Professional Documents
Culture Documents
World
World
Uploaded by
Shaik HamedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
World
World
Uploaded by
Shaik HamedCopyright:
Available Formats
Hooke in 1665.
Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and
Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that
cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms,.
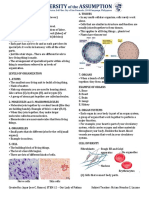
Animal Cell Structure:
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, with the presence of true nucleus; multicellular
large and advanced membrane bound organelles. Like plant cells, animal cells
have same organelles except the cell wall, chloroplasts, number of vacuoles and
many more. Due to the absence of cell wall the shape of an animal cell is
irregular. Animal cells are enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-
bound nucleus and organelles. .
Function of Cell:
Cell wall: It helps in protecting the plasma membrane and plays a vital role in
supporting and protecting the cells. It is a thick outer layer made of cellulose.
Cell membrane: All animal cells are surrounded by a protective membrane which is
called as cell-membrane or plasma membrane. It is also called as cytoplasmic
membrane. Plasma membrane is a thin, elastic and semi-permeable membrane. the
function of cell membrane is a natural protective boundary around the cell.
Cytoplasm: It is a membrane, which protects the cell by keeping the cell organelles
separate from each other. This helps to keep a cell in stable. Cytoplasm is the site,
where many vital biochemical reactions take place.
Nucleus: They are the membrane bound organelles, which are found in all eukaryotic
cells. It is the very important organelle of a cell as it controls the complete activity of
a cell and also plays a vital role in reproduction.
Nuclear membrane: The bilayer membrane, which protects the nucleus by
surrounding around it and acts as a barrier between the cell nucleus and other organs
of a cell.
Nucleolus: It is an important membrane found inside the nucleus. It plays a vital role
in the production of cell’s ribosome.
Chromosomes: It is made up of DNA and stored in the nucleus, which contains the
instructions for traits and characteristics. (Chroma = Colour, Soma = body)
Endoplasmic reticulum: It helps in the movement of materials around the cell. It
contains an enzyme that helps in building molecules and in manufacturing of proteins.
The main function of this organelle is storage and secretion.
Ribosome: It plays a vital role in protein synthesis.
Mitochondria: They are double membrane, filamentous organelles, which play a
vital role in generating and transforming the energy. Mitochondria play a vital role in
various functions of the cell metabolisms including oxidative phosphorylation. these
are rod like structure. it is called as “Power House” of cell.
Golgi Bodies: It helps in the movement of materials within the cell.
Lysosomes: It is also called as suicidal bags as it helps in cell renewal and break
down old cell parts.
Vacuoles: It helps plants in maintaining its shape and it also stores water, food,
wastes, etc.
Chloroplast: They are the site of photosynthesis, which are present in
chlorophyll bacteria, blue-green algae, etc.
Organisation of Cell
Cells contain a variety of internal structures called organelles
An organelle is a cell component that performs a specific function in that cell
Just as the organs of a multicellular organism carry out the organism’s life functions,
the organelles of a cell maintain the life of the cell
There are many different cells; however, there are certain features common to all cells
The entire cell is surrounded by a thin cell membrane
All membranes have the same thickness and basic structure
Organelles often have their own membranes too – once again, these membranes have
a similar structure
The nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts all have double membranes, more
correctly called envelopes
Because membranes are fluid mosaics, the molecules
You might also like
- Examination Questions and Answers in Basic Anatomy and Physiology. 2000 Multiple Choice Questions - Martin CaonDocument508 pagesExamination Questions and Answers in Basic Anatomy and Physiology. 2000 Multiple Choice Questions - Martin CaonMiguel Angel Mendoza Zabalaga67% (6)
- Zoology Reviewer 1Document3 pagesZoology Reviewer 1Jojit Espiritu100% (1)
- Cell Organelle Chart Key 2011Document3 pagesCell Organelle Chart Key 2011Angel Silva Vicente50% (2)
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- Cell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."Document6 pagesCell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."Woobin Real100% (1)
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- Cell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."Document5 pagesCell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."shankaram shankaram100% (1)
- The Cell - ZoologyDocument7 pagesThe Cell - ZoologyEthel May GranilNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structue and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Structue and FunctionsDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Cells TissuesDocument7 pagesCells TissuesNisha ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Biology Note Grade 8 Chapter: CellsDocument7 pagesBiology Note Grade 8 Chapter: CellsAfrida AnnanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocument4 pagesThe Cell: Types of CellsAllen MurilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocument19 pagesCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (2)
- Submitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955Document9 pagesSubmitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955mahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept About CELLDocument11 pagesBasic Concept About CELLjack omeNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- 1.1cell ConceptDocument10 pages1.1cell ConceptMokariya SanjayNo ratings yet
- Inte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Document11 pagesInte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- CELLS BiologyDocument8 pagesCELLS BiologyKYLENE ABELLANANo ratings yet
