Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Philosopies of Education
Uploaded by
Than They Carel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
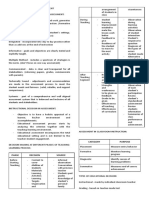
14 views3 pages1. Behaviorism focuses on observable behavior and modifying behavior through conditioning and shaping using rewards and punishments. The teacher's role is to manipulate the learning environment to present stimuli to shape students' behavior.
2. Essentialism aims to teach essential skills and subjects like reading, writing and arithmetic. The teacher leads students in mastering core subject matter.
3. Linguistic philosophy emphasizes developing communication skills through experiential dialogue. The teacher facilitates interaction to help students express themselves clearly.
Original Description:
Philosophy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Behaviorism focuses on observable behavior and modifying behavior through conditioning and shaping using rewards and punishments. The teacher's role is to manipulate the learning environment to present stimuli to shape students' behavior.
2. Essentialism aims to teach essential skills and subjects like reading, writing and arithmetic. The teacher leads students in mastering core subject matter.
3. Linguistic philosophy emphasizes developing communication skills through experiential dialogue. The teacher facilitates interaction to help students express themselves clearly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesPhilosopies of Education
Uploaded by
Than They Carel1. Behaviorism focuses on observable behavior and modifying behavior through conditioning and shaping using rewards and punishments. The teacher's role is to manipulate the learning environment to present stimuli to shape students' behavior.
2. Essentialism aims to teach essential skills and subjects like reading, writing and arithmetic. The teacher leads students in mastering core subject matter.
3. Linguistic philosophy emphasizes developing communication skills through experiential dialogue. The teacher facilitates interaction to help students express themselves clearly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
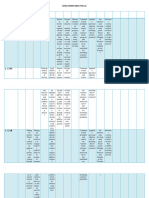
Philosopies of Proponent/s Major Goals/Objective Curriculum Methods of Role of the Teacher Role of the school
Education ideas/Beliefs s Teaching
John B. Watson - Observabl - For the - Teach - Ought to - Manipulate - Manage
Behaviorism Ivan Pavlov e modific students arrange the learning the
B.F. Skinner behavior, ation to environme environmen behavior
was the and respond ntal t and of the
only shaping favourably conditions present students
reliable of to various so that stimuli, through
source of student stimuli in students using developm
informatio s’ the can make conditionin ent of
n. behavio environme the g and social policies,
- Stresses r by nt. responses learning to procedure
the providin - Learning to stimuli; shape s, rules
importanc g for a tasks in - Ought to students’ and
e of the favoura which make the behavior. regulation
environm ble behavior stimuli - Learn the s.
ent in environ can be clear and theory and - Initiate
shaping ment. directly interesting the and
an - Enginee observed, to capture techniques guarantee
individual’ r measured, and hold of a safe,
s environ and the conditionin collegial
behavior. ments evaluated. learners’ g process and
- An idea that attention; and use caring
that efficient and them environm
behavior ly - Ought to effectively. ent.
is maximiz provide - Facilitate - Implemen
acquired e appropriat reinforceme ta
through learning e nt to try to Behavior
conditioni . incentives increase Interventi
ng. The to desired on Plan
system is reinforce behavior. (BIP) such
based on positive as
rewards responses extracurri
and and cular
punishme weaken or activities
nts. eliminate with
negative measurab
ones le goals as
(Trespeces, necessary.
1995).
Essentialisim Wiliam Bagley - Often called as This philosophy - To teach Emphasizes the - Leader and - Ensure
(1874-1946) “traditionalism” contends that the mastery of subject the center master of
or “conservatism”. teachers teach essential matter. of the essential
- Refers to the for the learners of life. classroom. skills.
“Basic Education”. to acquire basic - Emphasize - Prepare
- A belief that knowledge, s on the students
something is skills and values. essential for real
necessary or to skills (4 life
teach the basic R`s) and situations.
subjects. essential - Teach
subjects students
such as to
English, communi
Math and cate
Foreign clearly
Language. and
logically.
