 pagesJ176 + 2401 Is Equal: Directions Against Correct Answer: (Bank P0. 2003)Shashi YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 10: - Number Patterns - Triangular, Square and Pentagonal Numbers - Derive Formulae From Number PatternsDocument36 pagesLecture Week 10: - Number Patterns - Triangular, Square and Pentagonal Numbers - Derive Formulae From Number PatternsPeiEnOng100% (2)
- Geometric NumbersDocument12 pagesGeometric NumbersGaro OhanogluNo ratings yet
- Strange pairs of numbers with mirror image squaresDocument1 pageStrange pairs of numbers with mirror image squaresSandip KunduNo ratings yet
- Grade VLLL: MATH Worksheets: 2021-2022Document5 pagesGrade VLLL: MATH Worksheets: 2021-2022Kankan PragnyaNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Jan2021 Class 9 Maths Chapter 4Document28 pagesRD Sharma Jan2021 Class 9 Maths Chapter 4dgfthhjyhntttNo ratings yet
- Triangular NumberDocument5 pagesTriangular Numberalokaryan6No ratings yet
- Geomantic FiguresDocument34 pagesGeomantic FiguresFrater Akenu100% (1)
- 2014 10 30 Polygonal NumbersDocument1 page2014 10 30 Polygonal NumberssamjshahNo ratings yet