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDocument24 pagesCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsJaspher Joshua CallangaNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- Cell TheoryDocument45 pagesCell Theoryjustine caintoyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science BDocument5 pagesReviewer in Science BAshliah Aira MarohomNo ratings yet
- What Is Cytology? What Is Cell?Document3 pagesWhat Is Cytology? What Is Cell?Elcee QuindozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument26 pagesCellsNairita LetipoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- What Is A CellDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Celljose de jesus sanchezNo ratings yet
- General Biology: Lab 3 First Stage Shahad EmadDocument19 pagesGeneral Biology: Lab 3 First Stage Shahad EmadIraqiNo ratings yet
- Foundation - 1 RecapDocument15 pagesFoundation - 1 RecapSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- GsciDocument9 pagesGscimahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- Cell DefinitionDocument14 pagesCell DefinitionFarhan AliNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- CELLS For Class8Document15 pagesCELLS For Class8cbseiscNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?Document5 pagesChapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?HeroNo ratings yet
- What Is A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesWhat Is A MicroscopeMcj TeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"Document12 pagesBasic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"cbseiscNo ratings yet
- Plant CellsDocument4 pagesPlant CellsjoyfrangonzagaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument10 pagesThe CellAbeer Alnajjar عبير النجارNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPrashant PatilNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 - CellDocument9 pagesTOPIC 2 - CellAl Johan Atienza100% (1)
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocument8 pagesThe Cell: Types of CellsushapvermaNo ratings yet
- Diagram of Plant CellDocument4 pagesDiagram of Plant CellekongNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells - De, Nition, Diagram, Structure & FunctionDocument2 pagesPlant Cells - De, Nition, Diagram, Structure & FunctionJoseph OloruntobaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Functions PDFViswasriNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesMd AurangjebNo ratings yet
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision NotesDocument14 pagesGrade-9 Cbse Chapter-5 Revision NotesNoel MammenNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument31 pagesCellsPranav ShindeNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture No.1 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Topic:-Plant CellDocument11 pagesOnline Lecture No.1 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Topic:-Plant CellwatashiwayakinikuNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells PDFDocument7 pagesPlant Cells PDFMarcus Ben AlgerreNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDocument28 pagesAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Notes Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument6 pages9th Class Notes Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifepralexprajapatiNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chapter 6 - Muscular SystemDocument61 pagesChapter 6 - Muscular Systemchelsearariza100% (5)
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Sci5Document32 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Sci5Joseph CunananNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following:: Module:1 Laboratory Techniques in Pathology LabDocument5 pagesAnswer The Following:: Module:1 Laboratory Techniques in Pathology LabDUC Q. NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Human Diseases and Conditions 6th Edition by FrazierDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Human Diseases and Conditions 6th Edition by Fraziersquireenmabbyzc7meu100% (52)
- POGILbloodtyping NewDocument6 pagesPOGILbloodtyping Newbrittanyai.sbcNo ratings yet
- AP Module4 Trans DiazDocument18 pagesAP Module4 Trans DiazJohn Rafael DiazNo ratings yet
- Blood BankDocument84 pagesBlood Bankmanni1001100% (4)
- Punam Jaiswal UG-II Anomalous Secondary Growth in BoerhaaviaDocument4 pagesPunam Jaiswal UG-II Anomalous Secondary Growth in BoerhaaviaPratistha ShauryaNo ratings yet
- Cartilage: Histology Dr. BernalDocument4 pagesCartilage: Histology Dr. BernalA18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- Blood and Heart Review NotesDocument19 pagesBlood and Heart Review NotesElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document168 pagesGeneral Biology 1BEANo ratings yet
- Bio 103 Lab 5 Plant Anatomy PDFDocument12 pagesBio 103 Lab 5 Plant Anatomy PDFPanida SnaNo ratings yet
- Staining of Connective TissueDocument3 pagesStaining of Connective TissueJey TeeNo ratings yet
- Compilation of BB Lec ReviewerDocument19 pagesCompilation of BB Lec ReviewerKenj Yolleth IbañezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 A Tour of The CellDocument4 pagesChapter 4 A Tour of The Cellmzunl254760% (1)
- ABO Blood GroupDocument41 pagesABO Blood GroupSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant CellDocument4 pagesTypes of Plant CellKathleen Castañeda FernandezNo ratings yet
- Histology Lecture #2Document9 pagesHistology Lecture #2رشيد عليانNo ratings yet
- Full Summary of Edexcel IAL 2018 Chapter 4Document20 pagesFull Summary of Edexcel IAL 2018 Chapter 4North AbordoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Cells PowerpointDocument7 pagesProkaryote Cells Powerpointrengar gamerNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Ciliated Epithelium Is A Category of EpitheliumDocument20 pagesCiliated Epithelium Is A Category of EpitheliumMisnawatiNo ratings yet
- Cells Questions Magnification CalculationsDocument15 pagesCells Questions Magnification CalculationssophiaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Its FunctionsDocument25 pagesCell Parts and Its FunctionsSen Armario100% (1)
- General BiologyDocument19 pagesGeneral BiologyHannah RodriguezNo ratings yet