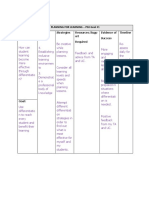
Linguistic - Charles - Focuses - To - Language - Experientia - Teacher - Serves as
Philosophy Pierce on develop and l way facilitates a place to
- Benjami language the communic dialogue interplay
n Whorf and commu ation among of minds
- Ludwig communic nication learners. and
Wittgens ation skills. hearts.
tein - Mastery - To
- Noam of express
Chomsky communic himself/
ation skills herself
clearly.
- To
develop
in the
learner
the skill
to send
and
receive
messag
es
correctl
y.
Reconstructio - Theodor - Social - To - Focus on - Communit - Lead the - Primary
nism e reform improve present y-based young in agent of
Burghard and and future projects designing social
Hurt reconstr trends and - Problem- programs change
Brameld uct issues of oriented for social, - Critical
(1904- society national method educational examinati
1987) educati and ,practical, on of
on for internatio and cultural
change nal economic heritage
interest. change. - Center of
controver
sy where
student
discuss
controver
sial
issues,
political
and
education
You might also like
- Learning TheoriesDocument2 pagesLearning Theories2015 Ens RAMOS GUERRERO LINDA MAGALY100% (1)
- Motivating and Rewarding University Teachers to Improve Student Learning: A Guide for Faculty and AdministratorsFrom EverandMotivating and Rewarding University Teachers to Improve Student Learning: A Guide for Faculty and AdministratorsNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation of FNMIDocument1 pageAssessment and Evaluation of FNMIGenuine ManNo ratings yet
- Behavioral TheoryDocument3 pagesBehavioral TheoryApril MonterosoNo ratings yet
- Overview TableDocument2 pagesOverview Tableapi-429103878No ratings yet
- DataDocument1 pageDataapi-351067106No ratings yet
- COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS Classroom ManagementDocument21 pagesCOMPARATIVE ANALYSIS Classroom ManagementEllaNo ratings yet
- Renz Morales Module 4Document20 pagesRenz Morales Module 4Renz MoralesNo ratings yet
- Supporting Appropriate Behavior: Living With AutismDocument4 pagesSupporting Appropriate Behavior: Living With AutismDarkoNo ratings yet
- Discipline Model Name and Theorists Goal Model Outcomes/expectations Elements Actions/stepsDocument5 pagesDiscipline Model Name and Theorists Goal Model Outcomes/expectations Elements Actions/stepsValeria AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Group 3 TOS REPORTINGDocument10 pagesGroup 3 TOS REPORTINGAaron OsorioNo ratings yet
- Comparing Learning TheoriesDocument8 pagesComparing Learning Theoriesfimmee2006No ratings yet
- Reviewer - ProfEd7Document2 pagesReviewer - ProfEd7Chelsy Kate RoxasNo ratings yet
- Math 139Document8 pagesMath 139PERATER, JELLY A.No ratings yet
- Module 11Document5 pagesModule 11Aprylle Maye MauyaoNo ratings yet
- Ilp-Liping LiangDocument4 pagesIlp-Liping Liangapi-483317340No ratings yet
- Individual Behaviour Plan Zepplin Mcswain Year 1 2018Document3 pagesIndividual Behaviour Plan Zepplin Mcswain Year 1 2018api-354629458No ratings yet
- Ed 064815Document9 pagesEd 064815Leo GondayaoNo ratings yet
- BBB Powerpoint Group OneDocument15 pagesBBB Powerpoint Group Oneeayebare0No ratings yet
- 7 Waysoflearning 2Document26 pages7 Waysoflearning 2AgnesNo ratings yet
- AIP ResiliencyDocument6 pagesAIP ResiliencyClaudine LofrancoNo ratings yet
- Miss Joanna Molabola Grade 6Document6 pagesMiss Joanna Molabola Grade 6Jinky BracamonteNo ratings yet
- Comparison Learning TheoriesDocument1 pageComparison Learning Theoriesapi-458648695No ratings yet
- Tyler's Model Taba's Model: SimilaritiesDocument2 pagesTyler's Model Taba's Model: SimilaritiesMariam D. MarcojosNo ratings yet
- Waupan - John Mark - BEED3B - Activity 2Document7 pagesWaupan - John Mark - BEED3B - Activity 2Reginelie PadogNo ratings yet
- Waupan - John Mark - BEED3B - Activity 2Document7 pagesWaupan - John Mark - BEED3B - Activity 2Reginelie PadogNo ratings yet
- DAISY Individual-Learning-Monitoring-Plan - Lagging-BehindDocument2 pagesDAISY Individual-Learning-Monitoring-Plan - Lagging-BehindLadyAngelIgnacioValgunaNo ratings yet
- Baby Lou Vere. Epp Lesson 10Document5 pagesBaby Lou Vere. Epp Lesson 10Baby Lou VereNo ratings yet
- Resti - Applied LinguisticsDocument9 pagesResti - Applied LinguisticsRestia NingsihNo ratings yet
- Mcleod Professional Learning ToolDocument2 pagesMcleod Professional Learning Toolapi-571896524No ratings yet
- Observation No.1: Behaviorist Theory in Learning: See Last Page)Document6 pagesObservation No.1: Behaviorist Theory in Learning: See Last Page)BEVERLY GAMAONo ratings yet
- Individual PaperDocument9 pagesIndividual PaperApple SangreNo ratings yet
- Health Education (Midterm) : PPT Based NotesDocument7 pagesHealth Education (Midterm) : PPT Based NotesKysha HuangNo ratings yet
- Professional Learning PlanDocument6 pagesProfessional Learning Planapi-425784694No ratings yet
- Act FaciDocument28 pagesAct Faciricapearl.zorillaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Matrix For Established Theories of LearningDocument6 pagesSynthesis Matrix For Established Theories of LearningReyArañoSandovalNo ratings yet
- Group1 Assignment1Document1 pageGroup1 Assignment1api-216963445No ratings yet
- Ipcrf DPDocument1 pageIpcrf DPEunice Nemeño OfficialNo ratings yet
- Learning: Theory and Research: in This SectionDocument37 pagesLearning: Theory and Research: in This SectionGeraldine TanangonanNo ratings yet
- Individual Learning Monitoring Plan Template SjcnhsDocument3 pagesIndividual Learning Monitoring Plan Template SjcnhsJannette Jane100% (2)
- Development Needs For LACDocument9 pagesDevelopment Needs For LACNicathotz ZaratanNo ratings yet
- GoalsDocument3 pagesGoalsapi-350656357No ratings yet
- Kirkpatrick Evaluation MethodDocument13 pagesKirkpatrick Evaluation MethodToto SubagyoNo ratings yet
- PedologyDocument9 pagesPedologyRashmi NNo ratings yet
- SHS - Performance Monitoring and Coaching FormDocument6 pagesSHS - Performance Monitoring and Coaching FormRomeo PilongoNo ratings yet
- Child 390r Guidance Theory Worksheet-2 1Document4 pagesChild 390r Guidance Theory Worksheet-2 1api-709409044No ratings yet
- Observation No.1: Behaviorist Theory in LearningDocument6 pagesObservation No.1: Behaviorist Theory in LearningMariecar DadapNo ratings yet
- ED101 Final-Dela CruzDocument1 pageED101 Final-Dela CruzCheloumae Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: St. Carmen Salles SchoolDocument2 pagesCurriculum Map: St. Carmen Salles SchoolJohn Dave AbañoNo ratings yet
- Bip FormDocument4 pagesBip Formapi-526732343No ratings yet
- Action Plan (Humss 11-3)Document4 pagesAction Plan (Humss 11-3)raifahnoaimamacoteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 EducPsychDocument5 pagesChapter 14 EducPsychAdam VidaNo ratings yet
- Aproximando-Se de Um Entendimento Conceitual Da Cinética e Inibição Enzimática - Desenvolvimento de Uma Atividade de Pesquisa de Aprendizado Ativo para Os Principais Cursos de Pré-Saúde e Não-CiênciasDocument4 pagesAproximando-Se de Um Entendimento Conceitual Da Cinética e Inibição Enzimática - Desenvolvimento de Uma Atividade de Pesquisa de Aprendizado Ativo para Os Principais Cursos de Pré-Saúde e Não-CiênciasRenan OliveiraNo ratings yet
- I. Step 4 TEACHINGDocument18 pagesI. Step 4 TEACHINGBrandon CuarezNo ratings yet
- Classroom ManagementDocument1 pageClassroom ManagementMaria Lorena Castro MendozaNo ratings yet
- PR 2Document6 pagesPR 2jessie OcsNo ratings yet
- Ilp Sarahclingan 502h Spring24Document6 pagesIlp Sarahclingan 502h Spring24api-679242917No ratings yet
- Ilp Sarahclingan 502h Spring24Document6 pagesIlp Sarahclingan 502h Spring24api-679242917No ratings yet
- FS1 - EP5 (1) JoshuaDocument9 pagesFS1 - EP5 (1) JoshuaJose Carlo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Session Guide in Integrative ApproachDocument2 pagesSession Guide in Integrative ApproachGlaiza AsuncionNo ratings yet
- What Is Pyshcology: Biology CounselDocument19 pagesWhat Is Pyshcology: Biology CounselRichita NichaniNo ratings yet
- Health Education PPT by Jane 2Document29 pagesHealth Education PPT by Jane 2powerpointcarlNo ratings yet
- DLL MAPEH 3rd-Quarter Week-2Document10 pagesDLL MAPEH 3rd-Quarter Week-2Clarissa Flores Madlao MendozaNo ratings yet
- #2 Observation Checklist For FS 1 Topic 1Document2 pages#2 Observation Checklist For FS 1 Topic 1Loraine Magistrado AbonitaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Special Education Field Observation 1Document5 pagesRunning Head: Special Education Field Observation 1api-302071047No ratings yet
- Psychomotor Skills PP2 Term 2Document4 pagesPsychomotor Skills PP2 Term 2Joril MayendeNo ratings yet
- 9 Understanding Individual BehaviorDocument33 pages9 Understanding Individual BehaviorJesse NoelNo ratings yet
- Self ClassificationDocument2 pagesSelf Classificationapi-385015476No ratings yet
- Woods, Luiselli, Tomassone - 2013 - Functional Analysis and Intervention For Chronic RuminationDocument5 pagesWoods, Luiselli, Tomassone - 2013 - Functional Analysis and Intervention For Chronic RuminationJohnNo ratings yet
- Educat 2Document3 pagesEducat 2Abdul Hafeez SolangiNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Psychology For Managers Chapter 3 LearningDocument24 pagesEssentials of Psychology For Managers Chapter 3 LearningShreya JoriNo ratings yet
- Emilys Formal Observation 4 WorksheetDocument2 pagesEmilys Formal Observation 4 Worksheetapi-347062025No ratings yet
- Diffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Document4 pagesDiffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Charlie Meriales0% (1)
- Bandura ImitationDocument31 pagesBandura ImitationZarirah YusofNo ratings yet
- Political Behaviour NoteDocument41 pagesPolitical Behaviour NoteFito Nwidum92% (12)
- Teacher Appraisal FormDocument3 pagesTeacher Appraisal FormFify SantiagoNo ratings yet
- What Is Classroom Observation Guide For ReportingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Classroom Observation Guide For ReportingMark Bryan CervantesNo ratings yet
- Linguistic Philosophy Group-7Document19 pagesLinguistic Philosophy Group-7Alwin AsuncionNo ratings yet
- BES Human Learning Notes 2021Document48 pagesBES Human Learning Notes 2021SadaticloNo ratings yet
- Constructivism Examined PDFDocument14 pagesConstructivism Examined PDFBrian WoodNo ratings yet
- Counseling Basics - Judy Harrow EtcDocument48 pagesCounseling Basics - Judy Harrow EtcSushmita100% (1)
- Classroom Management TheoriesDocument12 pagesClassroom Management Theoriesapi-302418583No ratings yet
- Making Sandwiches Libro Versión RevisadaDocument75 pagesMaking Sandwiches Libro Versión RevisadaRoderick Richmond100% (3)
- Content Theory of MotivationDocument15 pagesContent Theory of Motivationمرزا عبداللہNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development: Presented By: Marvelyn Fuggan ManeclangDocument98 pagesCurriculum Development: Presented By: Marvelyn Fuggan ManeclangMarvelyn Maneclang Catubag83% (18)
- Sofia Debrot - ResumeDocument1 pageSofia Debrot - Resumeapi-726847144No ratings yet
- Facilitating LearningDocument4 pagesFacilitating LearningMay-Ann S. CahiligNo ratings yet
- Gilbert RyleDocument6 pagesGilbert RyleDea Lyn BaculaNo ratings yet